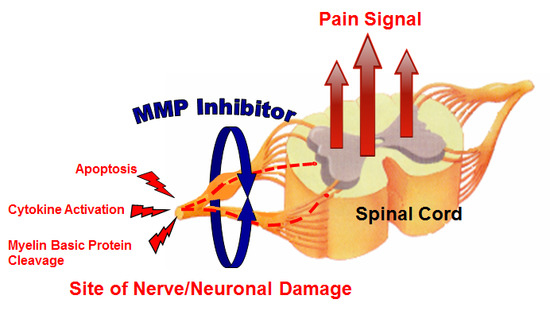
Biomarker Analysis of Orally Dosed, Dual Active, Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Inhibitor, AQU-118, in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Attenuation of von Frey Mechanical Allodynia by Oral Administration of AQU-118 in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL)-Rat Model
2.2. Transcript Expression Changes in the DRG 20 Days after SNL-Surgery (D5) between Vehicle and Sham Groups
2.3. Protein Level Changes in the DRG 20 Days after SNL-Surgery (D5) between Vehicle and Sham Groups
2.4. Protein Level Changes in the DRG 20 Days after SNL-Surgery (D5) between AQU-118 and Vehicle Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Testing of Orally Administered AQU-118 in the SNL-Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
4.1.1. Animals
4.1.2. Von Frey Test for Mechanical Allodynia
4.2. Pre-Operative Baseline Testing
4.3. Post-Operative Testing
4.3.1. Compound Formulation/Administration
4.3.2. Tissue Collection & Preparation
4.4. RNA and cDNA Preparation for qPCR
4.5. qPCR Analysis
PCR Efficiency Target (ΔCtsample for Target)/PCR Efficiency GAPDH (ΔCtsample for GAPDH)
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References and Note
- Harden, N.; Cohen, M. Unmet needs in the management of neuropathic pain. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2003, 25, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, S. The neuropathic pain market. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fleur, M.; Underwood, J.L.; Rappolee, D.A.; Werb, Z. Basement membrane and repair of injury to peripheral nerve: Defining a potential role for macrophages, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeo, J.A.; Colburn, R.W.; Nichols, M.; Malhotra, A. Interleukin-6-mediated hyperalgesia/allodynia and increased spinal IL-6 expression in a rat mononeuropathy model. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweitzer, S.M.; Colburn, R.W.; Rutkowski, M.; DeLeo, J.A. Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1 beta expression that correlates with pain behaviour in the rat. Brain Res. 1999, 829, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Schmidt, C.; Weishaupt, A.; Toyka, K.V.; Sommer, C. Serial determination of tumor necrosis factor-alpha content in rat sciatic nerve after chronic constriction injury. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 160, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, H.; Dippel, N.; Mader, M.; Frank, W.; Bruck, W. Matrix metalloproteinase expression and inhibition after sciatic nerve axotomy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafers, M.; Sorkin, L.S.; Geis, C.; Shubayev, V.I. Spinal nerve ligation induces transient upregulation of tumor necrosis factor 1 and 2 in injured and adjacent uninjured dorsal root ganglia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 347, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, J.; Korostynski, M.; Kaminska, D.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Osikowicz, M.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocki, R.; Przewlocka, B. Interleukin-1 alpha has antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activities in a rat neuropathic pain model. Pain 2008, 138, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brkic, M.; Balusu, S.; Libert, C.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. Friends or Foes: Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Multifaceted Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases, Mediators of Inflammation; Hindawi Publishing Corp.: Cairo, Egypt, 2015; 27p. [Google Scholar]
- Tokito, A.; Jougasaki, M. Matrix metalloproteinases in non-neoplastic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Park, J.Y.; Zhuang, Z.Y.; Tan, P.H.; Gao, Y.J.; Roy, K.; Corfas, G.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Kato, K.; Dolkas, J.; Kikuchi, S.; Myers, R.R.; Shubayev, V.I. MMPs initiate Schwann cell-mediated MBP degradation and mechanical nociception after nerve damage. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2008, 39, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henry, M.A.; Fairchild, D.D.; Patil, M.J.; Hanania, T.; Hain, H.S.; Davis, S.F.; Malekiani, S.A.; Hu, A.; Sucholeiki, R.; Nix, D.; Sucholeiki, I. Effect of a novel, orally active matrix metalloproteinease-2 and-9 inhibitor in spinal and trigeminal rat models of neuropathic pain. J. Oral Fac. Pain Headache 2015, 29, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Sucholeiki, I. Compounds and Methods for the Treatment of Pain and Other Disorders. U.S. Patent PCT US2011/026848, WO 2012/118498 A1, 9 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovy, V.; Brazda, V.; Klusakova, I.; Svzenska, I.H. Bilateral elevation of interleukin-6 protein and mRNA in both lumbar and cervical dorsal root ganglia following unilateral chronic compression injury of the sciatic nerve. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Figueroa, K.W.; Li, K.W.; Boroujerdi, A.; Yolo, T.; Luo, Z.D. Profiling of dynamically changed gene expression in dorsal root ganglia post peripheral nerve injury and a critical role of injury-induced glial fibrillary acetic protein in maintenance of pain behaviors. Pain 2009, 143, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekiguchi, M.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Konno, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Homma, Y.; Kikuchi, S. Comparison of neuropathic pain and neuronal apoptosis following nerve root or spinal nerve compression. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- IL-6 antibodies (21 kDa) for Western blot were commercially obtained from ThermoFisher, R & D systems and Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Antibodies from R & D Systems and ThermoFisher passed validation with known controls and were then used to measure the level in DRG.
- Gygi, S.P.; Rochon, Y.; Franza, R.B.; Aebersold, R. Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.S.; Santiago, M.F.; Marques, S.A.; Allodi, S.; Martinez, A.M.B. Diversity among satellite glial cells in dorsal root ganglia of the rat. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitesides, G.T.; Munglani, R. Cell death in the superficial dorsal horn in a model of neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 64, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E.K.; Levine, J.D. Caspase signaling in neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2896–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Broom, D.C.; Youn, D.-H.; Mills, C.D.; Kohono, T.; Suter, M.R.; Moore, K.A.; Decosterd, I.; Coggeshall, R.E.; Woolf, C.J. Blocking caspase activity prevents trans-synaptic neuronal apoptosis and the loss of inhibition in Lamina II of the dorsal Horn after peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7317–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradl, G.; Herlyn, P.; Finke, B.; Bierer, P.; Wree, A.; Witt, M.; Mittlmeier, T.; Vollmar, B. A pan-caspase inhibitor reduces myocyte apoptosis and neuropathic pain in rats with chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 116, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, E.; Rodhe, J.; Burguillos, M.A.; Venero, J.L.; Joseph, B. Regulation of caspase-3 processing by cIAP2 controls the switch between pro-inflammatory activation and cell death in microglia. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, M.D.; Cavallucci, V.; Cecconi, F. Neuronal caspase-3 signaling: Not only cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Lo, E.H. Induction of caspase-mediated cell death by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral endothelial cells after hypoxia-reoxygenation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Muneer, P.M.; Conte, A.A.; Haldar, D.; Long, M.; Patel, R.K.; Santhakumar, V.; Overall, C.M.; Pfister, B.J. Traumatic brain injury induced matrix metalloproteinase 2 cleaves CXCL12α(stromal cell derived factor 1α) and causes neurodegeneration. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Chung, J.M. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992, 50, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.M.; Kim, H.K.; Chung, K. Segmental spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Menalled, L.B.; Kudwa, A.E.; Miller, S.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Watson-Johnson, J.; Keating, N.; Ruiz, M.; Mushlin, R.; Alosio, W.; McConnell, K.; et al. Comprehensive behavioral and molecular characterization of a new knock-in mouse model of Huntington’s disease: zQ175. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menalled, L.B.; Kudwa, A.E.; Oakeshott, S.; Farrar, A.; Paterson, N.; Filippov, I.; Miller, S.; Kwan, M.; Olsen, M.; Beltran, J.; et al. Genetic deletion of transglutaminase 2 does not rescue the phenotypic deficits observed in R6/2 and zQ175 mouse models of Huntington’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Group | #Rats | Route | Dose 1,5 (mg/kg) | Compound | Dosing Days | von-Frey Testing Days 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | P.O. | NA 2 | Sham | NA 2 | 1,3,5 |
| 2 | 40 | P.O. | NA 3 | Vehicle 3 | 1–5 | 1,3,5 |
| 3 | 10 | P.O. | 100 | Gabapentin | 1,3,5 4 | 1,3,5 |
| 4 | 20 | P.O. | 160 | AQU-118 | 1–15 | 1,3,5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwan, M.Y.; Choo, A.; Hanania, T.; Ghavami, A.; Beltran, J.; Shea, J.; Barboza, A.; Hu, A.; Fowler, M.; Neelagiri, V.R.; et al. Biomarker Analysis of Orally Dosed, Dual Active, Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Inhibitor, AQU-118, in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040811
Kwan MY, Choo A, Hanania T, Ghavami A, Beltran J, Shea J, Barboza A, Hu A, Fowler M, Neelagiri VR, et al. Biomarker Analysis of Orally Dosed, Dual Active, Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Inhibitor, AQU-118, in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(4):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040811
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwan, Mei Yee, Anthony Choo, Taleen Hanania, Afshin Ghavami, Jose Beltran, John Shea, Amidi Barboza, Andrew Hu, Marcie Fowler, Venugopal Rao Neelagiri, and et al. 2019. "Biomarker Analysis of Orally Dosed, Dual Active, Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Inhibitor, AQU-118, in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 4: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040811
APA StyleKwan, M. Y., Choo, A., Hanania, T., Ghavami, A., Beltran, J., Shea, J., Barboza, A., Hu, A., Fowler, M., Neelagiri, V. R., & Sucholeiki, I. (2019). Biomarker Analysis of Orally Dosed, Dual Active, Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 Inhibitor, AQU-118, in the Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(4), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040811