The Number of Liver Galectin-3 Positive Cells Is Dually Correlated with NAFLD Severity in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Number of Gal-3 Positive Cells Correlates with the Severity of Disease in Children with NAFLD
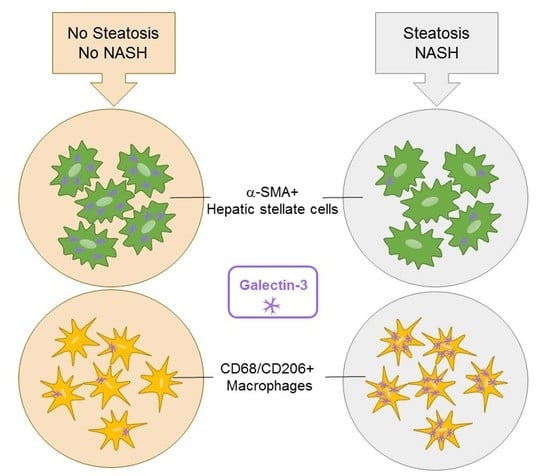
2.2. The Number of CD68/Gal-3 Positive Cells Decreases with Severity of Disease in Children with NAFLD
2.3. The Number of CD68/CD206/Gal-3 Positive Cells Decreases with the Severity of Disease in Children with NAFLD
2.4. Bile Duct Cells Express Gal-3 in Children with NAFLD
2.5. The Number of α-Smooth Muscle Actin (SMA)/Gal-3+ Cells Increases with the Severity of Fibrosis in Children with NAFLD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Anthropometrics
4.3. Laboratory Tests
4.4. Liver Biopsies
4.5. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| Gal-3 | Galectin-3 |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyltransferase |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NAS | NAFLD activity score |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
References
- Brunt, E.M.; Wong, V.W.; Nobili, V.; Day, C.P.; Sookoian, S.; Maher, J.J.; Bugianesi, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiniakos, D.G.; Vos, M.B.; Brunt, E.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathology and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, R.; Barritt, A.S., 4th; Calmus, Y.; Scatton, O.; Runge, T.; Lebray, P.; Poynard, T.; Ratziu, V.; Conti, F. NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, V.; Alisi, A.; Newton, K.P.; Schwimmer, J.B. Comparison of the Phenotype and Approach to Pediatric vs Adult Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Cianfarani, S.; Manco, M.; Agostoni, C.; Nobili, V. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome in adolescents: Pathogenetic role of genetic background and intrauterine environment. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Vajro, P. Pre-natal and post-natal environment monitoring to prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alisi, A.; Carpino, G.; Oliveira, F.L.; Panera, N.; Nobili, V.; Gaudio, E. The Role of Tissue Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation on NAFLD Pathogenesis and Its Clinical Implications. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 8162421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, M.; Rolig, A.S.; Redmond, W.L. The role of Galectin-3 in modulating tumor growth and immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1434467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.C.; Li, J.; Gao, J. Functions of galectin-3 and its role in fibrotic diseases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Soh, A.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, H. Galectin-3 as a novel biomarker for disease diagnosis and a target for therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.K.; Dowling, C.A.; Jeng, K.C.; Chen, J.T.; Yang, R.Y.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-3 expression is induced in cirrhotic liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.L.; Frazão, P.; Chammas, R.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T.; Borojevic, R.; Takiya, C.M.; El-Cheikh, M.C. Kinetics of mobilization and differentiation of lymphohematopoietic cells during experimental murine schistosomiasis in galectin-3−/− mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, N.C.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Farnworth, S.L.; Poirier, F.; Russo, F.P.; Iredale, J.P.; Haslett, C.; Simpson, K.J.; Sethi, T. Galectin-3 regulates myofibroblast activation and hepatic fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5060–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.X.; Chen, X.; Hsu, D.K.; Baghy, K.; Serizawa, N.; Scott, F.; Takada, Y.; Takada, Y.; Fukada, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Galectin-3 modulates phagocytosis-induced stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G439–G446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomoto, K.; Tsuneyama, K.; Abdel Aziz, H.O.; Takahashi, H.; Murai, Y.; Cui, Z.G.; Fujimoto, M.; Kato, I.; Hiraga, K.; Hsu, D.K.; et al. Disrupted galectin-3 causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in male mice. J. Pathol. 2006, 210, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftic, I.; Jovicic, N.; Pantic, J.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Pejnovic, N. Galectin-3 Ablation Enhances Liver Steatosis, but Attenuates Inflammation and IL-33-Dependent Fibrosis in Obesogenic Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejnovic, N.N.; Pantic, J.M.; Jovanovic, I.P.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Milovanovic, M.Z.; Nikolic, I.G.; Zdravkovic, N.S.; Djukic, A.L.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. Galectin-3 deficiency accelerates high-fat diet-induced obesity and amplifies inflammation in adipose tissue and pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Takasaki, I.; Tabuchi, Y.; Tsuneyama, K. Deficiency in galectin-3 promotes hepatic injury in CDAA diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 959824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Hsu, D.K.; Zuberi, R.I.; Kuwabara, I.; Chi, E.Y.; Henderson, W.R., Jr. Expression and function of galectin-3, a beta-galactoside-binding lectin, in human monocytes and macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 147, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iacobini, C.; Menini, S.; Ricci, C.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Scipioni, A.; Salvi, L.; Cordone, S.; Delucchi, F.; Serino, M.; Federici, M.; et al. Galectin-3 ablation protects mice from diet-induced NASH: A major scavenging role for galectin-3 in liver. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, A.C.; Sun, R.; Choi, H.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Role of Galectin-3 in Classical and Alternative Macrophage Activation in the Liver Following Acetaminophen Intoxication. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, A.C.; Sun, R.; Mishin, V.; Hall, L.B.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Role of Galectin-3 in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Inflammatory Mediator Production. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 127, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.; Benkdane, M.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Bonnafous, S.; Louvet, A.; Lafdil, F.; Pecker, F.; Tran, A.; Gual, P.; Mallat, A.; et al. M2 Kupffer Cells Promote M1 Kupffer Cell Apoptosis: A Protective Mechanism against Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpino, G.; Nobili, V.; Renzi, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Stronati, L.; Franchitto, A.; Alisi, A.; Onori, P.; de Vito, R.; Alpini, G.; et al. Macrophage Activation in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Correlates with Hepatic Progenitor Cell Response via Wnt3a Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazankov, K.; Jørgensen, S.M.D.; Thomsen, K.L.; Møller, H.J.; Vilstrup, H.; George, J.; Schuppan, D.; Grønbæk, H. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, W.C.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Lu, W.Y.; Jung, J.; Boulter, L.; Henderson, N.C.; Simpson, K.J.; Schotanus, B.; Wojtacha, D.; Bird, T.G.; et al. Galectin-3 Regulates Hepatic Progenitor Cell Expansion During Liver Injury. Gut 2015, 64, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepreux, S.; Desmoulière, A. Human liver myofibroblasts during development and diseases with a focus on portal (myo) fibroblasts. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Koyama, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, H.Y.; Liang, S.; Kim, I.H.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. Promising Therapy Candidates for Liver Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, S.A.; De Freitas Souza, B.S.; Sá Barreto, E.P.; Kaneto, C.M.; Neto, H.A.; Azevedo, C.M.; Guimarães, E.T.; De Freitas, L.A.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, R.; Soares, M.B. Reduction of Galectin-3 Expression and Liver Fibrosis after Cell Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cirrhosis. Cytotherapy 2012, 14, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, P.G.; Zomer, E. Therapy of experimental NASH and fibrosis with galectin inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, P.G.; Chou, H.; Zomer, E.; Hong, F.; Klyosov, A.; Fiel, M.I.; Friedman, S.L. Regression of fibrosis and reversal of cirrhosis in rats by galectin inhibitors in thioacetamide-induced liver disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Marri, S.R.; Chalasani, N.; Kohli, R.; Aronstein, W.; Thompson, G.A.; Irish, W.; Miles, M.V.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Lawitz, E.; et al. Randomised clinical study: GR-MD-02, a galectin-3 inhibitor, vs. placebo in patients having non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with advanced fibrosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohman, T.G.; Roche, A.F.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciari, E.; Milani, S.; Balsamo, A.; Spada, E.; Bona, G.; Cavallo, L.; Cerutti, F.; Gargantini, L.; Greggio, N.; Tonini, G.; et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: IR and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Wilson, L.A.; Unalp, A.; Behling, C.E.; Lavine, J.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. NASH Clinical Research NetworkA list of members of the Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network can be found in the Appendix. Portal chronic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A histologic marker of advanced NAFLD-clinicopathologic correlations from the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network. Hepatology 2009, 49, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | Mean | S.D. |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 12.36 | 2.88 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.60 | 17.77 |
| Height (cm) | 153.1 | 16.42 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.00 | 5.37 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 85.83 | 8.51 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dl) | 119.3 | 63.04 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 154.8 | 33.89 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dl) | 45.04 | 8.77 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dl) | 95.46 | 32.65 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 47.93 | 39.80 |
| AST (IU/L) | 33.85 | 16.74 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 20.50 | 15.11 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 82.60 | 10.39 |
| Insulin (U/L) | 21.20 | 10.25 |
| HOMA-IR | 4.19 | 2.21 |
| Histologic Traits | Mean of Scores | S.D. |
|---|---|---|
| Steatosis | 1.50 | 1.13 |
| Lobular Inflammation | 1.15 | 0.42 |
| Portal Inflammation | 1.15 | 0.42 |
| Ballooning | 1.02 | 0.57 |
| NAS | 3.70 | 1.53 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, F.L.; Panera, N.; De Stefanis, C.; Mosca, A.; D’Oria, V.; Crudele, A.; De Vito, R.; Nobili, V.; Alisi, A. The Number of Liver Galectin-3 Positive Cells Is Dually Correlated with NAFLD Severity in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143460
de Oliveira FL, Panera N, De Stefanis C, Mosca A, D’Oria V, Crudele A, De Vito R, Nobili V, Alisi A. The Number of Liver Galectin-3 Positive Cells Is Dually Correlated with NAFLD Severity in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143460
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Felipe Leite, Nadia Panera, Cristiano De Stefanis, Antonella Mosca, Valentina D’Oria, Annalisa Crudele, Rita De Vito, Valerio Nobili, and Anna Alisi. 2019. "The Number of Liver Galectin-3 Positive Cells Is Dually Correlated with NAFLD Severity in Children" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143460
APA Stylede Oliveira, F. L., Panera, N., De Stefanis, C., Mosca, A., D’Oria, V., Crudele, A., De Vito, R., Nobili, V., & Alisi, A. (2019). The Number of Liver Galectin-3 Positive Cells Is Dually Correlated with NAFLD Severity in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3460. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143460