Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4-Associated KChIP Proteins in the Rat Cerebellum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
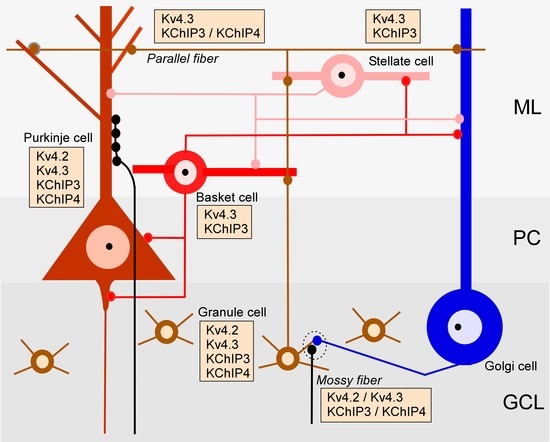
2.1. Regional Distribution of Kv4 and KChIPs in the Cerebellum
2.2. Subcellular Localisation of KChIP3 in the Cerebellum
2.3. Subcellular Localisation of KChIP4 in the Cerebellum
2.4. Subcellular Localisation of Kv4 in the Cerebellum
3. Discussion
3.1. KChIP3 and KChIP4 Are Expressed in Purkinje Cells and Granule Cells
3.2. KChIP and Kv4 Compartmentalisation in Cerebellar Neurons
3.3. Other Subcellular Locations for KChIP and Kv4 α Subunits Are Possible
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Antibodies and Chemicals
4.3. Immunohistochemistry for Light Microscopy
4.4. Immunohistochemistry for Electron Microscopy
4.5. Quantification of KChIPs and Kv4 Channel Immunoreactivities
4.6. Controls
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sotelo, C. Cellular and genetic regulation of the development of the cerebellar system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 72, 295–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M. Cerebellar Long-Term Depression: Characterization, Signal Transduction, and Functional Roles. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1143–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M. Cerebellar circuitry as a neuronal machine. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 78, 272–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillitoe, R.V.; Joyner, A.L. Morphology, molecular codes, and circuitry produce the three-dimensional complexity of the cerebellum. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 549–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, J.S. Subcellular localization of K+ channels in mammalian brain neurons: Remarkable precision in the midst of extraordinary complexity. Neuron 2015, 85, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, S.G.; Varga, A.W.; Yuan, L.-L.; Anderson, A.E.; Sweatt, J.D.; Schrader, L.A. Structure and function of Kv4-family transient potassium channels. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 803–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerng, H.H.; Pfaffinger, P.J.; Covarrubias, M. Molecular physiology and modulation of somatodendritic A-type potassium channels. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.D.; Choi, E.K.; Luo, Y.; Lilliehook, C.; Crowley, A.C.; Merriam, D.E.; Wasco, W. Calsenilin: A calcium-binding protein that interacts with the presenilins and regulates the levels of a presenilin fragment. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohashi, Y.; Hatano, N.; Ohya, S.; Takikawa, R.; Watabiki, T.; Takasugi, N.; Imaizumi, Y.; Tomita, T.; Iwatsubo, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of CALP/KChIP4, a novel EF-hand protein interacting with presenilin 2 and voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14965–14975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, W.F.; Bowlby, M.R.; Betty, M.; Cao, J.; Ling, H.-P.; Mendoza, G.; Hinson, J.W.; Mattsson, K.I.; Strassle, B.W.; Trimmer, J.S.; et al. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature 2000, 403, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, M.S.; Ozaita, A.; Amarillo, Y.; Vega-Saenz de Miera, E.; Ma, Y.; Mo, W.; Goldberg, E.M.; Misumi, Y.; Ikehara, Y.; Neubert, T.A.; et al. The CD26-related dipeptidyl aminopeptidase-like protein DPPX is a critical component of neuronal A-type K+ channels. Neuron 2003, 37, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmqvist, M.H.; Cao, J.; Hernandez-Pineda, R.; Jacobson, M.D.; Carroll, K.I.; Sung, M.A.; Betty, M.; Ge, P.; Gilbride, K.J.; Brown, M.E.; et al. Elimination of fast inactivation in Kv4 A-type potassium channels by an auxiliary subunit domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pruunsild, P.; Timmusk, T. Structure, alternative splicing, and expression of the human and mouse KCNIP gene family. Genomics 2005, 86, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongs, O.; Schwarz, J.R. Ancillary subunits associated with voltage-dependent K+ channels. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 755–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, R.; Misonou, H.; Campomanes, C.R.; Anderson, A.E.; Schrader, L.A.; Doliveira, L.C.; Carroll, K.I.; Sweatt, J.D.; Rhodes, K.J.; Trimmer, J.S. A fundamental role for KChIPs in determining the molecular properties and trafficking of Kv4.2 potassium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36445–36454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasdemir, B.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Prior, I.A.; Tepikin, A.V.; Burgoyne, R.D. Traffic of Kv4 K+ channels mediated by KChIP1 is via a novel post-ER vesicular pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menegola, M.; Trimmer, J.S. Unanticipated region- and cell-specific downregulation of individual KChIP auxiliary subunit isotypes in Kv4.2 knock-out mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12137–12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Kovacs, I.; Zhang, Z. Differential distribution of KChIPs mRNAs in adult mouse brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 128, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, K.J.; Carroll, K.I.; Sung, M.A.; Doliveira, L.C.; Monaghan, M.M.; Burke, S.L.; Strassle, B.W.; Buchwalder, L.; Menegola, M.; Cao, J.; et al. KChIPs and Kv4 alpha subunits as integral components of A-type potassium channels in mammalian brain. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7903–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, J.; Rainnie, D.G. Expression and distribution of Kv4 potassium channel subunits and potassium channel interacting proteins in subpopulations of interneurons in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strassle, B.W.; Menegola, M.; Rhodes, K.J.; Trimmer, J.S. Light and electron microscopic analysis of KChIP and Kv4 localization in rat cerebellar granule cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 484, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serôdio, P.; Rudy, B. Differential expression of Kv4 K+ channel subunits mediating subthreshold transient K+ (A-type) currents in rat brain. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 79, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfaro-Ruíz, R.; Aguado, C.; Martín-Belmonte, A.; Moreno-Martínez, A.E.; Luján, R. Expression, Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 Channels in the Rodent Hippocampus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibata, R.; Nakahira, K.; Shibasaki, K.; Wakazono, Y.; Imoto, K.; Ikenaka, K. A-type K+ current mediated by the Kv4 channel regulates the generation of action potential in developing cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 4145–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacco, T.; Tempia, F. A-type potassium currents active at subthreshold potentials in mouse cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Physiol. 2002, 543, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Y.; Liang, P.; Wang, K.W. Enhanced trafficking of tetrameric Kv4.3 channels by KChIP1 clamping. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaur, M.L.; Chou, C.C.; Shih, Y.H.; Wang, H.L. Cloning, expression and CNS distribution of Kv4.3, an A-type K+ channel alpha subunit. FEBS Lett. 1997, 400, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amarillo, Y.; De Santiago-Castillo, J.A.; Dougherty, K.; Maffie, J.; Kwon, E.; Covarrubias, M.; Rudy, B. Ternary Kv4.2 channels recapitulate voltage-dependent inactivation kinetics of A-type K+ channels in cerebellar granule neurons. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.P.; Zhan, X.; Zamponi, G.W.; Turner, R.W. Long-Term Potentiation at the Mossy Fiber-Granule Cell Relay Invokes Postsynaptic Second-Messenger Regulation of Kv4 Channels. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11196–11207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinás, R.R. The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: Insights into central nervous system function. Science 1988, 242, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, L.-L.; Zhao, C.; Birnbaum, S.G.; Frick, A.; Jung, W.E.; Schwarz, T.L.; Sweatt, J.D.; Johnston, D. Deletion of Kv4.2 gene eliminates dendritic A-type K+ current and enhances induction of long-term potentiation in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12143–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoxha, E.; Balbo, I.; Miniaci, M.C.; Tempia, F. Purkinje Cell Signaling Deficits in Animal Models of Ataxia. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, C.A.; Kalmar, L.; Matiasek, K.; Mari, L.; Kyöstilä, K.; Lohi, H.; Schofield, E.C.; Mellersh, C.S.; De Risio, L.; Ricketts, S.L. Characterisation of canine KCNIP4: A novel gene for cerebellar ataxia identified by whole-genome sequencing two affected Norwegian Buhund dogs. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cull-Candy, S.G.; Marshall, C.G.; Ogden, D. Voltage-activated membrane currents in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J. Physiol. 1989, 414, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, M.; Tsaur, M.L.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y. Subcellular segregation of two A-type K+ channel proteins in rat central neurons. Neuron 1992, 9, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, G.; Widmer, H. Clustering of KV4.2 potassium channels in postsynaptic membrane of rat supraoptic neurons: An ultrastructural study. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinno, S.; Jeromin, A.; Kosaka, T. Postsynaptic and extrasynaptic localization of Kv4.2 channels in the mouse hippocampal region, with special reference to targeted clustering at gabaergic synapses. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhalter, A.; Gonchar, Y.; Mellor, R.L.; Nerbonne, J.M. Differential expression of I(A) channel subunits Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in mouse visual cortical neurons and synapses. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12274–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoyne, R.D. Neuronal calcium sensor proteins: Generating diversity in neuronal Ca2+ signalling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitazawa, M.; Kubo, Y.; Nakajo, K. The stoichiometry and biophysical properties of the Kv4 potassium channel complex with K+ channel-interacting protein (KChIP) subunits are variable, depending on the relative expression level. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17597–17609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, K.; Xiong, H.; Shin, Y.; Wang, D.; Deerinck, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ellisman, M.H.; Lipton, S.A.; Tong, G.; Descalzi, G.; et al. Roles of KChIP1 in the regulation of GABA-mediated transmission and behavioral anxiety. Mol. Brain 2010, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buxbaum, J.D. A role for calsenilin and related proteins in multiple aspects of neuronal function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciruela, F.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Sahlholm, K.; Fernández-Alacid, L.; Nicolau, J.C.; Watanabe, M.; Luján, R. Evidence for oligomerization between GABAB receptors and GIRK channels containing the GIRK1 and GIRK3 subunits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, A.; Prestori, F.; Rossi, P.; Taglietti, V.; D’Angelo, E. Presynaptic current changes at the mossy fiber-granule cell synapse of cerebellum during LTP. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lujan, R.; Nusser, Z.; Roberts, J.D.; Shigemoto, R.; Somogyi, P. Perisynaptic location of metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR1 and mGluR5 on dendrites and dendritic spines in the rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luján, R.; Shigemoto, R. Localization of metabotropic GABA receptor subunits GABAB1 and GABAB2 relative to synaptic sites in the rat developing cerebellum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfaro-Ruíz, R.; Aguado, C.; Martín-Belmonte, A.; Moreno-Martínez, A.E.; Luján, R. Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4-Associated KChIP Proteins in the Rat Cerebellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176403
Alfaro-Ruíz R, Aguado C, Martín-Belmonte A, Moreno-Martínez AE, Luján R. Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4-Associated KChIP Proteins in the Rat Cerebellum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(17):6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176403
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfaro-Ruíz, Rocío, Carolina Aguado, Alejandro Martín-Belmonte, Ana Esther Moreno-Martínez, and Rafael Luján. 2020. "Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4-Associated KChIP Proteins in the Rat Cerebellum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 17: 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176403
APA StyleAlfaro-Ruíz, R., Aguado, C., Martín-Belmonte, A., Moreno-Martínez, A. E., & Luján, R. (2020). Cellular and Subcellular Localisation of Kv4-Associated KChIP Proteins in the Rat Cerebellum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(17), 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176403