Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis of Grape Hyacinth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of MaDFR
2.2. Anthocyanin Accumulation and MaDFR Expression in Grape Hyacinth
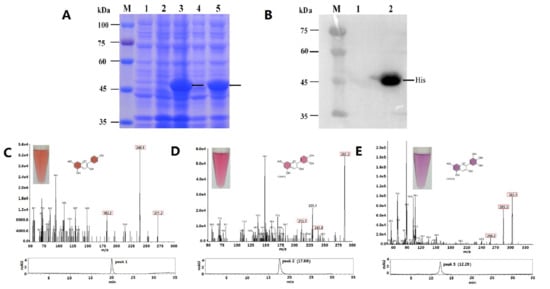
2.3. Functional Expression in E. coli and Enzyme Assay
2.4. Enhanced Production of Anthocyanins by Introducing MaDFR into Transgenic Tobacco
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Cloning of the MaDFR Gene
4.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Expression Analysis of MaDFR by qRT-PCR
4.5. Plasmid Construction
4.6. Heterologous Expression of MaDFR and in Vitro Enzyme Assay
4.7. Analysis of MaDFR Reaction Products
4.8. Stable Transformation of Tobacco
4.9. Quantification of Anthocyanin Content
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CK | transgenic tobacco lines transformed with empty vector (control) |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| OE-MaDFR | MaDFR overexpressed tobacco lines |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| Cy | cyaniding |
| Dp | delphinidin |
| Pg | pelargonidin |
| DHQ | dihydroquercetin |
| DHM | dihydromyricetin |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| CHS | chalcone synthase |
| CHI | chalconeisomerase |
| F3H | flavanone 3-hydroxylase |
| F3′H | flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase |
| F3′5′H | flavonoid 3′5′-hydroxylase |
| DFR | dihydroflavonol 4-reductase |
| ANS | anthocyanidin synthase |
| UFGT | anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase |
| MYBs | MYB transcription factors |
| bHLHs | basic helix-loop-helix proteins |
| WDR | WD repeat protein |
| EBGs | early biosynthetic genes |
| LBGs | late biosynthetic genes |
References
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, N.; Miyahara, T.; Okamoto, M.; Hirose, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Hatano, S.; Ozeki, Y. Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase activity is associated with the intensity of flower colors in delphinium. Plant Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, S.; Asano, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakano, M. Analyses of anthocyanidins and anthocyanins in flowers of muscari spp. Bull. Fac. Agric. Niigata Univ. 2002, 55, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Anthocyanin Profiles in Flowers of Grape Hyacinth. Molecules 2017, 22, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.T.; Yi, H.; Shin, B.; Oh, B.J.; Cheong, H.; Choi, G. Cymbidium hybrida dihydroflavonol 4-reductase does not efficiently reduce dihydrokaempferol to produce orange pelargonidin-type anthocyanins. Plant J. 2010, 19, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkmann, G.; Ruhnau, B. Distinct Substrate Specificity of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase from Flowers of Petunia hybrida. Z. Für Nat. C 1987, 42, 1146–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, J. Reduction of Dihydrokaempferol by Vitis vinfera Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase to Produce Orange Pelargonidin-Type Anthocyanins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F. Flower colour and cytochromes P450. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20120432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heller, W.; Forkmann, G.; Britsch, L.; Grisebach, H. Enzymatic reduction of (+)-dihydroflavonols to flavan-3,4-cis-diols with flower extracts from Matthiola incana and its role in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Planta 1985, 165, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhnau, B.; Forkmann, G.; Ruhnau, B.; Forkmann, G. Flavan-3,4-diols in anthocyanin biosynthesis, enzymatic formation with flower extracts from Callistephus chinensis. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.T.; Ryu, S.; Yi, H.; Shin, B.; Cheong, H.; Choi, G. Alteration of a single amino acid changes the substrate specificity of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase. Plant J. 2010, 25, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; You, M.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Ha, S.H. RNAi-mediated suppression of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase in tobacco allows fine-tuning of flower color and flux through the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.; Heidmann, I.; Forkmann, G.; Saedler, H. A new petunia flower colour generated by transformation of a mutant with a maize gene. Nature 1987, 330, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumoto, Y.; Fukuchimizutani, M.; Fukui, Y.; Brugliera, F.; Holton, T.A.; Karan, M.; Nakamura, N.; Yonekurasakakibara, K.; Togami, J.; Pigeaire, A. Engineering of the Rose Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway Successfully Generated Blue-Hued Flowers Accumulating Delphinidin. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, D.R. Evolution of flavors and scents. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.Y.; Jackson, L.A.; Ferreira, D.; Paiva, N.L. Molecular and Biochemical Analysis of Two cDNA Clones Encoding Dihydroflavonol-4-Reductase from Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, P.; Granier, T.; d’Estaintot, B.L.; Manigand, C.; Bathany, K.; Schmitter, J.M.; Lauvergeat, V.; Hamdi, S.; Gallois, B. Crystal structure of grape dihydroflavonol 4-reductase, a key enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, S.; Teeri, T.; Forkmann, G. Heterologous expression of dihydroflavonol 4-reductases from various plants. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haselmair-Gosch, C.; Miosic, S.; Nitarska, D.; Roth, B.L.; Walliser, B.; Paltram, R.; Lucaciu, R.C.; Eidenberger, L.; Rattei, T.; Olbricht, K.; et al. Great Cause—Small Effect: Undeclared Genetically Engineered Orange Petunias Harbor an Inefficient Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiang, M.; Fan, Y.; Yang, C.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.; Liao, Z. A Root-Preferential DFR-Like Gene Encoding Dihydrokaempferol Reductase Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis of Purple-Fleshed Sweet Potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Cai, X.; Shan, X.; Gao, R.; Yang, S.; Han, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase genes from Freesia hybrida play important and partially overlapping roles in the biosynthesis of flavonoids. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miosic, S.; Thill, J.; Milosevic, M.; Gosch, C.; Pober, S.; Molitor, C.; Ejaz, S.; Rompel, A.; Stich, K.; Halbwirth, H. Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Genes Encode Enzymes with Contrasting Substrate Specificity and Show Divergent Gene Expression Profiles in Fragaria Species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitakanta, P.; Que, K.; David, Z.; Werkman, J.R.; Xie, C.H.; Barunava, P.; Ling, Y. Isolation and functional characterization of a floral tissue-specific R2R3 MYB regulator from tobacco. Planta 2010, 231, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Yanhong, B.; Sitakanta, P.; Barunava, P.; Werkman, J.R.; Xie, C.H.; Ling, Y. Flavonoid-related basic helix-loop-helix regulators, NtAn1a and NtAn1b, of tobacco have originated from two ancestors and are functionally active. Planta 2011, 234, 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama, Y.; Katsumoto, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Fukuchimizutani, M.; Ohkawa, H.; Kusumi, T.; Iwashita, T.; Tanaka, Y. Molecular characterization of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway and flower color modification of Nierembergia sp. Plant Biotechnol. 2006, 23, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovy, A.; De, V.R.; Kemper, M.; Schijlen, E.; Almenar, P.M.; Muir, S.; Collins, G.; Robinson, S.; Verhoeyen, M.; Hughes, S. High-flavonol tomatoes resulting from the heterologous expression of the maize transcription factor genes LC and C1. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2509–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, N.; Yoshioka, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Nakayama, M.; Douzono, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Aida, R. Generation of blue chrysanthemums by anthocyanin B-ring hydroxylation and glucosylation and its coloration mechanism. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, S.F.; Brugliera, F. Genetic Modification in Floriculture. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, S.; Tian, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y. Transcriptome sequencing and metabolite analysis reveals the role of delphinidin metabolism in flower colour in grape hyacinth. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Su, B.; Zhang, H.; Gong, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Du, L. Identification and Functional Analysis of a Flavonol Synthase Gene from Grape Hyacinth. Molecules 2019, 24, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Ectopic expression of VpSTS29, a stilbene synthase gene from Vitis pseudoreticulata, indicates STS presence in cytosolic oil bodies. Planta 2018, 248, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Lou, Q.; Liu, Y. Ectopic Expression of the Grape Hyacinth (Muscari armeniacum) R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Gene, MaAN2, Induces Anthocyanin Accumulation in Tobacco. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Nakano, M. Agrobacterium -mediated production of transgenic plants of Muscari armeniacum Leichtl. ex Bak. Plant Cell Rep. 2002, 20, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zeng, S.; Gong, X.; Wei, G.; Liao, S.; Chen, J.; Wei, S.; Lv, H.; Ying, W. Elucidating the biosynthetic and regulatory mechanisms of flavonoid-derived bioactive components in Epimedium sagittatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sponga, F.; Deitzer, G.F.; Mancinelli, A.L. Cryptochrome, Phytochrome, and the Photoregulation of Anthocyanin Production under Blue Light. Plant Physiol. 1986, 82, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.S.; Gao, J.M.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, L.F.; Li, C.H. Rapid separation and identification of anthocyanins from flowers of Viola yedoensis and V. prionantha by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 23, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Khaldun, A.B.M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Lv, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y. A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Regulates the Flavonol Biosynthetic Pathway in a Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plant, Epimedium sagittatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Substrates | Enzymatic Product | Content (μg/mL) ± SE |
|---|---|---|
| DHK | Pg | 5.03 ± 0.000262 c |
| DHQ | Cy | 6.45 ± 0.000383 b |
| DHM | Dp | 11.71 ± 0.000493 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Lou, Q.; Ma, J.; Su, B.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y. Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis of Grape Hyacinth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194743
Liu H, Lou Q, Ma J, Su B, Gao Z, Liu Y. Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis of Grape Hyacinth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194743
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongli, Qian Lou, Junren Ma, Beibei Su, Zhuangzhuang Gao, and Yali Liu. 2019. "Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis of Grape Hyacinth" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194743
APA StyleLiu, H., Lou, Q., Ma, J., Su, B., Gao, Z., & Liu, Y. (2019). Cloning and Functional Characterization of Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Gene Involved in Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis of Grape Hyacinth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(19), 4743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194743