Potential Functions of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome Inhabiting the Length of the Rat Digest Tract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
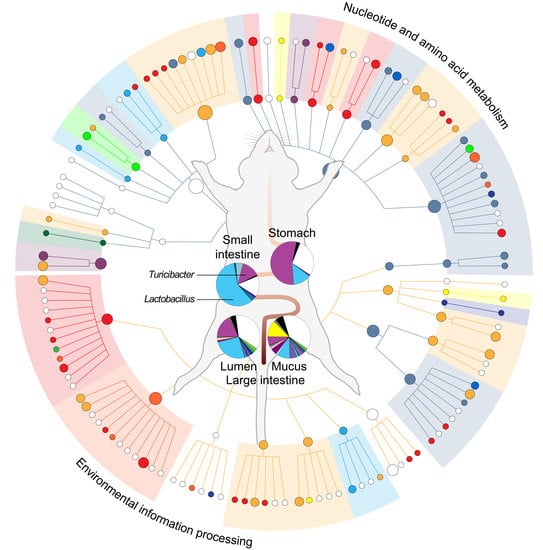
2.1. Metabolic Heterogeneity in the Community Function
2.2. Module-Centric Metabolic Reconstruction of the Rat Gastrointestinal (GI) Microbiome
2.3. Functional Overlaps in the Murine GI Microbiome
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Stagaman, K.; Dethlefsen, L.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Relman, D.A. The application of ecological theory toward an understanding of the human microbiome. Science 2012, 336, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manichanh, C.; Rigottier-Gois, L.; Bonnaud, E.; Gloux, K.; Pelletier, E.; Frangeul, L.; Nalin, R.; Jarrin, C.; Chardon, P.; Marteau, P.; et al. Reduced diversity of faecal microbiota in Crohn’s disease revealed by a metagenomic approach. Gut 2006, 55, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.J.; Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007, 448, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Nakatsu, G.; Han, J.; Xu, W.; Xiao, X.; Kwong, T.N.Y.; Tsoi, H.; Wu, W.K.K.; et al. Gavage of Fecal Samples from Patients with Colorectal Cancer Promotes Intestinal Carcinogenesis in Germ-Free and Conventional Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Neufeld, K.-A.M. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muegge, B.D.; Kuczynski, J.; Knights, D.; Clemente, J.C.; González, A.; Fontana, L.; Henrissat, B.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science 2011, 332, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke, F.; Luginbühl, P.; Ivanova, N.; Ghassemian, M.; Richardson, T.H.; Stege, J.T.; Cayouette, M.; McHardy, A.C.; Djordjevic, G.; Aboushadi, N.; et al. Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 2007, 450, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Methé, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Pop, M.; Creasy, H.H.; Giglio, M.G.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; et al. A framework for human microbiome research. Nature 2012, 486, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Sonne, S.B.; Xia, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, X.; Long, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. A catalog of the mouse gut metagenome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; Mao, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, W. Microbial Biogeography and Core Microbiota of the Rat Digestive Tract. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; Fitzgerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.L.V.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.M.; Metzker, M.L.; Muzny, D.M.; Sodergren, E.J.; Scherer, S.; Scott, G.; Steffen, D.; Worley, K.C.; Burch, P.E.; et al. Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 2004, 428, 493–521. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The Sequence of the Human Genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterston, R.H.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Birney, E.; Rogers, J.; Abril, J.F.; Agarwal, P.; Agarwala, R.; Ainscough, R.; Alexandersson, M.; An, P.; et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature 2002, 420, 520–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Belzer, C.; Goossens, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Thas, O.; De Weirdt, R.; Kerckhof, F.M.; Van De Wiele, T. Butyrate-producing Clostridium cluster XIVa species specifically colonize mucins in an in vitro gut model. ISME J. 2013, 7, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.O.; Santos, K.A.; Satter, L.D. Protein Degradation in Rumen and Amino Acid Absorption in Small Intestine of Lactating Dairy Cattle Fed Heat-Treated Whole Soybeans. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, C.G.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Camarca, A.; Silano, M.; Losito, I.; De Vincenzi, M.; De Bari, M.D.; Palmisano, F.; Maurano, F.; et al. Highly efficient gluten degradation by lactobacilli and fungal proteases during food processing: New perspectives for celiac disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4499–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadda, S.; Oliver, G.; Vignolo, G. Protein degradation by Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus casei in a sausage model system. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Kotera, M.; Tokimatsu, T.; Nakagawa, Z.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. Modular architecture of metabolic pathways revealed by conserved sequences of reactions. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, B.; Dahlqvist, A.; Lundh, G.; Sjövall, J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J. Clin. Investig. 1957, 36, 1521–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendler, S.J.; Lancaster, C.A.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Duhig, T.; Peat, N.; Burchell, J.; Pemberton, L.; Lalani, E.N.; Wilson, D. Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor-associated polymorphic epithelial mucin. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15286–15293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salyers, A.A.; Vercellotti, J.R.; West, S.E.H.; Wilkins, T.D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Shankar, R.A.; Chzhan, M.; Samouilov, A.; Kuppusamy, P.; Zweier, J.L. Noninvasive measurement of anatomic structure and intraluminal oxygenation in the gastrointestinal tract of living mice with spatial and spectral EPR imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albenberg, L.; Esipova, T.V.; Judge, C.P.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, J.; Laughlin, A.; Grunberg, S.; Baldassano, R.N.; Lewis, J.D.; Li, H.; et al. Correlation between intraluminal oxygen gradient and radial partitioning of intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as vitamin suppliers to their host: A gut microbiota perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, P.; Mehta, P.K. From cofactor to enzymes. The molecular evolution of pyridoxal-5’-phosphate-dependent enzymes. The Chem. Rec. 2001, 1, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.N.; Lv, X.; Wang, K.; Duan, L.P.; Nie, Y.; Wu, X.L. Bacterial community mapping of the mouse gastrointestinal tract. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, G.M.; Friedrichsen, H.J.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Spatial organization of intestinal microbiota in the mouse ascending colon. ISME J. 2011, 5, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Limenitakis, J.P.; Fuhrer, T.; Geuking, M.B.; Lawson, M.A.; Wyss, M.; Brugiroux, S.; Keller, I.; Macpherson, J.A.; Rupp, S.; et al. The outer mucus layer hosts a distinct intestinal microbial niche. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohl, K.D.; Miller, A.W.; Marvin, J.E.; Mackie, R.; Dearing, M.D. Herbivorous rodents (Neotoma spp.) harbour abundant and active foregut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, J.C.; Lynch, M.D.; Senadheera, D.B.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Goldberg, M.B.; Cvitkovitch, D.G.; Croitoru, K.; Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Neufeld, J.D. Bacterial biogeography of the human digestive tract. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E.; et al. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubucker, S.; Segata, N.; Goll, J.; Schubert, A.M.; Izard, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Zucker, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Metabolic Reconstruction for Metagenomic Data and Its Application to the Human Microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Doak, T.G. A Parsimony Approach to Biological Pathway Reconstruction/Inference for Metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Weingart, G.; Tickle, T.L.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Potential Functions of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome Inhabiting the Length of the Rat Digest Tract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051232
Li D, Chen H, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W. Potential Functions of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome Inhabiting the Length of the Rat Digest Tract. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051232
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongyao, Haiqin Chen, Jianxin Zhao, Hao Zhang, and Wei Chen. 2019. "Potential Functions of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome Inhabiting the Length of the Rat Digest Tract" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051232
APA StyleLi, D., Chen, H., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., & Chen, W. (2019). Potential Functions of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome Inhabiting the Length of the Rat Digest Tract. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051232