Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Effects of MgD on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Action
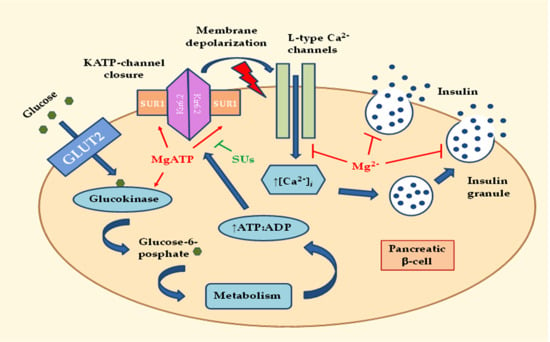
2.1. Effects of MgD on Insulin Secretion
2.2. Effects of MgD on Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity
2.2.1. Effects of MgD-Induced Hyperinsulinemia on Downstream Insulin Signaling
2.2.2. Effects of MgD on Activity of the Insulin-Signaling Kinases
2.3. Effects of MgD on Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation
2.4. Effects of MgD on Key Mg2+-Dependent Enzymes of Carbohydrate and Energy Metabolism
3. Genetic Relationships between MgD and T2D
4. Main Causes and Risk Factors for MgD
4.1. Decreased Intake of Mg2+ from the Food or Drinking Water
4.2. Increased Loss of Mg2+ through the Kidneys
4.3. Impaired Intestinal Absorption of Mg2+
5. Mg2+ Supplementation and Dietary Approaches for Improving Insulin Sensitivity in T2D
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roden, M.; Petersen, K.; Shulman, G. Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes. In Textbook of Diabetes, 5th ed.; Holt, R.I., Cockram, C., Flyvbjerg, A., Goldstein, B.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York City, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 174–186. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Adams, H.; Kubena, K.; Guo, S. Etiology of Metabolic Syndrome and Dietary Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunkhe, V.A.; Veluthakal, R.; Kahn, S.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Novel approaches to restore beta cell function in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Bidasee, K.R.; Adeghate, E.; Howarth, C.F.; D’Souza, A.; Singh, R.B. Left ventricle structural remodelling in prediabetes and overt type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Goto-Kakizaki rat. World Heart J. 2017, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kolte, D.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Khera, S.; Sica, D.A.; Frishman, W.H. Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K.; Halacheva, L. Role of magnesium deficiency in promoting atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial stiffening as risk factors for hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Qian, Q. Genetics of magnesium disorders. Kidney Dis. 2017, 3, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNair, P.; Christensen, M.S.; Christiansen, C.; Madsbad, S.; Transbøl, I.B. Renal hypomagnesaemia in human diabetes mellitus: Its relation to glucose homeostasis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 12, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Vormann, J. Magnesium and Kidney Health-More on the ‘Forgotten Electrolyte’. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 44, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, M.; Elisaf, M.S. Proton pump inhibitor-induced hypomagnesemia: A new challenge. World J. Nephrol. 2012, 1, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.E.; Chubb, S.P.; Davis, W.A.; Davis, T.M. The relationship between hypomagnesemia, metformin therapy and cardiovascular disease complicating type 2 diabetes: The Fremantle Diabetes Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, T. The biochemical function of Mg2+ in insulin secretion, insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and the cardiometabolic syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2012, 1, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, H.; Wanner, C. Magnesium in disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i25–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gommers, L.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J.; de Baaij, J.H. Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes: A vicious circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, V.L.; MacDonald, P.E.; Klip, A. The cell biology of systemic insulin function. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straub, S.G.; Sharp, G.W. Glucose-stimulated signaling pathways in biphasic insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2002, 18, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepton, S. Beta-Cell Function and Failure; InTech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Puljung, M.C.; Vedovato, N. Neonatal diabetes and the KATP channel: From mutation to therapy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolova, H.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal is decreased in normal subjects with relatively low plasma magnesium concentrations. Metabolism 2000, 49, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor: A multi-step process involving structural changes in both the ligand and the receptor. Bioessays 2009, 31, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rodelo, C.; Roura-Guiberna, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: An update. Gaceta Médica de México 2017, 153, 214–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, C.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Hsu, M.J. Exploring the evolutionary relationship of insulin receptor substrate family using computational biology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardilovich, K.; Pankratz, S.L.; Shaw, L.M. Expression and function of the insulin receptor substrate proteins in cancer. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Fluckey, J.D.; Chakraborty, S.; Muthuchamy, M. Hyperglycemia-and hyperinsulinemia-induced insulin resistance causes alterations in cellular bioenergetics and activation of inflammatory signaling in lymphatic muscle. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2744–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanik, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Škrha, J.; Dankner, R.; Zick, Y.; Roth, J. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: Is hyperinsulinemia the cart or the horse? Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S262–S268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boura-Halfon, S.; Zick, Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E581–E591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Bardicef, O.; Bardicef, M.; Resnick, L.M. Altered ionic effects of insulin in hypertension: Role of basal ion levels in determining cellular responsiveness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, F. Mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 508409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, R.J.; He, K. Magnesium physiology and pathogenic mechanisms that contribute to the development of the metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: How are they interlinked? J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hou, S.; Lim, S.T.; Tomar, A.; Yu, H.; Lim, Y.; Hanson, D.A.; Uryu, S.A.; Molina, J.; Mitra, S.K. Tumor necrosis factor-α stimulates focal adhesion kinase activity required for mitogen-activated kinase-associated interleukin 6 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17450–17459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandehloo, H.; Gorgani-Firuzjaee, S.; Panahi, G.; Meshkani, R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 228–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Bermudez-Peña, C.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Severe hypomagnesemia and low-grade inflammation in metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2011, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Ellis, T. Magnesium intake and serum C-reactive protein levels in children. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Woolson, R.F. Dietary magnesium and C-reactive protein levels. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Xun, P.; Liu, K.; Loria, C.; Yokota, K.; Jacobs, D.R.; He, K. Magnesium intake in relation to systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and the incidence of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavani, M.; Ramalho, T.; Koboziev, I.; Monique, L.J.; Jayarathne, S.; Ramalingam, L.; Filgueiras, L.R.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance: Review of mechanisms mediating anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Investig. Med. 2017, 65, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Boparai, R.K.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Studies on the development of an insulin resistant rat model by chronic feeding of low magnesium high sucrose diet. Magnes. Res. 2004, 17, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Voma, C.; Romani, A.M. Role of Magnesium in the Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Homeostasis; InTech: London, UK, 2014; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Silva, B.; Gary, R.K. The GSK3 kinase inhibitor lithium produces unexpected hyperphosphorylation of β-catenin, a GSK3 substrate, in human glioblastoma cells. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio030874. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, M.; Wandosell, F. Deconstructing GSK-3: The fine regulation of its activity. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 2011, 479249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilchova, I.; Klacanova, K.; Tatarkova, Z.; Kaplan, P.; Racay, P. The Involvement of Mg2+ in Regulation of Cellular and Mitochondrial Functions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, L.; Garfinkel, D. Magnesium regulation of the glycolytic pathway and the enzymes involved. Magnesium 1985, 4, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrè, S.; de Baaij, J.H.; Ferreira, P.; Germann, R.; de Klerk, J.B.; Lavrijsen, M.; van Zeeland, F.; Venselaar, H.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; Hoenderop, J.G.; et al. Mutations in PCBD1 cause hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalat, S.; Woolf, A.S.; Johnstone, K.A.; Wirsing, A.; Harries, L.W.; Long, D.A.; Hennekam, R.C.; Ledermann, S.E.; Rees, L.; van’t Hoff, W.; et al. HNF1B mutations associate with hypomagnesemia and renal magnesium wasting. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.K.; Chacko, S.A.; Song, Y.; Cho, M.; Eaton, C.B.; Wu, W.C.H.; Liu, S. Genetic Variations in Magnesium-Related Ion Channels May Affect Diabetes Risk among African American and Hispanic American Women 1–3. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Regulation of magnesium balance: Lessons learned from human genetic disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i15–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altura, B.M.; Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, T.; Shah, N.C. Sudden cardiac death in infants, children and young adults: Possible roles of dietary magnesium intake and generation of platelet-activating factor in coronary arteries. J. Heart Health 2016, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.; Sullivan, K.R. Low Dietary Magnesium Intake and Hypertension. World J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 6, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, P.; Preziosi, P.; Durlach, V.; Valeix, P.; Ribas, L.; Bouzid, D.; Favier, A.; Hercberg, S. Dietary magnesium intake in a French adult population. Magnes. Res. 1997, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.A.; Ismail, N.A. Magnesium: A mineral essential for health yet generally underestimated or even ignored. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 6, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. The high heart health value of drinking-water magnesium. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ridaura, R.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Rosenberg, L.; Krishnan, S.; Palmer, J.R. Dietary calcium and magnesium, major food sources, and risk of type 2 diabetes in US black women. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausalya, P.J.; Amasheh, S.; Günzel, D.; Wurps, H.; Müller, D.; Fromm, M.; Hunziker, W. Disease-associated mutations affect intracellular traffic and paracellular Mg2+ transport function of Claudin-16. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Cohen, R.A. Hypomagnesemia in a patient with an eating disorder. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, A12–A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes: An Update. Int. J. Diabetes Clin. Res. 2015, 2, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Intestinal absorption and factors influencing bioavailability of magnesium—An update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, R.; Wallace, T.C.; Rosanoff, A. Magnesium. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimke, H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Molecular basis of epithelial Ca2+ and Mg2+ transport: Insights from the TRP channel family. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic subjects: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Tamez-Perez, H.E.; González-González, G.E.; Salinas-Martinez, A.M.; Montes-Villarreal, J.; Trevino-Ortiz, J.H.; Rodriguez-Moran, M. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic subjects with insulin resistance. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, K.; Levitan, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Liu, S. Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on glycaemic control in Type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled trials. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, S.A.; Sul, J.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; LeBlanc, J.; You, Y.; Butch, A.; Liu, S. Magnesium supplementation, metabolic and inflammatory markers, and global genomic and proteomic profiling: A randomized, double-blind, controlled, crossover trial in overweight individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Völker, K.; Golf, S.W.; Wadepuhl, M.; Kraus, A. Oral magnesium supplementation reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects—A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solati, M.; Ouspid, E.; Hosseini, S.; Soltani, N.; Keshavarz, M.; Dehghani, M. Oral magnesium supplementation in type II diabetic patients. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2014, 28, 67. [Google Scholar]
- ELDerawi, W.; Naser, I.; Taleb, M.; Abutair, A. The Effects of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Glycemic Response among Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Nutrients 2019, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Schindler, C. Clinically and pharmacologically relevant interactions of antidiabetic drugs. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forouhi, N.G.; Misra, A.; Mohan, V.; Taylor, R.; Yancy, W. Dietary and nutritional approaches for prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Br. Med. J. 2018, 361, k2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.M.; Steck, S.E.; Fung, T.T.; Zhang, J.; Hazlett, L.J.; Han, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Merchant, A.T. Mediterranean diet, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) style diet, and metabolic health in US adults. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.P. DASH eating plan: An eating pattern for diabetes management. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| General: Anxiety, agitation, irritability, headache, loss of appetite, and nausea. |
| Musculature: Muscle spasm and tetany. |
| CNS/Nerves: Nervousness, migraine, depression, poor memory, low stress tolerance, paraesthesia, tremor, and seizures. |
| Metabolism: Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction, IR, decreased glucose tolerance, increased risk of MetS and T2D, dyslipoproteinemia, disorders of vitamin D metabolism, resistance to PTH, and osteoporosis. |
| Cardiovascular system: Arrhythmias, coronary spasm, atherosclerosis, hypertension, arterial stiffness, endothelial dysfunction, and increased platelet aggregation. |
| Electrolytes: Sodium retention, hypokalemia, and hypocalcemia. |
| Study | Mg2+ Intake (mg/day) | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Rodrguez-Moran et al., 2003 [71] | 50 mL MgCl2 solution (50 g MgCl2 per 1000 mL solution) daily for 16 weeks. | Oral supplementation with MgCl2 solution restores serum Mg2+ levels, improving insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in T2D patients with decreased serum Mg2+ levels |
| Guerrero-Romero et al., 2004 [72] | MgCl2 2.5 g daily for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in hypomagnesemic non-diabetic subjects |
| Song et al., 2006 [73] | 360 mg/day for 4–16 weeks | Oral Mg2+ supplementation reduces plasma fasting glucose levels and increases HDL cholesterol in patients with T2D |
| Chacko et al., 2011 [74] | 500 mg/day for 4 weeks | Mg2+ treatment significantly improves fasting C-peptide concentrations and fasting insulin concentrations |
| Mooren et al., 2011 [75] | 365 mg/day for 6 months | Mg2+ supplementation resulted in a significant improvement in fasting plasma glucose and insulin sensitivity in normomagnesemic, overweight non-diabetic subjects |
| Solati et al., 2014 [76] | 300 mg/day for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation has beneficial effects on blood glucose, lipid profile, and blood pressure in patients with T2D |
| ELDerawi et al., 2019 [77] | 250 mg/day for 3 months | Oral Mg2+ supplementation reduces IR and improves glycemic control in T2D patients |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostov, K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
Kostov K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostov, Krasimir. 2019. "Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351
APA StyleKostov, K. (2019). Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061351