Targeting Brain Disease in MPSII: Preclinical Evaluation of IDS-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. NPs Characterization
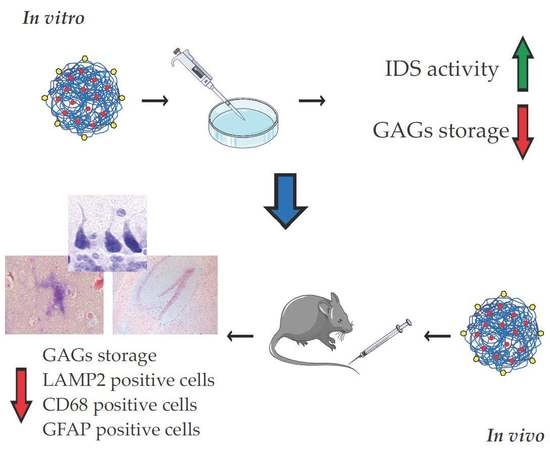
2.2. In Vitro Analysis of u-NPs-IDS Efficacy
2.3. In Vivo Analysis of g7-NPs-IDS Efficacy
2.3.1. Histochemical and Biochemical Analysis of GAG Deposits
2.3.2. Histological and Immunohistochemical Brain Analysis
2.3.3. Evaluation of the Neuroinflammation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Nanoparticles Preparation and Chemico-Physical Characterization
3.3. IDS Content
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Mouse Model
3.6. Brain-Capillary Depletion
3.7. IDS Enzyme Assay
3.8. Measurement of Cells, Tissues, and Urinary GAG Content
3.9. Alcian Blue and Toluidine Staining and Immunohistochemistry
3.10. Microscopy Analysis
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPS | Mucopolysaccharidosis |
| MPSII | Mucopolysaccharidosis type II |
| IDS | Iduronate 2-sulfatase |
| NPs | nanoparticles |
| g7 | Gly-L-Phe-D-Thr-Gly-L-Phe-L-Leu-L-Ser(O-β-D-Glucose)-CONH2 |
| g7-NPs | Brain targeted NPs |
| g7-NPs-IDS | g7-NPs loaded with IDS enzyme |
| LSDs | Lysosomal storage disorders |
| GAG | Glycosaminoglycan |
| ERT | Enzyme replacement therapy |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| PLGA | Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) |
| Ids-ko | Ids knockout |
| Wt | Wild-type |
| UT | Untreated |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| NBT/BCIP | nitro-blue tetrazolium chloride/5-bromo-4-chloro-3′-indolyphosphate p-toluidine salt |
References
- Martin, R.; Beck, M.; Eng, C.; Giugliani, R.; Harmatz, P.; Munoz, V.; Muenzer, J. Recognition and diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter syndrome). Pediatrics 2008, 121, e377–e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomanin, R.; Zanetti, A.; D’Avanzo, F.; Rampazzo, A.; Gasparotto, N.; Parini, R.; Pascarella, A.; Concolino, D.; Procopio, E.; Fiumara, A.; et al. Clinical efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy in paediatric Hunter patients, an independent study of 3.5 years. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenzer, J.; Jones, S.A.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Harmatz, P.; Mendelsohn, N.J.; Guffon, N.; Giugliani, R.; Burton, B.K.; Scarpa, M.; Beck, M.; et al. Ten years of the Hunter Outcome Survey (HOS): Insights, achievements, and lessons learned from a global patient registry. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenzer, J.; Wraith, J.E.; Beck, M.; Giugliani, R.; Harmatz, P.; Eng, C.M.; Vellodi, A.; Martin, R.; Ramaswami, U.; Gucsavas-Calikoglu, M.; et al. A phase II/III clinical study of enzyme replacement therapy with idursulfase in mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter syndrome). Genet. Med. 2006, 8, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-López, J.; Moltó-Abad, M.; Muñoz-Delgado, C.; Morales-Conejo, M.; Ceberio-Hualde, L.; del Toro, M. Efficacy of Idursulfase therapy in patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis type II who initiated enzyme replacement therapy in adult age. A systematic review of the literature. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Franco, J.F.; El Dib, R.; Agarwal, A.; Soares, D.; Milhan, N.V.M.; Albano, L.M.J.; Kim, C.A. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I, II and VI and response to enzyme replacement therapy: Results from a single-center case series study. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2017, 6, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenzer, J.; Giugliani, R.; Scarpa, M.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Jego, V.; Beck, M. Clinical outcomes in idursulfase-treated patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II: 3-year data from the hunter outcome survey (HOS). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpa, M. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. In GeneReviews; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Muenzer, J.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Fan, Z.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Perry, V.; Santra, S.; Solanki, G.A.; Mascelli, M.A.; Pan, L.; Wang, N.; et al. A phase I/II study of intrathecal idursulfase-IT in children with severe mucopolysaccharidosis II. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Ko, A.-R.; Kwak, M.J.; Kim, S.; Sohn, Y.B.; Park, S.W.; Jin, D.-K. Effect of systemic high dose enzyme replacement therapy on the improvement of CNS defects in a mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calias, P.; Papisov, M.; Pan, J.; Savioli, N.; Belov, V.; Huang, Y.; Lotterhand, J.; Alessandrini, M.; Liu, N.; Fischman, A.J.; et al. CNS penetration of intrathecal-lumbar idursulfase in the monkey, dog and mouse: implications for neurological outcomes of lysosomal storage disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Shimizu, H.; Fukuda, T.; Kawagoe, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Shimada, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Ida, H.; Ohashi, T.; Morimoto, H.; et al. Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) procedure for mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II) by intraventricular administration (IVA) in murine MPS II. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, Y.B.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Ko, A.-R.; Nam, M.H.; Jin, D.-K. Improvement of CNS defects via continuous intrathecal enzyme replacement by osmotic pump in mucopolysaccharidosis type II mice. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2013, 161A, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleitz, H.F.; Liao, A.Y.; Cook, J.R.; Rowlston, S.F.; Forte, G.M.; D’Souza, Z.; O’Leary, C.; Holley, R.J.; Bigger, B.W. Brain-targeted stem cell gene therapy corrects mucopolysaccharidosis type II via multiple mechanisms. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laoharawee, K.; Podetz-Pedersen, K.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Evenstar, L.B.; Kitto, K.F.; Nan, Z.; Fairbanks, C.A.; Low, W.C.; Kozarsky, K.F.; McIvor, R.S. Prevention of Neurocognitive Deficiency in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II Mice by Central Nervous System-Directed, AAV9-Mediated Iduronate Sulfatase Gene Transfer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, C.; Katz, N.; Louboutin, J.-P.; Bell, P.; Yu, H.; Nayal, M.; Kozarsky, K.; O’Brien, W.T.; Goode, T.; Wilson, J.M. Delivery of an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector into Cerebrospinal Fluid Attenuates Central Nervous System Disease in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friso, A.; Tomanin, R.; Salvalaio, M.; Scarpa, M. Genistein reduces glycosaminoglycan levels in a mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonoda, H.; Morimoto, H.; Yoden, E.; Koshimura, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Golovina, G.; Takagi, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Minami, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; et al. A Blood-Brain-Barrier-Penetrating Anti-human Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Neuronopathic Mucopolysaccharidosis II. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boado, R.J.; Ka-Wai Hui, E.; Zhiqiang Lu, J.; Pardridge, W.M. Insulin receptor antibody-iduronate 2-sulfatase fusion protein: pharmacokinetics, anti-drug antibody, and safety pharmacology in Rhesus monkeys. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, A.R.; Lee, S.-S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Nam, J.-S.; Chakraborty, C. Advances in nanocarriers enabled brain targeted drug delivery across blood brain barrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Northrup, L.; Bhowmick, T.; Muro, S. Enhanced delivery of alpha-glucosidase for Pompe disease by ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers: comparative performance of a strategy for three distinct lysosomal storage disorders. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, T.; Muhlstein, A.; Yaghootfam, C.; Maksimenko, O.; Shipulo, E.; Gelperina, S.; Kreuter, J.; Gieselmann, V.; Matzner, U. Potential of surfactant-coated nanoparticles to improve brain delivery of arylsulfatase A. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teleanu, D.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.; Volceanov, A.; Teleanu, R. Blood-Brain Delivery Methods Using Nanotechnology. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabrucker, A.M.; Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Pederzoli, F.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Tosi, G. Nanoparticle transport across the blood brain barrier. Tissue barriers 2016, 4, e1153568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvalaio, M.; Rigon, L.; Belletti, D.; D’Avanzo, F.; Pederzoli, F.; Ruozi, B.; Marin, O.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Scarpa, M.; et al. Targeted polymeric nanoparticles for brain delivery of high molecular weight molecules in lysosomal storage disorders. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, G.; Costantino, L.; Rivasi, F.; Ruozi, B.; Leo, E.; Vergoni, A.V.; Tacchi, R.; Bertolini, A.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F. Targeting the central nervous system: in vivo experiments with peptide-derivatized nanoparticles loaded with Loperamide and Rhodamine-123. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, G.; Vilella, A.; Chhabra, R.; Schmeisser, M.J.; Boeckers, T.M.; Ruozi, B.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Zoli, M.; Grabrucker, A.M. Insight on the fate of CNS-targeted nanoparticles. Part II: Intercellular neuronal cell-to-cell transport. J. Control. Release 2014, 177, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Di Paolo, E.; Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Ferrari Bardile, C.; Leoni, V.; Caccia, C.; Brilli, E.; Di Donato, S.; et al. Cholesterol-loaded nanoparticles ameliorate synaptic and cognitive function in Huntington’s disease mice. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1547–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, D.; Grabrucker, A.M.; Pederzoli, F.; Menerath, I.; Vandelli, M.A.; Tosi, G.; Duskey, T.J.; Forni, F.; Ruozi, B. Hybrid nanoparticles as a new technological approach to enhance the delivery of cholesterol into the brain. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, M.; Polito, V.A.; Pepe, S.; Mann, L.; D’Azzo, A.; Auricchio, A.; Ballabio, A.; Cosma, M.P. Correction of Hunter syndrome in the MPSII mouse model by AAV2/8-mediated gene delivery. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Kang, L.; Jennings, J.S.; Moy, S.S.; Perez, A.; Dirosario, J.; McCarty, D.M.; Muenzer, J. Significantly increased lifespan and improved behavioral performances by rAAV gene delivery in adult mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB mice. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, A.R.; Pan, J.; Lamsa, J.C.; Muenzer, J. The characterization of a murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter syndrome). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friso, A.; Tomanin, R.; Alba, S.; Gasparotto, N.; Puicher, E.P.; Fusco, M.; Hortelano, G.; Muenzer, J.; Marin, O.; Zacchello, F.; et al. Reduction of GAG storage in MPS II mouse model following implantation of encapsulated recombinant myoblasts. J. Gene Med. 2005, 7, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triguero, D.; Buciak, J.; Pardridge, W.M. Capillary depletion method for quantification of blood-brain barrier transport of circulating peptides and plasma proteins. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voznyi, Y.V.; Keulemans, J.L.; van Diggelen, O.P. A fluorimetric enzyme assay for the diagnosis of MPS II (Hunter disease). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2001, 24, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friso, A.; Tomanin, R.; Zanetti, A.; Mennuni, C.; Calvaruso, F.; La Monica, N.; Marin, O.; Zacchello, F.; Scarpa, M. Gene therapy of Hunter syndrome: evaluation of the efficiency of muscle electro gene transfer for the production and release of recombinant iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornsson, S. Simultaneous preparation and quantitation of proteoglycans by precipitation with alcian blue. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 210, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, J.G.; Wevers, R.A.; Liebrand-van Sambeek, R. Measuring urinary glycosaminoglycans in the presence of protein: an improved screening procedure for mucopolysaccharidoses based on dimethylmethylene blue. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 803–807. [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge, W.M. The blood-brain barrier: bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, V.A.; Abbondante, S.; Polishchuk, R.S.; Nusco, E.; Salvia, R.; Cosma, M.P. Correction of CNS defects in the MPSII mouse model via systemic enzyme replacement therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4871–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvalaio, M.; D’Avanzo, F.; Rigon, L.; Zanetti, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Valle, G.; Scarpa, M.; Tomanin, R. Brain RNA-seq profiling of the mucopolysaccharidosis type II mouse model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | Z-Average a nm | PDI a | ζ-pot a mV | mg of IDS/100 mg NPs | EE% b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| u-NPs-IDS | 205 (12) | 0.190 (0.02) | −36 (3) | 3.1 (0.3) | 31% |
| g7-NPs-IDS | 203 (11) | 0.214 (0.03) | −34 (5) | 1.5 (0.9) | 15% |
| g7-NPs | 197 (12) | 0.182 (0.01) | −32 (4) | / | / |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rigon, L.; Salvalaio, M.; Pederzoli, F.; Legnini, E.; Duskey, J.T.; D’Avanzo, F.; De Filippis, C.; Ruozi, B.; Marin, O.; Vandelli, M.A.; et al. Targeting Brain Disease in MPSII: Preclinical Evaluation of IDS-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082014
Rigon L, Salvalaio M, Pederzoli F, Legnini E, Duskey JT, D’Avanzo F, De Filippis C, Ruozi B, Marin O, Vandelli MA, et al. Targeting Brain Disease in MPSII: Preclinical Evaluation of IDS-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(8):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082014
Chicago/Turabian StyleRigon, Laura, Marika Salvalaio, Francesca Pederzoli, Elisa Legnini, Jason Thomas Duskey, Francesca D’Avanzo, Concetta De Filippis, Barbara Ruozi, Oriano Marin, Maria Angela Vandelli, and et al. 2019. "Targeting Brain Disease in MPSII: Preclinical Evaluation of IDS-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 8: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082014
APA StyleRigon, L., Salvalaio, M., Pederzoli, F., Legnini, E., Duskey, J. T., D’Avanzo, F., De Filippis, C., Ruozi, B., Marin, O., Vandelli, M. A., Ottonelli, I., Scarpa, M., Tosi, G., & Tomanin, R. (2019). Targeting Brain Disease in MPSII: Preclinical Evaluation of IDS-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(8), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20082014