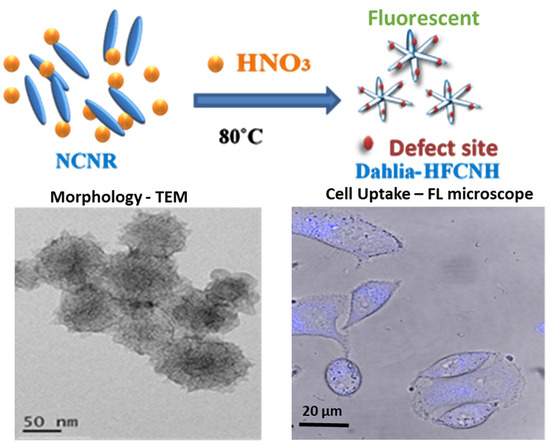
Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn as a Bio-Imaging PROBE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Morphology Details of Dahlia-Like HFCNH
2.2. Chemical Composition of HFCNH
3. Discussion.
3.1. Elemental Analysis of HFCNH
3.2. Absorbance and Fluorescence Properties of HFCNH
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials Required
4.2. Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn (HFCNH) from Carbon Nanorice (NCNR) via Chemical Oxidation
4.3. Characterization of HFCNH
4.4. Fluorescence Cell Image
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasilios, G.; Jason, A.P.; Jiri, T.; Radek, Z. Board family of carbon nano allotropies: Classification chemistry and application of fullerenes, carbondots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar]
- Chechetka, S.A.; Zhang, M.; Yudassaka, M.; Miyako, E. Physicochemically functionalized carbon nanohorns for multi-dimensional cancer elimination. Carbon 2016, 97, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousis, N.; Martinez, I.S.; Ewels, C.P.; Tagmatarchis, N. Structure, properties, functionalization and application of carbon nanohorns. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4850–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Yudasaka, M.; Yamada, R.; Bandow, S.; Suenaga, K.; Kokai, F.; Takahashi, K. Nano-aggregates of single- walled graphitic carbon nano-horns. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 309, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Bandow, S.; Iijima, S. Synthesis of carbon nanohorn particle by simple pulsed ignited between pre heated carbon rods arc discharge. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 389, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, K.; Shi, Z.; Gu, Z.; Xu, S. Synthesis of single-wall carbon nanohorns by arc-discharge in air and their formation mechanism. Carbon 2010, 48, 1580–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M. Device and Method for Production of Carbon Nanotube, Fullerene and Their Derivatives. U.S. Patent 7,125,525 EP 1428794; (Filed 2003, granted 2006), 24 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Rinzler, A.G.; Dai, H.J.; Hafner, H.J.; Bradley, R.K.; Boul, P.J.; Lu, A.; Lverson, T.; Shelimov, K.; Huffman, C.B.; et al. Fullerene Pipes. Science 1998, 280, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Meziani, M.J.; Sun, Y.P. Functionalized carbon naotubes for polymeric nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, E.; Dalai, A.; Adjaye, J. Functionalization and characterisation of carbon nanohorns (CNHs) for Hydro treating of Gas oils. Top. Catal. 2014, 57, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekyarova, E.; Kaneko, K.; Yudasaka, M.; Kasuya, D.; Iijina, S.; Huidobro, A. Controlled opening of single –wall carbon nanohorns by heat treatment in Carbon dioxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 4479–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekyarova, E.; Kaneko, K.; Yudasaka, M.; Kasuya, D.; Iijina, S. Oxidation and porosity evaluation of budlike single-wall carbon nanohon Aggregates. Langmuir 2002, 18, 4138–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.F.; Dorn, H.C.; Geohegan, D.; Zhang, C. Assembly of single-wall carbon nanohorn supported liposome particles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.T.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y.P. Carbon dDots for optical imaging in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, W.W.W.; Hui, Y.Y.; Tsai, P.C.; Chang, H.C. Fluorescent nanodiomanod; A versatile tool for long–term cell tracking, super-resolution imaging, and nanoscale temperature sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, A.; Sun, S. Recent Application of Carbon nanomaterials in fluorescence biosensing and bioimaging. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11346–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guosong, H.; Shuo, D.; Antaris, A.L.; Hongjie, D. Carbon nanomaterials for biological imaging and nonmedicinal therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10816–10906. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, P.S.; Tsai, H.C.; Iame, T. In-situ hydrothermal Synthesis of carbon nanorice using Nafion as a template. Carbon 2014, 77, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheol, M.Y.; Daisuke, K.; Masako, Y.; Sumio, I.; Katsumi, K. Microporosity development of single wall carbon nanohorn with chemically induced coalescence of assembly Structure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17775–17778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Merenad, E.L.; Castleman, A.W., Jr. Reaction of water cluster with nitric acid. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 3554–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minfang, Z.; Masako, Y.; Kumiko, A.; Jin, M.; Sumio, I. Light assisted oxidation of single wall carbon nanohorns for abundant creation of oxygen groups that enable chemical modification with proteins to enhance biocompatibility. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W. FT-IR study of Nafion Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, D.K.; Lim, S.T. Preparation and characterization of a water- soluble chitosan-heparin complex. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.C.; Arindam, S.; Jana, N.R.; Rupa, S. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterisation, and bioimaging application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 11, 18546–18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.J.; Yong, J.K.; Jong, H.H.; Masako, Y.; Iijima, S.; Hirofumi, K.; Yoong, A.K.; Katsumi, K.; Cheol, M.Y. Thermal-treatment-induced enhancement in effective surface area of single wall carbon nanohorns for supercapcitor application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 25877–25883. [Google Scholar]
- Shigenroi, U.; Hiroaki, H.; Yoshiyuki, H.; Hirofumi, K.; Kunimitsu, T.; Hideki, S.; Masahiko, A.; Masako, Y.; Sumio, I.; Katusmi, K. Direct evidence on C-C single bonding in single wall carbon nanohorn aggregates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Peter, M. Studies of carbon nanotube and fluorinated nanotube by X-ray and ultra-violet photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5427–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxim, N.T.; Warren, T.F.; Giulio, L.; Daniel, E.R.; Sivaram, A. Effect of mild nitric acid oxidation on dispersability, size, and structure of single wall carbon nanotube. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5765–5772. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Hongling, Z.; Quan, Q.; Yanlian, Y.; Zhongfa, L.; Xinyong, G.; Zuliang, D. Effect of chemical oxidation on the structure of single wall carbn nanotube. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 3712–3718. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdev, A.; Ishita, M.; Uday Kumar, S.; Bharat, B.; Poornima, D.; Gopinath, P. A novel one- step synthesis of PEG passivated multicolour fluorescent carbon dots for potential bio labeling application. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16958–16961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.Y.; Ming, W.; Huan, C.C.; Kuan, M.C.; Yueh, C.Y. Bright Fluorescent nanodiamonds: No photo bleaching and low cytotoxicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17604–17605. [Google Scholar]
- Neugar, F.; Zappe, A.; Jelezko, F.; Tietz, C.; Boudou, J.P.; Krueger, A.; Wrachtrup, J. Dynamics of diamond nanoparticles in solution and cells. Nano. Lett. 2007, 7, 3588–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizumi, Y.; Yudasaka, M.; Kim, J.; Sakakita, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Okazaki, T. Oxygen-doped carbon nanotubes for near-infrared fluorescent labels and imaging probes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6272. [Google Scholar]
- Demchenko, A.P.; Dekaliuk, M.O. Novel fluorescent carbonic nanomaterials for sensing and imaging. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parasuraman, P.S.; Parasuraman, V.R.; Anbazhagan, R.; Tsai, H.-C.; Lai, J.-Y. Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn as a Bio-Imaging PROBE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122977
Parasuraman PS, Parasuraman VR, Anbazhagan R, Tsai H-C, Lai J-Y. Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn as a Bio-Imaging PROBE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(12):2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122977
Chicago/Turabian StyleParasuraman, Perumalswamy Sekar, Vijaya Rohini Parasuraman, Rajeshkumar Anbazhagan, Hsieh-Chih Tsai, and Juin-Yih Lai. 2019. "Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn as a Bio-Imaging PROBE" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 12: 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122977
APA StyleParasuraman, P. S., Parasuraman, V. R., Anbazhagan, R., Tsai, H. -C., & Lai, J. -Y. (2019). Synthesis of “Dahlia-Like” Hydrophilic Fluorescent Carbon Nanohorn as a Bio-Imaging PROBE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(12), 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122977