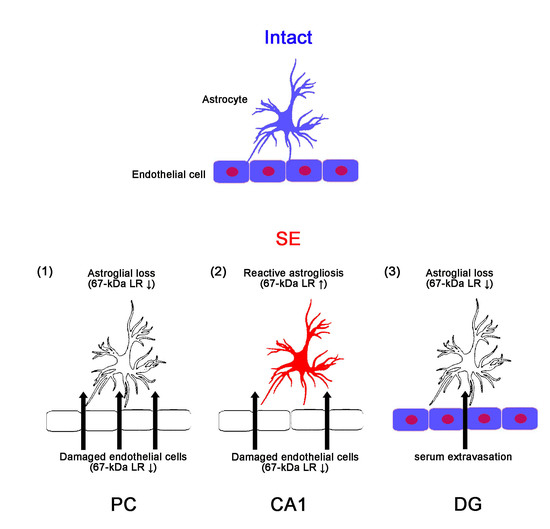
The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. SE Differently Affects Expression Levels of 67-kDa LR, Dystrophin, and AQP4 in the Hippocampus and the PC
2.2. The 67-kDa LR Neutralization Decreases Dystrophin-AQP4 Expressions in the PC and the Hippocampus
2.3. The 67-kDa LR Neutralization Increases ERK1/2, but Not JNK, Phosphorylation
2.4. The 67-kDa LR Neutralization Does Not Affect PEA15 Phosphorylations
2.5. The 67-kDa LR Neutralization Increases the Susceptibility to SE Induction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Chemicals
4.2. Surgery
4.3. SE Induction and Electroencephalogram (EEG) Analysis
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Temkin, N.R. Risk factors for posttraumatic seizures in adults. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.P.; Leblanc, G.G.; Brooks-Kayal, A.; Jensen, F.E.; Lowenstein, D.H.; Noebels, J.L.; Spencer, D.D.; Swann, J.W. Curing epilepsy: Progress and future directions. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 14, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Yeo, S.I.; Ryu, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.S.; Jo, S.M.; Kang, T.C. Astroglial loss and edema formation in the rat piriform cortex and hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 4612–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheen, S.H.; Kim, J.E.; Ryu, H.J.; Yang, Y.; Choi, K.C.; Kang, T.C. Decrease in dystrophin expression prior to disruption of brain-blood barrier within the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2011, 1369, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Kang, T.C. Cellular and regional specific changes in multidrug efflux transporter expression during recovery of vasogenic edema in the rat hippocampus and piriform cortex. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigau, V.; Morin, M.; Rousset, M.C.; de Bock, F.; Lebrun, A.; Coubes, P.; Picot, M.C.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Bockaert, J.; Crespel, A.; et al. Angiogenesis is associated with blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2007, 130, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyboll, J.; Kortesmaa, J.; Cao, R.; Soininen, R.; Wang, L.; Iivanainen, A.; Sorokin, L.; Risling, M.; Cao, Y.; Tryggvason, K. Deletion of the laminin alpha4 chain leads to impaired microvessel maturation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, J.H. Laminins and their roles in mammals. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2008, 71, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesot, H.; Kuhl, U.; Mark, K. Isolation of a laminin-binding protein from muscle cell membranes. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.; Castronovo, V.; Schmitt, M.C.; Wewer, U.M.; Claysmith, A.P.; Liotta, L.A.; Sobel, M.E. Evidence for a precursor of the high-affinity metastasis-associated murine laminin receptor. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 7476–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffery, P.; Neve, R.L.; Drager, U.C. A dorso-ventral asymmetry in the embryonic retina defined by protein conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8570–8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohgo, A.; Takasawa, S.; Munakata, H.; Yonekura, H.; Hayashi, N.; Okamoto, H. Structural determination and characterization of a 40 kDa protein isolated from rat 40 S ribosomal subunit. FEBS Lett. 1994, 340, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, R.; Martignone, S.; Menard, S.; Colnaghi, M.I. Laminin receptor expression and function in small-cell lung carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 8, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardini, E.; Sporchia, B.; Pollegioni, L.; Modugno, M.; Ghirelli, C.; Castiglioni, F.; Tagliabue, E.; Ménard, S. Identification of a novel function for 67-kDa laminin receptor: Increase in laminin degradation rate and release of motility fragments. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Choi, S.H.; Kong, M.J.; Kang, T.C. Dysfunction of 67-kDa laminin receptor disrupts BBB integrity via impaired dystrophin/AQP4 complex and p38 MAPK/VEGF activation following status epilepticus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givant-Horwitz, V.; Davidson, B.; Reich, R. Laminin-induced signaling in tumor cells: The role of the M(r) 67,000 laminin receptor. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3572–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formisano, P.; Ragno, P.; Pesapane, A.; Alfano, D.; Alberobello, A.T.; Rea, V.E.; Giusto, R.; Rossi, F.W.; Beguinot, F.; Rossi, G.; et al. PED/PEA-15 interacts with the 67 kD laminin receptor and regulates cell adhesion, migration, proliferation and apoptosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiory, F.; Formisano, P.; Perruolo, G.; Beguinot, F. Frontiers: PED/PEA-15, a multifunctional protein controlling cell survival and glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E592–E601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, H.; Danziger, N.; Cordier, J.; Glowinski, J.; Chneiweiss, H. Characterization of PEA-15, a major substrate for protein kinase C in astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar]
- Estellés, A.; Yokoyama, M.; Nothias, F.; Vincent, J.D.; Glowinski, J.; Vernier, P.; Chneiweiss, H. The major astrocytic phosphoprotein PEA-15 is encoded by two mRNAs conserved on their full length in mouse and human. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14800–14806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, M.; Cordier, J.; Glowinski, J.; Girault, J.A.; Chneiweiss, H. Endothelin induces a calcium-dependent phosphorylation of PEA-15 in intact astrocytes: Identification of Ser104 and Ser116 phosphorylated, respectively, by protein kinase C and calcium/calmodulin kinase II in vitro. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trencia, A.; Perfetti, A.; Cassese, A.; Vigliotta, G.; Miele, C.; Oriente, F.; Santopietro, S.; Giacco, F.; Condorelli, G.; Formisano, P.; et al. Protein kinase B/Akt binds and phosphorylates PED/PEA-15, stabilizing its antiapoptotic action. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4511–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.; Chou, F.L.; Glading, A.; Schaefer, E.; Ginsberg, M.H. Phosphorylation of phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes (PEA-15) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent transcription and cell proliferation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 3552–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloui, H.; von Boxberg, Y.; Vinh, J.; Weiss, S.; Rossier, J.; Nothias, F.; Stettler, O. Cellular prion protein/laminin receptor: Distribution in adult central nervous system and characterization of an isoform associated with a subtype of cortical neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, K.; Chetty, C.J.; Khumalo, T.; Da Costa Dias, B.; Ferreira, E.; Malindisa, S.T.; Caveney, R.; Letsolo, B.T.; Weiss, S.F. Novel patented therapeutic approaches targeting the 37/67 kDa laminin receptor for treatment of cancer and Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, J.D.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Froehner, S.C.; Agre, P.; Adams, M.E. Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of Aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14108–14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nico, B.; Frigeri, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Corsi, P.; Ribatti, D.; Quondamatteo, F.; Herken, R.; Girolamo, F.; Marzullo, A.; Svelto, M.; et al. Severe alterations of endothelial and glial cells in the blood-brain barrier of dystrophic mdx mice. Glia 2003, 42, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg, H.; Noell, S.; Mack, A.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Fallier-Becker, P. Brain endothelial cells and the glio-vascular complex. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 335, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.E.; Kwak, S.E.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, D.W.; Kwon, O.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, T.C. Spatiotemporal characteristics of astroglial death in the rat hippocampo-entorhinal complex following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 511, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, T.C. PARP1 activation/expression modulates regional-specific neuronal and glial responses to seizure in a hemodynamic-independent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, E.; Dreier, J.P.; Ivens, S.; Bechmann, I.; Tomkins, O.; Heinemann, U.; Friedman, A. Lasting blood-brain barrier disruption induces epileptic focus in the rat somatosensory cortex. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7829–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Manley, G.T.; Krishna, S.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, O.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Manley, G.T.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 gene deletion in mice increases focal edema associated with staphylococcal brain abscess. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warth, A.; Kröger, S.; Wolburg, H. Redistribution of aquaporin-4 in human glioblastoma correlates with loss of agrin immunoreactivity from brain capillary basal laminae. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 107, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enger, R.; Gundersen, G.A.; Haj-Yasein, N.N.; Eilert-Olsen, M.; Thoren, A.E.; Vindedal, G.F.; Petersen, P.H.; Skare, Ø.; Nedergaard, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. Molecular scaffolds underpinning macroglial polarization: An analysis of retinal Müller cells and brain astrocytes in mouse. Glia 2012, 60, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Mathari, B.; Sene, A.; Charles-Messance, H.; Vacca, O.; Guillonneau, X.; Grepin, C.; Sennlaub, F.; Sahel, J.A.; Rendon, A.; Tadayoni, R. Dystrophin Dp71 gene deletion induces retinal vascular inflammation and capillary degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vacca, O.; Charles-Messance, H.; El Mathari, B.; Sene, A.; Barbe, P.; Fouquet, S.; Aragón, J.; Darche, M.; Giocanti-Aurégan, A.; Paques, M.; et al. AAV-mediated gene therapy in Dystrophin-Dp71 deficient mouse leads to blood-retinal barrier restoration and oedema reabsorption. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3070–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolburg, H.; Noell, S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Mack, A.F.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K. The disturbed blood-brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, L.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Turski, W.A.; Meldrum, B.S. Excitatory neurotransmission within substantia nigra pars reticulata regulates threshold for seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: Effects of intranigral 2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate and N-methyl-D-aspartate. Neuroscience 1986, 18, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Schwarz, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Kleinrok, Z.; Turski, L. Limbic seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: A behavioural, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study. Behav. Brain Res. 1983, 9, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, D.G. The temporal evolution of neuronal damage from pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1996, 725, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.C.; Kim, D.S.; Kwak, S.E.; Kim, J.E.; Won, M.H.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Kwon, O.S. Epileptogenic roles of astroglial death and regeneration in the dentate gyrus of experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Glia 2006, 54, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Ingvar, M. Loss of immunoreactivity for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in astrocytes as a marker for profound tissue damage in substantia nigra and basal cortical areas after status epilepticus induced by pilocarpine in rat. Glia 1994, 12, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Ingvar, M. Laminar damage of neurons and astrocytes in neocortex and hippocampus of rat after long-lasting status epilepticus induced by pilocarpine. Epilepsy Res. Suppl. 1996, 12, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, H.; Koga, K.; Fujimura, Y.; Yamada, K. A receptor for green tea polyphenol EGCG. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 380–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, E.B.; Choi, H.G.; Sung, N.Y.; Byun, E.H. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits TLR4 signaling through the 67-kDa laminin receptor on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated dendritic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.F.; Xie, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, J.J.; Gao, Y.F.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, L.S. Inhibition of EMMPRIN and MMP-9 Expression by Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate through 67-kDa Laminin Receptor in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.C.; Chang, H.H.; Liu, H.C.; Hsiao, C.H.; Lee, M.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Hung, P.F.; Liu, C.W.; Kao, Y.H. Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits insulin stimulation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte mitogenesis via the 67-kDa laminin receptor pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 297, C121–C132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ku, H.C.; Liu, H.S.; Hung, P.F.; Chen, C.L.; Liu, H.C.; Chang, H.H.; Tsuei, Y.W.; Shih, L.J.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, C.M.; et al. Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits IGF-I and IGF-II stimulation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte mitogenesis via the 67-kDa laminin receptor, but not AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.F.; Zhao, W.J.; Xu, L.X.; Dong, L.P.; Yang, S.H.; Yuan, F. Downregulation of aquaporin 4 expression through extracellular signal-regulated kinases1/2 activation in cultured astrocytes following scratch-injury. Biomed. Env. Sci. 2015, 28, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.L.; Fang, S.H.; Shi, W.Z.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, Y.B.; Zhang, W.P.; Wei, E.Q. CysLT2 receptor-mediated AQP4 up-regulation is involved in ischemic-like injury through activation of ERK and p38 MAPK in rat astrocytes. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Sheilabi, M.A.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Kitchen, P.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Conner, M.T.; Princivalle, A.P. Transcriptome analysis suggests a role for the differential expression of cerebral aquaporins and the MAPK signalling pathway in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.R.; Kang, T.C. TRPC6-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation prevents dentate granule cell degeneration via inhibiting mitochondrial elongation. Neuropharmacology 2017, 121, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. Nucleocytoplasmic p27(Kip1) export is required for ERK1/2-mediated reactive astroglial proliferation following status epilepticus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, S.J.; Hyun, H.W.; Kang, T.C. Leptomycin B attenuates neuronal death via PKA- and PP2B-mediated ERK1/2 activation in the rat hippocampus following status epilepticus. Brain Res. 2017, 1670, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, P.; Yao, L.; Jin, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pang, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. Hypoxia promotes metastasis in human gastric cancer by up-regulating the 67-kDa laminin receptor. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, P.; Wan, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, M.; Qiu, G.; Zhuo, F.; Xu, S.; Huo, J.; Ju, Y.; et al. Dystroglycan is involved in the activation of ERK pathway inducing the change of AQP4 expression in scratch-injured astrocytes. Brain Res. 2019, 1721, 146347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, C.; Simoneau, S.; Rey, C.; Vana, K.; Rieger, R.; Lasmézas, C.I.; Weiss, S. The 37 kDa/67 kDa laminin receptor is required for PrP(Sc) propagation in scrapie-infected neuronal cells. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salama, R.H.; Muramatsu, H.; Zou, K.; Inui, T.; Kimura, T.; Muramatsu, T. Midkine binds to 37-kDa laminin binding protein precursor, leading to nuclear transport of the complex. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 270, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, K.J.; Goti, D.; Stins, M.F.; Shin, S.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Kim, K.S. 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor modulates cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1-mediated RhoA activation and bacterial uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16857–16862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. p47Phox/CDK5/DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission evokes PV cell degeneration in the rat dentate gyrus following status epilepticus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. Differential roles of mitochondrial translocation of active caspase-3 and HMGB1 in neuronal death induced by status epilepticus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gundimeda, U.; McNeill, T.H.; Barseghian, B.A.; Tzeng, W.S.; Rayudu, D.V.; Cadenas, E.; Gopalakrishna, R. Polyphenols from green tea prevent antineuritogenic action of Nogo-A via 67-kDa laminin receptor and hydrogen peroxide. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uva, L.; Librizzi, L.; Marchi, N.; Noe, F.; Bongiovanni, R.; Vezzani, A.; Janigro, D.; de Curtis, M. Acute induction of epileptiform discharges by pilocarpine in the in vitro isolated guinea-pig brain requires enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability. Neuroscience 2008, 151, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roch, C.; Leroy, C.; Nehlig, A.; Namer, I.J. Magnetic resonance imaging in the study of the lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy in adult rats. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binder, D.K.; Yao, X.; Zador, Z.; Sick, T.J.; Verkman, A.S.; Manley, G.T. Increased seizure duration and slowed potassium kinetics in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Glia 2006, 53, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Hsu, M.S.; Seldin, M.M.; Arellano, J.L.; Binder, D.K. Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 235, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Williamson, A.; Palomba, M.; Eid, T.; de Lanerolle, N.C.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Adams, M.E.; Froehner, S.C.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Delayed K+ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: Phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophin-null mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003, 100, 13615–13620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salatino, J.W.; Ludwig, K.A.; Kozai, T.D.Y.; Purcell, E.K. Glial responses to implanted electrodes in the brain. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsdell, J.S.; Gulland, F.M. Domoic acid epileptic disease. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1185–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaughan, D.N.; Jackson, G.D. The piriform cortex and human focal epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danziger, N.; Yokoyama, M.; Jay, T.; Cordier, J.; Glowinski, J.; Chneiweiss, H. Cellular expression, developmental regulation, and phylogenic conservation of PEA-15, the astrocytic major phosphoprotein and protein kinase C substrate. J. Neurochem. 1995, 64, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, C.; André, V.; Covolan, L.; Ferrandon, A.; Marescaux, C.; Nehlig, A. C-Fos, Jun D and HSP72 immunoreactivity, and neuronal injury following lithium-pilocarpine induced status epilepticus in immature and adult rats. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 63, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Antigen. | Host | Manufacturer (Catalog Number) | Dilution Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| 67-kDa LR | Rabbit Rabbit | Abcam (#ab133645) Abcam, (#ab133775) | 1:1000 (WB) 1:500 (IH) |
| AQP4 | Rabbit | Alomone labs (#AQP-004) | 1:5000 (WB) |
| Dystrophin | Rabbit | Abcam (#ab15277) | 1:5000 (WB) |
| ERK1/2 | Rabbit | Biorbyt (Orb160960) | 1:2,000 (WB) 1:100 (IH) |
| GFAP | Mouse | Millipore (#MAB3402) | 1:5000 (IH) |
| Iba-1 | Mouse | Abcam (#ab15690) | 1:100 (IH) |
| JNK | Rabbit | Protein tech (10023-1-AP) | 1:1000 |
| Laminin | Rabbit | Abcam (#ab11575) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| NeuN | Guinea pig | Millipore (#ABN90P) | 1:1000 (IH) |
| Phospho (p)-p38 MAPK | Rabbit | Abbiotec (#251246) | 1:200 (WB) |
| p38 MAPK | Rabbit | Cell signaling (#9212) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| PEA15 | Rabbit | Antibodies-online, (ABIN1737975) | 1:500 (WB) |
| pERK1/2 | Rabbit | Bioss (bs-3330R) | 1:1000 (WB) 1:100 (IH) |
| pJNK | Rabbit | Millipore (#07-105) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| pPEA15-S104 | Rabbit | Antibodies-online (ABIN744683) | 1:500 (WB) |
| pPEA15-S116 | Rabbit | Antibodies-online, (ABIN744698) | 1:500 (WB) |
| rat IgG | Goat | Vector (#PI-9400) | 1:200 (IH) |
| SMI-71 | Mouse | Covance (#SMI-71R) | 1:1000 (IH) |
| VEGF | Rabbit | Abcam (#ab46154) | 1:1000 (WB) |
| β-actin | Mouse | Sigma (#A5316) | 1:5000 (WB) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Kang, T.-C. The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236025
Park H, Kang T-C. The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):6025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236025
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hana, and Tae-Cheon Kang. 2019. "The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 6025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236025
APA StylePark, H., & Kang, T. -C. (2019). The Regional Specific Alterations in BBB Permeability are Relevant to the Differential Responses of 67-kDa LR Expression in Endothelial Cells and Astrocytes Following Status Epilepticus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236025