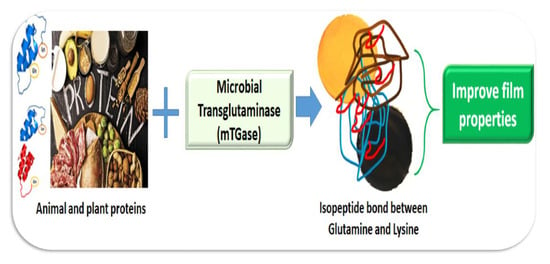
Microbial Transglutaminase as a Tool to Improve the Features of Hydrocolloid-Based Bioplastics
Abstract
:1. Plastic Pollution
2. Protein-Based Bioplastics
Reinforcement of Bioplastics
3. Proteins From Animals
3.1. Collagen
3.2. Myofibrillar Proteins
3.3. Milk Proteins
3.3.1. Caseins
3.3.2. Whey Proteins
3.4. Egg Proteins
3.4.1. Albumen Proteins
3.4.2. Yolk Proteins
4. Proteins From Plants
4.1. Cereal and Pseudocereal Species
4.1.1. Quinoa Proteins
4.1.2. Wheat Gluten
4.1.3. Corn Zein
4.2. Legumes
4.2.1. Soy Proteins
4.2.2. White Bean Proteins
4.2.3. Bitter Vetch Proteins
4.2.4. Grass Pea Proteins
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| mTGase | microbial transglutaminase |
| MW | milk whey |
References
- Rajendran, N.; Puppala, S.; Sneha Raj, M.; Ruth Angeeleena, B.; Rajam, C. Seaweeds can be a new source for bioplastics. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 5, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, A.; Burgos, N.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Natural pectin polysaccharides as edible coatings. Coatings 2015, 5, 865–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porta, R. The plastics sunset and the bio-plastics sunrise. Coatings 2019, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Di Pierro, P.; Gunning, P.; Mackie, A.; Porta, R.; Mariniello, L. Characterization of Citrus pectin edible films containing transglutaminase-modified phaseolin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Fai, A.E.C.; Andrade, C.T.; Picciani, P.H.; Azero, E.G.; Gonçalves, É.C. Edible films and coatings based on biodegradable residues applied to acerolas (Malpighia punicifolia L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, R.; Di Pierro, P.; Rossi-Marquez, G.; Mariniello, L.; Kadivar, M.; Arabestani, A. Microstructure and properties of bitter vetch (Vicia ervilia) protein films reinforced by microbial transglutaminase. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Di Pierro, P.; Sabbah, M.; Regalado-Gonzales, C.; Mariniello, L.; Kadivar, M.; Arabestani, A. Blend films of pectin and bitter vetch (Vicia ervilia) proteins: Properties and effect of transglutaminase. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 36, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmar, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Sabbah, M.; Sanchez, A.; Villalonga Santana, R.; Mariniello, L. Effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the physicochemical properties of pectin packaging material for strawberry wrapping. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultin, E.J. The circular economye A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Bian, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, W. Application of protein-based films and coatings for food packaging: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salama, H.E.; Aziz, M.S.A.; Sabaa, M.W. Novel biodegradable and antibacterial edible films based on alginate and chitosan biguanidine hydrochloride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popović, S.Z.; Lazić, V.L.; Hromiš, N.M.; Šuput, D.Z.; Bulut, S.N. Chapter 8—Biopolymer packaging materials for food shelf-life prolongation. In Biopolymers for Food Design; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 223–277. [Google Scholar]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Mariniello, L.; Ring, S. Extraction and characterization of Foeniculum vulgare pectins and their use to prepare biopolymer films in the presence of phaseolin protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Moschetti, G.; Aponte, M.; Masi, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Porta, R. Fennel waste-based films suitable for protecting cultivations. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3008–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Proteins as agricultural polymers for packaging production. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommet, M.; Redl, A.; Morel, M.-H.; Guilbert, S. Study of wheat gluten plasticization with fatty acids. Polymer 2003, 44, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, L.; Di Pierro, P.; Esposito, C.; Sorrentino, A.; Masi, P.; Porta, R. Preparation and mechanical properties of edible pectin-soy flour films obtained in the absence or presence of transglutaminase. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 102, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Porta, R. Use of the enzyme transglutaminase to prepare hydrocolloid-based edible films suitable for the food industry. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 136, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Porta, R. Swelling, mechanical, and barrier properties of albedo-based films prepared in the presence of phaseolin cross-linked or not by transglutaminase. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2394–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porta, R.; Mariniello, L.; di Pierro, P.; Sorrentino, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L. Transglutaminase crosslinked pectin and chitosan-based edible films: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strop, P. Versatility of microbial transglutaminase. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; Mariniello, L. Transglutaminase protein substrates of food interest. In Enzymes in Food Technology: Improvement and Innovation; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 293–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Sirangelo, I.; de Simone, C.; Di Pierro, P.; Porta, R.; Mariniello, L. Higher susceptibility to amyloid fibril formation of the recombinant ovine prion protein modified by transglutaminase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Bats, I.; Di Pierro, P.; Villalonga-Santana, R.; Garcia-Almendarez, B.; Porta, R. Bioactive mesoporous silica nanocomposite films obtained from native and transglutaminase-crosslinked bitter vetch proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Roviello, V.; Esposito, M.; Mariniello, L. Preparation and characterization of bioplastics from grass pea flour cast in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Coatings 2018, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorde, K.L.; Ananthanarayan, L. Effect of transglutaminase treatment on properties of coconut protein-guar gum composite film. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, M.; Delgado-Sánchez, L.F.; Ríos-Romo, R.A.; García-Almendárez, B.E.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; Méndez-Méndez, J.V.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Di Pierro, P.; Regalado-González, C. Effect of transglutaminase cross-linking in protein isolates from a mixture of two quinoa varieties with chitosan on the physicochemical properties of edible films. Coatings 2019, 9, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Mu, G. Improved structure-stability and packaging characters of crosslinked collagen fiber-based film with casein, keratin and SPI. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4942–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Diaz, K.; Cobos, Á.; Fernández-Valle, M.E.; Díaz, O.; Cambero, M.I. Characterization of edible films from whey proteins treated with heat, ultrasounds and/or transglutaminase. Application in cheese slices packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, T.; Song, Y.; Qian, F.; Tuo, Y.; Mu, G. Mechanical properties of whey protein concentrate based film improved by the coexistence of nanocrystalline cellulose and transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouravand, F.; Jooyandeh, H.; Barzegar, H.; Hojjati, M. mechanical, barrier and structural properties of whey protein isolate-based films treated by microbial transglutaminase. J. Microbiol. Biotech. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 960–964. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, A.; Tapia, C.; Abugoch, L. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound treatment in combination with transglutaminase and nanoparticles on structural, mechanical, and physicochemical properties of quinoa proteins/chitosan edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, M.; Altamimi, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Schiraldi, C.; Cammarota, M.; Porta, R. Black edible films from protein-containing defatted cake of Nigella sativa seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, K.; Turhan, S.; Saricaoglu, F.T.; Tural, S. Improvement of physicochemical, mechanical, thermal and surface properties of anchovy by-product protein films by addition of transglutaminase, and the correlation between secondary structure and mechanical properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z. Cross-linking and film-forming properties of transglutaminase-modified collagen fibers tailored by denaturation temperature. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Ye, R. Improved mechanical properties and thermal-stability of collagen fiber based film by crosslinking with casein, keratin or SPI: Effect of crosslinking process and concentrations of proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, W. Improved thermal-stability and mechanical properties of type I collagen by crosslinking with casein, keratin and soy protein isolate using transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, B.I.; Jung, S.T.; Park, H.J. Biopolymer composite films based on κ-carrageenan and chitosan. Mater. Res. Bull. 2001, 36, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, J.W. Partially purified collagen from refiner discharge of pacific whiting surimi processing. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, c511–c516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Bae, H.J.; Whiteside, W.S.; Park, H.J. Influence of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on properties of fish gelatin films. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E376–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, S.; Sandoval, G.; Palos, I.; Tellez, S.; Aguirre-Loredo, Y.; Velazquez, G. The effect of relative humidity on tensile strength and water vapor permeability in chitosan, fish gelatin and transglutaminase edible films. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, Y. The muscle ultrastructure: A structural perspective of the sarcomere. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 3016–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Han, M.; Pan, L.; Xing, T.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Solubilization of myosin in a solution of low ionic strength L-histidine: Significance of the imidazole ring. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiku, Y.; Hamaguchi, P.Y.; Tanaka, M. Effect of pH on the preparation of edible films based on fish myofibrillar proteins. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercel, F.; Stroiu, M.; Alexe, P.; IaniĠchi, D. Characterization of myofibrillar chicken breast proteins for obtain protein films and biodegradable coating generation. Agric. Agric. Sci. Proced. 2015, 6, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayli, D.; Turhan, S.; Saricaoglu, F.T. Edible packaging film derived from mechanically deboned chicken meat proteins: Effect of transglutaminase on physicochemical properties. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaewprachu, P.; Osako, K.; Tongdeesoontorn, W.; Rawdkuen, S. The effects of microbial transglutaminase on the properties of fish myofibrillar protein film. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 12, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamzad, H.; Paighambari, S.Y.; Shabanpour, B.; Ojagh, S.M.; Mousavi, S.M. Improvement of fish protein film with nanoclay and transglutaminase for food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, D.G.; Corredig, M. The structure of the casein micelle of milk and its changes during processing. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgitte, M.C.; Esben, S.S.; Peter, H.; Torben, E.P.; Lone, K.R. Localization of potential transglutaminase cross-linking sites in bovine caseins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar]
- Chambi, H.; Grosso, C. Edible films produced with gelatin and casein cross-linked with transglutaminase. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, S.S.; Wang, B.; Biswas, M.A.S.; Oh, J.-H. Physical, morphological, and barrier properties of edible casein films with wax applications. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C255–C259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Chang, C.; Li, X.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Films based on egg white protein and succinylated casein cross-linked with transglutaminase. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Pilli, S.; Kumar, L.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Cheese whey: A potential resource to transform into bioprotein, functional/nutritional proteins and bioactive peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalrazeq, M.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Esposito, M.; Fenderico, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Porta, R. Glycerol-Plasticized films obtained from whey proteins denatured at alkaline pH. Coatings 2019, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limsawat, P.; Pruksasri, S. Separation of lactose from milk by ultrafiltration. Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 2010, 3, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, H. Milk-derived bioactive peptides: From science to applications. J. Funct. Foods. 2009, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, O.; Spotti, M.J.; Schaffter, S.; Corvalan, C.M.; Campanella, O.H. Rheological and structural characterization of whey protein gelation induced by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, P.; Rossi-Marquez, G.; Mariniello, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Villalonga, R.; Porta, R. Effect of transglutaminase on the mechanical and barrier properties of whey protein/pectin films prepared at complexation pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, P.; Chico, B.; Villalonga, R.; Mariniello, L.; Damiao, A.E.; Masi, P.; Porta, R. Chitosan-whey protein edible films produced in the absence or presence of transglutaminase: Analysis of their mechanical and barrier properties. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernàndez-Balada, E.; Taylor, M.M.; Phillips, J.G.; Marmer, W.N.; Brown, E.M. Properties of biopolymers produced by transglutaminase treatment of whey protein isolate and gelatin. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3638–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhisel-Broadbent, J.; Dintzis, H.M.; Dintzis, R.Z.; Sampson, H.A. Allergenicity and antigenicity of chicken egg ovomucoid (Gal d III) compared with ovalbumin (Gal d I) in children with egg allergy and in mice. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeland, T. A clinical and immunological study of allergy to hen’s egg white. II. Antigens in hen’s egg white studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis (CIE). Allergy 1982, 37, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.-T.; Mine, Y.; Tung, M.A. Transglutaminase cross-linked egg white protein films: tensile properties and oxygen permeability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4022–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Rigby, N.M.; Wellner, N.; Ridout, M.; Husband, F.; Mackie, A.R. Microbial transglutaminase-mediated modification of ovalbumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, P.; Chico, B.; Villalonga, R.; Mariniello, L.; Masi, P.; Porta, R. Transglutaminase-catalyzed preparation of chitosan-ovalbumin films. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcet, I.; Sáez, S.; Rendueles, M.; Díaz, M. Edible films from residual delipidated egg yolk proteins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Janes, M.E.; Chaiya, B.; Brennan, M.A.; Brennan, C.S.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Gluten-free bakery and pasta products: Prevalence and quality improvement. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 53, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoenlechner, R.; Mandala, I.; Kiskini, A.; Kostaropoulos, A.; Berghofer, E. Effect of water, albumen and fat on the quality of gluten-free bread containing amaranth. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Masi, P.; Bracciale, A.; Aiello, A.; Nicolai, M.A.; Ferranti, P. Effect of added enzymes and quinoa flour on dough characteristics and sensory quality of a gluten-free bakery product. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.-B.; Wild, F.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lindner, M.; Schmid, M.; Weckel, V.; Müller, K.; Rodriguez, P.; Staebler, A.; et al. State of the art in the development and properties of protein-based films and coatings and their applicability to cellulose based products: An extensive review. Coatings 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinshui, W.; Yuwei, Z.; Mouming, Z. Development and physical properties of film of wheat gluten cross-linked by transglutaminase. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2005, 20, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larré, C.; Desserme, J.; Barbot, J.; Gueguen, J. Properties of deamidated gluten films enzymatically crosslinked. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1520–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Chiang, I.-C. Properties of MTGase treated gluten film. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Yuan, J.; Wang, P.; Sun, H.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q. Facilitation of α-polylysine in TGase-mediated cross- linking modification for gluten and its effect on properties of gluten films. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 73, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, J. Comparison of extraction methods for evaluating zein content of maize grain. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, L.C.; Parris, N. Serial batch extraction of zein milled maize. Ind. Crops Prod. Int. J. 2002, 15, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Edible films and coatings as active layers. In Active Food Packaging; Rooney, M.L., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 111–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Padua, G.W. Water barrier properties of zein-oleic acid films. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa de Almeida, C.; Tafari Catelam, K.; Lopes Cornélio, M.; Lopes Filho, J. Morphological and structural characteristics of zein biofilms with added xanthan gum. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pena Serna, C.; Lopes Filho, J.F. Biodegradable Zein-Based Blend Films: Structural, Mechanical and Barrier Properties. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 53, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Wang, B.; Field, P.D.; Aglan, H.A. Characteristics of edible films made from dairy proteins and zein hydrolysate cross-linked with transglutaminase. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamba, K.; Li, Y.; Hategekimana, J.; Liu, F.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Effect of type of plasticizers on mechanical and water barrier properties of transglutaminase cross-linked zein-oleic acid composite films. Int. J. Food Eng. 2016, 12, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamba, K.; Li, Y.; Hategekimana, J.; Zehadi, M.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Evaluation of mechanical and water barrier properties of transglutaminase cross-linked zein films incorporated with oleic acid. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamba, K.; Li, Y.; Hategekimana, J.; Ma, J.; Zhong, F. Effect of drying temperature and pH alteration on mechanical and water barrier properties of transglutaminase cross linked zein-oleic acid composite films. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Xin, R.; Dong, M.; Mariniello, L. Microbial transglutaminase-mediated polymerization in the presence of lactic acid bacteria affects antigenicity of soy protein component present in bio-tofu. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 53, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Carpentieri, A.; Pasquino, R.; Dong, M.; Mariniello, L. Gelling behavior of bio-tofu coagulated by microbial transglutaminase combined with lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, P.; Mariniello, L.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Masi, P.; Porta, R. Solubility and permeability properties of edible pectin-soy flour films obtained in the absence or presence of transglutaminase. Food Biotechnol. 2005, 19, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, P.; Mariniello, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Villalonga, R.; Chico, B.; Porta, R. Putrescine-polysaccharide conjugates as transglutaminase substrates and their possible use in producing cross-linked films. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.H.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, Q.-B.; Yang, X.-Q. Effect of transglutaminase treatment on the properties of cast films of soy protein isolates. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, Q.-B.; Tang, C.-H.; Yang, X.-Q. Effect of transglutaminase on properties of cast films from food proteins. J. South. Chin. Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2006, 34, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Di Pierro, P.; Romano, R.; Masi, P.; Mariniello, L. Impact of transglutaminase treatment on properties and in vitro digestibility of white bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flour. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Masi, P.; Mariniello, L. Impact of dehulling on the physico-chemical properties and in vitro protein digestion of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabestani, A.; Kadivar, M.; Amoresano, A.; Illiano, A.; Di Pierro, P.; Porta, R. Bitter vetch (Vicia ervilia) seed protein concentrate as possible source for production of bilayered films and biodegradable containers. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Esposito, M.; Mariniello, L.; Regalado-Gonzales, C.; Porta, R. Plasticizing Effects of Polyamines in Protein-Based Films. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granati, E.; Bisignano, V.; Chiaretti, D.; Crino, P.; Polignano, G.B. Characterization of Italian and exotic Lathyrus germplasm for quality traits. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2003, 50, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; Masi, P.; Aponte, M.; Mariniello, L. Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) flour: Microstructure, physico-chemical properties and in vitro digestion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani-Levi, C.; Alvito, P.; Andrés, A.; Assunço, R.; Barbera, R.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Bourlieug, C.; Brodkorbi, A.; Cillae, A.; Deglaireh, A.; et al. Extending in vitro digestion models to specific human populations: Expert perspectives, practical tools and bio-relevant information. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 60, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; Masi, P.; Romano, R.; Mariniello, L. Structure and in vitro digestibility of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) flour following transglutaminase treatment. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein-Based Film Type | mTGase Effect on the Films | References |
|---|---|---|
| Bitter vetch proteins/mesoporous silica nanocomposite | Decrease in mechanical properties and decrease in gas permeability | [24] |
| Grass pea protein | Films more resistant and digested to a less extent under gastrointestinal physiological conditions | [25] |
| Coconut protein/guar gum | Enhancement of physico-chemical properties, such as mechanical, barrier properties and thermal features | [26] |
| Two quinoa varieties/chitosan | Enhancement of edible film physical properties | [27] |
| Collagen fiber/casein, keratin or SPI | Improved structure stability and packaging characters | [28] |
| Whey protein/heat ultrasounds | The properties of films were unaffected except their color | [29] |
| Whey protein concentrate/nanocrystalline cellulose | Mechanical properties enhancement | [30] |
| Whey protein isolate | Improved mechanical properties, gas permeability, and morphology properties | [31] |
| Quinoa protein/chitosan | Enhanced thermal stability and tensile strength. Elongation at break reduction | [32] |
| Nigella sativa seed proteins | Improved mechanical and barrier properties | [33] |
| Proteins from anchovy by-products | Improved mechanical, barrier, and surface properties | [34] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Fusco, A.; Al-Asmar, A.; Mariniello, L. Microbial Transglutaminase as a Tool to Improve the Features of Hydrocolloid-Based Bioplastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103656
Giosafatto CVL, Fusco A, Al-Asmar A, Mariniello L. Microbial Transglutaminase as a Tool to Improve the Features of Hydrocolloid-Based Bioplastics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103656
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiosafatto, C. Valeria L., Antonio Fusco, Asmaa Al-Asmar, and Loredana Mariniello. 2020. "Microbial Transglutaminase as a Tool to Improve the Features of Hydrocolloid-Based Bioplastics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103656
APA StyleGiosafatto, C. V. L., Fusco, A., Al-Asmar, A., & Mariniello, L. (2020). Microbial Transglutaminase as a Tool to Improve the Features of Hydrocolloid-Based Bioplastics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103656