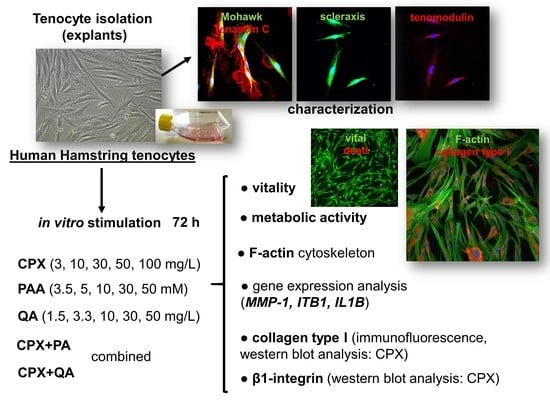
Uremic Toxins and Ciprofloxacin Affect Human Tenocytes In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2.1. Effects of Ciprofloxacin and Uremic Toxins on Tenocyte Metabolic Activity
2.2. Tenocyte Survival
2.3. Effects of Ciprofloxacin and Uremic Toxins on Tenocyte Gene Expression
2.4. Effects of Ciprofloxacin and Uremic Toxins on Tenocyte Collagen Synthesis, Cytoskeleton, and MMP-1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Agents Used for Tenocyte Stimulation
4.2. Tenocyte Isolation and Culture
4.3. Tenocyte Stimulation with Ciprofloxacin and Uremic Toxins
4.4. AlamarBlue Assay
4.5. Vitality Assay
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence Microscopical Analysis
4.8. Western Blot Analysis and Densitometric Evaluation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPX | ciprofloxacin |
| DAPI | 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindol |
| DTT | dithiothreitol |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGTA | ethylene glycol-bis(aminoethyl ether)-N, N, N′, N′-tetraacetic acid |
| FCS | fetal calf serum |
| HEPES | 2-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine)-ethanesulfonate |
| HPRT | hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5diphenyltetrazoliumbromide |
| OD | optical density |
| PAA | phenylacetic acid |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| QA | quinolinic acid |
| RT | room temperature |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Bailey, R.R.; Kirk, J.A.; Peddie, B.A. Norfloxacin-induced rheumatic disease. N. Z. Med. J. 1983, 96, 590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Bruschini, H.; Cury, J.; Srougi, M.; de Cesar-Netto, C.; Fonseca, L.F.; Maffulli, N. Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Achilles Tendon Disorders: Update on a Neglected Complication. Urology 2017, 113, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabyat, R.M.; Raisch, D.W.; McKoy, J.M.; Bennett, C.L. Fluoroquinolone-associated tendon-rupture: A summary of reports in the Food and Drug Administration’s adverse event reporting system. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzopoulos, G.; Stamatakos, M.; Vasiliadis, G.; Skandalakis, P. Rupture of adductor longus tendon due to ciprofloxacin. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2005, 71, 743–745. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, T.G. A rare case of ciprofloxacin-induced bilateral rupture of the Achilles tendon. BMJ Case Rep. 2009, 2009, bcr0820080697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidel, J.; Clarke, T.; Mathew, B. To cipro or not to cipro: Bilateral achilles ruptures with the use of quinolones. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2015, 105, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shybut, T.B.; Puckett, E.R. Triceps Ruptures after Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: A Report of 2 Cases. Sports Health 2017, 9, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Fackrell, R.; Henderson, E. Ciprofloxacin-associated bilateral iliopsoas tendon rupture: A case report. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyal, H.; Dennehy, J.; Barker, J.; Singla, U. Achilles is not alone!!! Ciprofloxacin induced tendinopathy of gluteal tendons. QJM 2016, 109, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeWolf, M.C.; Warhold, L.G. Ciprofloxacin-Induced Extensor Tendon Rupture in the Hand: A Case Report. JBJS Case Connect. 2015, 5, e301–e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimatsu, K.; Subramaniam, S.; Sim, H.; Aronowitz, P. Ciprofloxacin-induced tendinopathy of the gluteal tendons. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 1559–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawtharani, F.; Masrouha, K.Z.; Afeiche, N. Bilateral Achilles Tendon Ruptures Associated With Ciprofloxacin Use in the Setting of Minimal Change Disease: Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2016, 55, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Mendes, D.; Marques, F.B. Fluoroquinolones and the risk of tendon injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempfer, H.; Traweger, A. Tendon Vasculature in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauge, C.; Leclercq, S.; Conrozier, T.; Boumediene, K. TOL19-001 reduces inflammation and MMP expression in monolayer cultures of tendon cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Tang, F.T.; Wong, A.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Pang, J.H. Ciprofloxacin-mediated cell proliferation inhibition and G2/M cell cycle arrest in rat tendon cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, H.C.; Hsu, Y.H.; Lin, M.S.; Wu, C.W.; Pang, J.H. Ciprofloxacin-mediated inhibition of tenocyte migration and down-regulation of focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 607, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, C.P.; Chang, H.N.; Wong, A.M.; Lin, M.S.; Pang, J.H. Ciprofloxacin up-regulates tendon cells to express matrix metalloproteinase-2 with degradation of type I collagen. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.N.; Pang, J.H.; Chen, C.P.; Ko, P.C.; Lin, M.S.; Tsai, W.C.; Yang, Y.M. The effect of aging on migration, proliferation, and collagen expression of tenocytes in response to ciprofloxacin. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempka, G.; Ahr, H.J.; Ruther, W.; Schluter, G. Effects of fluoroquinolones and glucocorticoids on cultivated tendon cells in vitro. Toxicol. In Vitro 1996, 10, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.J.; Schar, M.O.; Wanivenhaus, F.; Chen, T.; Attia, E.; Binder, N.B.; Otero, M.; Gilbert, S.L.; Nguyen, J.T.; Chaudhury, S.; et al. Fluoroquinolones impair tendon healing in a rat rotator cuff repair model: A preliminary study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.; Pettinari, L.; Martinelli, C.; Colombo, G.; Portinaro, N.; Dalle-Donne, I.; d’Agostino, M.C.; Gagliano, N. New insights in extracellular matrix remodeling and collagen turnover related pathways in cultured human tenocytes after ciprofloxacin administration. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013, 3, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corps, A.N.; Harrall, R.L.; Curry, V.A.; Hazleman, B.L.; Riley, G.P. Contrasting effects of fluoroquinolone antibiotics on the expression of the collagenases, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-1 and -13, in human tendon-derived cells. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005, 44, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egerbacher, M.; Edinger, J.; Tschulenk, W. Effects of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin hydrochloride on canine and equine chondrocytes in culture. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaccia, D.R.; Aicale, R.; Tarantino, D.; Peretti, G.M.; Maffulli, N. Biological and chemical changes in fluoroquinolone-associated tendinopathies: A systematic review. Br. Med. Bull. 2019, 130, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, D.A.; Wallace, C.; Murphy, M.P.; Webster, N.R.; Galley, H.F. The mitochondria targeted antioxidant MitoQ protects against fluoroquinolone-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial membrane damage in human Achilles tendon cells. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleagasioglu, F.; Olcay, E. Fluoroquinolone-induced tendinopathy: Etiology and preventive measures. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2012, 226, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juras, V.; Winhofer, Y.; Szomolanyi, P.; Vosshenrich, J.; Hager, B.; Wolf, P.; Weber, M.; Luger, A.; Trattnig, S. Multiparametric MR Imaging Depicts Glycosaminoglycan Change in the Achilles Tendon during Ciprofloxacin Administration in Healthy Men: Initial Observation. Radiology 2015, 275, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Gelband, K. A Case-Based Approach to Evaluate the Potential Risks Associated with Fluoroquinolones and Steroids. Consult Pharm. 2016, 31, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, P.K.; Ho, C.T. Fluoroquinolone-induced Achilles tendinitis. Hong Kong Med. J. 2014, 20, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meneghello, A.; Bertoli, M. Tendon disease and adjacent bone erosion in dialysis patients. Br. J. Radiol. 1983, 56, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhole, R.; Flynn, J.C.; Marbury, T.C. Quadriceps tendon ruptures in uremia. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1985, 195, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.; Teruel, J.L.; Naya, M.T.; Ortuno, J. Bilateral rupture of the quadriceps tendon in uremia. Rev. Clin. Esp. 1991, 189, 348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schenkier, S.L.; Gertner, E. Massive soft tissue calcification causing complete loss of extensor tendon function in renal failure. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.F.; Yang, H.L.; Shi, W.D. Simultaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture in a patient with hyperparathyroidism undergoing long-term haemodialysis: A case report and literature review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yudd, M.; Llach, F. Current medical management of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 320, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T. Targeting protein-bound uremic toxins in chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T.; Yoshizumi, H.; Emoto, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Takeda, N.; Tatematsu, A.; Maeda, K. Accumulation of quinolinic acid in uremic serum and its removal by hemodialysis. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourde-Chiche, N.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Dignat-George, F.; Vanholder, R.; Brunet, P. Protein-bound toxins--update 2009. Semin. Dial 2009, 22, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotman, R.L.; Williamson, J.C.; Shoemaker, D.M.; Salzer, W.L. Antibiotic dosing in critically ill adult patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, J.F.; Yi, D.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Soula, H.A.; Chambert, S.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D.; Soulage, C.O. Determination of the binding properties of the uremic toxin phenylacetic acid to human serum albumin. Biochimie 2016, 125, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Raupachova, J.; Horl, W.H. The uraemic toxin phenylacetic acid contributes to inflammation by priming polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Nephrol. Dial Transpl. 2013, 28, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Westhoff, T.H.; Krauser, P.; Ignatius, R.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Zidek, W.; van der Giet, M. The uraemic toxin phenylacetic acid impairs macrophage function. Nephrol. Dial Transpl. 2008, 23, 3485–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morita, M.; Yano, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Sugimoto, T. Phenylacetic acid stimulates reactive oxygen species generation and tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion in vascular endothelial cells. Ther. Apher. Dial 2011, 15, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kanazawa, I.; Ogawa, N.; Hayashi, K.; Yamauchi, M.; Sugimoto, T. The uraemic toxin phenylacetic acid inhibits osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation: An implication for the pathogenesis of low turnover bone in chronic renal failure. Nephrol. Dial Transpl. 2007, 22, 3160–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, J.; van der Giet, M.; Jankowski, V.; Schmidt, S.; Hemeier, M.; Mahn, B.; Giebing, G.; Tolle, M.; Luftmann, H.; Schluter, H.; et al. Increased plasma phenylacetic acid in patients with end-stage renal failure inhibits iNOS expression. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, K.; Brzosko, S.; Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine, quinolinic acid—The new factors linked to carotid atherosclerosis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, D.; Koda, M.; Pawlak, S.; Wolczynski, S.; Buczko, W. Contribution of quinolinic acid in the development of anemia in renal insufficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2003, 284, F693–F700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawashima, Y.; Sanaka, T.; Sugino, N.; Takahashi, M.; Mizoguchi, H. Suppressive effect of quinolinic acid and hippuric acid on bone marrow erythroid growth and lymphocyte blast formation in uremia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1987, 223, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.C.; Yang, Y.M. Fluoroquinolone-associated tendinopathy. Chang Gung Med. J. 2011, 34, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, C.A.; Guay, D.R.; Awni, W.M.; Stein, D.J.; Peterson, P.K. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral ciprofloxacin in elderly patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1989, 33, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, D.M.; Roberts, J.A.; Roberts, M.S.; Liu, X.; Nair, P.; Cole, L.; Lipman, J.; Bellomo, R.; RENAL Replacement Therapy Study Investigators. Variability of antibiotic concentrations in critically ill patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: A multicentre pharmacokinetic study. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.A.; Uribe, F.; Moisen, S.D.; Fuster, A.P.; Selen, A.; Welling, P.G.; Painter, B. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of ciprofloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1984, 26, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tasoglu, O.; Ekiz, T.; Yenigun, D.; Akyuz, M.; Ozgirgin, N. Bilateral quadriceps and triceps tendon rupture in a hemodialysis patient. Hemodial. Int. 2016, 20, E19–E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Luo, P.; Zhi, S.; Zhou, R. A simultaneous bilateral quadriceps and patellar tendons rupture in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing long-term hemodialysis: A case report. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Wang, C.; Ruan, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Chen, F. Simultaneous spontaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture with secondary hyperparathyroidism in a patient receiving hemodialysis: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019, 98, e14809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, W.; Zribi, M.; Guidara, A.R.; Ben Jemaa, M.; Abid, A.; Krid, N.; Naceur, A.; Keskes, H. Spontaneous and simultaneous complete bilateral rupture of the quadriceps tendon in a patient receiving hemodialysis: A case report and literature review. World J. Orthop. 2018, 9, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, A.; Yousof Gomrokchi, A.; Elahifar, O.; Barmayoon, P.; Shojaei, S.F. Simultaneous bilateral rupture of patellar tendons in diabetic hemodialysis patient: A case report. Caspian J. Intern. Med. 2018, 9, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Moerenhout, K.; Gkagkalis, G.; Benoit, B.; Laflamme, G.Y. Simultaneous Ipsilateral Quadriceps and Triceps Tendon Rupture in a Patient with End-Stage Renal Failure. Case Rep. Orthop. 2018, 2018, 7602096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artan, A.S.; Basgoze, B. Bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture in a hemodialysis patient. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, V.N.; Venkatesh, M.; Kada, V.; Chakkalakkoombil, S.V. Spontaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture in a patient with renal failure. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medhi, B.; Kaur, H.; Prakash, A. Effect of ciprofloxacin-mediated inhibition on cell proliferation in rat tendon cells: Comment on the article by Tsai et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, D.; Tankiewicz, A.; Buczko, W. Kynurenine and its metabolites in the rat with experimental renal insufficiency. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 52, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, D.; Tankiewicz, A.; Mysliwiec, P.; Buczko, W. Tryptophan metabolism via the kynurenine pathway in experimental chronic renal failure. Nephron 2002, 90, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallee, M.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Brunet, P.; Burtey, S. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-activating effect of uremic toxins from tryptophan metabolism: A new concept to understand cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendzik, J.; Shakibaei, M.; Schafer-Korting, M.; Lode, H.; Stahlmann, R. Synergistic effects of dexamethasone and quinolones on human-derived tendon cells. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calderwood, D.A. Integrin activation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellis, S.L. Variant glycosylation: An underappreciated regulatory mechanism for beta1 integrins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1663, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Lin, X.; Sadoul, K.; Fournet, G.; Bouvard, D.; Vinogradova, O.; Joseph, B.; Block, M.R. Targeting Integrin-Dependent Adhesion and Signaling with 3-Arylquinoline and 3-Aryl-2-Quinolone Derivatives: A new Class of Integrin Antagonists. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidone, T.C.; Skeeters, A.V.; Oakes, P.W.; Voth, G.A. Multiscale model of integrin adhesion assembly. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Buono, A.; Oliva, F.; Longo, U.G.; Rodeo, S.A.; Orchard, J.; Denaro, V.; Maffulli, N. Metalloproteases and rotator cuff disease. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012, 21, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corps, A.N.; Harrall, R.L.; Curry, V.A.; Fenwick, S.A.; Hazleman, B.L.; Riley, G.P. Ciprofloxacin enhances the stimulation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 expression by interleukin-1beta in human tendon-derived cells. A potential mechanism of fluoroquinolone-induced tendinopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sodersten, F.; Hultenby, K.; Heinegard, D.; Johnston, C.; Ekman, S. Immunolocalization of collagens (I and III) and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein in the normal and injured equine superficial digital flexor tendon. Connect. Tissue Res. 2013, 54, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinemeier, K.M.; Schjerling, P.; Heinemeier, J.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M. Lack of tissue renewal in human adult Achilles tendon is revealed by nuclear bomb (14)C. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinemeier, K.M.; Schjerling, P.; Ohlenschlaeger, T.F.; Eismark, C.; Olsen, J.; Kjaer, M. Carbon-14 bomb pulse dating shows that tendinopathy is preceded by years of abnormally high collagen turnover. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4763–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berkoff, D.J.; Kallianos, S.A.; Eskildsen, S.M.; Weinhold, P.S. Use of an IL1-receptor antagonist to prevent the progression of tendinopathy in a rat model. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corps, A.N.; Curry, V.A.; Harrall, R.L.; Dutt, D.; Hazleman, B.L.; Riley, G.P. Ciprofloxacin reduces the stimulation of prostaglandin E(2) output by interleukin-1beta in human tendon-derived cells. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003, 42, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| MW (g/mol) | CN | CU | CM | Unit | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinolinic acid | 167 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 3.3 | mg/L | [37] |
| Phenylacetic acid | 136 | <1.4 | 467.2 | 474.6 | mg/L | [46] |
| Ciprofloxacin | 331 | 1.35 to 4.21 | 3.7 | 7.6 | mg/L | [51,52,53] |
| Gene Name | Amplicon Size | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|
| HPRT1 | 100 bp | Hs99999909_m1 |
| IL1B | 94 bp | Hs00174097_m1 |
| ITGB1 | 75 bp | Hs00559595_m1 |
| MMP-1 | 133 bp | Hs00233958_m1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popowski, E.; Kohl, B.; Schneider, T.; Jankowski, J.; Schulze-Tanzil, G. Uremic Toxins and Ciprofloxacin Affect Human Tenocytes In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124241
Popowski E, Kohl B, Schneider T, Jankowski J, Schulze-Tanzil G. Uremic Toxins and Ciprofloxacin Affect Human Tenocytes In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(12):4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124241
Chicago/Turabian StylePopowski, Erman, Benjamin Kohl, Tobias Schneider, Joachim Jankowski, and Gundula Schulze-Tanzil. 2020. "Uremic Toxins and Ciprofloxacin Affect Human Tenocytes In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 12: 4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124241
APA StylePopowski, E., Kohl, B., Schneider, T., Jankowski, J., & Schulze-Tanzil, G. (2020). Uremic Toxins and Ciprofloxacin Affect Human Tenocytes In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(12), 4241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124241