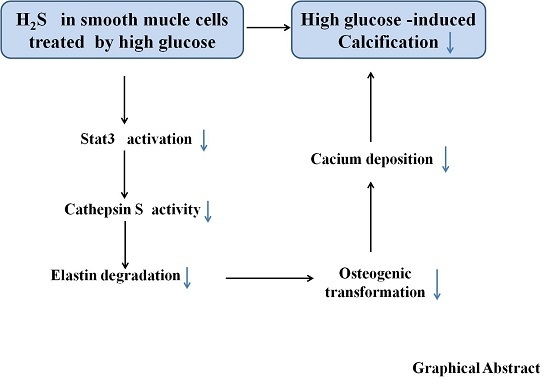
Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Elastin Loss and Attenuates Calcification Induced by High Glucose in Smooth Muscle Cells through Suppression of Stat3/Cathepsin S Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NaHS Treatment Attenuates Calcification in High Glucose (HG) Treated HASMCs.
2.2. NaHS Treatment Inhibits Osteogenic Transition of VSMC in HG Treated HASMCs.
2.3. Impaired Endogenous H2S Generating Enzyme Activity and Expression in HG-Treated HASMCs
2.4. Effect of Endogenous H2S on Stat3/CAS/Elastin Pathway
2.5. CAS Is Important in Calcification of Smooth Muscle Cells
2.6. Stat3 Inhibitor or Stat3 Silencing Inhibited Osteoblastic Differentiation, Decreased CAS Expression, but Increased Elastin Expression
2.7. Overexpression of WT-Stat3, but not that of Stat3 Mutant (C259S), Elevated CAS Protein Expression and Reduced Elastin Level in the Presence of HG
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Determination of Calcification
4.4. Measurement of Calcium Content
4.5. Measurement of Phosphorus Level
4.6. Measurement of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
4.7. Measurement of H2S Synthesis Enzymes Cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) Activity
4.8. Measurement of CAS Activity
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Immunofluorescence
4.11. Transfection of HASMCs with CAS and Stat3 Plasmid, and Stat3 siRNA
4.12. S-sulfhydration Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, D.; Mackenzie, N.C.; Farquharson, C.; Macrae, V.E. Mechanisms and clinical consequences of vascular calcification. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.M.; Simpson, C.L.; Stewart, J.A., Jr. The Role of AGE/RAGE Signaling in Diabetes-Mediated Vascular Calcification. J. Diab. Res. 2016, 2016, 6809703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, E.; Okuno, S.; Taniwaki, H.; Kizu, A.; Tsuchida, T.; Shioi, A.; Shoji, T.; Tabata, T.; Inaba, M.; Nishizawa, Y. Different risk factors for vascular calcification in end-stage renal disease between diabetics and nondiabetics: The respective importance of glycemic and phosphate control. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2008, 31, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.X.; Moe, S.M. Arterial calcification in diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2003, 3, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruska, K.A.; Mathew, S.; Lund, R.; Qiu, P.; Pratt, R. Hyperphosphatemia of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanzer, P.; Boehm, M.; Sorribas, V.; Thiriet, M.; Janzen, J.; Zeller, T.; St Hilaire, C.; Shanahan, C. Medial vascular calcification revisited: Review and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimentova, A.; Sagova, I.; Pridavkova, D.; Kantarova, D.; Makovicky, P.; Sadlonova, J.; Mokan, M. Diabetic Kidney Disease 3rd stage–laboratory markers of mineral bone disorder. Vnitr. Lek. 2016, 62, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Baktiroglu, S.; Yanar, F.; Ozata, I.H.; Oner, G.; Ercan, D. Arterial disease and vascular access in diabetic patients. J. Vasc. Access. 2016, 17 (Suppl. 1), S69–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, G.S.; Argyriou, C.; Antoniou, G.A.; Kantartzi, K.; Kriki, P.; Theodoridis, M.; Thodis, E.; Lazarides, M.K. Upper limb vascular calcification score as a predictor of mortality in diabetic hemodialysis patients. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.H.; Lu, M.; Hu, L.F.; Wong, P.T.; Webb, G.D.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide in the mammalian cardiovascular system. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 141–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Lu, M.; Xie, Z.Z.; Hua, F.; Xie, L.; Gao, J.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide prevents heart failure development via inhibition of renin release from mast cells in isoproterenol-treated rats. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Q.C.; Pan, T.T.; Hu, L.F.; Bian, J.S. Negative regulation of beta-adrenergic function by hydrogen sulphide in the rat hearts. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 44, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wang, R. H2S and Blood Vessels: An Overview. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 230, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, S.S.; Zakaria, M.N.; Abdel-Ghany, R.H.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A. Cystathionine-gamma lyase-derived hydrogen sulfide mediates the cardiovascular protective effects of moxonidine in diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 783, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Dong, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; et al. Exogenous H2S modulates mitochondrial fusion-fission to inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in a hyperglycemic state. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Luo, J.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Zeng, O.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Hydrogen sulfide exhibits cardioprotective effects by decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stress in a diabetic cardiomyopathy rat model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Suguro, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen sulfide stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, C.; Yang, J. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial fibrosis in diabetic rats through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bessueille, L.; Fakhry, M.; Hamade, E.; Badran, B.; Magne, D. Glucose stimulates chondrocyte differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells and calcification: A possible role for IL-1beta. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Guo, R.; Liu, C.; Fu, D.; Liu, F.; Hu, J.; Jiang, H. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis Contributing to High Glucose-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification. J. Vasc. Res. 2015, 52, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, K.; Llovera, G.; Recasens, M.; Chertoff, M.; Gimenez-Llort, L.; Gonzalez, B.; Acarin, L. Temporal expression of cytokines and signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 activation after neonatal hypoxia/ischemia in mice. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 35, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyanets, S.; Kaun, C.; Rychli, K.; Pfaffenberger, S.; Kastl, S.P.; Hohensinner, P.J.; Rega, G.; Katsaros, K.M.; Afonyushkin, T.; Bochkov, V.N.; et al. Oncostatin M-enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells involves PI3K-, p38 MAPK-, Erk1/2- and STAT1/STAT3-dependent pathways and is attenuated by interferon-gamma. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.W.; Kinzenbaw, D.A.; Modrick, M.L.; Faraci, F.M. Small-molecule inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 protect against angiotensin II-induced vascular dysfunction and hypertension. Hypertension 2013, 61, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakutani, Y.; Shioi, A.; Shoji, T.; Okazaki, H.; Koyama, H.; Emoto, M.; Inaba, M. Oncostatin M Promotes Osteoblastic Differentiation of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Through JAK3-STAT3 Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Li, J.; Hosoya, K.I.; Ratan, R.; Townes, T.; Zhang, S.X. Activating transcription factor 4 mediates hyperglycaemia-induced endothelial inflammation and retinal vascular leakage through activation of STAT3 in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simpson, C.L.; Lindley, S.; Eisenberg, C.; Basalyga, D.M.; Starcher, B.C.; Simionescu, D.T.; Vyavahare, N.R. Toward cell therapy for vascular calcification: Osteoclast-mediated demineralization of calcified elastin. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2007, 16, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrhovski, B.; Weiss, A.S. Biochemistry of tropoelastin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 258, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sukhova, G.K.; Sun, J.S.; Xu, W.H.; Libby, P.; Shi, G.P. Lysosomal cysteine proteases in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokhin, A.O.; Lythgo, P.A.; Gauthier, J.Y.; Percival, M.D.; Bromme, D. Pharmacological inhibition of cathepsin S decreases atherosclerotic lesions in Apoe−/−mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, E.; Aikawa, M.; Libby, P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Rusanescu, G.; Iwamoto, Y.; Fukuda, D.; Kohler, R.H.; Shi, G.P.; Jaffer, F.A.; et al. Arterial and aortic valve calcification abolished by elastolytic cathepsin S deficiency in chronic renal disease. Circulation 2009, 119, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarge, J.C.; Pini, M.; Pelloux, V.; Orasanu, G.; Hartmann, G.; Venteclef, N.; Sulpice, T.; Shi, G.P.; Clement, K.; Guerre-Millo, M. Cathepsin S inhibition lowers blood glucose levels in mice. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, H.; Kamon, H.; Sawa, S.; Park, S.J.; xKatunuma, N.; Ishihara, K.; Murakami, M.; Hirano, T. IL-6-STAT3 controls intracellular MHC class II alphabeta dimer level through cathepsin S activity in dendritic cells. Immunity 2005, 23, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.L.; Cheung, B.K.; Li, J.C.; Lau, A.S. A role for STAT3 and cathepsin S in IL-10 down-regulation of IFN-gamma-induced MHC class II molecule on primary human blood macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Macinkovic, I.; Devarie-Baez, N.O.; Pan, J.; Park, C.M.; Carroll, K.S.; Filipovic, M.R.; Xian, M. Detection of protein S-sulfhydration by a tag-switch technique. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shaw, P.E. A STAT3 dimer formed by inter-chain disulphide bridging during oxidative stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Raina, D.; Meyer, C.; Kufe, D. Triterpenoid CDDO-methyl ester inhibits the Janus-activated kinase-1 (JAK1)-->signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) pathway by direct inhibition of JAK1 and STAT3. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2920–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997, 277, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. Modes of physiologic H2S signaling in the brain and peripheral tissues. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ding, L.; Wu, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, L.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide reduces RAGE toxicity through inhibition of its dimer formation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Aikawa, M.; Zheng, C.; Aaron, J.; Lax, L.; Libby, P.; de Lima Filho, J.L.; Gruener, S.; Fingerle, J.; Haap, W.; et al. Selective cathepsin S inhibition attenuates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice with chronic renal disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salum, E.; Butlin, M.; Kals, J.; Zilmer, M.; Eha, J.; Avolio, A.P.; Arend, A.; Aunapuu, M.; Kampus, P. Angiotensin II receptor blocker telmisartan attenuates aortic stiffening and remodelling in STZ-diabetic rats. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narne, P.; Pandey, V.; Phanithi, P.B. Role of Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemic Stroke and the Emergent Epigenetic Underpinnings. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1749–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citi, V.; Piragine, E.; Testai, L.; Breschi, M.C.; Calderone, V.; Martelli, A. The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide and H2S-donors in Myocardial Protection Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4380–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.; Hyseni, I.; Pacini, A.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Morbidelli, L. Cross-talk between endogenous H2S and NO accounts for vascular protective activity of the metal-nonoate Zn(PipNONO)Cl. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Bian, J.S. The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Renal System. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Teng, X.; Li, H.; Xue, H.M.; Guo, Q.; Xiao, L.; Wu, Y.M. Hydrogen Sulfide Improves Vascular Calcification in Rats by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9095242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, C.R.; Dillon, K.M.; Matson, J.B. A review of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) donors: Chemistry and potential therapeutic applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.-B.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Kang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Ding, L.; Sethi, G.; Bian, J.-S. Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Elastin Loss and Attenuates Calcification Induced by High Glucose in Smooth Muscle Cells through Suppression of Stat3/Cathepsin S Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174202
Zhou Y-B, Zhou H, Li L, Kang Y, Cao X, Wu Z-Y, Ding L, Sethi G, Bian J-S. Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Elastin Loss and Attenuates Calcification Induced by High Glucose in Smooth Muscle Cells through Suppression of Stat3/Cathepsin S Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174202
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ye-Bo, Hong Zhou, Li Li, Ying Kang, Xu Cao, Zhi-Yuan Wu, Lei Ding, Gautam Sethi, and Jin-Song Bian. 2019. "Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Elastin Loss and Attenuates Calcification Induced by High Glucose in Smooth Muscle Cells through Suppression of Stat3/Cathepsin S Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174202
APA StyleZhou, Y. -B., Zhou, H., Li, L., Kang, Y., Cao, X., Wu, Z. -Y., Ding, L., Sethi, G., & Bian, J. -S. (2019). Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Elastin Loss and Attenuates Calcification Induced by High Glucose in Smooth Muscle Cells through Suppression of Stat3/Cathepsin S Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174202