Confined Dynamics of Water in Transmembrane Pore of TRPV1 Ion Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Translational Dynamics of Water along the Pore Axis
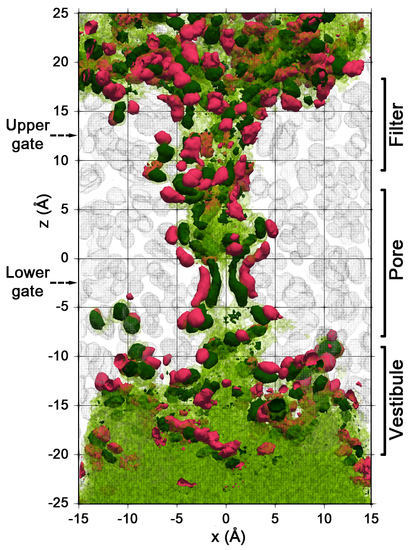
2.2. Spatial Distribution of Water in the Pore
2.3. Water Residence Time in the Hydration Shells of Polar and Nonpolar Protein Groups
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. System and Molecular Dynamics Protocol
4.2. MD Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| hb | Hydrogen bond |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| TM | Transmembrane |
| TRPV1 | Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid type 1 |
References
- Levy, Y.; Onuchic, J.N. Water mediation in protein folding and molecular recognition. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006, 35, 389–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, P. Water as an active constituent in cell biology. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatua, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Dynamical crossover of water confined within the amphiphilic nanocores of aggregated amyloid β peptides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14835–14845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, O.; Melchionna, S.; Laage, D.; Sterpone, F. The effect of protein composition on hydration dynamics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3570–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krylov, N.A.; Pentkovsky, V.M.; Efremov, R.G. Nontrivial behavior of water in the vicinity and inside lipid bilayers as probed by molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9428–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Water dynamics in the hydration shells of biomolecules. Cham. Rev. 2017, 117, 10694–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laage, D.; Hynes, J.T. A molecular jump mechanism of water reorientation. Science 2006, 310, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Perspective: Structure and ultrafast dynamics of biomolecular hydration shells. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Stirnemann, G.; Hynes, J.T. Why water reorientation slows without iceberg formation around hydrophobic solutes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterpone, F.; Stirnemann, G.; Hynes, J.T.; Laage, D. Water hydrogen-bond dynamics around amino acids: The key role of hydrophilic hydrogen-bond acceptor groups. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laage, D.; Thompson, W.H. Reorientation dynamics of nanoconfined water: Power-law decay, hydrogen-bond jumps, and test of a two-state model. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, A.C.; Duboue-Dijon, E.; Laage, D.; Thompson, W.H. Origins of the non-exponential reorientation dynamics of nanoconfined water. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabort, Y.S.; Kumar, H.; Dasgupta, C.; Maiti, P.K. Confined water: Structure, dynamics and thermodynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murail, S.; Vasiliu, T.; Neamtu, A.; Barboiu, M.; Sterpone, F.; Baaden, M. Water permeation across artificial I-quartet membrane channels: From structure to disorder. Faraday Discuss 2018, 209, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, S.; Yang, B.; Huo, J.; Zhang, X.; Bao, J.; Ruan, X.; He, G. Effect of hydrogen-bonding interaction on the arrangement and dynamics of water confined in a polyamide membrane: A molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 4719–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hub, J.S.; Grubmüller, H.; Groot, B.L. Dynamics and energetics of permeation through aquaporins. What do we learn from molecular dynamics simulations? Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 190, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areal, P.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Tucker, S.J. Hydrophobic gaiting in ion channels. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Lynch, C.I.; Klesse, G.; Oakley, G.E.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Tuncker, S.J.; Sansom, M.S.P. Water and hydrophobic gates in ion channels and nanopores. Faraday Discuss 2018, 209, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clapham, D.E. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 2003, 426, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.; Gupta, R.; Jordt, S.E.; Chen, Y.; Liedtke, W.B. Regulation of pain and itch by TRP channels. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature 2013, 504, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, E.; Liao, M.; Cheng, Y.; Julius, D. TRPV1 structures in distinct conformations reveal activation mechanisms. Nature 2013, 504, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 structures in nanodiscs reveal mechanisms of ligand and lipid action. Nature 2016, 534, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chugunov, A.O.; Volynsky, P.E.; Krylov, N.A.; Nolde, D.E.; Efremov, R.G. Temperature-sensitive gating of TRPV1 channel as probed by atomistic simulations of its trans- and juxtamembrane domains. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Huang, X.; Zhou, R.; Berne, B.J. Dynamics of water confined in the interdomain region of a multidomain protein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasimova, M.; Yazici, A.; Yudin, Y.; Granata, D.; Klein, M.L.; Rohacs, T.; Carnevale, V. Ion Channel Sensing: Are Fluctuations the Crux of the Matter? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterpone, F.; Stirnemann, G.; Laage, D. Magnitude and molecular origin of water slowdown next to a protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4116–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremov, R.G. Dielectric-dependent strength of interlipid hydrogen bonding in biomembranes: Model case study. J. Chem. Inf. Mod. 2019, 59, 2765–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayer, M.D.; Levinger, N.E. Analysis of water in confined geometries and at interfaces. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2010, 3, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, D. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trofimov, Y.A.; Krylov, N.A.; Efremov, R.G. Confined Dynamics of Water in Transmembrane Pore of TRPV1 Ion Channel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174285
Trofimov YA, Krylov NA, Efremov RG. Confined Dynamics of Water in Transmembrane Pore of TRPV1 Ion Channel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174285
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrofimov, Yury A., Nikolay A. Krylov, and Roman G. Efremov. 2019. "Confined Dynamics of Water in Transmembrane Pore of TRPV1 Ion Channel" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174285
APA StyleTrofimov, Y. A., Krylov, N. A., & Efremov, R. G. (2019). Confined Dynamics of Water in Transmembrane Pore of TRPV1 Ion Channel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174285