Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Signaling and Its Crosstalk with β1-Integrin Emerges as a Key Factor for Breast Cancer Chemosensitization upon Collagen Type 1 Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MAPK Signaling Is Activated by COL1 Binding of Cells, Even in the Absence of ITGB1
2.2. DDR1 Is Involved in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Cell Adhesion to COL1
2.3. ITGB1-DDR1 Crosstalk Includes MAPK Signaling
2.4. MAPK Pathway Is Crucial for COL1-Mediated Signaling and Can Be Interfered by ERK1/2-Inhibitor SCH772984
2.5. Combination of DDR1- or ERK1/2-Inhibitors with Cytostatics Displays Dose-Dependent Effects
2.6. Synergistic Effect Is Partly Dependent on MAPK Regulated ABC Transport Protein Involvement
2.7. ITGB1-Knockdown Is Compensated by Upregulation of ITGB4 and pEGFR
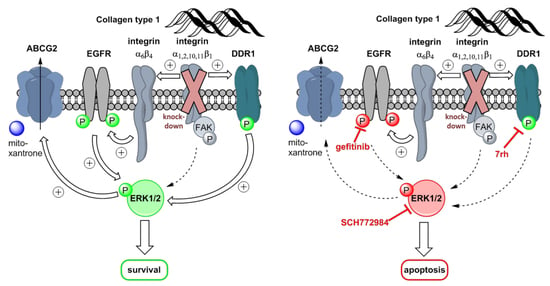
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Coating
4.3. Cell Adhesion
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. Proteome Profiler Array
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide
4.8. Functional Transporter Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCG2 | ATP-binding cassette super-family G member 2/breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| BC | breast cancer |
| BCC | breast cancer cell |
| CAM-DR | cell-adhesion-mediated drug resistance |
| DDR1 | discoidin domain receptor 1 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERK1/2 | extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 |
| Grb2 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HSP27 | heat shock protein 27 |
| ITGB1 | integrin β1 |
| ITGB4 | integrin β4 |
| kd | knockdown |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK1/2 | MAPK/ERK kinase 1 and 2 |
| p | phosphorylated |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| sc | scrambled |
| SOS | Son OF Sevenless |
| TNBC | triple-negative breast cancer |
| wt | wildtype |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Filho, J.S.; Tutt, A.N.J. Triple negative tumours: A critical review. Histopathology 2008, 52, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.L.; Cardoso Nunes, N.C.; Izetti, P.; de Mesquita, G.G.; de Melo, A.C. Triple negative breast cancer: A thorough review of biomarkers. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 145, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, A.; Bhattarai, S.; Sahoo, B.; Mongan, N.P.; Alsaleem, M.; Green, A.R.; Aleskandarany, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Pattni, S.; Li, X.B.; et al. Combined HER3-EGFR score in triple-negative breast cancer provides prognostic and predictive significance superior to individual biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; He, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, R.; Shi, Y.; Teng, X.; Qin, T. EGFR expression correlates with decreased disease-free survival in triple-negative breast cancer: A retrospective analysis based on a tissue microarray. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Jang, M.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, E.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, I.A.; et al. High EGFR gene copy number predicts poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakai, K.; Hung, M.-C.; Yamaguchi, H. A perspective on anti-EGFR therapies targeting triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.-X.; Wu, H.-T.; Li, X.-L.; Wen, X.-F.; Du, C.-W.; Zhang, G.-J. Collagen 1A1 (COL1A1) promotes metastasis of breast cancer and is a potential therapeutic target. Discov. Med. 2018, 25, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Giussani, M.; Landoni, E.; Merlino, G.; Turdo, F.; Veneroni, S.; Paolini, B.; Cappelletti, V.; Miceli, R.; Orlandi, R.; Triulzi, T.; et al. Extracellular matrix proteins as diagnostic markers of breast carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6280–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Deng, L.; Zhu, J.; Rychahou, P.G.; Xu, R. Prolyl-4-hydroxylase α subunit 2 promotes breast cancer progression and metastasis by regulating collagen deposition. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Kawasaki, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Nagata, K.; Li, Z.; Zhou, B.P.; et al. Hsp47 promotes cancer metastasis by enhancing collagen-dependent cancer cell-platelet interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3748–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioachim, E.; Charchanti, A.; Briasoulis, E.; Karavasilis, V.; Tsanou, H.; Arvanitis, D.L.; Agnantis, N.J.; Pavlidis, N. Immunohistochemical expression of extracellular matrix components tenascin, fibronectin, collagen type IV and laminin in breast cancer: Their prognostic value and role in tumour invasion and progression. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeldag, G.; Rice, A.; Del Río Hernández, A. Chemoresistance and the Self-Maintaining Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2018, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, G.-F.; Xu, R. Function of cancer cell-derived extracellular matrix in tumor progression. JCMT 2016, 2, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naba, A.; Clauser, K.R.; Lamar, J.M.; Carr, S.A.; Hynes, R.O. Extracellular matrix signatures of human mammary carcinoma identify novel metastasis promoters. Elife 2014, 3, e01308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rybinska, I.; Sandri, M.; Bianchi, F.; Orlandi, R.; de Cecco, L.; Gasparini, P.; Campiglio, M.; Paolini, B.; Sfondrini, L.; Tagliabue, E.; et al. Extracellular Matrix Features Discriminate Aggressive HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Who Benefit from Trastuzumab Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meads, M.B.; Gatenby, R.A.; Dalton, W.S. Environment-mediated drug resistance: A major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, J.S.; Cress, A.E.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Shtil, A.A.; Dalton, W.S. Cell Adhesion Mediated Drug Resistance (CAM-DR): Role of Integrins and Resistance to Apoptosis in Human Myeloma Cell Lines. Blood 1999, 93, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovitt, C.J.; Shelper, T.B.; Avery, V.M. Doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated by extracellular matrix proteins. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piva, M.B.R.; Jakubzig, B.; Bendas, G. Integrin Activation Contributes to Lower Cisplatin Sensitivity in MV3 Melanoma Cells by Inducing the Wnt Signalling Pathway. Cancers 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakubzig, B.; Baltes, F.; Henze, S.; Schlesinger, M.; Bendas, G. Mechanisms of Matrix-Induced Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer Cells-Deciphering Novel Potential Targets for a Cell Sensitization. Cancers 2018, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baltes, F.; Pfeifer, V.; Silbermann, K.; Caspers, J.; Wantoch von Rekowski, K.; Schlesinger, M.; Bendas, G. β1-Integrin binding to collagen type 1 transmits breast cancer cells into chemoresistance by activating ABC efflux transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitinger, B. Discoidin domain receptor functions in physiological and pathological conditions. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 310, 39–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hur, H.; Ham, I.-H.; Lee, D.; Jin, H.; Aguilera, K.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Han, S.-U.; Kwon, J.E.; Kim, Y.-B.; Ding, K.; et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 activity drives an aggressive phenotype in gastric carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toy, K.A.; Valiathan, R.R.; Núñez, F.; Kidwell, K.M.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Fridman, R.; Kleer, C.G. Tyrosine kinase discoidin domain receptors DDR1 and DDR2 are coordinately deregulated in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borza, C.M.; Pozzi, A. Discoidin domain receptors in disease. Matrix Biol. 2014, 34, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, W.; Gish, G.D.; Alves, F.; Pawson, T. The Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Are Activated by Collagen. Mol. Cell 1997, 1, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, B.; Bühren, S.; Böck, B.; Alves, F.; Vogel, W.F.; Kiefer, F. Migration inhibition of mammary epithelial cells by Syk is blocked in the presence of DDR1 receptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3757–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C.; Andersson, T.; Vogel, W.F. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 regulates breast cancer cell migration downstream of the receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 4011–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, C.; Tuariihionoa, A.; Bacou, M.; Souleyreau, W.; Sala, M.; Henriet, E.; Bikfalvi, A.; Saltel, F.; Auguste, P. DDR1 and DDR2 physical interaction leads to signaling interconnection but with possible distinct functions. Cell Adh. Migr. 2018, 12, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-R.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Lo, F.-Y.; Tang, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-K. DDR1 promotes E-cadherin stability via inhibition of integrin-β1-Src activation-mediated E-cadherin endocytosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Bihan, D.; Chang, F.; Huang, P.H.; Farndale, R.W.; Leitinger, B. Discoidin domain receptors promote α1β1- and α2β1-integrin mediated cell adhesion to collagen by enhancing integrin activation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongusaha, P.P.; Kim, J.-I.; Fang, L.; Wong, T.W.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Aaronson, S.A.; Lee, S.W. p53 induction and activation of DDR1 kinase counteract p53-mediated apoptosis and influence p53 regulation through a positive feedback loop. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Ongusaha, P.P.; Yang, Y.S.; Park, J.-M.; Aaronson, S.A.; Lee, S.W. Discoidin domain receptor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase induces cyclooxygenase-2 and promotes chemoresistance through nuclear factor-kappaB pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8123–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-C.; Zhang, Y.; He, S.-J.; Li, M.-M.; Cai, X.-L.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.-M.; Cao, J. TM4SF1 Promotes Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer via Regulating the Expression of DDR1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Pu, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qiu, Z.; Xiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W. Transmembrane-4 L-six family member-1 (TM4SF1) promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, invasion and chemo-resistance through regulating the DDR1/Akt/ERK-mTOR axis. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.-L.; Valiathan, R.R.; Arkwright, R.; Sohail, A.; Mihai, C.; Kumarasiri, M.; Mahasenan, K.V.; Mobashery, S.; Huang, P.; Agarwal, G.; et al. Discoidin domain receptors: Unique receptor tyrosine kinases in collagen-mediated signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7430–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tornillo, G.; Knowlson, C.; Kendrick, H.; Cooke, J.; Mirza, H.; Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez, I.; Vivanco, M.D.M.; Buckley, N.E.; Grigoriadis, A.; Smalley, M.J. Dual Mechanisms of LYN Kinase Dysregulation Drive Aggressive Behavior in Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3674–3692.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilancio, A.; Migliaccio, A. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase assay in breast cancer cell extracts. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1204, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paplomata, E.; O’Regan, R. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer: Targets, trials and biomarkers. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2014, 6, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, E.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Askarian-Amiri, M.; Rewcastle, G.W.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C. Relationships between signaling pathway usage and sensitivity to a pathway inhibitor: Examination of trametinib responses in cultured breast cancer lines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saby, C.; Collin, G.; Sinane, M.; Buache, E.; van Gulick, L.; Saltel, F.; Maquoi, E.; Morjani, H. DDR1 and MT1-MMP Expression Levels Are Determinant for Triggering BIK-Mediated Apoptosis by 3D Type I Collagen Matrix in Invasive Basal-Like Breast Carcinoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Duan, L.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; et al. Discovery and optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo1,5-apyrimidin-6-yl)ethynyl)benzamides as novel selective and orally bioavailable discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.-P.; Chen, W.-D.; Peng, J.-R.; Xu, Y.-D.; Cai, Q.; Feng, G.-K.; Ding, K.; Zhu, X.-F.; Guan, Z. Antitumor activity of 7RH, a discoidin domain receptor 1 inhibitor, alone or in combination with dasatinib exhibits antitumor effects in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 3598–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robitaille, H.; Simard-Bisson, C.; Larouche, D.; Tanguay, R.M.; Blouin, R.; Germain, L. The small heat-shock protein Hsp27 undergoes ERK-dependent phosphorylation and redistribution to the cytoskeleton in response to dual leucine zipper-bearing kinase expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidyasagar, A.; Wilson, N.A.; Djamali, A. Heat shock protein 27 (HSP27): Biomarker of disease and therapeutic target. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair 2012, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huafeng, J.; Deqing, Z.; Yong, D.; Yulian, Z.; Ailing, H. A cross-talk between integrin β4 and epidermal growth factor receptor induces gefitinib chemoresistance to gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tai, Y.-L.; Chu, P.-Y.; Lai, I.-R.; Wang, M.-Y.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Guan, J.-L.; Liou, J.-Y.; Shen, T.-L. An EGFR/Src-dependent β4 integrin/FAK complex contributes to malignancy of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Bronte, V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crawford, R.R.; Potukuchi, P.K.; Schuetz, E.G.; Schuetz, J.D. Beyond Competitive Inhibition: Regulation of ABC Transporters by Kinases and Protein-Protein Interactions as Potential Mechanisms of Drug-Drug Interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alday-Parejo, B.; Stupp, R.; Rüegg, C. Are Integrins Still Practicable Targets for Anti-Cancer Therapy? Cancers 2019, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, H.; Song, J.; Zheng, J. Discoidin domain receptor 1: New star in cancer-targeted therapy and its complex role in breast carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3403–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.; Woo, Y.; Valiathan, R.R.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, H.-R.C.; Fridman, R.; Moon, A. Discoidin domain receptor 1 is a novel transcriptional target of ZEB1 in breast epithelial cells undergoing H-Ras-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E508-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Tang, M.-J. Dichotomy of the function of DDR1 in cells and disease progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 118473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Hui, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, Z.; Ning, Y. Suppressing miR-199a-3p by promoter methylation contributes to tumor aggressiveness and cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer through promoting DDR1 expression. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cader, F.Z.; Vockerodt, M.; Bose, S.; Nagy, E.; Brundler, M.-A.; Kearns, P.; Murray, P.G. The EBV oncogene LMP1 protects lymphoma cells from cell death through the collagen-mediated activation of DDR1. Blood 2013, 122, 4237–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rammal, H.; Saby, C.; Magnien, K.; Van-Gulick, L.; Garnotel, R.; Buache, E.; El Btaouri, H.; Jeannesson, P.; Morjani, H. Discoidin Domain Receptors: Potential Actors and Targets in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.; Waters, B.; Spiegel, K.; Alnadaf, T.; Manley, P.W.; Buchdunger, E.; Walker, C.; Jarai, G. Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, K.Y.; Huang, H.; Du, W.; Hagopian, M.M.; Wang, Z.; Hinz, S.; Hwang, T.H.; Wang, H.; Fleming, J.B.; Castrillon, D.H.; et al. Inhibition of Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 Reduces Collagen-mediated Tumorigenicity in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2473–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisticò, P.; Di Modugno, F.; Spada, S.; Bissell, M.J. β1 and β4 integrins: From breast development to clinical practice. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Isaji, T.; Hang, Q.; Im, S.; Fukuda, T.; Gu, J. Distinct effects of β1 integrin on cell proliferation and cellular signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuhlmiller, T.J.; Miller, S.M.; Zawistowski, J.S.; Nakamura, K.; Beltran, A.S.; Duncan, J.S.; Angus, S.P.; Collins, K.A.L.; Granger, D.A.; Reuther, R.A.; et al. Inhibition of Lapatinib-Induced Kinome Reprogramming in ERBB2-Positive Breast Cancer by Targeting BET Family Bromodomains. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canonici, A.; Browne, A.L.; Ibrahim, M.F.K.; Fanning, K.P.; Roche, S.; Conlon, N.T.; O’Neill, F.; Meiller, J.; Cremona, M.; Morgan, C.; et al. Combined targeting EGFR and SRC as a potential novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835919897546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-Y.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, S.-w.; Hwang, J.J.; Lim, C.; Lee, G.; Seo, J.; Cho, S.Y.; et al. Dual inhibition of MEK1/2 and EGFR synergistically induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in EGFR inhibitor-resistant lung cancer cells via BIM upregulation. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caumanns, J.J.; van Wijngaarden, A.; Kol, A.; Meersma, G.J.; Jalving, M.; Bernards, R.; van der Zee, A.G.J.; Wisman, G.B.A.; de Jong, S. Low-dose triple drug combination targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and the MAPK pathway is an effective approach in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 461, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfankuchen, D.B.; Baltes, F.; Batool, T.; Li, J.-P.; Schlesinger, M.; Bendas, G. Heparin antagonizes cisplatin resistance of A2780 ovarian cancer cells by affecting the Wnt signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67553–67566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, S.C.; Silbermann, K.; Wiese, M. Phenyltetrazolyl-phenylamides: Substituent impact on modulation capability and selectivity toward the efflux protein ABCG2 and investigation of interaction with the transporter. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baltes, F.; Caspers, J.; Henze, S.; Schlesinger, M.; Bendas, G. Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Signaling and Its Crosstalk with β1-Integrin Emerges as a Key Factor for Breast Cancer Chemosensitization upon Collagen Type 1 Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144956
Baltes F, Caspers J, Henze S, Schlesinger M, Bendas G. Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Signaling and Its Crosstalk with β1-Integrin Emerges as a Key Factor for Breast Cancer Chemosensitization upon Collagen Type 1 Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144956
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaltes, Fabian, Julia Caspers, Svenja Henze, Martin Schlesinger, and Gerd Bendas. 2020. "Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Signaling and Its Crosstalk with β1-Integrin Emerges as a Key Factor for Breast Cancer Chemosensitization upon Collagen Type 1 Binding" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144956
APA StyleBaltes, F., Caspers, J., Henze, S., Schlesinger, M., & Bendas, G. (2020). Targeting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Signaling and Its Crosstalk with β1-Integrin Emerges as a Key Factor for Breast Cancer Chemosensitization upon Collagen Type 1 Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144956