Cyclophilin A Promotes Inflammation in Acute Kidney Injury but Not in Renal Fibrosis
Abstract
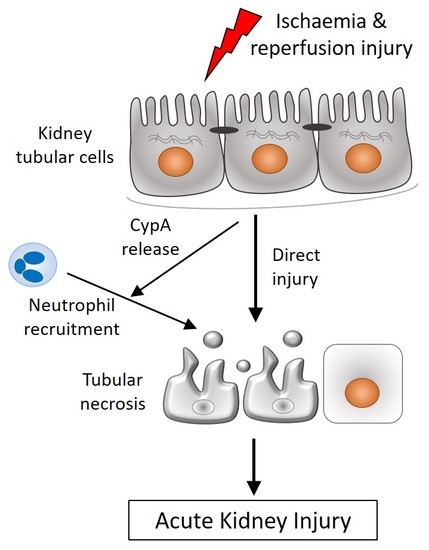
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CypA Deletion Protects against Acute Renal Failure, Tubular Damage and Cell Death in Renal IRI
2.2. CypA Deletion Protects against Leukocyte Infiltration in Renal IRI
2.3. CypA Deletion Does Not Protect against Tubular Damage in UUO
2.4. CypA Deletion Does Not Protect against Inflammation or Fibrosis in UUO
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Renal Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury (IRI)
4.3. Unilateral Ureteric Obstruction (UUO)
4.4. Renal Function
4.5. Histology
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Cell Culture Studies
4.9. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Qie, G.; Zhou, J. The roles of CD147 and/or cyclophilin A in kidney diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 728673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C. Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bukrinsky, M. Extracellular cyclophilins in health and disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, S.J.; Olive, D.; Gao, J.L.; Murphy, P.M.; Bukrinsky, M.I.; Constant, S.L. Cyclophilin A cooperates with MIP-2 to augment neutrophil migration. J. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 4, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.J.; Jeon, S.T.; Koh, E.M.; Cha, H.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, W.H. Cyclophilin A may contribute to the inflammatory processes in rheumatoid arthritis through induction of matrix degrading enzymes and inflammatory cytokines from macrophages. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Ge, H.; He, B. Pro-inflammatory activities induced by CyPA-EMMPRIN interaction in monocytes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dear, J.W.; Simpson, K.J.; Nicolai, M.P.J.; Catterson, J.H.; Street, J.; Huizinga, T.; Craig, D.G.; Dhaliwal, K.; Webb, S.; Bateman, D.N.; et al. Cyclophilin A Is a Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecule That Mediates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinina, A.; Zamkova, M.; Antoshina, E.; Trukhanova, L.; Gorkova, T.; Kazansky, D.; Khromykh, L. Analyses of the toxic properties of recombinant human Cyclophilin A in mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 16, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossum, S.; Mallett, S.; Barclay, A.N. The MRC OX-47 antigen is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with an unusual transmembrane sequence. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 21, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.J.; Jefferies, W.A.; Green, J.R.; Brandon, M.R.; Corthesy, P.; Puklavec, M.; Williams, A.F. Antigens of activated rat T lymphocytes including a molecule of 50,000 Mr detected only on CD4 positive T blasts. Mol. Immunol. 1987, 24, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, T. Basigin (CD147), a multifunctional transmembrane glycoprotein with various binding partners. J. Biochem. 2016, 159, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igakura, T.; Kadomatsu, K.; Kaname, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Fan, Q.W.; Miyauchi, T.; Toyama, Y.; Kuno, N.; Yuasa, S.; Takahashi, M.; et al. A null mutation in basigin, an immunoglobulin superfamily member, indicates its important roles in peri-implantation development and spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 1998, 194, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igakura, T.; Kadomatsu, K.; Taguchi, O.; Muramatsu, H.; Kaname, T.; Miyauchi, T.; Yamamura, K.; Arimura, K.; Muramatsu, T. Roles of basigin, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, in behavior as to an irritating odor, lymphocyte response, and blood-brain barrier. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 224, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neal, J.B.; Shaw, A.D.; Billings, F.T. Acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: Current understanding and future directions. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uber, A.M.; Sutherland, S.M. Nephrotoxins and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Nephrol. E-pub 24 Oct 2019. [CrossRef]
- Acedillo, R.R.; Wald, R.; McArthur, E.; Nash, D.M.; Silver, S.A.; James, M.T.; Schull, M.J.; Siew, E.D.; Matheny, M.E.; House, A.A.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Discharged Home from an Emergency Department with AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.A.; Lucas, B.J.; Selby, N.M. Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Cheng, Y.L.; Kuo, G.; Chen, S.W.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Tian, Y.C. Diagnostic Performance of Cyclophilin A in Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, P.F.; Su, S.L.; Tsai, C.C.; Wu, C.L.; Kuo, C.L.; Kor, C.T.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, C.S. Cyclophilin A and CD147 associate with progression of diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.F.; Su, C.W.; Wu, M.J.; Chen, C.H.; Fu, C.P.; Liu, C.S.; Hsieh, M. Urinary Cyclophilin A as a New Marker for Diabetic Nephropathy: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Diabetes Mellitus. Medicine 2015, 94, e1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, N.A.; El Helaly, R.M.; Ali, I.M.; Ebrahim, H.A.A.; Alayooti, M.M.; El Domiaty, H.A.; Aboelenin, H.M. Urinary Cyclophilin A and serum Cystatin C as biomarkers for diabetic nephropathy in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausner, J.M.; Paterson, I.S.; Goldman, G.; Kobzik, L.; Rodzen, C.; Lawrence, R.; Valeri, C.R.; Shepro, D.; Hechtman, H.B. Postischemic renal injury is mediated by neutrophils and leukotrienes. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 256, F794–F802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Kanellis, J.; Blease, K.; Ma, F.Y.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Promotes Myeloid Cell Recruitment and Kidney Damage after Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singbartl, K.; Ley, K. Protection from ischemia-reperfusion induced severe acute renal failure by blocking E-selectin. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Morrissey, J.; McCracken, R.; Tolley, T.; Liapis, H.; Klahr, S. Contributions of angiotensin II and tumor necrosis factor-alpha to the development of renal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2001, 280, F777–F785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchtler, S.; Grill, A.; Hofmarksrichter, S.; Stockert, P.; Schiechl-Brachner, G.; Rodriguez Gomez, M.; Neumayer, S.; Schmidbauer, K.; Talke, Y.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; et al. Cellular Origin and Functional Relevance of Collagen I Production in the Kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1859–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, N.C.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Farnworth, S.L.; Kipari, T.; Haslett, C.; Iredale, J.P.; Liu, F.T.; Hughes, J.; Sethi, T. Galectin-3 expression and secretion links macrophages to the promotion of renal fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, K.; Wada, T.; Furuichi, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Ishiwata, Y.; Asano, M.; Takeya, M.; Kuziel, W.A.; Matsushima, K.; Mukaida, N.; et al. Blockade of CCR2 ameliorates progressive fibrosis in kidney. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, S.A.; Jo, S.K.; Cho, W.Y.; Won, N.H.; Kim, H.K. Reduction of renal fibrosis as a result of liposome encapsulated clodronate induced macrophage depletion after unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2007, 105, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pefanis, A.; Ierino, F.L.; Murphy, J.M.; Cowan, P.J. Regulated necrosis in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devalaraja-Narashimha, K.; Diener, A.M.; Padanilam, B.J. Cyclophilin D gene ablation protects mice from ischemic renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F749–F759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, W.; Leong, K.G.; Ozols, E.; Tesch, G.H.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Ma, F.Y. Cyclophilin D promotes tubular cell damage and the development of interstitial fibrosis in the obstructed kidney. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2018, 45, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofferson, D.E.; Yuan, J. Cyclophilin A release as a biomarker of necrotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1942–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Sheldrake, T.A.; Dhaliwal, K.; Kipari, T.M.; Marson, L.P.; Kluth, D.C.; Hughes, J. Macrophage/monocyte depletion by clodronate, but not diphtheria toxin, improves renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Chander, V.; Chopra, K. Cyclosporine protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidneys. Toxicology 2005, 207, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seizer, P.; Ochmann, C.; Schonberger, T.; Zach, S.; Rose, M.; Borst, O.; Klingel, K.; Kandolf, R.; MacDonald, H.R.; Nowak, R.A.; et al. Disrupting the EMMPRIN (CD147)-cyclophilin A interaction reduces infarct size and preserves systolic function after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, N.; Yuzawa, Y.; Kosugi, T.; Hobo, A.; Sato, W.; Miwa, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Matsuo, S.; Kadomatsu, K. The E-selectin ligand basigin/CD147 is responsible for neutrophil recruitment in renal ischemia/reperfusion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Kou, P.; Zeng, Q.; Pei, G.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Xu, G.; Chen, S. CD4+ T Lymphocytes, especially Th2 cells, contribute to the progress of renal fibrosis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. CD4+ T cells: A potential player in renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapmeier, T.T.; Fearn, A.; Brown, K.; Chowdhury, P.; Sacks, S.H.; Sheerin, N.S.; Wong, W. Pivotal role of CD4+ T cells in renal fibrosis following ureteric obstruction. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, H.J.; Vielhauer, V.; Frink, M.; Linde, Y.; Cohen, C.D.; Blattner, S.M.; Kretzler, M.; Strutz, F.; Mack, M.; Grone, H.J.; et al. A chemokine receptor CCR-1 antagonist reduces renal fibrosis after unilateral ureter ligation. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarro, E.; Duran, M.; Rico, A.; Bou-Teen, D.; Fernandez-Majada, V.; Croatt, A.J.; Nath, K.A.; Salcedo, M.T.; Gundelach, J.H.; Batlle, D.; et al. Cyclophilins A and B Oppositely Regulate Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Phenotype. J. Mol. Cell Biol. E-pub 12 March 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, N.; Kosugi, T.; Sato, W.; Ishimoto, T.; Kojima, H.; Sato, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Maruyama, S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Matsuo, S.; et al. Basigin/CD147 promotes renal fibrosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.Y.; Tesch, G.H.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. ASK1/p38 signaling in renal tubular epithelial cells promotes renal fibrosis in the mouse obstructed kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1263–F1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.Y.; Tesch, G.H.; Ozols, E.; Xie, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. TGF-beta1-activated kinase-1 regulates inflammation and fibrosis in the obstructed kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 300, F1410–F1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leong, K.G.; Ozols, E.; Kanellis, J.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Ma, F.Y. Cyclophilin A Promotes Inflammation in Acute Kidney Injury but Not in Renal Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103667
Leong KG, Ozols E, Kanellis J, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ma FY. Cyclophilin A Promotes Inflammation in Acute Kidney Injury but Not in Renal Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103667
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeong, Khai Gene, Elyce Ozols, John Kanellis, David J. Nikolic-Paterson, and Frank Y. Ma. 2020. "Cyclophilin A Promotes Inflammation in Acute Kidney Injury but Not in Renal Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103667
APA StyleLeong, K. G., Ozols, E., Kanellis, J., Nikolic-Paterson, D. J., & Ma, F. Y. (2020). Cyclophilin A Promotes Inflammation in Acute Kidney Injury but Not in Renal Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103667