MicroRNA Signature in Human Normal and Tumoral Neural Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. miRNAs and Neurogenesis
1.2. Human Normal NSCs vs. Neural CSCs
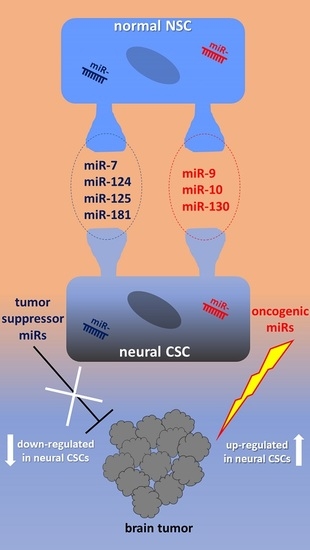
2. miRNAs in Human Normal NSCs
2.1. miR-9, miR-124, miR-125, miR-181
2.2. miR-7, miR-214
2.3. miR-302, miR-367
2.4. miR-10, miR-92, miR-130, miR-135
3. miRNAs in Human Neural CSCs
3.1. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs in Neural CSCs
3.2. OncomiRs in Neural CSCs
3.3. miRNAs in GSC Exosomes
3.4. miRNAs in Human Melanoma
3.5. miRNAs as Diagnostic, Prognostic and Predictive Tools
3.6. miRNAs and Their Therapeutic Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCG2 | ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily G Member 2 |
| ACVR1b | Activin A Receptor Type 1B |
| AKT | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| ALDH1A3 | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 Family Member A3 |
| BCL2 | BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator |
| BCL2L11/Bim | Bcl-2-Like Protein 11 |
| BMI-1 | BMI1 Proto-Oncogene, Polycomb Ring Finger |
| BMP | Bone Morphogenetic Protein |
| BMPR2 | Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor Type 2 |
| CAMTA1 | Calmodulin-Binding Transcription Activator 1 |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| CD133 | Prominin 1 |
| CD24 | Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cluster 4 Antigen |
| CD44 | Hematopoietic Cell E- and L-Selectin Ligand |
| CDC42 | Cell Division Cycle 42 |
| CDK | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase |
| CDKN1A/p21 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A |
| CDKN2A/p16 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A |
| CDX1 | Caudal-Type Homeobox 1 Protein |
| CHiP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| CHMP2B | Charged Multivesicular Body Protein 2B |
| C-KIT | KIT Proto-Oncogene, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CRISPR/Cas9 | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR-Associated Protein 9 |
| CSC | cancer stem cell |
| DACH1 | Dachshund Family Transcription Factor 1 |
| DGCR8 | Microprocessor Complex Subunit |
| Dicer1 | Dicer 1, Ribonuclease III |
| DIV | Days in vitro |
| EB | embryoid body |
| EFNA3 | Ephrin-A3 |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EMT | epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| EphB2 | EPH Receptor B2 |
| FACS | Fluorescence activated cell sorting |
| FGF-2 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box O1 |
| GBM | glioblastoma multiforme |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| GSC | glioma stem cell |
| HCS | human cortical spheroid |
| hESC | human embryonic stem cell |
| HES | Hes Family BHLH Transcription Factor |
| HGG | high grade glioma |
| HMGA | High Mobility Group AT-Hook |
| HEY1 | Hes Related Family BHLH Transcription Factor with YRPW Motif 1 |
| hNPC | human neural progenitor cell |
| hNSC | human neural stem cell line |
| hPSC | human pluripotent stem cell |
| ID4 | Inhibitor of Differentiation 4 |
| IMP | Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein |
| iPSC | induced Pluripotent Stem Cell |
| ISCU | Iron–Sulfur Cluster Scaffold Protein |
| JAM-A | Junctional Adhesion Molecule A |
| KIP | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor |
| KLF4 | Krüppel-like Factor 4 |
| LGALS3 | Galectin 3 |
| LHX2 | LIM Homeobox 2 |
| LIX1 | Limb and CNS Expressed 1 |
| MAP2 | Microtubule Associated Protein 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MB | medulloblastoma |
| MBNL1-3 | Muscleblind-like Splicing Regulator 1-3 |
| MEIS2 | Meis Homeobox 2 |
| MEK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MIF | Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor |
| MIIP | Migration and Invasion Inhibitory Protein |
| MMP-12 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 12 |
| MNT | MAX Network Transcriptional Repressor |
| MSC | melanocyte stem cell |
| NOTCH | Notch Receptor |
| NRAS | NRAS Proto-Oncogene, GTPase |
| NR2F2 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group F Member 2 |
| NSC | neural stem cell |
| OCT4 | Octamer-Binding Transcription Factor 4 |
| ONECUT | One Cut Homeobox |
| PAX6 | Paired Box 6 |
| PDCD4 | Programmed Cell Death 4 |
| PDGFR | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor |
| PEG10 | Paternally Expressed 10 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase C |
| PID1 | Phosphotyrosine Interaction Domain Containing 1 |
| PIM3 | Pim-3 Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase |
| PTBP1 | Polypyrimidine Tract Binding Protein 1 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog |
| RBPs | RNA-Binding Proteins |
| RECK | Reversion Inducing Cysteine Rich Protein with Kazal Motifs |
| REST | RE1-Silencing Transcription Factor |
| RISC | RNA induced silencing complex |
| RSRC1 | Arginine and Serine Rich Coiled-Coil 1 |
| RTVP-1 | Related to Testis-Specific, Vespid, And Pathogenesis Proteins 1 |
| SART3 | Spliceosome Associated Factor 3, U4/U6 Recycling Protein |
| SEC61G | SEC61 Translocon Gamma Subunit |
| SERTAD1 | SERTA Domain Containing 1 |
| SHH | Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Molecule |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| SMAD | SMAD Family Member |
| smNPC | small-molecule neural precursor cell |
| SNAI2 | Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 2 |
| SOX | Sex Determining Region Y-Box |
| S-TRAIL | Secretable form of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand |
| TET3 | Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 3 |
| TFAP2C/AP-2γ | Transcription Factor AP-2 Gamma |
| TGFβ | Transforming Growth Factor β |
| TLX | T Cell Leukemia Homeobox |
| TMZ | temozolomide |
| TPM1 | Tropomyosin 1 |
| TRBP | TAR RNA binding protein |
| TUBB3 | Tubulin Beta 3 Class III |
| VEGF-A | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
| WB | Western blot |
| WNT | Wingless-Related Integration Site |
| YBX1 | Y-Box Binding Protein 1 |
References
- Shao, N.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Yan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, H.; Menzel, C.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Khaitovich, P. Comprehensive survey of human brain microRNA by deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Zhang, J.; Thomson, A.M.; Lim, B.; Rigoutsos, I. MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature 2008, 455, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Tong, Y.; Steitz, J.A. Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 2007, 318, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørom, U.A.; Nielsen, F.C.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol. Cell. 2008, 30, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, J.I.; Goergen, D.; Zheng, J.; Song, Y.; Schüttler, C.G.; Fehr, C.; Jünemann, C.; Niepmann, M. Micro-RNA-122 stimulates translation of hepatitis C virus RNA. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 3300–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monni, E.; Congiu, T.; Massa, D.; Nat, R.; Diana, A. Human neurospheres: From stained sections to three-dimensional assembly. Transl. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, D.; Pillai, R.; Monni, E.; Kokaia, Z.; Diana, A. Expression analysis of pluripotency-associated genes in human fetal cortical and striatal neural stem cells during differentiation. Transl. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007, 5, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, S.; Kedaigle, A.J.; Simmons, S.K.; Nash, A.; Rocha, M.; Quadrato, G.; Paulsen, B.; Nguyen, L.; Adiconis, X.; Regev, A.; et al. Individual brain organoids reproducibly form cell diversity of the human cerebral cortex. Nature 2009, 570, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fineberg, S.K.; Kosik, K.S.; Davidson, B.L. MicroRNAs potentiate neural development. Neuron 2009, 64, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hsieh, J.; Wichterle, H.; Impey, S.; Banerjee, S.; Neveu, P.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA regulation of neural stem cells and neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14931–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J.; Wicha, M.S.; Chang, A.E.; Fan, W.; Chen, L.; Fan, M.; Li, Q. Regulatory Roles of miRNA in the Human Neural Stem Cell Transformation to Glioma Stem Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tuzesi, Á.; Kling, T.; Wenger, A.; Lunavat, T.R.; Jang, S.C.; Rydenhag, B.; Lötvall, J.; Pollard, S.M.; Danielsson, A.; Carén, H. Pediatric brain tumor cells release exosomes with a miRNA repertoire that differs from exosomes secreted by normal cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 90164–90175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Fu, J.; Wang, W.; Hofman, F.M.; Chen, T.C.; Chen, L. Distribution of cancer stem cells in two human brain gliomas. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.S. Cancer stem cells in brain tumors and their lineage hierarchy. Int. J. Stem Cells 2012, 5, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, C.J.; Altschuler, G.; Jeong, J.; Strømme, K.K.; Stangeland, B.; Murrell, W.; Grasmo-Wendler, U.H.; Myklebost, O.; Helseth, E.; Vik-Mo, E.O.; et al. Comparison of glioma stem cells to neural stem cells from the adult human brain identifies dysregulated Wnt-signaling and a fingerprint associated with clinical outcome. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2230–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Guedes, J.R.; Cardoso, A.L.; Morais, C.; Cunha, P.; Viegas, A.T.; Costa, R.; Jurado, A.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C. Recent trends in nanotechnology toward CNS diseases: Lipid-based nanoparticles and exosomes for targeted therapeutic delivery. In International Review of Neurobiology, 1st ed.; Al-Jamal, K.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; Volume 130, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Redzic, J.S.; Ung, T.H.; Graner, M.W. Glioblastoma extracellular vesicles: Reservoirs of potential biomarkers. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso Bavisotto, C.; Graziano, F.; Rappa, F.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Logozzi, M.; Fais, S.; Maugeri, R.; Bucchieri, F.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; et al. Exosomal chaperones and miRNAs in gliomagenesis: State-of-art and theranostics perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Antoun, T.J.; Hale, J.S.; Lathia, J.D.; Dombrowski, S.M. Brain Cancer Stem Cells in adults and children: Cell biology and therapeutic implications. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.G.; Turaga, S.M.; Sathyan, P.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Otvos, B.; Silver, D.J.; Hale, J.S.; Flavahan, W.A.; Zinn, P.O.; Sinyuk, M.; et al. Coordination of self-renewal in glioblastoma by integration of adhesion and microRNA signaling. NeuroOncology 2016, 18, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wan, X.; Alvarez, A.A.; James, C.D.; Song, X.; Yang, Y.; Sastry, N.; Nakano, I.; Sulman, E.P.; Hu, B.; et al. MIR93 (microRNA-93) regulates tumorigenicity and therapy response of glioblastoma by targeting autophagy. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agliano, A.; Calvo, A.; Box, C. The challenge of targeting cancer stem cells to halt metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheray, M.; Bégaud, G.; Deluche, E.; Nivet, A.; Battu, S.; Lalloué, F.; Verdier, M.; Bessette, B. Cancer Stem-Like Cells in glioblastoma. In Glioblastoma, 1st ed.; De Vleeschouwer, S., Ed.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2017; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Delaloy, C.; Liu, L.; Lee, J.A.; Su, H.; Shen, F.; Yang, G.Y.; Young, W.L.; Ivey, K.N.; Gao, F.B. MicroRNA-9 coordinates proliferation and migration of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaloy, C.; Gao, F.B. A new role for microRNA-9 in human neural progenitor cells. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2913–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschi, T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAS from mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.R.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Cha, K.Y.; Chung, H.M.; Yoon, H.S.; Moon, S.Y.; et al. Human embryonic stem cells express a unique set of microRNAs. Dev. Biol. 2004, 270, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boissart, C.; Nissan, X.; Girauld-Triboult, K.; Peschanski, M.; Benchoua, A. miR-125 potentiates early neural specification of human embryonic stem cells. Development 2012, 139, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rybak, A.; Fuchs, H.; Smirnova, L.; Brandt, C.; Pohl, E.E.; Nitsch, R.; Wulczyn, F.G. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Daley, G.Q.; Gregory, R.I. Selective blockade of microRNA processingby Lin28. Science 2008, 320, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappert, L.; Borghese, L.; Roese-Koerner, B.; Weinhold, S.; Koch, P.; Terstegge, S.; Uhrberg, M.; Wernet, P.; Brüstle, O. MicroRNA-based promotion of human neuronal differentiation and subtype specification. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roese-Koerner, B.; Stappert, L.; Berger, T.; Braun, N.C.; Velte, M.; Jungverdorben, J.; Evert, B.O.; Peitz, M.; Borghese, L.; Brüstle, O. Reciprocal regulation between bifunctional miR-9/9* and its transcriptional modulator Notch in human neural stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 7, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roese-Koerner, B.; Stappert, L.; Brüstle, O. Notch/Hes signaling and miR-9 engage in complex feedback interactions controlling neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Neurogenesis 2017, 4, e1313647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, P.; Opitz, T.; Steibeck, J.A.; Ladewig, J.; Brüstle, O. A rosette-type, self-renewing human ES cell-derived neural stem cell with potential for in vitro instructionand synaptic integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3225–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roese-Koerner, B.; Stappert, L.; Koch, P.; Brüstle, O.; Borghese, L. Pluripotent stem cell-derived somatic stem cells as tool to study the role of microRNAs in early human neural development. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krichevsky, A.M.; King, K.S.; Donahue, C.P.; Khrapko, K.; Kosik, K.S. A microRNA array reveals extensive regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA 2003, 9, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madelaine, R.; Sloan, S.A.; Huber, N.; Notwell, J.H.; Leung, L.C.; Skariah, G.; Halluin, C.; Paşca, S.P.; Bejerano, G.; Krasnow, M.A.; et al. MicroRNA-9 couples brain neurogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paşca, A.M.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Tian, Y.; Makinson, C.D.; Huber, N.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; O’Rourke, N.A.; Nguyen, K.D.; et al. Functional cortical neurons and astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, M.; Li, S.; Qi, T.; Mei, H.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; Tong, Q. microRNA-9 targets matrix metalloproteinase 14 to inhibit invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Githinji, J.; Mclaughlin, B.; Wilczek, K.; Nolta, J. Role of miRNAs in neuronal differentiation from human embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2012, 8, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, E.; Orso, F.; Cimino, D.; Tenaglia, E.; Lembo, A.; Quaglino, E.; Poliseno, L.; Haimovic, A.; Osella-Abate, S.; De Pittà, C.; et al. microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour progression through suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1990–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Kong, W.; He, L. MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res. 2008, 200868, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.; Brivanlou, A.H. A regulatory circuitry comprised of miR-302 and the transcription factors OCT4 and NRF2 regulates human embryonic stem cell differentiation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marson, A.; Levine, S.S.; Cole, M.F.; Frampton, G.M.; Brambrink, T.; Johnstone, S.; Guenther, M.G.; Johnston, W.K.; Wernig, M.; Newman, J.; et al. Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Cell 2008, 134, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipchina, I.; Elkabetz, Y.; Hafner, M.; Sheridan, R.; MIhailovic, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Studer, L.; Betel, D. Genome-wide identification of microRNA targets in human ES cells reveals a role for miR-302 in modulating BMP response. Genes Dev. 2019, 25, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, M.E.; Nelander Wahlestedt, J.; Åkerblom, M.; Kirkeby, A.; Malmevik, J.; Brattaas, P.L.; Jakobsson, J.; Parmar, M. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression in regionalized human neural progenitor cells reveals microRNA-10 as a caudalizing factor. Development 2015, 142, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lund, A.H. miR-10 in development and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhinge, A.; Poschmann, J.; Namboori, S.C.; Tian, X.; Jia Hui Loh, S.; Traczyk, A.; Prabhakar, S.; Stanton, L.W. MiR-135b is a direct PAX6 target and specifies human neuroectoderm by inhibiting TGFβ/BMP signaling. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcenty, K.; Wroblewska, J.P.; Rucinski, M.; Kozlowska, E.; Jopek, K.; Suchorska, W.M. MicroRNA profiling during neural differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.; Meays, B.M.; Madduri, L.S.V.; Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Niu, M.; Albahrani, A.; Guda, C.; Pendyala, G.; Fox, H.S.; et al. Downregulation of an evolutionary young miR-1290 in an iPSC-derived neural stem cell model of autism spectrum disorder. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 8710180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhagiar, A.; Ayers, D. Chemoresistance, Cancer Stem Cells, and miRNA influences: The case for neuroblastoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2015, 2015, 150634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Chang, S. Development of novel therapeutic agents by inhibition of oncogenic microRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, C.B.; Buchris, E.; Lee, H.K. miRNA Expression and Functions in Glioma and Glioma Stem Cells. In MicroRNA Targeted Cancer Therapy, 1st ed.; Sarkar, F.H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rolle, K. miRNA Multiplayers in glioma. From bench to bedside. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasayama, T.; Tanaka, K.; Kohmura, E. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Glioblastoma Biology and Biomarker. In Neurooncology, 1st ed.; Newer Developments; Agrawal, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 27–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Bian, E.B.; Li, J.; Li, J. New advances of microRNAs in glioma stem cells, with special emphasis on aberrant methylation of microRNAs. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mens, M.M.J.; Ghanbari, M. Cell cycle regulation of stem cells by microRNAs. Stem Cell Rev. 2018, 14, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, Z. MicroRNAs shaping cellular reprogramming. In AGO-Driven Non-Coding RNAs. Codes to Decode the Therapeutics of Diseases, 1st ed.; Mallick, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen, S.K.; Sørensen, M.D.; Hansen, A.; Knudsen, S.; Alvarado, A.G.; Lathia, J.D.; Kristensen, B.W. A 4-miRNA signature to predict survival in glioblastomas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, J.; Hashizume, R.; Felix, T.; Hariono, S.; Yu, M.; Berger, M.S.; Huse, J.T.; VandenBerg, S.R.; James, C.D.; Hodgson, J.G.; et al. Expression of miR-124 inhibits growth of medulloblastoma cells. NeuroOncology 2013, 15, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banelli, B.; Forlani, A.; Allemanni, G.; Morabito, A.; Pistillo, M.P.; Romani, M. MicroRNA in glioblastoma: An overview. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 7639084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, R.M.G. MiRNAs Expression Profiling and Modulation in Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Coimbra, Conbra, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, R.U.; Miyazaki, H.; Ochiya, T. The role of microRNAs in the regulation of cancer stem cells. Front. Genet. 2014, 4, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriksen, M.; Johnsen, K.B.; Olesen, P.; Pilgaard, L.; Duroux, M. MicroRNA expression signatures and their correlation with clinicopathological features in glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Mol. Med. 2014, 16, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godlewski, J.; Nowicki, M.O.; Bronisz, A.; Williams, S.; Otsuki, A.; Nuovo, G.; Raychaudhury, A.; Newton, H.B.; Chiocca, E.A.; Lawler, S. Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9125–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, A.; Harish, V.; Afzal, Z.; Chijioke, J.; Kedir, H.; Dusmatova, S.; Roy, A.; Ramalinga, M.; Harris, B.; Blancato, J.; et al. MicroRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme pathogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1917–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soheilifar, M.H.; Moshtaghian, A.; Maadi, H.; Izadi, F.; Saidijam, M. BMI1 roles in cancer stem cells and its association with microRNAs dysregulation in cancer: Emphasis on colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2018, 11, e82926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.M.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, L.; Guo, L.M.; Que, S.L.; Li, X.X.; Ge, J.W.; Wang, G.S.; Xiong, W.H.; et al. IDH1R132H decreases the proliferation of U87 glioma cells through upregulation of microRNA-128a. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6695–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, M.; Guan, Y.; Yoshimoto, K.; Hata, N.; Amano, T.; Nakamizo, A.; Sasaki, T. MicroRNAs in human malignant gliomas. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 732874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Neveu, P.; Dugas, J.C.; Gill, R.M.; Huillard, E.; Liu, C.; Zong, H.; Rowitch, D.H.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Pro-neural miR-128 is a glioma tumor suppressor that targets mitogenic kinases. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooj, A.K.; Ricklefs, F.; Mineo, M.; Nakano, I.; Chiocca, E.A.; Bronisz, A.; Godlewski, J. MicroRNA-mediated dynamic bidirectional shift between the subclasses of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell. Rep. 2017, 19, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.S.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, C.D. MiR-134 regulates the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma cells by reducing Nanog expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, A.; Wickremsekera, A.; Tan, S.T.; Peng, L.; Davis, P.F.; Itinteang, T. cancer stem cell hierarchy in glioblastoma multiforme. Front. Surg. 2016, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamim, S.; Vo, D.T.; Uren, P.J.; Qiao, M.; Bindewald, E.; Kasprzak, W.K.; Shapiro, B.A.; Nakaya, H.I.; Burns, S.C.; Araujo, P.R.; et al. Genomic analyses reveal broad impact of miR-137 on genes associated with malignant transformation and neuronal differentiation in glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bier, A.; Giladi, N.; Kronfeld, N.; Lee, H.K.; Cazacu, S.; Finniss, S.; Xiang, C.; Poisson, L.; deCarvalho, A.C.; Slavin, S.; et al. MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting RTVP 1. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.V.; Pillai, R.M. Implications of miR cluster 143/145 as universal anti-oncomiRs and their dysregulation during tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. Int. 2015, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, T.; Nowak, A.; Kakulas, F. Targeting aggressive cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengoji, R.; Macha, M.A.; Batra, S.K.; Shonka, N.A. Natural products: A hope for glioblastoma patients. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22194–22219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yao, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y. MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4. Cancer Lett. 2014, 355, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezcan, G.; Tunca, B.; Bekar, A.; Preusser, M.; Berghoff, A.S.; Egeli, U.; Cecener, G.; Ricken, G.; Budak, F.; Taskapılıoglu, M.O. microRNA expression pattern modulates temozolomide response in GBM tumors with cancer stem cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhu, G.; Luo, H.; Zhao, S. MicroRNA-203 As a stemness inhibitor of glioblastoma stem cells. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Birks, D.K.; Balakrishnan, I.; Alimova, I.; Harris, P.S.; Patel, P.R.; Handler, M.H.; Dubuc, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Foreman, N.K.; et al. MicroRNA 218 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting multiple cancer phenotype-associated genes in medulloblastoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Ma, J. MiR-608 inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma stem cells by targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrauwe, N.; Schlumpf, T.B.; Janiszewska, M.; Martin, P.; Cauderay, A.; Provero, P.; Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Paro, R.; Stamenkovic, I. The RNA binding protein IMP2 preserves glioblastoma stem cells by preventing let-7 target gene silencing. Cell. Rep. 2016, 15, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sana, J.; Busek, P.; Fadrus, P.; Besse, A.; Radova, L.; Vecera, M.; Reguli, S.; Stollinova Sromova, L.; Hilser, M.; Lipina, R.; et al. Identification of microRNAs differentially expressed in glioblastoma stem-like cells and their association with patient survival. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, B.B. Stress response of glioblastoma cells mediated by miR-17-5p targeting PTEN and the passenger strand miR-17-3p targeting MDM2. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokudome, T.; Sasaki, A.; Tsuji, M.; Udaka, Y.; Oyamada, H.; Tsuchiya, H.; Oguchi, K. Reduced PTEN expression and overexpression of miR-17-5p, -19a-3p, -19b-3p, -21-5p, -130b-3p, -221-3p and -222-3p by glioblastoma stem-like cells following irradiation. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriely, G.; Yi, M.; Narayan, R.S.; Niers, J.M.; Wurdinger, T.; Imitola, J.; Ligon, K.L.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.; Stephens, R.M.; et al. Human glioma growth is controlled by microRNA-10b. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3563–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guessous, F.; Alvarado-Velez, M.; Marcinkiewicz, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, J.; Heister, S.; Kefas, B.; Godlewski, J.; Schiff, D.; Purow, B.; et al. Oncogenic effects of miR-10b in glioblastoma stem cells. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 112, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Gabriely, G.; Volfovsky, N.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J.; Karmali, P.; Marcusson, E.; Peter, M.; Mohan, A.; et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting microRNA-10b in established intracranial glioblastoma: First steps toward the clinic. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, D.; Krishnan, R.; Panagal, M.; Sivakumar, P.; Gopinath, V.; Basam, V. Deciphering the role of microRNA 21 in cancer stem cells (CSCs). Genes Dis. 2016, 3, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galani, V.; Alexiou, G.A.; Miliaras, G.; Dimitriadis, E.; Triantafyllou, E.; Galani, A.; Goussia, A.; Kanavaros, P.; Trangas, T. expression of stem cell marker nestin and microRNA-21 in meningiomas. Turk. Neurosurg. 2015, 25, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zou, R.; Zhou, R.; Gong, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, T.; Tan, C.; Fang, J. miR-155 regulates glioma cells invasion and chemosensitivity by p38 isoforms in vitro. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Xue, Y. GAS5 suppresses malignancy of human glioma stem cells via a miR-196a-5p/FOXO1 feedback loop. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2017, 1864, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wei, J.; Guo, T.; Shen, Y.; Liu, F. Knockdown of miR-210 decreases hypoxic glioma stem cells stemness and radioresistance. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 326, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zage, P.E.; Whittle, S.B.; Shohet, J.M. CD114: A new member of the neural crest-derived cancer stem cell marker family. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtas, D.; Pilloni, L.; Diana, A.; Casula, L.; Tomei, S.; Piras, F.; Ferreli, C.; Maxia, C.; Perra, M.T. Tyrosinase and nestin immunohistochemical expression in melanocytic nevi as a histopathologic pattern to trace melanocyte differentiation and nevogenesis. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2019, 151, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Brenn, T.; Brown, E.R.; Doherty, V.; Melton, D.W. Differential expression of microRNAs during melanoma progression: miR-200c, miR-205 and miR-211 are downregulated in melanoma and act as tumour suppressors. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahranavardfard, P.; Firouzi, J.; Azimi, M.; Khosravani, P.; Heydari, R.; Emami Razavi, A.; Dorraj, M.; Keighobadi, F.; Ebrahimi, M. MicroRNA-203 reinforces stemness properties in melanoma and augments tumorigenesis in vivo. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, M.; Sztiller-Sikorska, M.; Czyz, M. Expression of miRNAs as important element of melanoma cell plasticity in response to microenvironmental stimuli. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Segura, M.F.; Belitskaya-Lévy, I.; Rose, A.E.; Zakrzewski, J.; Gaziel, A.; Hanniford, D.; Darvishian, F.; Berman, R.S.; Shapiro, R.L.; Pavlick, A.C.; et al. Melanoma MicroRNA signature predicts post-recurrence survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandarchi, B.; Jabbari, C.A.; Vedadi, A.; Navab, R. Molecular biology of normal melanocytes and melanoma cells. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fomeshi, M.R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Mowla, S.J.; Khosravani, P.; Firouzi, J.; Khayatzadeh, H. Evaluation of the expressions pattern of miR-10b, 21, 200c, 373 and 520c to find the correlation between epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and melanoma stem cell potential in isolated cancer stem cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2015, 20, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramuta, S.; Egyházi, S.; Rodolfo, M.; Witten, D.; Hansson, J.; Larsson, C.; Lui, W.O. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with mutational status and survival in malignant melanoma. J. Int. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Czyz, M. Role of miRNAs in melanoma metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbano, R.; Palumbo, O.; Pasculli, B.; Galasso, M.; Volinia, S.; D’Angelo, V.; Icolaro, N.; Coco, M.; Dimitri, L.; Graziano, P.; et al. A miRNA signature for defining aggressive phenotype and prognosis in gliomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrescu, G.E.D.; Sabo, A.A.; Torsin, L.I.; Calin, G.A.; Dragomir, M.P. MicroRNA based theranostics for brain cancer: Basic principles. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, M.; Fendler, W.; Zakrzewski, K.; Sikorska, B.; Grajkowska, W.; Dembowska-Bagińska, B.; Filipek, I.; Stefańczyk, Ł.; Liberski, P.P. Altered microRNA expression is associated with tumor grade, molecular background and outcome in childhood infratentorial ependymoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantawy, M.; Elzayat, M.G.; Yehia, D.; Taha, H. Identification of microRNA signature in different pediatric brain tumors. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 27–34, Erratum in 2018, 41, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiori, M.E.; Villanova, L.; De Maria, R. Cancer stem cells: At the forefront of personalized medicine and immunotherapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, C.; Guerfali, F.Z.; Laouini, D. MicroRNAs in diagnosis and therapeutics. In AGO-Driven Non-Coding RNAs. Codes to Decode the Therapeutics of Diseases, 1st ed.; Mallick, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 137–177. [Google Scholar]
- Anthiya, S.; Griveau, A.; Loussouarn, C.; Baril, P.; Garnett, M.; Issartel, J.P.; Garcion, E. MicroRNA-based drugs for brain tumors. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Yoo, J.Y.; Shu, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.G.; Jaime-Ramirez, A.C.; Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Cui, R.; et al. RNA nanoparticle-based targeted therapy for glioblastoma through inhibition of oncogenic miR-21. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.M.; Cardoso, A.L.; Custódia, C.; Cunha, P.; Pereira de Almeida, L.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C. MiRNA-21 silencing mediated by tumor-targeted nanoparticles combined with sunitinib: A new multimodal gene therapy approach for glioblastoma. J. Control Release 2015, 207, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.C.; Gao, J.Q. Exosomes as novel bio-carriers for gene and drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godlewski, J.; Lenart, J.; Salinska, E. MicroRNA in brain pathology: Neurodegeneration the other side of the brain cancer. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, V.; Nowicki, M.O.; Idriss, M.; Jimenez, M.A.; Lugli, G.; Hayes, J.L.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Zane, R.E.; Passaro, C.; Ligon, K.L.; et al. The functional synergism of microRNA clustering provides therapeutically relevant epigenetic interference in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diana, A.; Gaido, G.; Murtas, D. MicroRNA Signature in Human Normal and Tumoral Neural Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174123
Diana A, Gaido G, Murtas D. MicroRNA Signature in Human Normal and Tumoral Neural Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174123
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiana, Andrea, Giuseppe Gaido, and Daniela Murtas. 2019. "MicroRNA Signature in Human Normal and Tumoral Neural Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174123
APA StyleDiana, A., Gaido, G., & Murtas, D. (2019). MicroRNA Signature in Human Normal and Tumoral Neural Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174123