Interleukin (IL)-22 from IL-20 Subfamily of Cytokines Induces Colonic Epithelial Cell Proliferation Predominantly through ERK1/2 Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-22 but not IL-20 and IL-24 Promote Proliferation of Colonic Epithelial LS174T Cells
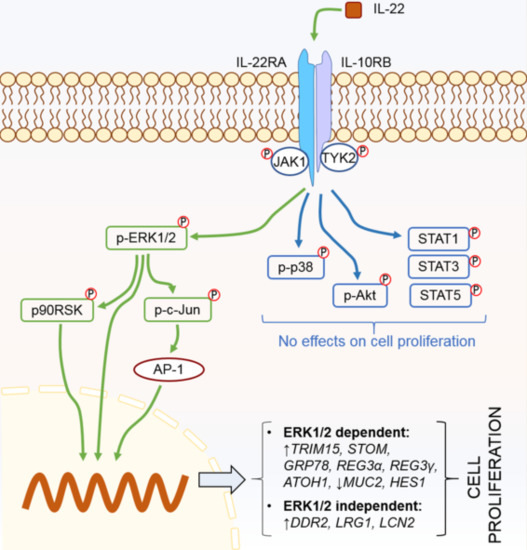
2.2. IL-22 Activates JAK-STAT, Akt, and Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cells
2.3. IL-22-Mediated Cell Proliferation Is Predominantly Controlled via the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway
2.4. p90RSK and c-Jun Are the Downstream Regulators of IL-22-Mediated ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway
2.5. IL-22-Modulated Pathways Are Associated with Epithelial Cell Proliferation
2.6. IL-22 Increases the Expression of Cell Proliferation and Migration-Associated Genes in Primary Mouse Intestinal Epithelial Cells
2.7. IL-22-Induced Effects Are Mediated through ERK1/2-Dependent and -Independent Transcriptional Modifications
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Antibodies Used in This Study
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Live-Cell Imaging for Cell Proliferation
4.5. Isolation and Maintenance of Primary Murine Intestinal Epithelial Cells
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.8. Transcriptomic Analyses Through RNA Sequencing
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGR2 | Anterior Gradient 2 |
| ATOH1 | Atonal BHLH transcription factor 1 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin dependent kinase 4 |
| DDR2 | Discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline |
| ERK | Extracellular regulatory kinase |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GLUT1 | Glucose transporter 1 |
| GRP78 | Binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) |
| HES1 | Hairy and enhancer of split-1 |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LCN2 | Lipocalin 2 |
| LRG1 | Leucine rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| mIECs | Murine intestinal epithelial cells |
| MMP7 | Matrix metalloprotease 7 |
| MUC2 | Mucin 2 |
| OSMR | Oncostatin M receptor |
| p90RSK | p90 ribosomal s6 kinase |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| REG3 | Regenerating family member 3 |
| SPDEF | SAM-pointed-domain-containing ETS transcription factor |
| STAT | Directory of open access journals |
| STOM | Stomatin |
| sXBP1 | Spliced X-box binding protein 1 |
| TIMP1 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 |
| TRIM15 | Tripartite motif containing 15 |
References
- Henderson, P.; van Limbergen, J.E.; Schwarze, J.; Wilson, D.C. Function of the intestinal epithelium and its dysregulation in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonetti, P.J. War and peace at mucosal surfaces. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niess, J.H.; Hruz, P.; Kaymak, T. The Interleukin-20 Cytokines in Intestinal Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, O.B.; Pociask, D.A.; Hodzic, Z.; Kolls, J.K.; Good, M. Interleukin-22 Signaling in the Regulation of Intestinal Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutz, S.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines—From host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickert, G.; Neufert, C.; Leppkes, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wittkopf, N.; Warntjen, M.; Lehr, H.A.; Hirth, S.; Weigmann, B.; Wirtz, S.; et al. STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to mucosal wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindemans, C.A.; Calafiore, M.; Mertelsmann, A.M.; O’Connor, M.H.; Dudakov, J.A.; Jenq, R.R.; Velardi, E.; Young, L.F.; Smith, O.M.; Lawrence, G.; et al. Interleukin-22 promotes intestinal-stem-cell-mediated epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 528, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwarycz, B.; Gracz, A.D.; Rivera, K.R.; Williamson, I.A.; Samsa, L.A.; Starmer, J.; Daniele, M.A.; Salter-Cid, L.; Zhao, Q.; Magness, S.T. IL22 Inhibits Epithelial Stem Cell Expansion in an Ileal Organoid Model. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronke, K.; Hernandez, P.P.; Zimmermann, J.; Klose, C.S.N.; Kofoed-Branzk, M.; Guendel, F.; Witkowski, M.; Tizian, C.; Amann, L.; Schumacher, F.; et al. Interleukin-22 protects intestinal stem cells against genotoxic stress. Nature 2019, 566, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Borg, D.J.; Harcourt, B.E.; Tong, H.; Sheng, Y.H.; Ng, C.P.; Das, I.; Wang, R.; Chen, A.C.; Loudovaris, T.; et al. Glycemic control in diabetes is restored by therapeutic manipulation of cytokines that regulate beta cell stress. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.E.; Stockinger, B.; Helmby, H. IL-22 mediates goblet cell hyperplasia and worm expulsion in intestinal helminth infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.S.; Cui, W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 2016, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrimon, N.; Pitsouli, C.; Shilo, B.Z. Signaling mechanisms controlling cell fate and embryonic patterning. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a005975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, A.; Benchabane, H.; Wang, Z.; Ahmed, Y. Regulation of Stem Cell Proliferation and Cell Fate Specification by Wingless/Wnt Signaling Gradients Enriched at Adult Intestinal Compartment Boundaries. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, A.S.; Aslam, U.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Meta-analysis of the turnover of intestinal epithelia in preclinical animal species and humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, G.; Fan, X. The effect of ghrelin on cell proliferation in small intestinal IEC-6 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2013, 67, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Shimomura, Y.; Andoh, A.; Bhan, A.K.; Blumberg, R.S.; Xavier, R.J.; Mizoguchi, A. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zenewicz, L.A.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Stevens, S.; Flavell, R.A. Innate and adaptive interleukin-22 protects mice from inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity 2008, 29, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolumam, G.; Wu, X.; Lee, W.P.; Hackney, J.A.; Zavala-Solorio, J.; Gandham, V.; Danilenko, D.M.; Arora, P.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, W. IL-22R Ligands IL-20, IL-22, and IL-24 Promote Wound Healing in Diabetic db/db Mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, S.M.; Valdez, P.A.; Wu, J.; Jung, K.; Zhong, F.; Hall, L.; Kasman, I.; Winer, J.; Modrusan, Z.; Danilenko, D.M.; et al. The effects of IL-20 subfamily cytokines on reconstituted human epidermis suggest potential roles in cutaneous innate defense and pathogenic adaptive immunity in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, K.; Witte, E.; Wallace, E.; Docke, W.D.; Kunz, S.; Asadullah, K.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W.; Sabat, R. IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: A potential role in psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, R.; Ouyang, W.; Wolk, K. Therapeutic opportunities of the IL-22-IL-22R1 system. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Rao, J.N.; Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Zou, T.; Turner, D.J.; Wang, J.Y. Akt kinase activation blocks apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells by inhibiting caspase-3 after polyamine depletion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22539–22547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Zhao, W.; Luo, Y.; Xi, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, G.; Guo, J.; Xu, C. Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type I (SPINK1) promotes BRL-3A cell proliferation via p38, ERK, and JNK pathways. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.R.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L.Q.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.F.; Zheng, X.H.; Lian, X.L.; Huang, H.F.; Chen, Y.Z. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of myeloid leukemia cells through PI3K-AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3630–3644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shingyochi, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Tajima, S.; Tanaka, R.; Mizuno, H.; Tobita, M. A Low-Level Carbon Dioxide Laser Promotes Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration through Activation of Akt, ERK, and JNK. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoba, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Shibata, S.; Masaki, E.; Emala, C.W., Sr.; Mizuta, K. The free fatty acid receptor 1 promotes airway smooth muscle cell proliferation through MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L333–L348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Poteet-Smith, C.E.; Xu, Y.; Errington, T.M.; Hecht, S.M.; Lannigan, D.A. Identification of the first specific inhibitor of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) reveals an unexpected role for RSK in cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, D.E.; Errington, T.M.; Smith, J.A.; Frierson, H.F., Jr.; Weber, M.J.; Lannigan, D.A. The serine/threonine protein kinase, p90 ribosomal S6 kinase, is an important regulator of prostate cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3108–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwin, J.; Drews, N.; Ali, S.; Stamschror, J.; Sorenson, M.; Rajah, T.T. Effect of genistein on p90RSK phosphorylation and cell proliferation in T47D breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.J.; Bae, J.; Wang, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Min, Y.S.; Je, H.D.; Sohn, U.D. The p90rsk-mediated signaling of ethanol-induced cell proliferation in HepG2 cell line. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 20, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.Y.; Tang, F.; Yao, K.; Lu, C.; Zhu, F.; Zheng, D.; Pugliese, A.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Cyclin-dependent kinase-3-mediated c-Jun phosphorylation at Ser63 and Ser73 enhances cell transformation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoudou-Bai, A.; Goussia, A.; Batistatou, A.; Stefanou, D.; Malamou-Mitsi, V.; Kanavaros, P. The expression levels of JunB, JunD and p-c-Jun are positively correlated with tumor cell proliferation in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaulian, E. AP-1-The Jun proteins: Oncogenes or tumor suppressors in disguise? Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.P.; Bershadsky, A.D. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchil, P.D.; Pawliczek, T.; Reynolds, T.D.; Ding, S.; Hinz, A.; Munro, J.B.; Huang, F.; Floyd, R.W.; Yang, H.; Hamilton, W.L.; et al. TRIM15 is a focal adhesion protein that regulates focal adhesion disassembly. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3928–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Lu, C.; Hong, J. TRIM15 Exerts Anti-Tumor Effects Through Suppressing Cancer Cell Invasion in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 8033–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, O.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.H.; Woo, Y.M.; Kang, J.H.; Yoon, H.G.; Bae, S.K.; Songyang, Z.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, Y. Role of the focal adhesion protein TRIM15 in colon cancer development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, M.P.; Thompson, R.J.; Eshcol, J.O.; Wemmie, J.A.; Benson, C.J. Stomatin modulates gating of acid-sensing ion channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53886–53891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Hayashi, H.; Ebina, Y.; Prohaska, R.; Ismail-Beigi, F. Association of stomatin (band 7.2b) with Glut1 glucose transporter. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 372, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Xiao, Y.P.; Laipis, P.J.; Fletcher, B.S.; Frost, S.C. Glucose deprivation enhances targeting of GLUT1 to lipid rafts in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E568–E576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, I.; Hisaki, T.; Sugiura, K.; Naito, K.; Kano, K. Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) regulates proliferation of endochondral cells in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 427, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, B.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.K. DDR2 inhibition reduces migration and invasion of murine metastatic melanoma cells by suppressing MMP2/9 expression through ERK/NF-kappaB pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2015, 47, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaso, E.; Labrador, J.P.; Wang, L.; Ikeda, K.; Eng, F.J.; Klein, R.; Lovett, D.H.; Lin, H.C.; Friedman, S.L. Discoidin domain receptor 2 regulates fibroblast proliferation and migration through the extracellular matrix in association with transcriptional activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, J.; Olaso, E. Role of discoidin domain receptor 2 in wound healing. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Abraham, S.; McKenzie, J.A.G.; Jeffs, N.; Swire, M.; Tripathi, V.B.; Luhmann, U.F.O.; Lange, C.A.K.; Zhai, Z.; Arthur, H.M.; et al. LRG1 promotes angiogenesis by modulating endothelial TGF-beta signalling. Nature 2013, 499, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, L.C.; Druhan, L.J.; Avalos, B.R. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of leucine-rich alpha2-glycoprotein, a novel marker of granulocytic differentiation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulhane, M.; Murray, L.; Lourie, R.; Tong, H.; Sheng, Y.H.; Wang, R.; Kang, A.; Schreiber, V.; Wong, K.Y.; Magor, G.; et al. High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, K.; Tran, F.; Ito, G.; Sheibani-Tezerji, R.; Lipinski, S.; Kuiper, J.W.; Tschurtschenthaler, M.; Saveljeva, S.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Hasler, R.; et al. ATG16L1 orchestrates interleukin-22 signaling in the intestinal epithelium via cGAS-STING. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2868–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.; Talwar, P.; Parimisetty, A.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Ravanan, P. A Molecular Web: Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschen, A.R.; Adolph, T.E.; Gerner, R.R.; Wieser, V.; Tilg, H. Lipocalin-2: A Master Mediator of Intestinal and Metabolic Inflammation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Yeoh, B.S.; Chassaing, B.; Zhang, B.; Saha, P.; Xiao, X.; Awasthi, D.; Shashidharamurthy, R.; Dikshit, M.; Gewirtz, A.; et al. Microbiota-inducible Innate Immune, Siderophore Binding Protein Lipocalin 2 is Critical for Intestinal Homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, N.R.; Rodvold, J.; Almanza, G.; Perez, A.F.; Wheeler, M.C.; Zanetti, M. ER stress drives Lipocalin 2 upregulation in prostate cancer cells in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X. Lipocalin 2 deficiency inhibits cell proliferation, autophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse embryonic cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 351, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; De Jesus, K.; Zhao, H.; Takasawa, S.; Shi, B.; Srikant, C.B.; Liu, J.L. Overexpression of Reg3alpha increases cell growth and the levels of cyclin D1 and CDK4 in insulinoma cells. Growth Factors 2009, 27, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Cao, H.; Du, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, M. Reg3g overexpression promotes beta cell regeneration and induces immune tolerance in nonobese-diabetic mouse model. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Muehleisen, B.; Radek, K.A.; Park, H.J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Lei, H.; Quan, Y.; et al. The antimicrobial protein REG3A regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation after skin injury. Immunity 2012, 37, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, H.; Stappenbeck, T.S. In vitro expansion and genetic modification of gastrointestinal stem cells in spheroid culture. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moniruzzaman, M.; Wang, R.; Jeet, V.; McGuckin, M.A.; Hasnain, S.Z. Interleukin (IL)-22 from IL-20 Subfamily of Cytokines Induces Colonic Epithelial Cell Proliferation Predominantly through ERK1/2 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143468
Moniruzzaman M, Wang R, Jeet V, McGuckin MA, Hasnain SZ. Interleukin (IL)-22 from IL-20 Subfamily of Cytokines Induces Colonic Epithelial Cell Proliferation Predominantly through ERK1/2 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143468
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoniruzzaman, Md., Ran Wang, Varinder Jeet, Michael A. McGuckin, and Sumaira Z. Hasnain. 2019. "Interleukin (IL)-22 from IL-20 Subfamily of Cytokines Induces Colonic Epithelial Cell Proliferation Predominantly through ERK1/2 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143468
APA StyleMoniruzzaman, M., Wang, R., Jeet, V., McGuckin, M. A., & Hasnain, S. Z. (2019). Interleukin (IL)-22 from IL-20 Subfamily of Cytokines Induces Colonic Epithelial Cell Proliferation Predominantly through ERK1/2 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143468