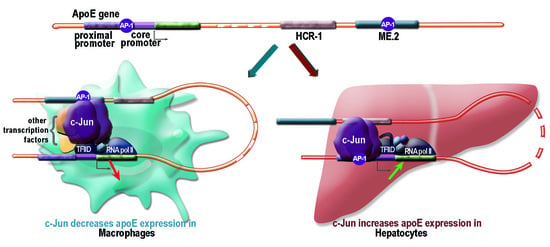
The Opposite Effect of c-Jun Transcription Factor on Apolipoprotein E Gene Regulation in Hepatocytes and Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Apolipoprotein E Expression Was Differentially Modulated by AP-1 Transcription Factors in Hepatocytes and in Macrophages
2.2. Overexpression of c-Jun Transcription Factors in Macrophages Repressed apoE Promoter Activity, a Process Enhanced by the Multienhancer
2.3. In hepatocytes, c-Jun Factors Bound to the apoE Promoter and Upregulated Its Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plasmid Constructions
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Transfection
4.5. Real-Time PCR
4.6. DNA Pull-Down Assays
4.7. Immunoblotting
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
4.9. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| apoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| bp | Base pair |
| ChIP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| DNAP | DNA pull-down assays |
| HCR | Hepatic control region |
| HRP | Horse radish peroxidase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| ME | Multienhancer |
| MLP | Minimal late promoter |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacryl amide gel electrophoresis |
References
- Utermann, G.; Jaeschke, M.; Menzel, J. Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type III: Deficiency of a specific apolipoprotein (apo E-III) in the very-low-density lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1975, 56, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahley, R.W.; Innerarity, T.L.; Rall, S.C., Jr.; Weisgraber, K.H. Plasma lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1277–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Marzolo, M.P.; Bu, G. Differential functions of members of the low density lipoprotein receptor family suggested by their distinct endocytosis rates. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18000–18006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Herz, J.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein E receptors: Normal biology and roles in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockx, M.; Traini, M.; Kritharides, L. Cell-specific production, secretion, and function of apolipoprotein E. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2018, 96, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: Structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72 Pt A, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiselli, G.; Schaefer, E.J.; Gascon, P.; Breser, H.B., Jr. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Science 1981, 214, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Gregg, R.E.; Ghiselli, G.; Forte, T.M.; Ordovas, J.M.; Zech, L.A.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cladaras, C.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.; Zannis, V.I. The molecular basis of a familial apoE deficiency. An acceptor splice site mutation in the third intron of the deficient apoE gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddick, R.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Maeda, N. Atherosclerosis in mice lacking apo E. Evaluation of lesional development and progression. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1994, 14, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellosta, S.; Mahley, R.W.; Sanan, D.A.; Murata, J.; Newland, D.L.; Taylor, J.M.; Pitas, R.E. Macrophage-specific expression of human apolipoprotein E reduces atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic apolipoprotein E-null mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti, I.; Pedrelli, M.; Poti, F.; Stomeo, G.; Gomaraschi, M.; Calabresi, L.; Bernini, F. Macrophage, but not systemic, apolipoprotein E is necessary for macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaisen, B.; Teisberg, P.; Gedde-Dahl, T., Jr. The locus for apolipoprotein E (apoE) is linked to the complement component C3 (C3) locus on chromosome 19 in man. Hum. Genet. 1982, 62, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, Y.K.; Chang, D.J.; Reardon, C.A.; Davies, G.E.; Mahley, R.W.; Taylor, J.M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the human apolipoprotein E gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, C.M.; Walker, D.; Taylor, J.M. Evolutionary duplication of a hepatic control region in the human apolipoprotein E gene locus. Identification of a second region that confers high level and liver-specific expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26278–26281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, C.M.; Taylor, S.; Taylor, J.M. Two hepatic enhancers, HCR.1 and HCR.2, coordinate the liver expression of the entire human apolipoprotein E/C-I/C-IV/C-II gene cluster. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29113–29119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.J.; Allan, C.; Grehan, S.; Tse, E.; Moran, C.; Taylor, J.M. Duplicated downstream enhancers control expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene in macrophages and adipose tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31567–31572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardassis, D.; Gafencu, A.; Zannis, V.I.; Davalos, A. Regulation of HDL genes: Transcriptional, posttranscriptional, and posttranslational. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 224, 113–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafencu, A.V.; Robciuc, M.R.; Fuior, E.; Zannis, V.I.; Kardassis, D.; Simionescu, M. Inflammatory signaling pathways regulating ApoE gene expression in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 21776–21785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavri, S.; Trusca, V.G.; Simionescu, M.; Gafencu, A.V. Metformin reduces the endotoxin-induced down-regulation of apolipoprotein E gene expression in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.; Angel, P.; Schorpp-Kistner, M. AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5965–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamph, W.W.; Wamsley, P.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Verma, I.M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature 1988, 334, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel, P.; Hattori, K.; Smeal, T.; Karin, M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 1988, 55, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Imagawa, M.; Chiu, R.; Stein, B.; Imbra, R.J.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Jonat, C.; Herrlich, P.; Karin, M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 1987, 49, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, R.; Boyle, W.J.; Meek, J.; Smeal, T.; Hunter, T.; Karin, M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell 1988, 54, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, G.H.; Allen, K.E.; Clark, W.; Funk, M.; Gillespie, D.A. Analysis of the interaction between c-Jun and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33429–33435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosatos, K.; Sanoudou, D.; Kypreos, K.E.; Kardassis, D.; Zannis, V.I. A dominant negative form of the transcription factor c-Jun affects genes that have opposing effects on lipid homeostasis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19556–19564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, K.; Frech, K.; Karas, H.; Wingender, E.; Werner, T. MatInd and MatInspector: New fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4878–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.Y.; Harmony, J.A.; Innerarity, T.L.; Mahley, R.W. Immunoregulatory plasma lipoproteins. Role of apoprotein E and apoprotein B. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 11775–11781. [Google Scholar]
- Ishigami, M.; Swertfeger, D.K.; Granholm, N.A.; Hui, D.Y. Apolipoprotein E inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation by suppressing signal transduction and preventing cell entry to G1 phase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20156–20161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baitsch, D.; Bock, H.H.; Engel, T.; Telgmann, R.; Muller-Tidow, C.; Varga, G.; Bot, M.; Herz, J.; Robenek, H.; von Eckardstein, A.; et al. Apolipoprotein E induces antiinflammatory phenotype in macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusca, V.G.; Fuior, E.V.; Fenyo, I.M.; Kardassis, D.; Simionescu, M.; Gafencu, A.V. Differential action of glucocorticoids on apolipoprotein E gene expression in macrophages and hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepniak, E.; Ricci, R.; Eferl, R.; Sumara, G.; Sumara, I.; Rath, M.; Hui, L.; Wagner, E.F. c-Jun/AP-1 controls liver regeneration by repressing p53/p21 and p38 MAPK activity. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beers, A.; Haas, M.J.; Wong, N.C.; Mooradian, A.D. Inhibition of apolipoprotein AI gene expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha: Roles for MEK/ERK and JNK signaling. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 2408–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; Lavrentiadou, S.N.; Zannis, V.I.; Kardassis, D. Transactivation of the ApoCIII promoter by ATF-2 and repression by members of the Jun family. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 14078–14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosialou, I.; Krasagakis, K.; Kardassis, D. Opposite regulation of the human apolipoprotein M gene by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 and Jun transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17259–17269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusca, V.G.; Fuior, E.V.; Florea, I.C.; Kardassis, D.; Simionescu, M.; Gafencu, A.V. Macrophage-specific up-regulation of apolipoprotein E gene expression by STAT1 is achieved via long range genomic interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13891–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thymiakou, E.; Zannis, V.I.; Kardassis, D. Physical and functional interactions between liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor and Sp1 modulate the transcriptional induction of the human ATP binding cassette transporter A1 gene by oxysterols and retinoids. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 11473–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trusca, V.G.; Fuior, E.V.; Kardassis, D.; Simionescu, M.; Gafencu, A.V. The Opposite Effect of c-Jun Transcription Factor on Apolipoprotein E Gene Regulation in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061471
Trusca VG, Fuior EV, Kardassis D, Simionescu M, Gafencu AV. The Opposite Effect of c-Jun Transcription Factor on Apolipoprotein E Gene Regulation in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061471
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrusca, Violeta G., Elena V. Fuior, Dimitris Kardassis, Maya Simionescu, and Anca V. Gafencu. 2019. "The Opposite Effect of c-Jun Transcription Factor on Apolipoprotein E Gene Regulation in Hepatocytes and Macrophages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061471
APA StyleTrusca, V. G., Fuior, E. V., Kardassis, D., Simionescu, M., & Gafencu, A. V. (2019). The Opposite Effect of c-Jun Transcription Factor on Apolipoprotein E Gene Regulation in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061471