Enhancement of Particle Alignment Using Silicone Oil Plasticizer and Its Effects on the Field-Dependent Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Tensile Strength of MRE with SO
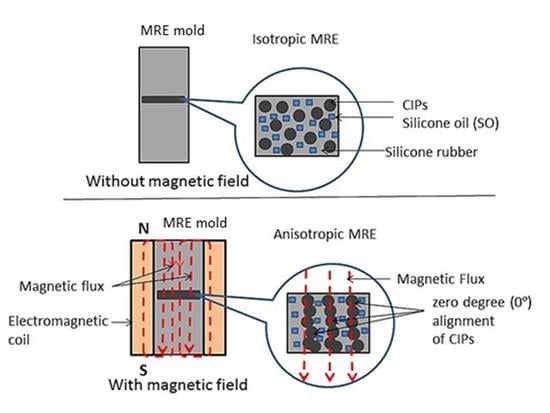
2.2. Morphology of MRE with SO
2.3. Rheological Properties with SO
2.3.1. Magnetic Field Sweep
2.3.2. Strain Sweep
2.3.3. Frequency Sweep
3. Sample Preparation
4. Characterization
4.1. Tensile Test
4.2. Morphological Test
4.3. Rheological Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kashima, S.; Miyasaka, F.; Hirata, K. Novel Soft Actuator Using Magnetorheological Elastomer. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Golnaraghi, M.F.; Heppler, G.R. Experimental Research and Modeling of Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2004, 15, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokaad, A.Z.B.; Hudha, K.; Nasir, M.Z.B.M. Simulation and experimental studies on the behaviour of a magnetorheological damper under impact loading. Int. J. Struct. Eng. 2011, 2, 164–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, I.I.M.; Mazlan, S.A.; Imaduddin, F.; Zamzuri, H.; Choi, S.B.; Kikuchi, T. An investigation on the mitigation of end-stop impacts in a magnetorheological damper operated by the mixed mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Hong, S.R.; Cheong, C.C.; Park, Y.K. Comparison of field-controlled characteristics between ER and MR clutches. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.Q. Analysis and design of a cylindrical magneto-rheological fluid brake. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khairi, M.H.; Mazlan, S.A.; Choi, S.; Abdul Aziz, S.A.; Mohamad, N.; Hapipi, N.M.; Nordin, N. Role of Additives in Enhancing the Rheological Properties of Magnetorheological Solids: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1800696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Zhang, Q.; Elkins, J.; Gordaninejad, F.; Evrensel, C. Development and characterization of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatandoost, H.; Norouzi, M.; Alehashem, S.M.S.; Smoukov, S.K. A novel phenomenological model for dynamic behavior of magnetorheological elastomers in tension-compression mode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.S.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, Y.G. Modified silane-coated carbonyl iron/natural rubber composite elastomer and its magnetorheological performance. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, S.A.; Sutrisno, J.; Zamzuri, H. Potential Applications of Magnetorheological Elastomers. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 663, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, J. A Highly Adjustable Base Isolator Utilizing Magnetorheological Elastomer: Experimental Testing and Modeling. J. Vib. Acoust. 2015, 137, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, H. A state-of-the-art review on magnetorheological elastomer devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guðmundsson, I. A Feasibility Study of Magnetorheological Elastomers for a Potential Application in Prosthetic Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland, 3 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Kamaruddin, S.; Ismail, N.I.N.; Choi, S.B.; Sharif, A.H.R. Fabrication and investigation on field-dependent properties of natural rubber based magneto-rheological elastomer isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Borin, D.Y.; Bakhtiiarov, A.V.; Storozhenko, P.A. Magnetic properties of hybrid elastomers with magnetically hard fillers: Rotation of particles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 035060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, C.; Curcio, S.; Dejchanchaiwong, R.; Tekasakul, P. Influence of Shrinkage during Natural Rubber Sheet Drying: Numerical Modeling of Heat and Mass Transfer Influence of shrinkage during natural rubber sheet drying: Numerical modeling of heat and mass transfer. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 149, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Dwivedy, S.K.; Murthy, K.S.R.K. Fabrication and characterization of magnetorheological elastomer with carbon black. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokander, M.; Stenberg, B. Improving the magnetorheological effect in isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Zhang, X.Z. A study of the magnetorheological effect of bimodal particle based magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, T.; Kratina, O.; Sedlacik, M. Porous magnetic materials based on EPDM rubber filled with carbonyl iron particles. Compos. Struct. 2018, 192, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kchit, N.; Bossis, G. Piezoresistivity of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masłowski, M.; Zaborski, M. Smart Materials Based on Magnetorheological Composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 714, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezoi, V. Magnetic Elastomers Based On Nanocrystalline Magnetite Particles. Mater. Mech. 2014, 9, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Khimi, S.R.; Pickering, K.L. Comparison of dynamic properties of magnetorheological elastomers with existing antivibration rubbers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 83, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.F.; Li, W.H.; Alici, G.; Du, H.; Deng, Y.M. Microstructure and magnetorheology of graphite-based MR elastomers. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordina, B.; Tiwari, R.K.; Setua, D.K.; Sharma, A. Magnetorheology of Polydimethylsiloxane Elastomer/FeCo3 Nanocomposite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 25684–25703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, P.Q. Fabrication and characterization of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Hoag, S.W. Plasticizer Effects on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Solvent Cast Soluplus® Films. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2013, 14, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Kanauchi, S.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T.; Tamesue, S.; Yamauchi, T. Effect of Plasticizer on the Magnetoelastic Behavior for Magnetic Polyurethane Elastomers. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Nakano, M. Fabrication and characterisation of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomer with 45° iron particle alignment at various silicone oil concentrations. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.C. Model of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 3348–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, S.; Xu, Z.; Xu, F. A model of magnetorheological elastomer based on chi-square distribution.pdf. J. Funct. Mater. 2016, 47, 9063–9067. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Gong, X.L.; Li, W.H. Effect of carbon black on the mechanical performances of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Gong, X.L.; Xuan, S.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Effect of cross-link density of the matrix on the damping properties of magnetorheological elastomers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Gong, X.L.; Fan, Y.; Xuan, S. Preparation and mechanical properties of the magnetorheological elastomer based on natural rubber/rosin glycerin hybrid matrix. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, A. The Dynamic Properties of Carbon Black-Loaded Natural Rubber Vulcanizates. Part I. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1962, 6, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Qi, S.; Fu, J.; Zhu, M.; Chen, D. Understanding the reinforcing behaviors of polyaniline-modified carbonyl iron particles in magnetorheological elastomer based on polyurethane/epoxy resin IPNs matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Ecker, E.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Experimental study of the magnetic field enhanced Payne effect in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, L.Z. Dynamic Viscoelastic Behavior of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube–Reinforced Magnetorheological (MR) Nanocomposites. J. Nanomech. Micromech. 2014, 4, A4013014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wei, D.; Zhao, J. Mechanical properties, Payne effect, and Mullins effect of thermoplastic vulcanizates based on high-impact polystyrene and styrene-butadiene rubber compatibilized by styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 1154–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, N.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Choi, S.B.; Imaduddin, F.; Abdul, S.A.A.; Khairi, M.H.A. Rheological properties of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers featuring an epoxidized natural rubber. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khairi, M.H.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ku Ahmad, K.Z.; Choi, S.B.; Abdul Aziz, S.A.; Yunus, N.A. The field-dependent complex modulus of magnetorheological elastomers consisting of sucrose acetate isobutyrate ester. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.K.; Gong, X.L.; Fan, Y.C.; Xia, H.S. Improving the magnetorheological properties of polyurethane magnetorheological elastomer through plasticization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| No. | Sample | G0 (MPa) | Gmax (MPa) | ΔG (MPa) | Relative MR Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | iso SO 0% | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 55 |
| 2. | iso SO 5% | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 65 |
| 3. | iso SO 10% | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 146 |
| 4. | iso SO 15% | 0.08 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 343 |
| 5. | ani SO 0% | 0.40 | 0.98 | 0.58 | 145 |
| 6. | ani SO 5% | 0.20 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 330 |
| 7. | ani SO 10% | 0.16 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 444 |
| 8. | ani SO 15% | 0.12 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 646 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad Khairi, M.H.; Abd Fatah, A.Y.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah, U.; Nordin, N.A.; Nik Ismail, N.I.; Choi, S.B.; Abdul Aziz, S.A. Enhancement of Particle Alignment Using Silicone Oil Plasticizer and Its Effects on the Field-Dependent Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174085
Ahmad Khairi MH, Abd Fatah AY, Mazlan SA, Ubaidillah U, Nordin NA, Nik Ismail NI, Choi SB, Abdul Aziz SA. Enhancement of Particle Alignment Using Silicone Oil Plasticizer and Its Effects on the Field-Dependent Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174085
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad Khairi, Muntaz Hana, Abdul Yasser Abd Fatah, Saiful Amri Mazlan, U. Ubaidillah, Nur Azmah Nordin, Nik Intan Nik Ismail, Seung Bok Choi, and Siti Aishah Abdul Aziz. 2019. "Enhancement of Particle Alignment Using Silicone Oil Plasticizer and Its Effects on the Field-Dependent Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174085
APA StyleAhmad Khairi, M. H., Abd Fatah, A. Y., Mazlan, S. A., Ubaidillah, U., Nordin, N. A., Nik Ismail, N. I., Choi, S. B., & Abdul Aziz, S. A. (2019). Enhancement of Particle Alignment Using Silicone Oil Plasticizer and Its Effects on the Field-Dependent Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174085