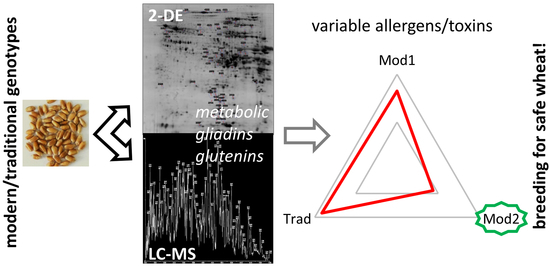
Comprehensive Comparison of Clinically Relevant Grain Proteins in Modern and Traditional Bread Wheat Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Separation of Grain Proteins by Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
2.2. Label-Free Quantification Complemented the Comparison Between Bread Wheat Cultivars
2.3. Effective Workflow to Overcome the Analytical Challenges of Grain Proteome Profiling
2.4. Both Gluten and Non-Gluten Proteins Contain Allergenic or Toxic Motifs
2.5. Modern Breeding, Traditional Landraces, and Biotechnology for Safe Wheat
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material and Protein Extraction
3.2. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
3.3. In-Gel Digestion and Filter-Aided Sample Preparation
3.4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Protein Identification from Gel Spots
3.5. Relative Quantification by Direct Mass Spectrometry and Bioinformatics
3.6. Data Availability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMW | high molecular weight |
| LMW | low molecular weight |
| UHPLC | ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography |
| EQB | equilibration buffer |
| FASP | filter-aided sample preparation |
| NA | not available |
| PTM | post-translational modification |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| 2-DE | two-dimensional gel electrophoresis |
References
- Kuźniar, A.; Włodarczyk, K.; Grządziel, J.; Goraj, W.; Gałązka, A.; Wolińska, A. Culture-independent analysis of an endophytic core microbiome in two species of wheat: Triticum aestivum L. (cv. ‘Hondia’) and the first report of microbiota in Triticum spelta L. (cv. ‘Rokosz’). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43, 126025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G.; Lafiandra, D. Genetics of Wheat Gluten Proteins. In Advances in Genetics; Hall, J.C., Dunlap, J.C., Friedmann, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; ISBN 00652660.
- Payne, P.I. Genetics of wheat storage proteins and the effect of allelic variation on bread-making quality. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 1987, 38, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Xia, X.; Yan, Y.; Appels, R.; Mahmood, T.; He, Z. Wheat seed storage proteins: Advances in molecular genetics, diversity and breeding applications. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Beom, H.-R.; Altenbach, S.B.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Kang, C.-S.; Yoon, U.-H.; Gupta, R.; Kim, S.-T.; Ahn, S.-N.; et al. Comprehensive identification of LMW-GS genes and their protein products in a common wheat variety. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, A.; Békés, F.; Wrigley, C.W. Wheat Proteins. In Applied Food Protein Chemistry; Ustunol, Z., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 303, p. 219. ISBN 9781118860588. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Humanes, J.; Pistón, F.; Rosell, C.M.; Barro, F. Significant down-regulation of γ-gliadins has minor effect on gluten and starch properties of bread wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shewry, P.R.; Tatham, A.S. Improving wheat to remove coeliac epitopes but retain functionality. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.-W.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yue, G.; Liu, X.; Qin, H.; Zhang, K.; Dong, L.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of complex wheat gliadins, the dominant carriers of celiac disease epitopes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Khatkar, B.S. Relationship of gliadin and glutenin proteins with dough rheology, flour pasting and bread making performance of wheat varieties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, E.; Bernardo, A.; Soler, C.; Jouve, N. Relationship between common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) gluten proteins and dough rheological properties: Gluten proteins and rheological properties in wheat. Euphytica 2005, 143, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Sanders, D.S.; Grünewald, R.A.; Woodroofe, N.; Boscolo, S.; Aeschlimann, D. Gluten sensitivity: From gut to brain. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapone, A.; Bai, J.C.; Ciacci, C.; Dolinsek, J.; Green, P.H.R.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Rostami, K.; Sanders, D.S.; Schumann, M.; et al. Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: Consensus on new nomenclature and classification. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scherf, K.A.; Koehler, P.; Wieser, H. Gluten and wheat sensitivities—An overview. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarca, A.; Anderson, R.P.; Mamone, G.; Fierro, O.; Facchiano, A.; Costantini, S.; Zanzi, D.; Sidney, J.; Auricchio, S.; Sette, A.; et al. Intestinal T cell responses to gluten peptides are largely heterogeneous: Implications for a peptide-based therapy in celiac disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4158–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamone, G.; Picariello, G.; Addeo, F.; Ferranti, P. Proteomic analysis in allergy and intolerance to wheat products. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2011, 8, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebener, S.; Tanaka, C.K.; Uhde, M.; Zone, J.J.; Vensel, W.H.; Kasarda, D.D.; Beams, L.; Briani, C.; Green, P.H.R.; Altenbach, S.B.; et al. Specific nongluten proteins of wheat are novel target antigens in celiac disease humoral response. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junker, Y.; Zeissig, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Barisani, D.; Wieser, H.; Leffler, D.A.; Zevallos, V.; Libermann, T.A.; Dillon, S.; Freitag, T.L.; et al. Wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors drive intestinal inflammation via activation of toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2395–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenbach, S.B.; Tanaka, C.K.; Allen, P.V. Quantitative proteomic analysis of wheat grain proteins reveals differential effects of silencing of omega-5 gliadin genes in transgenic lines. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistón, F.; Gil-Humanes, J.; Rodríguez-Quijano, M.; Barro, F. Down-regulating γ-gliadins in bread wheat leads to non-specific increases in other gluten proteins and has no major effect on dough gluten strength. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spaenij-Dekking, L.; Kooy-Winkelaar, Y.; Van Veelen, P.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Jonker, H.; Van Soest, L.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Bosch, D.; Gilissen, L.J.W.J.; Koning, F. Natural variation in toxicity of wheat: Potential for selection of nontoxic varieties for celiac disease patients. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Nunes, F.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Branlard, G.; Igrejas, G. New insights into wheat toxicity: Breeding did not seem to contribute to a prevalence of potential celiac disease’s immunostimulatory epitopes. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malalgoda, M.; Meinhardt, S.W.; Simsek, S. Detection and quantitation of immunogenic epitopes related to celiac disease in historical and modern hard red spring wheat cultivars. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewry, P.R. Do ancient types of wheat have health benefits compared with modern bread wheat? J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompa, M.; Giuliani, M.M.; Palermo, C.; Agriesti, F.; Centonze, D.; Flagella, Z. Comparative analysis of gluten proteins in three durum wheat cultivars by a proteomic approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2606–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahata, E.; Maruyama-Funatsuki, W.; Nishio, Z.; Tabiki, T.; Takata, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanida, M.; Saruyama, H. Wheat cultivar-specific proteins in grain revealed by 2-DE and their application to cultivar identification of flour. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Molina, M.D.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S.; Masci, S.; Barro, F. Comparative proteomic analysis of two transgenic low-gliadin wheat lines and non-transgenic wheat control. J. Proteom. 2017, 165, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vensel, W.H.; Dupont, F.M.; Sloane, S.; Altenbach, S.B. Effect of cleavage enzyme, search algorithm and decoy database on mass spectrometric identification of wheat gluten proteins. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Esteso, M.J.; Nørgaard, J.; Brohée, M.; Haraszi, R.; Maquet, A.; O’Connor, G. Defining the wheat gluten peptide fingerprint via a discovery and targeted proteomics approach. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, K.A.; Poms, R.E. Recent developments in analytical methods for tracing gluten. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Teshima, R. Proteomics-based allergen analysis in plants. J. Proteom. 2013, 93, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollier, V.; Denery-Papini, S.; Brossard, C.; Tessier, D. Meta-analysis of IgE-binding allergen epitopes. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 153, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokooji, T.; Kurihara, S.; Murakami, T.; Chinuki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Morita, E.; Harada, S.; Ishii, K.; Hiragun, M.; Hide, M.; et al. Characterization of causative allergens for wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis sensitized with hydrolyzed wheat proteins in facial soap. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reig-Otero, Y.; Mañes, J.; Manyes, L. Amylase-trypsin inhibitors in wheat and other cereals as potential activators of the effects of nonceliac gluten sensitivity. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameri, H.; Denery-Papini, S.; Pietri, M.; Tranquet, O.; Larré, C.; Drouet, M.; Paty, E.; Jonathan, A.-M.; Beaudouin, E.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.-A.; et al. Molecular and immunological characterization of wheat Serpin (Tri a 33). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Li, M.; Yu, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Q.; Li, K.; et al. Transformation of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with avenin-like b gene improves flour mixing properties. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrachina, M.N.; Sueiro, A.M.; Casas, V.; Izquierdo, I.; Hermida-Nogueira, L.; Guitián, E.; Casanueva, F.F.; Abián, J.; Carrascal, M.; Pardo, M.; et al. A combination of proteomic approaches identifies a panel of circulating extracellular vesicle proteins related to the risk of suffering cardiovascular disease in obese patients. Proteomics 2019, 19, 1800248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, M.; Nunes-Miranda, J.D.; Branlard, G.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Igrejas, G. One hundred years of grain omics: Identifying the glutens that feed the world. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4702–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, I.; Lagrain, B.; Brunnbauer, M.; Delcour, J.A.; Koehler, P. Improved identification of wheat gluten proteins through alkylation of cysteine residues and peptide-based mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uvackova, L.; Skultety, L.; Bekesova, S.; McClain, S.; Hajduch, M. The MSE-proteomic analysis of gliadins and glutenins in wheat grain identifies and quantifies proteins associated with celiac disease and baker’s asthma. J. Proteom. 2013, 93, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromilow, S.; Gethings, L.A.; Langridge, J.I.; Shewry, P.R.; Buckley, M.; Bromley, M.J.; Mills, E.N.C. Comprehensive proteomic profiling of wheat gluten using a combination of data-independent and data-dependent acquisition. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Gao, L.-Y.; Li, N.; Li, X.-H.; Ma, W.-J.; Appels, R.; Yan, Y.-M. Proteomic analysis of albumins and globulins from wheat variety Chinese spring and its fine deletion line 3BS-8. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13398–13413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gell, G.; Kovács, K.; Veres, G.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Juhász, A. Characterization of globulin storage proteins of a low prolamin cereal species in relation to celiac disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.; Beom, H.-R.; Jang, Y.-R.; Altenbach, S.B.; Vensel, W.H.; Simon-Buss, A.; Lim, S.-H.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, J.-Y. Proteomic profiling and epitope analysis of the complex α-, γ-, and ω-gliadin families in a commercial bread wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akagawa, M.; Handoyo, T.; Ishii, T.; Kumazawa, S.; Morita, N.; Suyama, K. Proteomic analysis of wheat flour allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6863–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Rasi, C.; Palazzo, P.; Scala, E. Allergen databases: Current status and perspectives. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009, 9, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, A.; Haraszi, R.; Maulis, C. ProPepper: A curated database for identification and analysis of peptide and immune-responsive epitope composition of cereal grain protein families. Database 2015, 2015, bav100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromilow, S.; Gethings, L.A.; Buckley, M.; Bromley, M.; Shewry, P.R.; Langridge, J.I.; Mills, E.N.C. A curated gluten protein sequence database to support development of proteomics methods for determination of gluten in gluten-free foods. J. Proteom. 2017, 163, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Den Broeck, H.C.; Cordewener, J.H.G.; Nessen, M.A.; America, A.H.P.; van der Meer, I.M. Label free targeted detection and quantification of celiac disease immunogenic epitopes by mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1391, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malalgoda, M.; Ohm, J.-B.; Meinhardt, S.; Simsek, S. Association between gluten protein composition and breadmaking quality characteristics in historical and modern spring wheat. Cereal Chem. 2018, 95, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.C.; Akar, T.; Baresel, J.P.; Bebeli, P.J.; Bettencourt, E.; Bladenopoulos, K.V.; Czembor, J.H.; Fasoula, D.A.; Katsiotis, A.; Koutis, K.; et al. Cereal landraces for sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregová, E.; Hermuth, J.; Kraic, J.; Dotlačil, L. Protein heterogeneity in European wheat landraces and obsolete cultivars. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1999, 46, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, R.; Masci, S.; Rogniaux, H.; Tranquet, O.; Brossard, C.; Lafiandra, D.; Moneret-Vautrin, D.A.; Denery-Papini, S.; Larré, C. Assessment of the allergenicity of soluble fractions from GM and commercial genotypes of wheats. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-León, S.; Gil-Humanes, J.; Ozuna, C.V.; Giménez, M.J.; Sousa, C.; Voytas, D.F.; Barro, F. Low-gluten, nontransgenic wheat engineered with CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Рибалка, О.; Мoргун, Б.; Пoчинoк, В. Сучасні дoслідження якoсті зерна пшениці у світі: Генетика, біoтехнoлoгія та харчoва цінність запасних білків. Физиoлoгия и биoхимия культурных растений 2012, 44, 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Metakovsky, E.; Melnik, V.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Upelniek, V.; Carrillo, J.M. A catalog of gliadin alleles: Polymorphism of 20th-century common wheat germplasm. Crop J. 2018, 6, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, F.M.; Vensel, W.H.; Tanaka, C.K.; Hurkman, W.J.; Altenbach, S.B. Deciphering the complexities of the wheat flour proteome using quantitative two-dimensional electrophoresis, three proteases and tandem mass spectrometry. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Distler, U.; Kuharev, J.; Navarro, P.; Tenzer, S. Label-free quantification in ion mobility-enhanced data-independent acquisition proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, S.; Šubr, Z.; Kováč, A.; Fialová, I.; Beke, G.; Danchenko, M. Cucumber mosaic virus resistance: Comparative proteomics of contrasting Cucumis sativus cultivars after long-term infection. J. Proteom. 2020, 214, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spot # | UniProt Accession | Protein Name (Genetic Locus) | Function | Allergen or Toxin | Protein Group | Panna/Sotnytsia | Panna/Ukrainka | Sotnytsia/Ukrainka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4126 | B2Y2Q6 | LMW-B2 glutenin (Glu-B3-2) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 1.07 | 2.51 | 2.34 |
| 1066 | P08488 | HMW-12 glutenin (HMW-GS DY) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | −2.12 | 1.19 | 2.53 |
| 4114 | P08488 | HMW-12 glutenin (HMW-GS DY) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | −2.37 | −2.82 | −1.19 |
| 390 | P08489 | HMW-PW212 glutenin | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | −11.01 | 1.08 | 11.84 |
| 4045 | P10388 | HMW-DX5 glutenin (Glu-1D-1D) | Nutrient reservoir and starch binding activity | √ | Glutenin | 2.65 | 1.09 | −2.43 |
| 4332 | P10388 | HMW-DX5 glutenin (Glu-1D-1D) | Nutrient reservoir and starch binding activity | √ | Glutenin | 3.00 | 1.34 | −2.24 |
| 4345 | P10388 | HMW-DX5 glutenin (Glu-1D-1D) | Nutrient reservoir and starch binding activity | √ | Glutenin | 2.47 | −1.18 | −2.91 |
| 4351 | P10388 | HMW-DX5 glutenin (Glu-1D-1D) | Nutrient reservoir and starch binding activity | √ | Glutenin | 4.14 | 1.09 | −3.79 |
| 1896 | A1EHE7 | γ-gliadin D3 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −1.32 | 2.61 | 3.45 |
| 1961 | A1EHE7 | γ-gliadin D3 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −1.36 | −3.97 | −2.92 |
| 3866 | I0IT62 | α/β-gliadin | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 1.40 | −3.72 | −5.20 |
| 1649 | M9TG60 | γ-gliadin A1 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 1.24 | −4.40 | −5.47 |
| 1656 | M9TG60 | γ-gliadin A1 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 1.37 | −4.09 | −5.59 |
| 4220 | M9TG60 | γ-gliadin A1 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −1.04 | −3.67 | −3.53 |
| 1669 | P04722 | α/β-gliadin AII | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −1.32 | 2.57 | 3.37 |
| 4403 | P04722 | α/β-gliadin AII | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −1.03 | 2.49 | 2.57 |
| 1803 | P21292 | γ-gliadin | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 5.59 | 4.47 | −1.25 |
| 4179 | P21292 | γ-gliadin | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 3.09 | 2.78 | −1.11 |
| 2078 | Q94G92 | γ-gliadin D4 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −2.60 | 1.35 | 3.50 |
| 2161 | Q94G92 | γ-gliadin D4 (Gli1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | −3.40 | 1.11 | 3.78 |
| 4491 | A0A1D5T3T7 | Similar to δ-gliadin D1, obsolete | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | 1.18 | −4.30 | −5.08 | |
| 2645 | A0A3B5YPZ7 | Similar to avenin-like protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | 4.00 | 1.04 | −3.86 | |
| 2689 | A0A3B5YPZ7 | Similar to avenin-like protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | 6.03 | −1.14 | −6.86 | |
| 4169 | A0A3B5YPZ7 | Similar to avenin-like protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | −3.16 | 1.07 | 3.37 | |
| 4481 | A0A3B5YPZ7 | Similar to avenin-like protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | 3.90 | −1.03 | −4.03 | |
| 4482 | A0A3B5YPZ7 | Similar to avenin-like protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | 4.33 | −1.10 | −4.77 | |
| 1581 | Q41593 | Serpin-Z1A (WZCI) | Serine protease inhibitor, extracellular | √ | Metabolic | 1.88 | −1.57 | −2.95 |
| 3607 | Q43691 | Trypsin/α-amylase inhibitor CMX2 | Serine protease inhibitor, secreted | √ | Metabolic | 2.63 | 2.70 | 1.03 |
| 4404 | A0A1D5US94 | Methyltransferase | Protein dimerization activity | Metabolic | −1.87 | 1.61 | 3.00 | |
| 1084 | A0A1D5YFA7 | Similar to β-amylase, obsolete | Hydrolysis of (1->4)-α-D-glucosidic linkages in polysaccharides | Metabolic | −2.55 | 1.82 | 4.64 | |
| 2386 | A0A1D5ZTV0 | Similar to serpin-N3.2, obsolete | Serine protease inhibitor, extracellular | Metabolic | −2.38 | 1.24 | 2.94 | |
| 1025 | A0A1D6A827 | Dehydrin, obsolete | Stress response | Metabolic | −1.21 | −7.08 | −5.86 | |
| 969 | A0A1D6D1Q3 | Pyrophosphate—fructose 6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase subunit β (PFP-β) | Glycolysis, cytoplasm | Metabolic | 2.32 | −1.33 | −3.10 | |
| 2335 | A0A1D6RH21 | Similar to dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), obsolete | Glutathione S-transferase domain | Metabolic | −5.31 | −1.14 | 4.65 | |
| 1169 | A0A1D6S518 | UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase | Biosynthesis of saccharides, cytoplasm | Metabolic | −1.72 | −2.94 | −1.71 | |
| 2719 | A0A3B5XV32 | Cupin domain protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | 2.60 | −1.51 | −3.94 | |
| 4272 | A0A3B6ILV9 | Similar to globulin 3 | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | −2.10 | −2.73 | −1.30 | |
| 3358 | A0A3B6IN56 | Similar to alanine-tRNA ligase | Protein synthesis | Metabolic | −2.93 | −1.22 | 2.41 | |
| 1082 | A0A3B6KSH4 | Similar to β-amylase | Hydrolysis of (1->4)-α-D-glucosidic linkages in polysaccharides | Metabolic | 2.60 | 1.10 | −2.36 | |
| 4055 | A0A3B6MYZ0 | Similar to globulin-1 S allele | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | −4.81 | 1.19 | 5.73 | |
| 1051 | I6QQ39 | Globulin-3A (Glo-3A) | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | 2.66 | 1.35 | −1.97 | |
| 4155 | I6QQ39 | Globulin-3A (Glo-3A) | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | −3.09 | −2.27 | 1.37 | |
| 1315 | A0A1D5VMG1 | Uncharacterized protein, obsolete | NA | Metabolic | 3.19 | 1.03 | −3.11 | |
| 950 | A0A3B5Z536 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | −5.44 | −1.58 | 3.44 | |
| 1289 | A0A3B6G0N3 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | −2.63 | −1.28 | 2.06 | |
| 4162 | A0A3B6JER7 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | 4.48 | 5.18 | 1.16 | |
| 4171 | A0A3B6JER7 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | 3.51 | 3.74 | 1.06 | |
| 4489 | A0A3B6LGL1 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | 5.72 | 5.05 | −1.13 | |
| 4008 | A0A3B6PFQ8 | Uncharacterized protein | NA | Metabolic | −4.11 | −4.38 | −1.06 |
| UniProt Accession | Protein Name (Genetic Locus) | Function | Allergen or Toxin | Protein Group | Panna/Sotnytsia | Panna/Ukrainka | Sotnytsia/Ukrainka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6SPZ3 | LMW-A2 glutenin (Glu-A3-11) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 6.39 | −1.25 | −7.99 |
| Q00M56 | LMW-D1 glutenin (Glu-D3-3) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 2.31 | −1.39 | −3.21 |
| P10386 | LMW-1D1 glutenin (Glu-D3-2) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 1.45 | −1.92 | −2.78 |
| D2DII3 | LMW glutenin subunit (Glu-A3-16) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 4.52 | −1.30 | −5.88 |
| B2Y2Q6 | LMW-B2 glutenin (Glu-B3-2) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 11.01 | 1.07 | −10.24 |
| B2Y2Q1 | LMW glutenin subunit (Glu-B3-1) | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Glutenin | 3.06 | 1.07 | −2.86 |
| A0A1D5S346 | Similar to γ-gliadin, obsolete | Nutrient reservoir activity | √ | Gliadin | 1.48 | −1.81 | −2.68 |
| P0CZ10 | Avenin-like a6 | Nutrient reservoir activity | Gliadin | −3.06 | −3.38 | −1.11 | |
| A0A3B6K9J4 | Thaumatin family protein | Multiple disulfide bonds | Metabolic | −1.78 | 1.44 | 2.56 | |
| A0A3B5XV32 | Cupin domain protein | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | 2.91 | 1.44 | −2.02 | |
| A0A1D5Y5R1 | Cupin domain protein, obsolete | Nutrient reservoir activity | Metabolic | −2.74 | −2.57 | 1.07 | |
| A0A3B6SDE7 | Uncharacterized membrane protein | Integral component of membrane | Metabolic | −4.88 | 1.08 | 5.25 |
| UniProt Accession | Protein Name (Genetic Locus) | Allergome Identifier | Protein Group | # of Epitopes ProPepper | # of Celiac Motifs GluPro | Density of Celiac Motifs GluPro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P08489 | HMW-PW212 glutenin | Tri a 26 | Glutenin | 48 | 18 | 0.02 |
| P08488 | HMW-12 glutenin (HMW-GS DY) | Tri a 26 | Glutenin | 6 | 3 | < 0.01 |
| P10388 | HMW-DX5 glutenin (Glu-1D-1D) | Tri a 26 | Glutenin | 49 | 5 | 0.01 |
| B2Y2Q6 | LMW-B2 glutenin (Glu-B3-2) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | 9 | 5 | 0.01 |
| Q6SPZ3 | LMW-A2 glutenin (Glu-A3-11) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | NA | 11 | 0.03 |
| Q00M56 | LMW-D1 glutenin (Glu-D3-3) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | 7 | 5 | 0.01 |
| D2DII3 | LMW glutenin subunit (Glu-A3-16) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | 8 | NA | NA |
| B2Y2Q1 | LMW glutenin subunit (Glu-B3-1) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | 12 | 4 | 0.01 |
| P10386 | LMW-1D1 glutenin (Glu-D3-2) | Tri a 36 | Glutenin | 6 | 4 | 0.01 |
| I0IT62 | α/β-gliadin | NA | Gliadin | 43 | 13 | 0.04 |
| P04722 | α/β-gliadin AII | NA | Gliadin | 127 | 22 | 0.08 |
| P21292 | γ-gliadin | Tri a 20 | Gliadin | 59 | 46 | 0.15 |
| A1EHE7 | γ-gliadin D3 (Gli1) | Tri a 20 | Gliadin | 49 | 37 | 0.13 |
| Q94G92 | γ-gliadin D4 (Gli1) | Tri a 20 | Gliadin | 40 | 23 | 0.08 |
| A0A1D5S346 | Similar to γ-gliadin, obsolete | Tri a 20 | Gliadin | NA | NA | NA |
| M9TG60 | γ-gliadin A1 (Gli1) | Tri a 20 | Gliadin | 44 | 31 | 0.09 |
| Q41593 | Serpin-Z1A (WZCI) | Tri a 33 | Metabolic | NA | NA | NA |
| Q43691 | Trypsin/α-amylase inhibitor CMX2 | Tri a CMX | Metabolic | NA | NA | NA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lakhneko, O.; Danchenko, M.; Morgun, B.; Kováč, A.; Majerová, P.; Škultéty, Ľ. Comprehensive Comparison of Clinically Relevant Grain Proteins in Modern and Traditional Bread Wheat Cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103445
Lakhneko O, Danchenko M, Morgun B, Kováč A, Majerová P, Škultéty Ľ. Comprehensive Comparison of Clinically Relevant Grain Proteins in Modern and Traditional Bread Wheat Cultivars. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103445
Chicago/Turabian StyleLakhneko, Olha, Maksym Danchenko, Bogdan Morgun, Andrej Kováč, Petra Majerová, and Ľudovit Škultéty. 2020. "Comprehensive Comparison of Clinically Relevant Grain Proteins in Modern and Traditional Bread Wheat Cultivars" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103445
APA StyleLakhneko, O., Danchenko, M., Morgun, B., Kováč, A., Majerová, P., & Škultéty, Ľ. (2020). Comprehensive Comparison of Clinically Relevant Grain Proteins in Modern and Traditional Bread Wheat Cultivars. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103445