Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma
Abstract
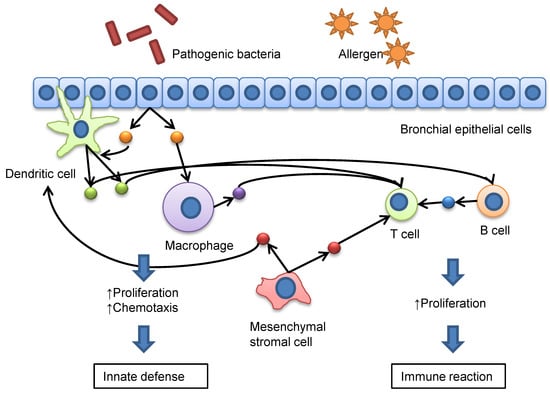
:1. Introduction
2. EVs in BA Pathogenesis
2.1. EV-Secreting Cells in the Respiratory System
2.2. Allergen-Induced Airway Inflammation
2.3. Functions of EVs in BA Pathogenesis
2.3.1. EVs From Hematopoietic Cells
2.3.2. EVs from Lung Structural Cells
2.3.3. Role of miRNA in EVs
2.3.4. Novel Function of EVs
3. EVs as Potential Biomarkers of BA
4. EVs as Potential Therapeutic Targets for BA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALIX | ALG-2 interacting protein X |
| BA | Bronchial asthma |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| BEC | Bronchial epithelial cell |
| CCL | CC-chemokine ligand |
| CCR | CC-chemokine receptor |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CSE | Cigarette smoke extract |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| EBC | Exhaled breath condensate |
| ECP | Eosinophil cationic protein |
| EPO | Eosinophil peroxidase |
| ESCRT | Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GPIbα | Glycoprotein Ibα |
| HDM | House-dust mite |
| HLA-DR | Human leukocyte antigen D-related |
| HSP | Heat-shock protein |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MBP | Major basic protein |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 |
| MDCK | Madin–Darby canine kidney cell |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stromal cell |
| MUC | Mucin |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| PG | Prostaglandin |
| PSGL-1 | P-selectin/P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SOCS | Suppressor of cytokine signaling |
| TH | T helper |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| Treg | T regulatory |
| TSG | Tumor susceptibility |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Wolf, P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trams, E.G.; Lauter, C.J.; Salem, N.; Heine, U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 645, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- György, B.; Szabó, T.G.; Pásztói, M.; Pál, Z.; Misják, P.; Aradi, B.; László, V.; Pállinger, E.; Pap, E.; Kittel, A.; et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2667–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.H.; Boura, E.; Carlson, L.A.; Różycki, B. Membrane budding. Cell 2010, 143, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez, F.; Frenette, G.; Sullivan, R. Epididymosomes and prostasomes: Their roles in posttesticular maturation of the sperm cells. J. Androl. 2003, 24, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, A.; Jalabert, A.; Chikh, K.; Pesenti, S.; Euthine, V.; Granjon, A.; Errazuriz, E.; Lefai, E.; Vidal, H.; Rome, S. Myotube-derived exosomal miRNAs downregulate Sirtuin1 in myoblasts during muscle cell differentiation. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L. Exosomes/microvesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Fujikake, N.; Popiel, H.A.; Kikuchi, H.; Futaki, S.; Wada, K.; Nagai, Y. Intercellular chaperone transmission via exosomes contributes to maintenance of protein homeostasis at the organismal level. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2497–E2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baixauli, F.; López-Otín, C.; Mittelbrunn, M. Exosomes and autophagy: Coordinated mechanisms for the maintenance of cellular fitness. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswad, H.; Forterre, A.; Wiklander, O.P.; Vial, G.; Danty-Berger, E.; Jalabert, A.; Lamazière, A.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Ott, C.; et al. Exosomes participate in the alteration of muscle homeostasis during lipid-induced insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caby, M.P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filén, J.J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admyre, C.; Grunewald, J.; Thyberg, J.; Gripenbäck, S.; Tornling, G.; Eklund, A.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with major histocompatibility complex class II and co-stimulatory molecules are present in human BAL fluid. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristov, M.; Erl, W.; Linder, S.; Weber, P.C. Apoptotic bodies from endothelial cells enhance the number and initiate the differentiation of human endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Blood 2004, 104, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciardiello, C.; Cavallini, L.; Spinelli, C.; Yang, J.; Reis-Sobreiro, M.; de Candia, P.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Di Vizio, D. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: New Frontiers of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörsam, B.; Reiners, K.S.; von Strandmann, E.P. Cancer-derived extracellular vesicles: Friend and foe of tumour immunosurveillance. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorey, J.S.; Cheng, Y.; Singh, P.P.; Smith, V.L. Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host-pathogen interactions. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. Characteristics and Roles of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Chanda, D.; Duncan, S.R.; Thannickal, V.J.; Deshane, J.S. Exosomes in immunoregulation of chronic lung diseases. Allergy 2017, 72, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, B.; Cañas, J.A.; Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; Del Pozo, V. Novel Modulators of Asthma and Allergy: Exosomes and MicroRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Alipoor, S.D.; Varahram, M.; Jamaati, H.; Garssen, J.; Mumby, S.E.; Adcock, I.M. Exosomes in Severe Asthma: Update in Their Roles and Potential in Therapy. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2862187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlund, C.J.E.; Eklund, A.; Grunewald, J.; Gabrielsson, S. Pulmonary Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Local and Systemic Inflammation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, N.; Marazuela, E.G.; Segura, E.; Fernández-García, H.; Villalba, M.; Théry, C.; Rodríguez, R.; Batanero, E. Exosomes from bronchoalveolar fluid of tolerized mice prevent allergic reaction. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Ahmad, T.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, B. Proinflammatory role of epithelial cell-derived exosomes in allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1194–1203.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levänen, B.; Bhakta, N.R.; Torregrosa Paredes, P.; Barbeau, R.; Hiltbrunner, S.; Pollack, J.L.; Sköld, C.M.; Svartengren, M.; Grunewald, J.; Gabrielsson, S.; et al. Altered microRNA profiles in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exosomes in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, K.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Heijnen, H.F.; Stoorvogel, W.; Geuze, H.J. Exosome: From internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 19, 3365–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Kadota, T.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.G.; Kim, S.H.; Gao, J.; Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Osorio, J.C.; Rosas, I.O.; Wu, M.; Tesfaigzi, Y.; Jin, Y. CCN1 secretion and cleavage regulate the lung epithelial cell functions after cigarette smoke. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L326–L337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesimer, M.; Gupta, R. Physical characterization and profiling of airway epithelial derived exosomes using light scattering. Methods 2015, 87, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesimer, M.; Scull, M.; Brighton, B.; DeMaria, G.; Burns, K.; O’Neal, W.; Pickles, R.J.; Sheehan, J.K. Characterization of exosome-like vesicles released from human tracheobronchial ciliated epithelium: A possible role in innate defense. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pua, H.H.; Happ, H.C.; Gray, C.J.; Mar, D.J.; Chiou, N.T.; Hesse, L.E.; Ansel, K.M. Increased Hematopoietic Extracellular RNAs and Vesicles in the Lung during Allergic Airway Responses. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 933–944.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.; Wang, Y.; Dakhlallah, D.; Moldovan, L.; Agarwal, K.; Batte, K.; Shah, P.; Wisler, J.; Eubank, T.D.; Tridandapani, S.; et al. Macrophage microvesicles induce macrophage differentiation and miR-223 transfer. Blood 2013, 121, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Niida, S.; Azuma, E.; Yanagibashi, T.; Muramatsu, M.; Huang, T.T.; Sagara, H.; Higaki, S.; Ikutani, M.; Nagai, Y.; et al. Inflammation-induced endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles modulate the cellular status of pericytes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Regnault, A.; Lozier, A.; Wolfers, J.; Flament, C.; Tenza, D.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: Dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokos, D.; Le Panse, S.; Villa, I.; Rousselle, J.C.; Peronet, R.; David, B.; Namane, A.; Mécheri, S. Mast cell-dependent B and T lymphocyte activation is mediated by the secretion of immunologically active exosomes. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, D.; Hao, H.; Tong, C.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Han, W. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Araya, J.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles in lung microenvironment and pathogenesis. Trends Mol Med 2015, 21, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol. Dial Transplant. 2012, 27, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Camussi, G. The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells: Role of extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 168, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdonnay, E.; Zasłona, Z.; Penke, L.R.; Speth, J.M.; Schneider, D.J.; Przybranowski, S.; Swanson, J.A.; Mancuso, P.; Freeman, C.M.; Curtis, J.L.; et al. Transcellular delivery of vesicular SOCS proteins from macrophages to epithelial cells blunts inflammatory signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, D.; Williams, K.J.; Liu, M.L. Tobacco smoke induces the generation of procoagulant microvesicles from human monocytes/macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordazzo, C.; Petrini, S.; Neri, T.; Lombardi, S.; Carmazzi, Y.; Pedrinelli, R.; Paggiaro, P.; Celi, A. Rapid shedding of proinflammatory microparticles by human mononuclear cells exposed to cigarette smoke is dependent on Ca2+ mobilization. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Williams, K.J.; Liu, M.L. Novel proteolytic microvesicles released from human macrophages after exposure to tobacco smoke. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.H.; Woeller, C.F.; Thatcher, T.H.; Pollock, S.J.; Small, E.M.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P. Activated Human Lung Fibroblasts Produce Extracellular Vesicles with Antifibrotic Prostaglandins. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, N.A.; Ortner, A.; Jacamo, R.O.; Reinisch, A.; Schallmoser, K.; Rohban, R.; Etchart, N.; Fruehwirth, M.; Beham-Schmid, C.; Andreeff, M.; et al. Oxygen sensing mesenchymal progenitors promote neo-vasculogenesis in a humanized mouse model in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wehner, R.; Bornhäuser, M.; Wassmuth, R.; Bachmann, M.; Schmitz, M. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells and their therapeutic consequences for immune-mediated disorders. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasoni, S.; Longaretti, L.; Rota, C.; Morigi, M.; Conti, S.; Gotti, E.; Capelli, C.; Introna, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eirin, A.; Riester, S.M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Tang, H.; Evans, J.M.; O’Brien, D.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, L.O. MicroRNA and mRNA cargo of extracellular vesicles from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Gene 2014, 551, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M.; Piliponsky, A.M. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnes, P.J. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauberger, E.; Peinhaupt, M.; Cazares, T.; Lindsley, A.W. Lipid Mediators of Allergic Disease: Pathways, Treatments, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. T-cell trafficking in asthma: Lipid mediators grease the way. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Hirata, M.; Tanaka, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Murata, T.; Kabashima, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ushikubi, F.; Aze, Y.; et al. Prostaglandin D2 as a mediator of allergic asthma. Science 2000, 287, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, J.G.; Worgall, T.S.; Worgall, S. Airway reactivity and sphingolipids-implications for childhood asthma. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2015, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Grimble, R.F. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation and immunity. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56 (Suppl. 3), S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legrand, F.; Klion, A.D. Biologic therapies targeting eosinophils: Current status and future prospects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, E.H.; Ten Brinke, A. New Anti-Eosinophil Drugs for Asthma and COPD: Targeting the Trait! Chest 2017, 152, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The immunology of asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, J.L.; Akbari, O. Regulatory T cells and type 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent asthma. Allergy 2017, 72, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kubatzky, K.F.; Mitra, D.K. An Update on Interleukin-9: From Its Cellular Source and Signal Transduction to Its Role in Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, V.R.; Reiners, K.S.; Hansen, H.P.; Topolar, D.; Simhadri, V.L.; Nohroudi, K.; Kufer, T.A.; Engert, A.; Pogge von Strandmann, E. Dendritic cells release HLA-B-associated transcript-3 positive exosomes to regulate natural killer function. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaud, S.; Terme, M.; Flament, C.; Taieb, J.; André, F.; Novault, S.; Escudier, B.; Robert, C.; Caillat-Zucman, S.; Tursz, T.; et al. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes promote natural killer cell activation and proliferation: A role for NKG2D ligands and IL-15Ralpha. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsugi-Kobukai, S.; Fujimaki, H.; Hotta, C.; Nakazawa, M.; Minami, M. MHC class I-mediated exogenous antigen presentation by exosomes secreted from immature and mature bone marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 89, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luketic, L.; Delanghe, J.; Sobol, P.T.; Yang, P.; Frotten, E.; Mossman, K.L.; Gauldie, J.; Bramson, J.; Wan, Y. Antigen presentation by exosomes released from peptide-pulsed dendritic cells is not suppressed by the presence of active CTL. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5024–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntasell, A.; Berger, A.C.; Roche, P.A. T cell-induced secretion of MHC class II-peptide complexes on B cell exosomes. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4263–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, V.; Fais, S.; Iero, M.; Lugini, L.; Canese, P.; Squarcina, P.; Zaccheddu, A.; Colone, M.; Arancia, G.; Gentile, M.; et al. Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: Role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreola, G.; Rivoltini, L.; Castelli, C.; Huber, V.; Perego, P.; Deho, P.; Squarcina, P.; Accornero, P.; Lozupone, F.; Lugini, L.; et al. Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Chaput, N.; Schartz, N.E.; Flament, C.; Aubert, N.; Bernard, J.; Lemonnier, F.; Raposo, G.; Escudier, B.; Hsu, D.H.; et al. Exosomes as potent cell-free peptide-based vaccine. I. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes transfer functional MHC class I/peptide complexes to dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Regnault, A.; Garin, J.; Wolfers, J.; Zitvogel, L.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Amigorena, S. Molecular characterization of dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Selective accumulation of the heat shock protein hsc73. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, E.; Guérin, C.; Hogg, N.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. CD8+ dendritic cells use LFA-1 to capture MHC-peptide complexes from exosomes in vivo. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.; De Pasquale, C.; Carrega, P.; Ferlazzo, G.; Bonaccorsi, I. Cross-dressing: An alternative mechanism for antigen presentation. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 168, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Duban, L.; Segura, E.; Véron, P.; Lantz, O.; Amigorena, S. Indirect activation of naïve CD4+ T cells by dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näslund, T.I.; Gehrmann, U.; Qazi, K.R.; Karlsson, M.C.; Gabrielsson, S. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes need to activate both T and B cells to induce antitumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admyre, C.; Bohle, B.; Johansson, S.M.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Valenta, R.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. B cell-derived exosomes can present allergen peptides and activate allergen-specific T cells to proliferate and produce TH2-like cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, S.I.; van Balkom, B.W.; Aalberts, M.; Heck, A.J.; Wauben, M.; Stoorvogel, W. MHC class II-associated proteins in B-cell exosomes and potential functional implications for exosome biogenesis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Turkes, A.; Dewitt, S.; Steadman, R.; Mason, M.D.; Hallett, M.B. Adhesion and signaling by B cell-derived exosomes: The role of integrins. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, K.; van Eijk, M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Jakobson, E.; de Groot, C.; Geuze, H.J. Follicular dendritic cells carry MHC class II-expressing microvesicles at their surface. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.; Kosco, M.; Stockinger, B. Novel pathways of antigen presentation for the maintenance of memory. Int. Immunol. 1991, 3, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hough, K.P.; Deshane, J.S. Exosomes in Allergic Airway Diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torregrosa Paredes, P.; Esser, J.; Admyre, C.; Nord, M.; Rahman, Q.K.; Lukic, A.; Rådmark, O.; Grönneberg, R.; Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A.; et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exosomes contribute to cytokine and leukotriene production in allergic asthma. Allergy 2012, 67, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Wilson, L.S.; Trevor, J.L.; Strenkowski, J.G.; Maina, N.; Kim, Y.I.; Spell, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Chanda, D.; Dager, J.R.; et al. Unique Lipid Signatures of Extracellular Vesicles from the Airways of Asthmatics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Bai, O.; Li, F.; Yuan, J.; Laferte, S.; Xiang, J. Mature dendritic cells pulsed with exosomes stimulate efficient cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses and antitumour immunity. Immunology 2007, 120, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Buschow, S.I.; Anderton, S.M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wauben, M.H. Activated T cells recruit exosomes secreted by dendritic cells via LFA-1. Blood 2009, 113, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esser, J.; Gehrmann, U.; D’Alexandri, F.L.; Hidalgo-Estévez, A.M.; Wheelock, C.E.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S.; Rådmark, O. Exosomes from human macrophages and dendritic cells contain enzymes for leukotriene biosynthesis and promote granulocyte migration. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1032–1040, 1040.e1–1040.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barry, O.P.; Pratico, D.; Lawson, J.A.; FitzGerald, G.A. Transcellular activation of platelets and endothelial cells by bioactive lipids in platelet microparticles. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuravi, S.J.; Harrison, P.; Rainger, G.E.; Nash, G.B. Ability of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Promote Neutrophil-Endothelial Cell Interactions. Inflammation 2019, 42, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossaint, J.; Kühne, K.; Skupski, J.; Van Aken, H.; Looney, M.R.; Hidalgo, A.; Zarbock, A. Directed transport of neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles enables platelet-mediated innate immune response. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeo, C.; Cañas, J.A.; Zafra, M.P.; Rojas Marco, A.; Fernández-Nieto, M.; Sanz, V.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Izquierdo, M.; Baixaulli, F.; Sastre, J.; et al. Exosome secretion by eosinophils: A possible role in asthma pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, J.A.; Sastre, B.; Mazzeo, C.; Fernández-Nieto, M.; Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; González-Guerra, A.; Izquierdo, M.; Barranco, P.; Quirce, S.; Sastre, J.; et al. Exosomes from eosinophils autoregulate and promote eosinophil functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cañas, J.A.; Sastre, B.; Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; Fernández-Nieto, M.; Barranco, P.; Quirce, S.; Sastre, J.; Del Pozo, V. Eosinophil-derived exosomes contribute to asthma remodelling by activating structural lung cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.; Roux-Dalvai, F.; Droit, A.; Lavoie, J.P. Neutrophil-Derived Exosomes: A New Mechanism Contributing to Airway Smooth Muscle Remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, R.; Tavakoli Tameh, A.; Parent, C.A. Exosomes Mediate LTB4 Release during Neutrophil Chemotaxis. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, A.; Ji, J.; Idborg, H.; Samuelsson, B.; Palmberg, L.; Gabrielsson, S.; Rådmark, O. Pulmonary epithelial cancer cells and their exosomes metabolize myeloid cell-derived leukotriene C4 to leukotriene D4. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Lipids in exosomes: Current knowledge and the way forward. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 66, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, N.J. Extracellular vesicles and ceramide: New mediators for macrophage chemotaxis? J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakazu, E.; Mauer, A.S.; Yin, M.; Malhi, H. Hepatocytes release ceramide-enriched pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles in an IRE1α-dependent manner. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podbielska, M.; Szulc, Z.M.; Kurowska, E.; Hogan, E.L.; Bielawski, J.; Bielawska, A.; Bhat, N.R. Cytokine-induced release of ceramide-enriched exosomes as a mediator of cell death signaling in an oligodendroglioma cell line. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 2028–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.A.; Sharif, A.S.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Lau, L.; Limbrey, R.; Howarth, P.; Drazen, J.M. Tissue factor-bearing exosome secretion from human mechanically stimulated bronchial epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, I.N.; Kurlander, R.; Bocharov, A.V.; Vishnyakova, T.G.; Chen, Z.; Remaley, A.T.; Csako, G.; Patterson, A.P.; Eggerman, T.L. Role of human CD36 in bacterial recognition, phagocytosis, and pathogen-induced JNK-mediated signaling. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazimek, K.; Bryniarski, K.; Askenase, P.W. Functions of Exosomes and Microbial Extracellular Vesicles in Allergy and Contact and Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 171, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.W.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, E.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeon, S.G.; Yang, J.M.; Lee, B.J.; Pyun, B.Y.; Gho, Y.S.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Staphylococcus aureus induce atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammation. Allergy 2011, 66, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, U.; Qazi, K.R.; Johansson, C.; Hultenby, K.; Karlsson, M.; Lundeberg, L.; Gabrielsson, S.; Scheynius, A. Nanovesicles from Malassezia sympodialis and host exosomes induce cytokine responses--novel mechanisms for host-microbe interactions in atopic eczema. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Tominaga, N.; Katsuda, T.; Ochiya, T. Trash or Treasure: Extracellular microRNAs and cell-to-cell communication. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Sanchez, M.A.; Liu, J.; Hannon, G.J.; Parker, R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, E.; Izaurralde, E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, T.; Cobos, F.A.; Schleich, F.; Sorbello, V.; Henket, M.; De Preter, K.; Bracke, K.R.; Conickx, G.; Mesnil, C.; Vandesompele, J.; et al. Asthma inflammatory phenotypes show differential microRNA expression in sputum. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seumois, G.; Vijayanand, P.; Eisley, C.J.; Omran, N.; Kalinke, L.; North, M.; Ganesan, A.P.; Simpson, L.J.; Hunkapiller, N.; Moltzahn, F.; et al. An integrated nano-scale approach to profile miRNAs in limited clinical samples. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol 2012, 1, 70–89. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Liang, X.; Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Wu, W.; Yan, Z. Identification of Exosomal miRNAs in Rats with Pulmonary Neutrophilic Inflammation Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Vigorito, E.; Clare, S.; Warren, M.V.; Couttet, P.; Soond, D.R.; van Dongen, S.; Grocock, R.J.; Das, P.P.; Miska, E.A.; et al. Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science 2007, 316, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmhäll, C.; Alawieh, S.; Lu, Y.; Sjöstrand, M.; Bossios, A.; Eldh, M.; Rådinger, M. MicroRNA-155 is essential for T(H)2-mediated allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation in the lung. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, J.; Collison, A.; Plank, M.; Phipps, S.; Foster, P.S. Antagonism of microRNA-126 suppresses the effector function of TH2 cells and the development of allergic airways disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18704–18709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collison, A.; Herbert, C.; Siegle, J.S.; Mattes, J.; Foster, P.S.; Kumar, R.K. Altered expression of microRNA in the airway wall in chronic asthma: miR-126 as a potential therapeutic target. BMC Pulm. Med. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pua, H.H.; Steiner, D.F.; Patel, S.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Ortiz-Carpena, J.F.; Kageyama, R.; Chiou, N.T.; Gallman, A.; de Kouchkovsky, D.; Jeker, L.T.; et al. MicroRNAs 24 and 27 Suppress Allergic Inflammation and Target a Network of Regulators of T Helper 2 Cell-Associated Cytokine Production. Immunity 2016, 44, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugaiyan, G.; da Cunha, A.P.; Ajay, A.K.; Joller, N.; Garo, L.P.; Kumaradevan, S.; Yosef, N.; Vaidya, V.S.; Weiner, H.L. MicroRNA-21 promotes Th17 differentiation and mediates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, R.J.; Deho, L.; Rusca, N.; Bartonicek, N.; Saini, H.K.; Enright, A.J.; Monticelli, S. MiR-221 influences effector functions and actin cytoskeleton in mast cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.B.; Xu, B.; Mei, J.J.; Li, D.; Liu, J.J.; Zhao, D.Y.; Liu, F. Inhibition of miRNA-221 suppresses the airway inflammation in asthma. Inflammation 2012, 35, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, Y.; Misawa, M. MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: MiR-133a and bronchial smooth muscle hyperresponsiveness in asthma. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 114, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Njah, J.; Sala, E.; Shiva, S.; St Croix, C.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Di, Y.P.; Leikauf, G.D.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, T.J.; Jackson, M.V.; Cunningham, E.K.; Kissenpfennig, A.; McAuley, D.F.; O’Kane, C.M.; Krasnodembskaya, A.D. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Macrophages in Clinically Relevant Lung Injury Models by Extracellular Vesicle Mitochondrial Transfer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2017, 196, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Trevor, J.L.; Strenkowski, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Chacko, B.K.; Tousif, S.; Chanda, D.; Steele, C.; Antony, V.B.; Dokland, T.; et al. Exosomal transfer of mitochondria from airway myeloid-derived regulatory cells to T cells. Redox Biol. 2018, 18, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfant, C.E.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide 1-phosphate: Expanding roles in cell signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4605–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Howard, T.D.; Zheng, S.L.; Haselkorn, T.; Peters, S.P.; Meyers, D.A.; Bleecker, E.R. Genome-wide association study of asthma identifies RAD50-IL13 and HLA-DR/DQ regions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 328–335.e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignola, A.M.; Campbell, A.M.; Chanez, P.; Bousquet, J.; Paul-Lacoste, P.; Michel, F.B.; Godard, P. HLA-DR and ICAM-1 expression on bronchial epithelial cells in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.E.; Korbie, D.; Anderson, W.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Trau, M. Analysis of exosome purification methods using a model liposome system and tunable-resistive pulse sensing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escola, J.M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Stoorvogel, W.; Griffith, J.M.; Yoshie, O.; Geuze, H.J. Selective enrichment of tetraspan proteins on the internal vesicles of multivesicular endosomes and on exosomes secreted by human B-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20121–20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Boussac, M.; Véron, P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P.; Raposo, G.; Garin, J.; Amigorena, S. Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: A secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7309–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Chisanga, D.; Ariyaratne, D.; Al Saffar, H.; Anand, S.; Zhao, K.; Samuel, M.; Pathan, M.; Jois, M.; Chilamkurti, N.; et al. ExoCarta: A Web-Based Compendium of Exosomal Cargo. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.C.; Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. Extracellular vesicle docking at the cellular port: Extracellular vesicle binding and uptake. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, Z.; Yáñez-Mó, M. Tetraspanins in extracellular vesicle formation and function. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R.; Kumar, M.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Sethi, T.; Pandey, R.; Malik, G.; et al. Exosome-enclosed microRNAs in exhaled breath hold potential for biomarker discovery in patients with pulmonary diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, M.; Chinchilli, V.; Banta, E.; Craig, T.; August, A.; Bascom, R.; Cantorna, M.; Harvill, E.; Ishmael, F.T. Differential expression of microRNAs in exhaled breath condensates of patients with asthma, patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and healthy adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, M.; Gao, X.H.; Zhou, L.; Mi, Q.S. Small RNAs have a large impact: Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for human diseases. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairoungdua, A.; Smith, D.L.; Pochard, P.; Hull, M.; Caplan, M.J. Exosome release of β-catenin: A novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, A.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Kemper, S.; Hattori, T.; Takigawa, M.; Brigstock, D.R. Exosomes mediate intercellular transfer of pro-fibrogenic connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) between hepatic stellate cells, the principal fibrotic cells in the liver. Surgery 2014, 156, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Charrier, A.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yu, B.; Agarwal, K.; Tsukamoto, H.; Lee, L.J.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Brigstock, D.R. Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkins, M.B.; Dasgupta, S.; Wang, G.; Zhu, G.; Bieberich, E. Exosome reduction in vivo is associated with lower amyloid plaque load in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.B.; Bellingham, S.A.; Hill, A.F. The neutral sphingomyelinase pathway regulates packaging of the prion protein into exosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3455–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, K.; Kanto, K.; Hatakeyama, K.; Ide, T.; Wakabayashi-Nakao, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Sakura, N.; Terashima, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mochizuki, T. Exosome-mediated extracellular release of polyadenylate-binding protein 1 in human metastatic duodenal cancer cells. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, G.; Cai, W.; Millard, R.W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Peng, T.; Fan, G.C. Cardiomyocytes mediate anti-angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic rats through the exosomal transfer of miR-320 into endothelial cells. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 74, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luberto, C.; Hassler, D.F.; Signorelli, P.; Okamoto, Y.; Sawai, H.; Boros, E.; Hazen-Martin, D.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A.; Smith, G.K. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death in MCF7 by a novel inhibitor of neutral sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41128–41139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogolludo, A.; Moreno, L.; Frazziano, G.; Moral-Sanz, J.; Menendez, C.; Castañeda, J.; González, C.; Villamor, E.; Perez-Vizcaino, F. Activation of neutral sphingomyelinase is involved in acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.A.; Gugiu, B.G.; Thomas, M.; Basseri, R.J.; Eliav, D.R.; Salomon, R.G.; Berliner, J.A. A role for neutral sphingomyelinase activation in the inhibition of LPS action by phospholipid oxidation products. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gon, Y.; Maruoka, S.; Inoue, T.; Kuroda, K.; Yamagishi, K.; Kozu, Y.; Shikano, S.; Soda, K.; Lötvall, J.; Hashimoto, S. Selective release of miRNAs via extracellular vesicles is associated with house-dust mite allergen-induced airway inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1586–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.F.; Borg, Z.D.; Goodwin, M.; Sokocevic, D.; Wagner, D.E.; Coffey, A.; Antunes, M.; Robinson, K.L.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S.; et al. Systemic Administration of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorates Aspergillus Hyphal Extract-Induced Allergic Airway Inflammation in Immunocompetent Mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.M.; Zhuansun, Y.X.; Chen, R.; Lin, L.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.G. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote immunosuppression of regulatory T cells in asthma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 363, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Long, Y.; Lei, Y.; Deng, X.; He, B.; Sheng, M.; Li, M.; Gu, Z. A novel micelle of coumarin derivative monoend-functionalized PEG for anti-tumor drug delivery: In vitro and in vivo study. J. Drug Target 2012, 20, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Giavaresi, G.; Lorico, A.; Alessandro, R. Extracellular Vesicles as Biological Shuttles for Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulagnier, K.; Motta, C.; Hamdi, S.; Roy, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Pageaux, J.F.; Kobayashi, T.; Salles, J.P.; Perret, B.; Bonnerot, C.; et al. Mast cell- and dendritic cell-derived exosomes display a specific lipid composition and an unusual membrane organization. Biochem. J. 2004, 380, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Harris, C.L.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Morgan, B.P. Antigen-presenting cell exosomes are protected from complement-mediated lysis by expression of CD55 and CD59. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.G. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: The anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrak, A.; Bolukbasi, M.F.; Ozdener, G.B.; Brenner, G.J.; Madlener, S.; Erkan, E.P.; Ströbel, T.; Breakefield, X.O.; Saydam, O. Genetically engineered microvesicles carrying suicide mRNA/protein inhibit schwannoma tumor growth. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Ji, T.; Zhu, M.; Anderson, G.J.; Wei, J.; Nie, G. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, B.; Hung, M.E.; Breakefield, X.O.; Leonard, J.N. Therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles: Clinical promise and open questions. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Stremersch, S.; Braeckmans, K.; de Smedt, S.C.; Hendrix, A.; Wood, M.J.A.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Raemdonck, K.; Vader, P. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.L.; Scott, M.J.; Wickline, S.A. Maximizing exosome colloidal stability following electroporation. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 448, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, J.A.; Sastre, B.; Rodrigo-Muñoz, J.M.; Del Pozo, V. Exosomes: A new approach to asthma pathology. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2019, 495, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, N.R.; Kim, S.H.; Ruffner, M.A.; Robbins, P.D. Therapeutic effect of exosomes from indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive dendritic cells in collagen-induced arthritis and delayed-type hypersensitivity disease models. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Chopp, M.; Meng, Y.; Katakowski, M.; Xin, H.; Mahmood, A.; Xiong, Y. Effect of exosomes derived from multipluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells on functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity in rats after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maguire, C.A.; Balaj, L.; Sivaraman, S.; Crommentuijn, M.H.; Ericsson, M.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Baranov, V.; Gianni, D.; Tannous, B.A.; Sena-Esteves, M.; et al. Microvesicle-associated AAV vector as a novel gene delivery system. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livshits, M.A.; Livshts, M.A.; Khomyakova, E.; Evtushenko, E.G.; Lazarev, V.N.; Kulemin, N.A.; Semina, S.E.; Generozov, E.V.; Govorun, V.M. Isolation of exosomes by differential centrifugation: Theoretical analysis of a commonly used protocol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksvold, M.P.; Neurauter, A.; Pedersen, K.W. Magnetic bead-based isolation of exosomes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1218, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.; Möller, A. Size Exclusion Chromatography: A Simple and Reliable Method for Exosome Purification. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez-Valero, A.; Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Carreras-Planella, L.; Franquesa, M.; Beyer, K.; Borràs, F.E. Size-Exclusion Chromatography-based isolation minimally alters Extracellular Vesicles’ characteristics compared to precipitating agents. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Simpson, R.J.; Greening, D.W. A Protocol for Isolation and Proteomic Characterization of Distinct Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes by Sequential Centrifugal Ultrafiltration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1545, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. A highly efficient method for isolating urinary exosomes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeyen, E.; Van Mol, K.; Baggerman, G.; Willems, H.; Boonen, K.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, A.; Schildermans, K.; Cho, W.C.; et al. Ultrafiltration and size exclusion chromatography combined with asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation for the isolation and characterisation of extracellular vesicles from urine. J. Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1490143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchial epithelial cells | Regulate the normal airway biology including homeostasis and innate defense | [36] |
| Macrophages | Maintain homeostasis and immune cell production | [38] |
| Endothelial cells | Activate neighboring pericytes through proinflammatory microRNAs | [39] |
| B cells | Activate immune system through antigen presentation | [40] |
| Dendritic cells | Modulate immune reactions through activating T and B cells | [41,42] |
| Mesenchymal stromal cells | Modulate the polarization of macrophages | [43] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagano, T.; Katsurada, M.; Dokuni, R.; Hazama, D.; Kiriu, T.; Umezawa, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102589
Nagano T, Katsurada M, Dokuni R, Hazama D, Kiriu T, Umezawa K, Kobayashi K, Nishimura Y. Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102589
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagano, Tatsuya, Masahiro Katsurada, Ryota Dokuni, Daisuke Hazama, Tatsunori Kiriu, Kanoko Umezawa, Kazuyuki Kobayashi, and Yoshihiro Nishimura. 2019. "Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102589
APA StyleNagano, T., Katsurada, M., Dokuni, R., Hazama, D., Kiriu, T., Umezawa, K., Kobayashi, K., & Nishimura, Y. (2019). Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102589