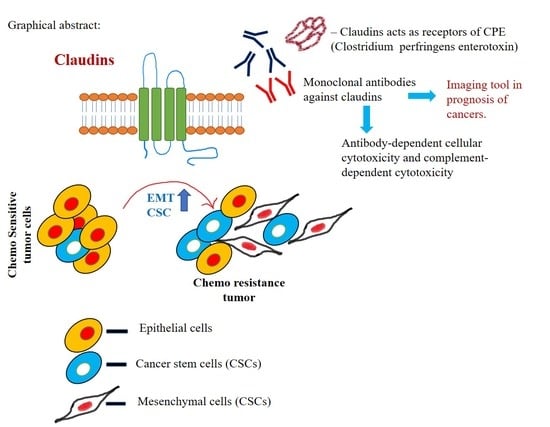
Role of Claudin Proteins in Regulating Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance-Potential Implication in Disease Prognosis and Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Tight Junctions
1.2. Claudins
2. Claudins as Oncogenic Signal Transducer
3. Claudins and Stem Cells
4. Claudins in Chemoresistance
5. Claudins in Prognosis
6. Claudins as Therapeutic Agents
7. Claudins as a Visualization Tool
8. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farquhar, M.G.; Palade, G.E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 375–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneeberger, E.E.; Lynch, R.D. The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C1213–C1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.M. Tight junctions/adherens junctions: basic structure and function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Mariscal, L.; Betanzos, A.; Nava, P.; Jaramillo, B.E. Tight junction proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2003, 81, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, B.R.; Siliciano, J.D.; Mooseker, M.S.; Goodenough, D.A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 103, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Citi, S.; Sabanay, H.; Jakes, R.; Geiger, B.; Kendrick-Jones, J. Cingulin, a new peripheral component of tight junctions. Nature 1988, 333, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Itoh, M.; Hirase, T.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, F.D.; Lopez, L.N.; Lin, H.W.; Davies, C.; Azevedo, R.B.; Gow, A.; Kachar, B. Distinct subdomain organization and molecular composition of a tight junction with adherens junction features. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunzel, D.; Yu, A.S. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelow, S.; Yu, A.S. Claudins and paracellular transport: an update. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2007, 16, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.; Protze, J.; Piontek, J. Assembly and function of claudins: Structure-function relationships based on homology models and crystal structures. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M. Occludin and claudins in tight-junction strands: leading or supporting players? Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M. Overcoming barriers in the study of tight junction functions: from occludin to claudin. Genes Cells 1998, 3, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Sasaki, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Tsukita, S. A single gene product, claudin-1 or -2, reconstitutes tight junction strands and recruits occludin in fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal-Nag, M.; Morin, P.J. The claudins. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelow, S.; Ahlstrom, R.; Yu, A.S. Biology of claudins. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F867–F876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunzel, D.; Fromm, M. Claudins and other tight junction proteins. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1819–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soini, Y. Expression of claudins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in various types of tumours. Histopathology 2005, 46, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlingmann, B.; Molina, S.A.; Koval, M. Claudins: Gatekeepers of lung epithelial function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 42, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amasheh, S.; Meiri, N.; Gitter, A.H.; Schoneberg, T.; Mankertz, J.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Mumm, J.B.; Herbst, R.; Kolbeck, R.; Wang, Y. IL-22 Increases Permeability of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions by Enhancing Claudin-2 Expression. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3316–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, R.; D’Souza, T.; Morin, P.J. Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in ovarian epithelial cells enhances invasion and is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7378–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morin, P.J. Claudin proteins in human cancer: promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9603–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kage, H.; Flodby, P.; Zhou, B.; Borok, Z. Dichotomous roles of claudins as tumor promoters or suppressors: Lessons from knockout mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4663–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohmoto, T.; Masuda, K.; Shoda, K.; Takahashi, R.; Ujiro, S.; Tange, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Otsuji, E.; Imoto, I. Claudin-6 is a single prognostic marker and functions as a tumor-promoting gene in a subgroup of intestinal type gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafang, L.; Qiong, W.; Yue, R.; Xiaoming, X.; Lina, Y.; Mingzi, Z.; Ting, Z.; Yulin, L.; Chengshi, Q. Role of Estrogen Receptor-alpha in the Regulation of Claudin-6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Breast Cancer 2011, 14, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rendon-Huerta, E.; Teresa, F.; Teresa, G.M.; Xochitl, G.S.; Georgina, A.F.; Veronica, Z.Z.; Montano, L.F. Distribution and expression pattern of claudins 6, 7, and 9 in diffuse- and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinomas. J. Gastrointest Cancer 2010, 41, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikari, A.; Watanabe, R.; Sato, T.; Taga, S.; Shimobaba, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Sugatani, J. Nuclear distribution of claudin-2 increases cell proliferation in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.C.; Pan, S.H.; Yang, S.C.; Yu, S.L.; Che, T.F.; Lin, C.W.; Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.C.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; et al. Claudin-1 is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ding, L.; Hong, H.; Hoggard, J.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y.H. Claudin-7 inhibits human lung cancer cell migration and invasion through ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, X.; Lin, X.; Alvarez, E.; Manorek, G.; Howell, S.B. Tight junction proteins claudin-3 and claudin-4 control tumor growth and metastases. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Ding, Y.H.; Li, W.J.; Ding, L. Claudin-7 gene knockout causes destruction of intestinal structure and animal death in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nubel, T.; Preobraschenski, J.; Tuncay, H.; Weiss, T.; Kuhn, S.; Ladwein, M.; Langbein, L.; Zoller, M. Claudin-7 regulates EpCAM-mediated functions in tumor progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimobaba, S.; Taga, S.; Akizuki, R.; Hichino, A.; Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Watanabe, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sugatani, J.; et al. Claudin-18 inhibits cell proliferation and motility mediated by inhibition of phosphorylation of PDK1 and Akt in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Muller, D.; Lele, S.M.; Washington, M.K.; Batra, S.K.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6592–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Yue, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Huo, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhen, H.; Yang, Y.; Cao, B. Claudin-3 Inhibits Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Invasion via Suppression of the Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, D.A.; Galimanis, C.E.; Webb, P.G.; Spillman, M.A.; Behbakht, K.; Neville, M.C.; Baumgartner, H.K. Claudin-4 activity in ovarian tumor cell apoptosis resistance and migration. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.; Quan, C. Tight junction protein claudin-6 inhibits growth and induces the apoptosis of cervical carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z.; Quan, C. Expression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 is associated with tight junction protein claudin-6 in cervical carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5535–5541. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B.; Deane, N.G.; No, Y.; Shiou, S.R.; Schmidt, C.; Neff, J.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.B.; Sharma, A.; Smith, J.J.; Krishnan, M.; Chen, X.; Eschrich, S.; Washington, M.K.; Yeatman, T.J.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Dhawan, P. Claudin-1 up-regulates the repressor ZEB-1 to inhibit E-cadherin expression in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 2140–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhat, A.A.; Pope, J.L.; Smith, J.J.; Ahmad, R.; Chen, X.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4570–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhawan, P.; Ahmad, R.; Chaturvedi, R.; Smith, J.J.; Midha, R.; Mittal, M.K.; Krishnan, M.; Chen, X.; Eschrich, S.; Yeatman, T.J.; et al. Claudin-2 expression increases tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells: role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3234–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, A.A.; Zelinski, T.; Xie, J.; Cooper, S.; Penner, C.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Identification of Claudin 1 Transcript Variants in Human Invasive Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oku, N.; Sasabe, E.; Ueta, E.; Yamamoto, T.; Osaki, T. Tight junction protein claudin-1 enhances the invasive activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by promoting cleavage of laminin-5 gamma2 chain via matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and membrane-type MMP-1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5251–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darido, C.; Buchert, M.; Pannequin, J.; Bastide, P.; Zalzali, H.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Bourgaux, J.F.; Garambois, V.; Jay, P.; Blache, P.; et al. Defective claudin-7 regulation by Tcf-4 and Sox-9 disrupts the polarity and increases the tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4258–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, T.L.; Ito, K.; Ko, T.K.; Liu, Q.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Yeoh, K.G.; Fukamachi, H.; Ito, Y. Claudin-1 has tumor suppressive activity and is a direct target of RUNX3 in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 255–265 e251-253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, R.; Mori, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, Z.; Olaru, A.V.; Hamilton, J.P.; David, S.; Selaru, F.M.; Yang, J.; Abraham, J.M.; et al. Silencing of claudin-11 is associated with increased invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. PLoS One 2009, 4, e8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Li, T. CLDN2 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells via down-regulating the afadin/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Tokumasu, R.; Kimura, H.; Tsukita, S. Role of claudin species-specific dynamics in reconstitution and remodeling of the zonula occludens. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Kubo, A.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. A peculiar internalization of claudins, tight junction-specific adhesion molecules, during the intercellular movement of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Honda, H.; Pazin, M.J.; D’Souza, T.; Ji, H.; Morin, P.J. Regulation of the CLDN3 gene in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, H.M.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, J.E.; Gye, M.C.; Erkin, O.C.; Koh, S.S.; Choi, Y.L.; et al. Claudin-4 overexpression is associated with epigenetic derepression in gastric carcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Cello, F.; Cope, L.; Li, H.; Jeschke, J.; Wang, W.; Baylin, S.B.; Zahnow, C.A. Methylation of the claudin 1 promoter is associated with loss of expression in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, M.; Singh, A.B.; Smith, J.J.; Sharma, A.; Chen, X.; Eschrich, S.; Yeatman, T.J.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Dhawan, P. HDAC inhibitors regulate claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cells through modulation of mRNA stability. Oncogene 2010, 29, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Estrada, O.M.; Culleres, A.; Soriano, F.X.; Peinado, H.; Bolos, V.; Martinez, F.O.; Reina, M.; Cano, A.; Fabre, M.; Vilaro, S. The transcription factors Slug and Snail act as repressors of Claudin-1 expression in epithelial cells. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, A.A.; Sharma, A.; Pope, J.; Krishnan, M.; Washington, M.K.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Caudal homeobox protein Cdx-2 cooperates with Wnt pathway to regulate claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, H.; Pazin, M.J.; Ji, H.; Wernyj, R.P.; Morin, P.J. Crucial roles of Sp1 and epigenetic modifications in the regulation of the CLDN4 promoter in ovarian cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21433–21444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shigetomi, K.; Ikenouchi, J. Regulation of the epithelial barrier by post-translational modifications of tight junction membrane proteins. J. Biochem. 2018, 163, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Claudin interactions in and out of the tight junction. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e25247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajagopal, N.; Irudayanathan, F.J.; Nangia, S. Palmitoylation of Claudin-5 Proteins Influences Their Lipid Domain Affinity and Tight Junction Assembly at the Blood-Brain Barrier Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.M.; Khan, I.B.; Hussain, M.; Idress, M.; Lu, J.; Tong, Y. Role of post translational modifications and novel crosstalk between phosphorylation and O-beta-GlcNAc modifications in human claudin-1, -3 and -4. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, A.D.; Fiori, J.L.; Camilli, T.C.; Leotlela, P.D.; O’Connell, M.P.; Frank, B.P.; Subaran, S.; Indig, F.E.; Taub, D.D.; Weeraratna, A.T. PKC and PKA phosphorylation affect the subcellular localization of claudin-1 in melanoma cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, T.; Indig, F.E.; Morin, P.J. Phosphorylation of claudin-4 by PKCepsilon regulates tight junction barrier function in ovarian cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3364–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, T.; Agarwal, R.; Morin, P.J. Phosphorylation of claudin-3 at threonine 192 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates tight junction barrier function in ovarian cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26233–26240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akizuki, R.; Shimobaba, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A. Claudin-5, -7, and -18 suppress proliferation mediated by inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt in human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ramirez, S.H.; Sato, S.; Kiyota, T.; Cerny, R.L.; Kaibuchi, K.; Persidsky, Y.; Ikezu, T. Phosphorylation of claudin-5 and occludin by rho kinase in brain endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, W.; Shabbiri, K.; Ijaz, B.; Asad, S.; Sarwar, M.T.; Gull, S.; Kausar, H.; Fouzia, K.; Shahid, I.; Hassan, S. Claudin-1 required for HCV virus entry has high potential for phosphorylation and O-glycosylation. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiler, S.; Mu, W.; Zoller, M.; Thuma, F. The importance of claudin-7 palmitoylation on membrane subdomain localization and metastasis-promoting activities. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biteau, B.; Hochmuth, C.E.; Jasper, H. Maintaining tissue homeostasis: dynamic control of somatic stem cell activity. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romito, A.; Cobellis, G. Pluripotent Stem Cells: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9451492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duinsbergen, D.; Salvatori, D.; Eriksson, M.; Mikkers, H. Tumors originating from induced pluripotent stem cells and methods for their prevention. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1176, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, U.; Nudel, N.; Benvenisty, N. Immunologic and chemical targeting of the tight-junction protein Claudin-6 eliminates tumorigenic human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ichikawa-Tomikawa, N.; Satohisa, S.; Akashi, Y.; Kanai, R.; Saito, T.; Sawada, N.; Chiba, H. The tight-junction protein claudin-6 induces epithelial differentiation from mouse F9 and embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Gong, Z.; Yang, G.; et al. Claudin 6: a novel surface marker for characterizing mouse pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turksen, K.; Troy, T.C. Claudin-6: a novel tight junction molecule is developmentally regulated in mouse embryonic epithelium. Dev. Dyn. 2001, 222, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdelyi-Belle, B.; Torok, G.; Apati, A.; Sarkadi, B.; Schaff, Z.; Kiss, A.; Homolya, L. Expression of Tight Junction Components in Hepatocyte-Like Cells Differentiated from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2015, 21, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, L.N.; Chow, E.K. Mechanisms of chemoresistance in cancer stem cells. Clin. Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nusse, R. Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miwa, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S.; Niikawa, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Furukawa, Y. Involvement of claudin-1 in the beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in human colorectal cancers. Oncol. Res. 2001, 12, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowrikumar, S.; Ahmad, R.; Uppada, S.B.; Washington, M.K.; Shi, C.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Upregulated claudin-1 expression promotes colitis-associated cancer by promoting beta-catenin phosphorylation and activation in Notch/p-AKT-dependent manner. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5321–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, A.; Parker, J.S.; Karginova, O.; Fan, C.; Livasy, C.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; He, X.; Perou, C.M. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Yin, W.; Ma, H.; Elshoura, I.; Wang, L. Targeting claudin-3 suppresses stem cell-like phenotype in nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer Manag. 2019, 8, LMT04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Flodby, P.; Luo, J.; Castillo, D.R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.X.; McConnell, A.; Varghese, B.; Li, G.; Chimge, N.O.; et al. Claudin-18-mediated YAP activity regulates lung stem and progenitor cell homeostasis and tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paquet-Fifield, S.; Koh, S.L.; Cheng, L.; Beyit, L.M.; Shembrey, C.; Molck, C.; Behrenbruch, C.; Papin, M.; Gironella, M.; Guelfi, S.; et al. Tight Junction Protein Claudin-2 Promotes Self-Renewal of Human Colorectal Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.C. The molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59950–59964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, T.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, L. Claudin-7 downregulation induces metastasis and invasion in colorectal cancer via the promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaries, S.; Siegel, P.M. The role of claudins in cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Wei, M.; Dong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, L.; et al. Claudin-3 expression increases the malignant potential of lung adenocarcinoma cells: role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23033–23047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Han, Z.G.; Shan, L. Low claudin-6 expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landers, K.A.; Samaratunga, H.; Teng, L.; Buck, M.; Burger, M.J.; Scells, B.; Lavin, M.F.; Gardiner, R.A. Identification of claudin-4 as a marker highly overexpressed in both primary and metastatic prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.L.; Changchien, T.T.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, C.M. Claudin-4 expression in gastric cancer cells enhances the invasion and is associated with the increased level of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 expression. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, S.; Terashima, M.; Satoh, J.; Soeta, N.; Saze, Z.; Kashimura, S.; Ohsuka, F.; Hoshino, Y.; Kogure, M.; Gotoh, M. Expression of tight-junction-associated proteins in human gastric cancer: downregulation of claudin-4 correlates with tumor aggressiveness and survival. Gastric Cancer 2009, 12, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, J.; Filipovic, A.; Giamas, G. Claudin-1 as a promoter of EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4871–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Moodie, A.; Blanchard, A.A.; Leygue, E.; Myal, Y. Claudin 1 in Breast Cancer: New Insights. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1960–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lin, D.; Xie, Y.; Dong, B.; Dang, Q.; Quan, C. CLDN6 enhances chemoresistance to ADM via AF-6/ERKs pathway in TNBC cell line MDAMB231. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 443, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Lin, X.; Manorek, G.; Howell, S.B. Claudin-3 and claudin-4 regulate sensitivity to cisplatin by controlling expression of the copper and cisplatin influx transporter CTR1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Sumi, T.; Zhi, X.; Yasui, T.; Honda, K.; Ishiko, O. Claudin-4: a potential therapeutic target in chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Jing, W. CLDN1 Increases Drug Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Activating Autophagy via Up-Regulation of ULK1 Phosphorylation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akizuki, R.; Maruhashi, R.; Eguchi, H.; Kitabatake, K.; Tsukimoto, M.; Furuta, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A. Decrease in paracellular permeability and chemosensitivity to doxorubicin by claudin-1 in spheroid culture models of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, R.; Heiler, S.; Mu, W.; Buchler, M.W.; Zoller, M.; Thuma, F. Claudin-7 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2046–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoggard, J.; Fan, J.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Sutton, L.; Chen, Y.H. Claudin-7 increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin through the upregulation of caspase pathway in human NCI-H522 lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lechpammer, M.; Resnick, M.B.; Sabo, E.; Yakirevich, E.; Greaves, W.O.; Sciandra, K.T.; Tavares, R.; Noble, L.C.; DeLellis, R.A.; Wang, L.J. The diagnostic and prognostic utility of claudin expression in renal cell neoplasms. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osunkoya, A.O.; Cohen, C.; Lawson, D.; Picken, M.M.; Amin, M.B.; Young, A.N. Claudin-7 and claudin-8: immunohistochemical markers for the differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Meng, X. Differences in the expression profiles of claudin proteins in human gastric carcinoma compared with nonneoplastic mucosa. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danzinger, S.; Tan, Y.Y.; Rudas, M.; Kastner, M.T.; Weingartshofer, S.; Muhr, D.; Singer, C.F.; kConFab, I. Differential Claudin 3 and EGFR Expression Predicts BRCA1 Mutation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2018, 36, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, M.; Alis, H.; Bas, K.; Karabulut, S.; Afsar, C.U.; Oguz, H.; Gunaldi, M.; Akarsu, C.; Kones, O.; Aykan, N.F. Clinical significance of serum claudin-1 and claudin-7 levels in patients with colorectal cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabatier, R.; Finetti, P.; Guille, A.; Adelaide, J.; Chaffanet, M.; Viens, P.; Birnbaum, D.; Bertucci, F. Claudin-low breast cancers: clinical, pathological, molecular and prognostic characterization. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nissinen, L.; Siljamaki, E.; Riihila, P.; Piipponen, M.; Farshchian, M.; Kivisaari, A.; Kallajoki, M.; Raiko, L.; Peltonen, J.; Peltonen, S.; et al. Expression of claudin-11 by tumor cells in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is dependent on the activity of p38delta. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, K.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Hallett, R.M.; Wu, Y.; Hassell, J.; Pond, G.R.; Levine, M.; Whelan, T.; Bane, A.L. Claudin-Low Breast Cancer; Clinical & Pathological Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhaya, P.; Barhoi, D.; Giri, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Giri, S. Joint detection of claudin-1 and junctional adhesion molecule-A as a therapeutic target in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 18117–18127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, C.H.; Steeg, P.S.; Figg, W.D. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuptrine, C.W.; Surana, R.; Weiner, L.M. Monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mailly, L.; Xiao, F.; Lupberger, J.; Wilson, G.K.; Aubert, P.; Duong, F.H.T.; Calabrese, D.; Leboeuf, C.; Fofana, I.; Thumann, C.; et al. Clearance of persistent hepatitis C virus infection in humanized mice using a claudin-1-targeting monoclonal antibody. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukasawa, M.; Nagase, S.; Shirasago, Y.; Iida, M.; Yamashita, M.; Endo, K.; Yagi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Wakita, T.; Hanada, K.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies against extracellular domains of claudin-1 block hepatitis C virus infection in a mouse model. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4866–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fofana, I.; Krieger, S.E.; Grunert, F.; Glauben, S.; Xiao, F.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Soulier, E.; Royer, C.; Thumann, C.; Mee, C.J.; et al. Monoclonal anti-claudin 1 antibodies prevent hepatitis C virus infection of primary human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 953–964, 964. e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Tawar, R.G.; Mailly, L.; Thumann, C.; Heydmann, L.; Durand, S.C.; Xiao, F.; Robinet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Zeisel, M.B.; et al. Humanisation of a claudin-1-specific monoclonal antibody for clinical prevention and cure of HCV infection without escape. Gut 2018, 67, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offner, S.; Hekele, A.; Teichmann, U.; Weinberger, S.; Gross, S.; Kufer, P.; Itin, C.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kohleisen, B. Epithelial tight junction proteins as potential antibody targets for pancarcinoma therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2005, 54, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, C.; Cocco, E.; Bignotti, E.; Moratto, D.; Bugatti, A.; Todeschini, P.; Bandiera, E.; Tassi, R.; Zanotti, L.; Pecorelli, S.; et al. Evaluation of a novel human IgG1 anti-claudin3 antibody that specifically recognizes its aberrantly localized antigen in ovarian cancer cells and that is suitable for selective drug delivery. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34617–34628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherradi, S.; Ayrolles-Torro, A.; Vezzo-Vie, N.; Gueguinou, N.; Denis, V.; Combes, E.; Boissiere, F.; Busson, M.; Canterel-Thouennon, L.; Mollevi, C.; et al. Antibody targeting of claudin-1 as a potential colorectal cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara-Tani, R.; Sasaki, T.; Luo, Y.; Goto, K.; Kawahara, I.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Kishi, S.; Mori, S.; Ohmori, H.; Kondoh, M.; et al. Anti-claudin-4 extracellular domain antibody enhances the antitumoral effects of chemotherapeutic and antibody drugs in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 37367–37378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin, U.; Schuler, M.; Richly, H.; Bauer, S.; Krilova, A.; Dechow, T.; Jerling, M.; Utsch, M.; Rohde, C.; Dhaene, K.; et al. A phase I dose-escalation study of IMAB362 (Zolbetuximab) in patients with advanced gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 100, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Toom, S.; Huang, Y. Anti-claudin 18.2 antibody as new targeted therapy for advanced gastric cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. The interaction of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin with receptor claudins. Anaerobe 2016, 41, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanov, V.; Whyard, T.C.; Waltzer, W.C.; Gabig, T.G. A claudin 3 and claudin 4-targeted Clostridium perfringens protoxin is selectively cytotoxic to PSA-producing prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 351, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal-Nag, M.; Battis, M.; Santin, A.D.; Morin, P.J. Claudin-6: a novel receptor for CPE-mediated cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Vali, M.; Korz, D.; Gabig, T.G.; Weitzman, S.A.; Argani, P.; Sukumar, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin elicits rapid and specific cytolysis of breast carcinoma cells mediated through tight junction proteins claudin 3 and 4. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cocco, E.; Shapiro, E.M.; Gasparrini, S.; Lopez, S.; Schwab, C.L.; Bellone, S.; Bortolomai, I.; Sumi, N.J.; Bonazzoli, E.; Nicoletti, R.; et al. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin C-terminal domain labeled to fluorescent dyes for in vivo visualization of micrometastatic chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahle, J.; Menzel, L.; Niesler, N.; Kobelt, D.; Aumann, J.; Rivera, M.; Walther, W. Rapid eradication of colon carcinoma by Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin suicidal gene therapy. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahle, J.; Aumann, J.; Kobelt, D.; Walther, W. Oncoleaking: Use of the Pore-Forming Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin (CPE) for Suicide Gene Therapy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1317, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, A.J.; Stroud, R.M. Claudin-9 structures reveal mechanism for toxin-induced gut barrier breakdown. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17817–17824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, A.; Leskau, M.; Schlingmann-Molina, B.L.; Hohmeier, S.C.; Alnajjar, S.; Murua Escobar, H.; Ngezahayo, A. Functionalization of gold-nanoparticles by the Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin C-terminus for tumor cell ablation using the gold nanoparticle-mediated laser perforation technique. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, A.; Lehrich, T.; Kalies, S.; Heisterkamp, A.; Ngezahayo, A. Parameters for Optoperforation-Induced Killing of Cancer Cells Using Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized With the C-terminal Fragment of Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres, J.B.; Knight, J.C.; Mosley, M.J.; Kersemans, V.; Koustoulidou, S.; Allen, D.; Kinchesh, P.; Smart, S.; Cornelissen, B. Imaging of Claudin-4 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using a Radiolabelled Anti-Claudin-4 Monoclonal Antibody. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwada, M.; Chihara, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Fujiwara, R.; Sasaki, T.; Fujii, K.; Ohmori, H.; Fujimoto, K.; et al. Pro-chemotherapeutic effects of antibody against extracellular domain of claudin-4 in bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabinsky, E.F.; Joshi, B.P.; Pant, A.; Zhou, J.; Duan, X.; Smith, A.; Kuick, R.; Fan, S.; Nusrat, A.; Owens, S.R.; et al. Overexpressed Claudin-1 Can Be Visualized Endoscopically in Colonic Adenomas In Vivo. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollandsworth, H.M.; Lwin, T.M.; Amirfakhri, S.; Filemoni, F.; Batra, S.K.; Hoffman, R.M.; Dhawan, P.; Bouvet, M. Anti-Claudin-1 Conjugated to a Near-Infrared Fluorophore Targets Colon Cancer in PDOX Mouse Models. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 242, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; von Hahn, T.; Tscherne, D.M.; Syder, A.J.; Panis, M.; Wolk, B.; Hatziioannou, T.; McKeating, J.A.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Rice, C.M. Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for a late step in entry. Nature 2007, 446, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, C.; Comper, F.; Bandiera, E.; Ravaggi, A.; Bignotti, E.; Tassi, R.A.; Pecorelli, S.; Santin, A.D. Development and characterization of a human single-chain antibody fragment against claudin-3: A novel therapeutic target in ovarian and uterine carcinomas. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 201, 70 e71–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, T.; Kondoh, M.; Kyuno, D.; Ito, T.; Kimura, Y.; Imamura, M.; Kohno, T.; Konno, T.; Furuhata, T.; Sawada, N.; et al. Claudin-4 binder C-CPE 194 enhances effects of anticancer agents on pancreatic cancer cell lines via a MAPK pathway. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, A.; Yuan, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, F.; Hou, P.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Ding, M.; Deng, H. Claudin-6 and claudin-9 function as additional coreceptors for hepatitis C virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12465–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Oshima, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Yamanaka, S.; Nishii, T.; Arai, H.; Inui, K.; Kaneko, T.; Nozawa, A.; Woo, T.; et al. Reduced expression of claudin-7 is associated with poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2010, 1, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.J.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, J.J.; Choi, H.Y.; Park, Y.A.; Jeon, H.K.; Sung, C.O.; Song, S.Y.; Lee, Y.Y.; Choi, C.H.; et al. High claudin-7 expression is associated with a poor response to platinum-based chemotherapy in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, M.; Iida, M.; Nagase, S.; Suzuki, H.; Watari, A.; Tada, M.; Okada, Y.; Doi, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Yagi, K.; et al. Creation of a Claudin-2 Binder and Its Tight Junction-Modulating Activity in a Human Intestinal Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 363, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

 - inhibition of claudin-7. The arrows indicate the upregulation and higher enrichment of the mentioned signaling molecules, colour is respective of each claudin.
- inhibition of claudin-7. The arrows indicate the upregulation and higher enrichment of the mentioned signaling molecules, colour is respective of each claudin.
 - inhibition of claudin-7. The arrows indicate the upregulation and higher enrichment of the mentioned signaling molecules, colour is respective of each claudin.
- inhibition of claudin-7. The arrows indicate the upregulation and higher enrichment of the mentioned signaling molecules, colour is respective of each claudin.

| Claudins Subtype | Cancer Type | Proto-Oncogene | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claudin-6 | Gastric cancer | Tumour promotor | [25] |
| Claudin-1 | Colon cancer | Tumour promotor | [40,45] |
| Claudin-3 | Ovarian cancer | Tumour promotor | [22] |
| Claudin-4 | Ovarian cancer | Tumour promotor | [22] |
| Claudin-6 | Breast cancer, Gastric cancer | Tumour promotor | [26,27] |
| Claudin-7 | Colon cancer | Tumour promotor | [46] |
| Claudin-2 | Lung cancer | Tumour promotor | [28] |
| Claudin-1 | Gastric cancer | Tumour suppressor | [47] |
| Claudin-1 | Lung cancer | Tumour suppressor | [29] |
| Claudin-3 | Ovarian cancer | Tumour suppressor | [31] |
| Claudin-4 | Ovarian cancer | Tumour suppressor | [31] |
| Claudin-7 | Lung cancer | Tumour suppressor | [30] |
| Claudin-11 | Gastric cancer | Tumour suppressor | [48] |
| Claudin-2 | Osteosarcoma | Tumour suppressor | [49] |
| Claudin Subtype | Stem Cell Related Functions | References |
|---|---|---|
| Claudin-6 | Early marker in embryonic stem cell.High expression in undifferentiated human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). Trigger epithelial morphogenesis in mouse stem cells. | [73,74] |
| Claudin-1 and 2 | Known to regulate the β-Catenin-TCF/LEF signaling pathway to regulate CSC. | [81] |
| Claudin low subtype in breast cancer | Enriched in stem cells and more EMT. | [83] |
| Claudin-3 | Regulation on cancer stemness and chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). | [84] |
| Claudin-18 | Triggers lung enlargement and parenchymal expansion by restrictions on stem/progenitor cell proliferation. | [85] |
| Claudin-2 | Enrich ALDHHigh cancer stem-like cells in heterogeneous colorectal cancer cell populations. | [86] |
| Claudins Subtype | Disease Type | Therapeutic Agent | Clinical Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Claudin-1 | Hepatitis C virus infection | Residues within the first extracellular loop. | Hepatitis C virus co-receptor. | [139] |
| Humanization of a claudin-1-specific monoclonal antibody. | Clinical prevention and cure of Hepatitis C virus(HCV) infection. | [118] | ||
| Claudin-6 | Ovarian cancer | Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (CPE) cytotoxicity. | CPE-mediated cytotoxicity in Ovarian cancer. | [127] |
| Claudin-3 | Ovarian cancer uterine carcinomas | Human anti-claudin-3 IgG1 antibody. | Candidate for antibody-drug conjugate therapeutic applications. | [120,140] |
| Claudin-1 | Colon cancer | Human claudin-1 (6F6 mAb). |
Suppressed survival, growth, and migration of claudin-1 positive cells. Suppressed tumor growth and liver metastasis formation. | [121] |
| Claudin-4 | Colorectal cancer | Anti-claudin-4 extracellular domain antibody. | Enhancer of anti-tumoral effects of chemotherapeutic agents. | [122] |
| Claudin-4 | Pancreatic Cancer (PDAC) | Indium-111 tagged anti-claudin-4 monoclonal antibody. | X-ray computed tomography sided detection of PDAC. | [135] |
| Claudin-18.2 | Gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer | Chimeric monoclonal antibody that binds to claudin-18.2 (NCT03504397) | Cell death through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. | [123] |
| Claudin-4 | Pancreatic cancer | Claudin-4 binder C-CPE 194 | Enhances Tazeffects of anticancer agents via a MAPK pathway. | [141] |
| Claudin-3 and 4 | Prostate cancer | Claudin-3 and claudin-4 targeted Clostridium perfringens protoxin | Selectively cytotoxic to PSA-producing prostate cancer cells. | [126] |
| Claudin-1 | Colon cancer | Peptide RTSPSSR, specific to claudin-1 against the extracellular loop of claudin-1. | Specific to human adenomas, hyperplastic polyps, and sessile serrated adenomas. | [137] |
| Claudin-1 | Colon cancer | Claudin-1 antibody conjugated with LI-COR IR800DyeCW | Near-infrared antibody-based imaging for visualization of colorectal tumors. | [138] |
| Claudin-9 | Hepatitis C virus infection | Residues N38 and V45 in the first extracellular loop (EL1) of claudin-9 are responsible for HCV entry. Also found in PBMS (peripheral blood mononuclear cell) contributing to extrahepatic HCV infection. | It can be implicated in the development of drugs to block HCV entry into the liver and peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMS). | [142] |
| Claudin-11 | Gastric Cancer | Hyper-methylation of claudin-11 promotor region leads to significant downregulation in gastric cancer. | Identification of the associated signaling cascades might lead to novel approaches in diagnosis and therapy for gastric cancer. | [48] |
| Claudin-7 | Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Reduced expression—Poor outcome Claudin-7 low NSCLC—Poor survival. Claudin-7 high NSCLC—High Survival. | Biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in patients with NSCLC. | [143] |
| Claudin-7 | Epithelial Ovarian cancer | Claudin-7 transcripts were significantly enhanced in epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients. Silencing claudin-7 displayed enhanced sensitivity to Cisplatin treatment. | Independent prognostic factor and a key protein in regulating response to platinum-based chemotherapy in the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). | [144] |
| Claudin-2 | Irritable bowel disease (IBD) | Anti-claudin-2 mAb 1A2 | Prevent cis- and trans-interactions of claudin-2, attenuating the formation of leaky tight junction (TJ) seals. | [145] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gowrikumar, S.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Role of Claudin Proteins in Regulating Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance-Potential Implication in Disease Prognosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010053
Gowrikumar S, Singh AB, Dhawan P. Role of Claudin Proteins in Regulating Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance-Potential Implication in Disease Prognosis and Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleGowrikumar, Saiprasad, Amar B. Singh, and Punita Dhawan. 2020. "Role of Claudin Proteins in Regulating Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance-Potential Implication in Disease Prognosis and Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010053
APA StyleGowrikumar, S., Singh, A. B., & Dhawan, P. (2020). Role of Claudin Proteins in Regulating Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance-Potential Implication in Disease Prognosis and Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010053