PDI-Mediated Reduction of Disulfide Bond on PSD95 Increases Spontaneous Seizure Activity by Regulating NR2A–PSD95 Interaction in Epileptic Rats Independent of S-Nitrosylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. S-Nitrosylation and Disulfide Bond Formation on PSD95 in Acute Seizure Model
2.2. S-Nitrosylation and Disulfide Bond Formation on PSD95 in Epileptic Rats
2.3. Effect of PDI Knockdown on S-Nitrosylation and Disulfide-Bond Formation on PSD95
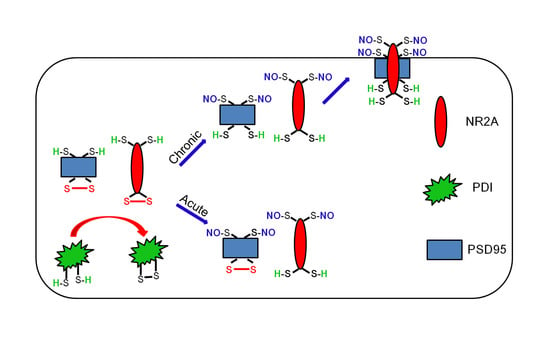
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Chemicals
4.2. Acute Seizure Model
4.3. Epileptic Rat Model
4.4. PDI Knockdown and Analysis of Chronic Seizure Activity
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Measurement of Total- and SNO-Thiols
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bliss, T.V.; Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.W.; Rothman, S.M. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, I.; MacDonald, J.F. NMDA receptor-dependent excitotoxicity: The role of intracellular Ca2+ release. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Ko, A.R.; Hyun, H.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, T.C. PLPP/CIN regulates bidirectional synaptic plasticity via GluN2A interaction with postsynaptic proteins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ko, A.R.; Hyun, H.W.; Min, S.J.; Kim, J.E. PDI regulates seizure activity via NMDA receptor redox in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipton, S.A.; Rosenberg, P.A. Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.B.; Tenneti, L.; Le, D.A.; Ortiz, J.; Bai, G.; Chen, H.S.; Lipton, S.A. Molecular basis of NMDA receptor-coupled ion channel modulation by S-nitrosylation. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A.; Choi, Y.B.; Takahashi, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Godzik, A.; Bankston, L.A. Cysteine regulation of protein function--as exemplified by NMDA-receptor modulation. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Longo, D.; Biagini, G.; Jones, R.S.; Avoli, M. The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 172, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Cho, K.O.; Rothschild, A.; Sheng, M. Heteromultimerization and NMDA receptor-clustering activity of Chapsyn-110, a member of the PSD-95 family of proteins. Neuron 1996, 17, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.; Niethammer, M.; Rothschild, A.; Jan, Y.N.; Sheng, M. Clustering of Shaker-type K+ channels by interaction with a family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases. Nature 1995, 378, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornau, H.C.; Schenker, L.T.; Kennedy, M.B.; Seeburg, P.H. Domain interaction between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 1995, 269, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niethammer, M.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M. Interaction between the C terminus of NMDA receptor subunits and multiple members of the PSD-95 family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sattler, R.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, W.Y.; Hafner, M.; MacDonald, J.F.; Tymianski, M. Specific coupling of NMDA receptor activation to nitric oxide neurotoxicity by PSD-95 protein. Science 1999, 284, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migaud, M.; Charlesworth, P.; Dempster, M.; Webster, L.C.; Watabe, A.M.; Makhinson, M.; He, Y.; Ramsay, M.F.; Morris, R.G.; Morrison, J.H.; et al. Enhanced long-term potentiation and impaired learning in mice with mutant postsynaptic density-95 protein. Nature 1998, 396, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseini, A.E.D.; Schnell, E.; Dakoji, S.; Sweeney, N.; Zhou, Q.; Prange, O.; Gauthier-Campbell, C.; Aguilera-Moreno, A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. Synaptic strength regulated by palmitate cycling on PSD-95. Cell 2002, 108, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topinka, J.R.; Bredt, D.S. N-terminal palmitoylation of PSD-95 regulates association with cell membranes and interaction with K+ channel Kv1.4. Neuron 1998, 20, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, P.T.; Cotman, C.W. Identification of glycoproteins and proteins at synapses in the central nervous system. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 786–793. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, Y.P.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M. Disulfide-linked head-to-head multimerization in the mechanism of ion channel clustering by PSD-95. Neuron 1997, 18, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, G.P.; Selvakumar, B.; Mukai, J.; Hester, L.D.; Wang, Y.; Gogos, J.A.; Snyder, S.H. S-nitrosylation and S-palmitoylation reciprocally regulate synaptic targeting of PSD-95. Neuron 2011, 71, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Ryu, H.J.; Kang, T.C. Status epilepticus induces vasogenic edema via tumor necrosis factor-α/endothelin-1-mediated two different pathways. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, A.R.; Hyun, H.W.; Min, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. Endothelin-1 induces LIMK2-mediated programmed necrotic neuronal death independent of NOS activity. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoi, N.; Fukata, M.; Fukata, Y. Synaptic plasticity regulated by protein-protein interactions and posttranslational modifications. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 297, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kornhuber, J.; Weller, M. Psychotogenicity and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonism: Implications for neuroprotective pharmacotherapy. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 41, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.G. Glutamate receptors in epilepsy. Prog. Brain Res. 1998, 116, 371–383. [Google Scholar]
- Dannhardt, G.; Kohl, B.K. The glycine site on the NMDA receptor: Structure-activity relationships and possible therapeutic applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 1998, 5, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, Y.P.; Sheng, M. Requirement of N-terminal cysteines of PSD-95 for PSD-95 multimerization and ternary complex formation, but not for binding to potassium channel Kv1.4. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takagi, N.; Logan, R.; Teves, L.; Wallace, M.C.; Gurd, J.W. Altered interaction between PSD-95 and the NMDA receptor following transient global ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarts, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Besshoh, S.; Arundine, M.; Gurd, J.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Salter, M.W.; Tymianski, M. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor- PSD-95 protein interactions. Science 2002, 298, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Chang, H.; Huang, L.T.; Lai, M.C.; Yang, C.H.; Wan, T.H.; Yang, S.N. Alterations in long- term seizure susceptibility and the complex of PSD-95 with NMDA receptor from animals previously exposed to perinatal hypoxia. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of developing rat cortical neurons after epileptiform discharges. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezuka, T.; Umemori, H.; Akiyama, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Yamamoto, T. PSD-95 promotes Fyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erreger, K.; Dravid, S.M.; Banke, T.G.; Wyllie, D.J.; Traynelis, S.F. Subunit-specific gating controls rat NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B NMDA channel kinetics and synaptic signalling profiles. J. Physiol. 2005, 563, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noritake, J.; Fukata, Y.; Iwanaga, T.; Hosomi, N.; Tsutsumi, R.; Matsuda, N.; Tani, H.; Iwanari, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; Kodama, T.; et al. Mobile DHHC palmitoylating enzyme mediates activity-sensitive synaptic targeting of PSD-95. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaffrey, S.R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Ferris, C.D.; Tempst, P.; Snyder, S.H. Protein S-nitrosylation: A physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, F.; Curia, G.; Marinelli, C.; Biagini, G. Increased perivascular laminin predicts damage to astrocytes in CA3 and piriform cortex following chemoconvulsive treatments. Neuroscience 2012, 218, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.M. Increased numbers of coassembled PSD-95 to NMDA-receptor subunits NR2B and NR1 in human epileptic cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finardi, A.; Gardoni, F.; Bassanini, S.; Lasio, G.; Cossu, M.; Tassi, L.; Caccia, C.; Taroni, F.; LoRusso, G.; Di Luca, M.; et al. NMDA receptor composition differs among anatomically diverse malformations of cortical development. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernia, S.; Rubio, T.; Heredia, M.; Rodríguez de Córdoba, S.; Sanz, P. Increased endoplasmic reticulum stress and decreased proteasomal function in lafora disease models lacking the phosphatase laforin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Kang, T.C. The P2X7 receptor-pannexin-1 complex decreases muscarini acetylcholine receptor- mediated seizure susceptibility in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, A.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Hyun, H.W.; Kim, J.E. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress protein responses in relation to spatio-temporal dynamics of astroglial responses to status epilepticus in rats. Neuroscience 2015, 307, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.R.; Kang, T.C. Blockade of endothelin B receptor improves the efficacy of levetiracetam in chronic epileptic rats. Seizure 2015, 31, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.-S.; Kim, J.-E. PDI-Mediated Reduction of Disulfide Bond on PSD95 Increases Spontaneous Seizure Activity by Regulating NR2A–PSD95 Interaction in Epileptic Rats Independent of S-Nitrosylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062094
Lee D-S, Kim J-E. PDI-Mediated Reduction of Disulfide Bond on PSD95 Increases Spontaneous Seizure Activity by Regulating NR2A–PSD95 Interaction in Epileptic Rats Independent of S-Nitrosylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Duk-Shin, and Ji-Eun Kim. 2020. "PDI-Mediated Reduction of Disulfide Bond on PSD95 Increases Spontaneous Seizure Activity by Regulating NR2A–PSD95 Interaction in Epileptic Rats Independent of S-Nitrosylation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062094
APA StyleLee, D. -S., & Kim, J. -E. (2020). PDI-Mediated Reduction of Disulfide Bond on PSD95 Increases Spontaneous Seizure Activity by Regulating NR2A–PSD95 Interaction in Epileptic Rats Independent of S-Nitrosylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062094