Silybin-Induced Apoptosis Occurs in Parallel to the Increase of Ceramides Synthesis and miRNAs Secretion in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Silybin Induced Cell Cycle Block and Apoptosis in HCC Cell Lines by Nitric Oxide Production
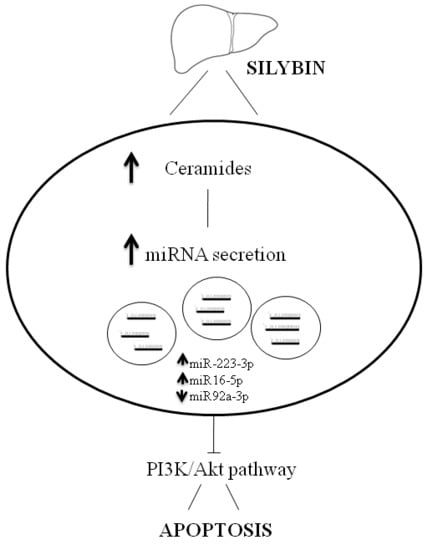
2.2. Effects of Silybin on Lipid Metabolism
2.3. Profiling of miRNAs Secreted into the Medium Following Treatment with Silybin
2.4. Silybin Increases the Citotoxic Effect of Sorafenib by Downregulating miR-92a
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Species (TBARS) Levels
4.3. Nitrite Levels
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Analysis
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. RNA Purification
4.8. miRNA Profiling and Real-Time PCR Analyses
4.9. Extraction of Lipid and MALDI-TOF MS Analysis
4.10. Drug Combination Studies
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic fatty liver steatohepatitis |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| IC50 | inhibitory concentration 50 |
| PI | Propidium Iodide |
References
- Loguercio, C.; Festi, D. Silybin and the liver: From basic research to clinical practice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2288–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiuso, P.; Scognamiglio, I.; Murolo, M.; Ferranti, P.; De Simone, C.; Rizzo, M.R.; Tuccillo, C.; Caraglia, M.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A. Serum oxidative stress markers and lipidomic profile to detect NASH patients responsive to an antioxidant treatment: A pilot study. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 169216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.L.; Kanwal, F.; El-Serag, H.B. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk for hepatocellular cancer, based on systematic review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1342–1359.e2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Fontana, R.J.; Su, G.L.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Emick, D.M.; Lok, A.S. NAFLD may be a common underlying liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starley, B.Q.; Calcagno, C.J.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: A weighty connection. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.M.; Pu, C.W.; Hou, Y.H.; Chen, Z.; Alanazy, M.; Hebbard, L. Non alcoholicsteatohepatitis a precursor for hepatocellular carcinoma development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16464–16473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, F.X.; Ribes, J.; Díaz, M.; Cléries, R. Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Teng, C.F.; Wu, H.C.; Tsai, H.W.; Chuang, H.C.; Tsai, T.F. Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-A in ground glass hepatocytes and its implication in hepatitis B virus hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forner, A.; Hessheimer, A.J.; Real, I.M.; Bruix, J. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006, 60, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Chan, P.; Epstein, R.; Poon, R.T.P. Management of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of targeted therapy. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Grisham, J.W. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Lee, J.T.; Chang, F.; Bertrand, F.E. Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2006, 46, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiuso, P.; Potenza, N.; Lombardi, A.; Ferrandino, I.; Monaco, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Vanacore, D.; Mosca, N.; Castiello, F.; Porto, S.; et al. MicroRNA-423-5p Promotes Autophagy in Cancer Cells and Is Increased in Serum From Hepatocarcinoma Patients Treated With Sorafenib. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 17, 4:e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deep, G.; Agarwal, R. Antimetastatic efficacy of silibinin: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential against cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J. Effects of nitric oxide on the biological behavior of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exper. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geller, J.I.; Szekely-Szucs, K.; Petak, I.; Doyle, B.; Houghton, J.A. p21 (Cip1) is a critical mediator of the cytotoxic action of thymidylate synthase inhibitors in colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6296–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitatani, K.; Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Hannun, Y.A. The sphingolipid salvage pathway in ceramide metabolism and signaling. Cell Signal. 2007, 20, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, K.; Gao, J.; Yu, F.; Chen, L.; Li, S. Expression and significance of PTEN and miR-92 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.K. Silymarin and skin cancer prevention: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, K.; Agarwal, R. Multitargeted therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaid, M.; Singh, T.; Prasad, R.; Katiyar, S.K. Silymarin inhibits melanoma cell growth both in vitro and in vivo by targeting cell cycle regulators, angiogenic biomarkers and induction of apoptosis. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis-Searles, P.R.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kim, N.C.; Graf, T.N.; Oberlies, N.H.; Wani, M.C.; Wall, M.E.; Agarwal, R.; Kroll, D.J. Milk thistle and prostate cancer: Differential effects of pure flavonolignans from Silybummarianum on antiproliferative end points in human prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4448–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Singh, R.P.; Ramasamy, K.; Raina, K.; Redente, E.F.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Malkinson, A.M.; Agarwal, R. Growth inhibition and regression of lung tumors by silibinin: Modulation of angiogenesis by macrophage-associated cytokines and nuclear factor-kappaB and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, S.C.; Chiou, H.L.; Chen, P.N.; Yang, S.F.; Hsieh, Y.S. Silibinin inhibits the invasion of human lung cancer cells via decreased productions of urokinase-plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol. Carcinog. 2004, 40, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.H.; Hur, S.M.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, W.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Yang, J.H. Silibinin prevents TPA-induced MMP-9 expression by down-regulation of COX-2 in human breast cancer cells. J. Ethno. Pharmacol. 2009, 126, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, M.G.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.W.; Hur, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; Nam, S.J. Silibinin suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer cells through inhibition of the MAPK pathway. Molecules 2009, 14, 4300–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Andreone, P.; Brisc, C.; Brisc, M.C.; Bugianesi, E.; Chiaramonte, M.; Cursaro, C.; Danila, M. Silybin combined with phosphatidylcholine and vitamin E in patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jason, R.; Hickok; Douglas, D. Thomas Nitric Oxide and Cancer Therapy: The Emperor has NO Clothes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 381–391. [Google Scholar]
- Muntane, J.; la Mata, M.D. Nitric oxide and cancer. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Morales, A.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Glycosphingolipids and cell death: One aim, many ways. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Tao, Y.; Shan, L.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Qian, Z.; Cai, F.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y. The Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; McNabola, A.; Wilkie, D. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway; inhibits tumor angiogenesis; and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kwon, C.H.; Woo, J.S.; Kim, Y.K. Silibinin inhibits glioma cell proliferation via Ca2+/ROS/MAPK-dependent mechanism in vitro and glioma tumor growth in vivo. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; ChirivaInternati, M.; Wachtel, M.S.; Frezza, E.E. Silibinin restores paclitaxel sensitivity to paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Yang, H.; Cui, T.; Pan, P.; Kabir, N.; Chen, D.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Combined treatment with sorafenib and silibinin synergistically targets both HCC cells and cancer stem cells by enhanced inhibition of the phosphorylation of STAT3/ERK/AKT. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 5, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, C.; Ferranti, P.; Picariello, G.; Scognamiglio, I.; Dicitore, A.; Addeo, F.; Chianese, L.; Stiuso, P. Peptides from water buffalo cheese whey induced senescence cell death via ceramide secretion in human colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, M.; Giuberti, G.; Zappavigna, S.; Perdonà, S.; Facchini, G.; Sperlongano, P.; Porto, S.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Buonerba, C.; Abbruzzese, A.; et al. Chondroitinsulphateenhances the antitumoractivity of gemcitabine and mitomycin-C in bladdercancercells with differentmechanisms. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| m/z | Assignment | Ctr | Sil |
|---|---|---|---|
| 545.56 ± 1 | Cer(t20:0/26:0) | + | + |
| 551.49 ± 1 | Cer(m18:1(4E)/18:0) | + | − |
| 599.92 ± 1 | Cer(t18:0/18:0(2OH)) | − | + |
| 567.63 ± 1 | Cer(d18:0/18:0) | + | + |
| 637.8 ± 1 | Cer(d14:1(4E)/26:0(2OH)) | − | + |
| 659.84 ± 1 | PE-Cer(d14:2(4E,6E)/20:0) | − | + |
| 675.76 ± 1 | PE-Cer(d16:1(4E)/19:0) | − | + |
| 703.9 ± C16 | Sphingomyelin | + | + |
| 725.84 ± 1 | Cer(t20:0/26:0) | + | + |
| 732.77 ± 1 | GlcCer(t18:1(8Z)/16:0(2OH[S])) | − | − |
| 760.98 ± 1 | GlcCer(t18:1(8Z)/18:0 | − | + |
| 782.76 ± 1 | PI-Cer(d20:0/14:0) | + | + |
| 788.77 ± 1 | C22 Sphingomyelin | − | − |
| Drug | IC50 μM (Drug Alone) | IC50 μM (Drug Combination) | CI50 | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorafenib | 5±0.02 | 1.25±0.003 | 0.4 | Strong synergism |
| Silybin | 68±0.03 | 51±0.01 |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fold Regulation | P Value | |
| Sil vs. ctr | −2.55 | 0.036 * |
| Sor vs. ctr | n.d | n.d |
| Sil/Sor vs. ctr | −5.55 | 0.002 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zappavigna, S.; Vanacore, D.; Lama, S.; Potenza, N.; Russo, A.; Ferranti, P.; Dallio, M.; Federico, A.; Loguercio, C.; Sperlongano, P.; et al. Silybin-Induced Apoptosis Occurs in Parallel to the Increase of Ceramides Synthesis and miRNAs Secretion in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092190
Zappavigna S, Vanacore D, Lama S, Potenza N, Russo A, Ferranti P, Dallio M, Federico A, Loguercio C, Sperlongano P, et al. Silybin-Induced Apoptosis Occurs in Parallel to the Increase of Ceramides Synthesis and miRNAs Secretion in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZappavigna, Silvia, Daniela Vanacore, Stefania Lama, Nicoletta Potenza, Aniello Russo, Pasquale Ferranti, Marcello Dallio, Alessandro Federico, Carmelina Loguercio, Pasquale Sperlongano, and et al. 2019. "Silybin-Induced Apoptosis Occurs in Parallel to the Increase of Ceramides Synthesis and miRNAs Secretion in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092190
APA StyleZappavigna, S., Vanacore, D., Lama, S., Potenza, N., Russo, A., Ferranti, P., Dallio, M., Federico, A., Loguercio, C., Sperlongano, P., Caraglia, M., & Stiuso, P. (2019). Silybin-Induced Apoptosis Occurs in Parallel to the Increase of Ceramides Synthesis and miRNAs Secretion in Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092190