Alu RNA Modulates the Expression of Cell Cycle Genes in Human Fibroblasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Alu Sequences, Vectors, and Cell Lines for Overexpression
2.2. Validation of Alu Overexpression
2.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
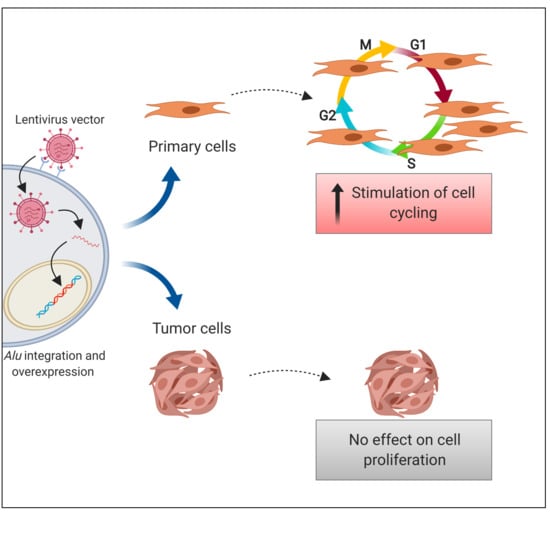
2.4. Alu RNA Promotes IMR90 Cell Cycle Progression
2.5. Location Analysis of Alu Elements at Differentially Expressed Loci
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cloning of Constructs
4.2. Cell Lines and Lentiviral Vector Transduction
4.3. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.4. RNA-Seq Procedure and Data Analysis
4.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. Bioinformatic Analyses on Promoter, 5′ UTR, 3′ UTR, and miRNA Content of Differentially Expressed Genes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| SINEs | short interspersed nuclear elements |
| L1 | non-LTR retroelements LINE-1 |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| FC | fold change |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| H1p | H1 promoter |
| PI | propidium iodide |
References
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Berger, A.; Strub, K. Multiple Roles of Alu-Related Noncoding RNAs. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2011, 51, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kriegs, J.O.; Churakov, G.; Jurka, J.; Brosius, J.; Schmitz, J. Evolutionary history of 7SL RNA-derived SINEs in Supraprimates. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeaux, M.S.; Roy-Engel, A.M.; Hedges, D.J.; Deininger, P.L. Diverse cis factors controlling Alu retrotransposition: What causes Alu elements to die? Genome Res. 2009, 19, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, R.; van Schaik, B.D.; van Batenburg, M.F.; Roos, M.; Monajemi, R.; Caron, H.; Bussemaker, H.J.; van Kampen, A.H. The human transcriptome map reveals extremes in gene density, intron length, GC content, and repeat pattern for domains of highly and weakly expressed genes. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, D.; Majumder, P.P.; Rao, C.B.; Brahmachari, S.K.; Mukerji, M. Nonrandom distribution of alu elements in genes of various functional categories: Insight from analysis of human chromosomes 21 and 22. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentin, Y. Emergence of master sequences in families of retroposons derived from 7sl RNA. Genetica 1994, 93, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, H.K.; Nishio, H.; Tavis, J.; Zielinski, R.; Dugaiczyk, A. Alu-mediated phylogenetic novelties in gene regulation and development. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-Maor, G.; Sorek, R.; Shomron, N.; Ast, G. The birth of an alternatively spliced exon: 3’ splice-site selection in Alu exons. Science 2003, 300, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Han, D.; Boyd-Kirkup, J.; Yu, X.; Han, J.J. Evolution of Alu elements toward enhancers. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, P.L.; Batzer, M.A. Alu repeats and human disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 1999, 67, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovchuk, P.; Goodrich, J.A.; Kugel, J.F. B2 RNA and Alu RNA repress transcription by disrupting contacts between RNA polymerase II and promoter DNA within assembled complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5569–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.L.; Carmichael, G.G. Gene regulation by SINES and inosines: Biological consequences of A-to-I editing of Alu element inverted repeats. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3294–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karijolich, J.; Zhao, Y.; Alla, R.; Glaunsinger, B. Genome-wide mapping of infection-induced SINE RNAs reveals a role in selective mRNA export. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6194–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.; Berger, A.; Scherrer, A.; Alkalaeva, E.; Strub, K. Alu RNA regulates the cellular pool of active ribosomes by targeted delivery of SRP9/14 to 40S subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2874–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarallo, V.; Hirano, Y.; Gelfand, B.D.; Dridi, S.; Kerur, N.; Kim, Y.; Cho, W.G.; Kaneko, H.; Fowler, B.J.; Bogdanovich, S.; et al. DICER1 loss and Alu RNA induce age-related macular degeneration via the NLRP3 inflammasome and MyD88. Cell 2012, 149, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, C.; Silberberg, G.; Behm, M.; Ohman, M. Alu elements shape the primate transcriptome by cis-regulation of RNA editing. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, E.; Mondala, P.K.; Santos, N.D.; Miller, A.C.; Pineda, G.; Jiang, Q.; Leu, H.; Ali, S.A.; Ganesan, A.P.; Wu, C.N.; et al. Alu-dependent RNA editing of GLI1 promotes malignant regeneration in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capshew, C.R.; Dusenbury, K.L.; Hundley, H.A. Inverted Alu dsRNA structures do not affect localization but can alter translation efficiency of human mRNAs independent of RNA editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8637–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, E.W.; Luo, D.; Seo, J.; Singh, N.N.; Singh, R.N. Human Survival Motor Neuron genes generate a vast repertoire of circular RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2884–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubelsky, Y.; Ulitsky, I. Sequences enriched in Alu repeats drive nuclear localization of long RNAs in human cells. Nature 2018, 555, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, D.; Vavrova-Anderson, J.; Oler, A.J.; Cowling, V.H.; Cairns, B.R.; White, R.J. SINE transcription by RNA polymerase III is suppressed by histone methylation but not by DNA methylation. Nat. Commun 2015, 6, 6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panning, B.; Smiley, J.R. Activation of expression of multiple subfamilies of human Alu elements by adenovirus type 5 and herpes simplex virus type 1. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 248, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariner, P.D.; Walters, R.D.; Espinoza, C.A.; Drullinger, L.F.; Wagner, S.D.; Kugel, J.F.; Goodrich, J.A. Human Alu RNA is a modular transacting repressor of mRNA transcription during heat shock. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.H.; Qiu, X.H.; Liu, H.Q. Increased level of polymerase III transcribed Alu RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. Mol. Carcinog. 2005, 42, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ruocco, F.; Basso, V.; Rivoire, M.; Mehlen, P.; Ambati, J.; De Falco, S.; Tarallo, V. Alu RNA accumulation induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by modulating miR-566 and is associated with cancer progression. Oncogene 2018, 37, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Dridi, S.; Tarallo, V.; Gelfand, B.D.; Fowler, B.J.; Cho, W.G.; Kleinman, M.E.; Ponicsan, S.L.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Chiodo, V.A.; et al. DICER1 deficit induces Alu RNA toxicity in age-related macular degeneration. Nature 2011, 471, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, K.; Fordis, C.M.; Corsico, C.D.; Howard, T.H.; Howard, B.H. Modulation of HeLa cell growth by transfected 7SL RNA and Alu gene sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar]
- Baryakin, D.N.; Semenov, D.V.; Savelyeva, A.V.; Koval, O.A.; Rabinov, I.V.; Kuligina, E.V.; Richter, V.A. Alu- and 7SL RNA Analogues Suppress MCF-7 Cell Viability through Modulating the Transcription of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Genes. Acta Naturae 2013, 5, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Tanasa, B.; Trabucchi, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Ohgi, K.A.; Rose, D.W.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. DICER- and AGO3-dependent generation of retinoic acid-induced DR2 Alu RNAs regulates human stem cell proliferation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Hernandez, A.; Gonzalez-Rico, F.J.; Roman, A.C.; Rico-Leo, E.; Alvarez-Barrientos, A.; Sanchez, L.; Macia, A.; Heras, S.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Merino, J.M.; et al. Alu retrotransposons promote differentiation of human carcinoma cells through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4665–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelnuovo, M.; Massone, S.; Tasso, R.; Fiorino, G.; Gatti, M.; Robello, M.; Gatta, E.; Berger, A.; Strub, K.; Florio, T.; et al. An Alu-like RNA promotes cell differentiation and reduces malignancy of human neuroblastoma cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, A.; Carnevali, D.; Bollati, V.; Fustinoni, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Dieci, G. Identification of RNA polymerase III-transcribed Alu loci by computational screening of RNA-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Bernards, R.; Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002, 296, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.M.; Liu, W.M.; Schmid, C.W. RNA polymerase III promoter and terminator elements affect Alu RNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.M.; West, N.C.; Rao, A.; Adhikari, P.; Aleman, C.; Barnes, A.P.; Deininger, P.L. Upstream flanking sequences and transcription of SINEs. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orioli, A. Novel insights into human RNA polymerase III transcription: Non canonical termination and biogenesis of potential regulatory RNAs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Parma, Parma, Italy, 12 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Baserga, S.J.; Steitz, J.A. The Diverse World of Small Ribonucleoproteins. In The RNA World, 1st ed.; Gesteland, R.F., Atkins, J.F., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Archive: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 24, pp. 359–381. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durrieu-Gaillard, S.; Dumay-Odelot, H.; Boldina, G.; Tourasse, N.J.; Allard, D.; Andre, F.; Macari, F.; Choquet, A.; Lagarde, P.; Drutel, G.; et al. Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription during transformation of human IMR90 fibroblasts with defined genetic elements. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Su, T.; Li, B.; Bonora, G.; Oberai, A.; Chan, Y.; Sasidharan, R.; Berk, A.J.; Pellegrini, M.; Kurdistani, S.K. Reorganization of the host epigenome by a viral oncogene. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, P.; Enroth, S.; Teichmann, M.; Jernberg Wiklund, H.; Smit, A.; Westermark, B.; Singh, U. Growth signals employ CGGBP1 to suppress transcription of Alu-SINEs. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirkmajer, S.; Chibalin, A.V. Serum starvation: Caveat emptor. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C272–C279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3’ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panning, B.; Smiley, J.R. Activation of RNA polymerase III transcription of human Alu repetitive elements by adenovirus type 5: Requirement for the E1b 58-kilodalton protein and the products of E4 open reading frames 3 and 6. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 3231–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, M.F.; Singh, K. Enhanced B2 transcription in simian virus 40-transformed cells is mediated through the formation of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on previously inactive genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7059–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L.; Blomer, U.; Gage, F.H.; Trono, D.; Verma, I.M. Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11382–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Okayama, H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1987, 7, 2745–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, T.; Kaibuchi, K.; Kishi, K.; Kishida, S.; Doi, K.; Hoshino, M.; Hattori, S.; Takai, Y. smg/rap1/Krev-1 p21s inhibit the signal pathway to the c-fos promoter/enhancer from c-Ki-ras p21 but not from c-raf-1 kinase in NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsen, T.; de Vlieg, J.; Alkema, W. BioVenn—A web application for the comparison and visualization of biological lists using area-proportional Venn diagrams. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | Genes with Alu in 3′ UTR | Total Number of Analyzed Genes | p-Value (Fisher exact test) | % of Genes with an Alu Element in Their 3′ UTR | % of Anti-sense Alu in Each Gene (Average) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome | 4838 | 19,836 | – | 24.39 | 49.22 |
| AluSq2_Up | 9 | 87 | 0.0005 | 10.34 | 66.67 |
| AluSq2_Down | 37 | 101 | 0.0019 | 36.63 | 55.63 |
| AluSx_Up | 25 | 147 | 0.0082 | 17.01 | 30.00 |
| AluSx_Down | 28 | 105 | 0.0761 | 26.67 | 68.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cantarella, S.; Carnevali, D.; Morselli, M.; Conti, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Montanini, B.; Dieci, G. Alu RNA Modulates the Expression of Cell Cycle Genes in Human Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133315
Cantarella S, Carnevali D, Morselli M, Conti A, Pellegrini M, Montanini B, Dieci G. Alu RNA Modulates the Expression of Cell Cycle Genes in Human Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(13):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133315
Chicago/Turabian StyleCantarella, Simona, Davide Carnevali, Marco Morselli, Anastasia Conti, Matteo Pellegrini, Barbara Montanini, and Giorgio Dieci. 2019. "Alu RNA Modulates the Expression of Cell Cycle Genes in Human Fibroblasts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 13: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133315
APA StyleCantarella, S., Carnevali, D., Morselli, M., Conti, A., Pellegrini, M., Montanini, B., & Dieci, G. (2019). Alu RNA Modulates the Expression of Cell Cycle Genes in Human Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133315