Flying Together: Drosophila as a Tool to Understand the Genetics of Human Alcoholism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Drosophila Melanogaster Is a Tractable Model for AUD
2.1. Advantages of Using Flies for AUD Research
2.2. Drosophila Alcohol Assays Establish Flies as an Effective AUD Model System
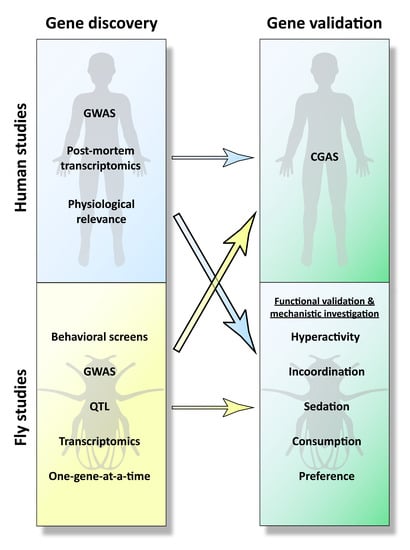
3. From Mammalian Gene Discovery to Fly Functional Testing
3.1. Human Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
3.2. Transcriptomics on Post-Mortem Human Tissue
3.3. Rodent GWAS, QTL Analyses, and Transcriptomics
3.4. Targeting Genes with Established Physiological Relevance
3.5. Summary of Human-to-Fly Approaches
4. From Fly Gene Discovery to Human Association
4.1. Behavioral Screens in Drosophila
4.2. Fly GWAS and QTL Analyses
4.3. Drosophila Transcriptomics
4.4. Summary of Fly-to-Human Studies
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATAC-seq | Assay for transposase-accessible chromatin-sequencing |
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| CGAS | Candidate gene association study |
| ChIP-seq | Chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing |
| DGRP | Drosophila Genetic Reference Panel |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FGFR | Fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| HDM | Histone demethylase |
| Men | Malic enzyme |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
| RNA-seq | RNA-sequencing |
| UAS | Upstream activating sequence |
References
- USA Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. National Survey on Drug Use and Health 2016 (NSDUH-2016-DS0001). 2018. Available online: https://datafiles.samhsa.gov/ (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Danaei, G.; Ding, E.L.; Mozaffarian, D.; Taylor, B.; Rehm, J.; Murray, C.J.; Ezzati, M. The preventable causes of death in the United States: Comparative risk assessment of dietary, lifestyle, and metabolic risk factors. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W.H.O. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, J.J.; Gonzales, K.R.; Bouchery, E.E.; Tomedi, L.E.; Brewer, R.D. 2010 National and State Costs of Excessive Alcohol Consumption. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, e73–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association (Ed.) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, D.; Oroszi, G.; Ducci, F. The genetics of addictions: Uncovering the genes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J. Cellular basis of memory for addiction. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trudell, J.R.; Messing, R.O.; Mayfield, J.; Harris, R.A. Alcohol dependence: Molecular and behavioral evidence. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, G.L.; Taber, K.; Vinton, E.; Crocker, A.J. Studying alcohol use disorder using Drosophila melanogaster in the era of ‘Big Data’. Behav. Brain Funct. BBF 2019, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, S.P.; Harris, R.A.; Ponomarev, I. Epigenetic modulation of brain gene networks for cocaine and alcohol abuse. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozova, T.V.; Mackay, T.F.; Anholt, R.R. Transcriptional networks for alcohol sensitivity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2011, 187, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponomarev, I.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene coexpression networks in human brain identify epigenetic modifications in alcohol dependence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, D.A.; López-León, S.; Shin, H.D.; Park, B.L.; Kim, D.-J. Meta-analysis of six genes (BDNF, DRD1, DRD3, DRD4, GRIN2B and MAOA) involved in neuroplasticity and the risk for alcohol dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 149, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.C.; Whitfield, J.B.; Martin, N.G.; Pergadia, M.L.; Goate, A.M.; Lind, P.A.; McEvoy, B.P.; Schrage, A.J.; Grant, J.D.; Chou, Y.-L.; et al. A Quantitative-Trait Genome-Wide Association Study of Alcoholism Risk in the Community: Findings and Implications. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Khoury, M.J. Implications of small effect sizes of individual genetic variants on the design and interpretation of genetic association studies of complex diseases. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, M.; Yang, S.Y.; Jeong, B.S.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, J.-W.; Chung, J.-H.; Kim, S.A. Association study of polymorphisms in N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor 2B subunits (GRIN2B) gene with Korean alcoholism. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 56, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenberg, H.J.; Foroud, T. Genetics and alcoholism. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenberg, H.J.; Foroud, T. Genetics of alcoholism. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawa, E.A.; Hall, S.D.; Lohoff, F.W. Overview of the Genetics of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Alcohol. (Oxf. Oxfs.) 2016, 51, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farris, S.P.; Arasappan, D.; Hunicke-Smith, S.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Transcriptome organization for chronic alcohol abuse in human brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korpi, E.R.; den Hollander, B.; Farooq, U.; Vashchinkina, E.; Rajkumar, R.; Nutt, D.J.; Hyytiä, P.; Dawe, G.S. Mechanisms of Action and Persistent Neuroplasticity by Drugs of Abuse. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 872–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nestler, E.J. Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, A.S.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene expression profiling in the human alcoholic brain. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, J.D.; Miller, A.P.; Gizer, I.R. Genetics of alcohol use disorder: A review. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.B.; Kranzler, H.R. Alcohol Dependence Genetics: Lessons Learned From Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) and Post-GWAS Analyses. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvatore, J.E.; Han, S.; Farris, S.P.; Mignogna, K.M.; Miles, M.F.; Agrawal, A. Beyond genome-wide significance: Integrative approaches to the interpretation and extension of GWAS findings for alcohol use disorder. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.M.; Yandell, M.D.; Wortman, J.R.; Gabor Miklos, G.L.; Nelson, C.R.; Hariharan, I.K.; Fortini, M.E.; Li, P.W.; Apweiler, R.; Fleischmann, W.; et al. Comparative genomics of the eukaryotes. Science (N.Y.) 2000, 287, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaun, K.R.; Devineni, A.V.; Heberlein, U. Drosophila melanogaster as a model to study drug addiction. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiter, L.T.; Potocki, L.; Chien, S.; Gribskov, M.; Bier, E. A systematic analysis of human disease-associated gene sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aquadro, C.F.; Bauer DuMont, V.; Reed, F.A. Genome-wide variation in the human and fruitfly: A comparison. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, N.A.; Sayed, R.; Zhang, Q.; Scoggin, S.; Eliazer, S.; Rothenfluh, A.; Buszczak, M. Systematic discovery of genetic modulation by Jumonji histone demethylases in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, A.W.; Lim, J.; Kliethermes, C.L.; Berger, K.H.; Joslyn, G.; Brush, G.; Xue, L.; Robertson, M.; Moore, M.S.; Vranizan, K.; et al. An evolutionary conserved role for anaplastic lymphoma kinase in behavioral responses to ethanol. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Aragam, N.; Zeng, M. A meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies identifies 3 new loci for alcohol dependence. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenberg, H.J.; Koller, D.L.; Xuei, X.; Wetherill, L.; McClintick, J.N.; Almasy, L.; Bierut, L.J.; Bucholz, K.K.; Goate, A.; Aliev, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates a region on chromosome 11. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Cao, X.; Chu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J. The Drosophila homolog of jwa is required for ethanol tolerance. Alcohol Alcohol. (Oxf. Oxfs.) 2008, 43, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovanen, L.; Saarikoski, S.T.; Haukka, J.; Pirkola, S.; Aromaa, A.; Lönnqvist, J.; Partonen, T. Circadian clock gene polymorphisms in alcohol use disorders and alcohol consumption. Alcohol Alcohol. (Oxf. Oxfs.) 2010, 45, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, J.B.; Ghezzi, A.; Lew, L.K.; Robles, R.B.; Cormack, L.; Atkinson, N.S. Circadian genes differentially affect tolerance to ethanol in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorgenson, E.; Thai, K.K.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Sakoda, L.C.; Kvale, M.N.; Banda, Y.; Schaefer, C.; Risch, N.; Mertens, J.; Weisner, C.; et al. Genetic contributors to variation in alcohol consumption vary by race/ethnicity in a large multi-ethnic genome-wide association study. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, M.; Wang, J.C.; Wetherill, L.; Le, N.; Bertelsen, S.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Budde, J.; Agrawal, A.; Bucholz, K.; Dick, D.; et al. A meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies to identify novel loci for maximum number of alcoholic drinks. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schumann, G.; Coin, L.J.; Lourdusamy, A.; Charoen, P.; Berger, K.H.; Stacey, D.; Desrivieres, S.; Aliev, F.A.; Khan, A.A.; Amin, N.; et al. Genome-wide association and genetic functional studies identify autism susceptibility candidate 2 gene (AUTS2) in the regulation of alcohol consumption. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7119–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayfield, R.D.; Lewohl, J.M.; Dodd, P.R.; Herlihy, A.; Liu, J.; Harris, R.A. Patterns of gene expression are altered in the frontal and motor cortices of human alcoholics. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.; Hill, J.S.; Farris, S.P.; Costin, B.; Martin, I.; Chan, C.L.; Alaimo, J.T.; Bettinger, J.C.; Davies, A.G.; Miles, M.F.; et al. Chloride intracellular channels modulate acute ethanol behaviors in Drosophila, Caenorhabditis elegans and mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, R.F.; Lewellyn, L.; DeLoyht, J.M.; Sennett, K.; Coffman, S.; Hewitt, M.; Bettinger, J.C.; Warrick, J.M.; Grotewiel, M. Contrasting influences of Drosophila white/mini-white on ethanol sensitivity in two different behavioral assays. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohnke, M.D.; Kolb, W.; Kohnke, A.M.; Lutz, U.; Schick, S.; Batra, A. DBH*444G/A polymorphism of the dopamine-beta-hydroxylase gene is associated with alcoholism but not with severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna Austria 1996) 2006, 113, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, U.W.; Wurst, F.M.; Ridinger, M.; Rujescu, D.; Fehr, C.; Koller, G.; Bondy, B.; Wodarz, N.; Soyka, M.; Zill, P. Association of functional DBH genetic variants with alcohol dependence risk and related depression and suicide attempt phenotypes: Results from a large multicenter association study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013, 133, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, H.; Ramond, J.; Singh, C.M.; Heberlein, U. Functional ethanol tolerance in Drosophila. Neuron 2000, 28, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, P. Mutations in Bacchus reveal a tyramine-dependent nuclear regulator for acute ethanol sensitivity in Drosophila. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Ruppert, M.; Hendrich, O.; Giang, T.; Ogueta, M.; Hampel, S.; Vollbach, M.; Büschges, A.; Scholz, H. Neuronal basis of innate olfactory attraction to ethanol in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, A.; Lynskey, M.T.; Todorov, A.A.; Schrage, A.J.; Littlefield, A.K.; Grant, J.D.; Zhu, Q.; Nelson, E.C.; Madden, P.A.; Bucholz, K.K.; et al. A candidate gene association study of alcohol consumption in young women. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, L.M.; Kalsi, G.; Aliev, F.; Kuo, P.H.; Prescott, C.A.; Patterson, D.G.; Walsh, D.; Dick, D.M.; Riley, B.P.; Kendler, K.S. Limited associations of dopamine system genes with alcohol dependence and related traits in the Irish Affected Sib Pair Study of Alcohol Dependence (IASPSAD). Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozova, T.V.; Huang, W.; Pray, V.A.; Whitham, T.; Anholt, R.R.; Mackay, T.F. Polymorphisms in early neurodevelopmental genes affect natural variation in alcohol sensitivity in adult drosophila. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, M.L.; Lamina, O.; Hogan, K.E.; Kliethermes, C.L. Common genes regulate food and ethanol intake in Drosophila. Alcohol (Fayettev. N. Y.) 2016, 53, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertes, D.A.; Kalsi, G.; Prescott, C.A.; Kuo, P.H.; Patterson, D.G.; Walsh, D.; Kendler, K.S.; Riley, B.P. Neurotransmitter and neuromodulator genes associated with a history of depressive symptoms in individuals with alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimers, M.A.; Riley, B.P.; Kalsi, G.; Kertes, D.A.; Kendler, K.S. Pathway based analysis of genotypes in relation to alcohol dependence. Pharm. J. 2012, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzitoyeva, S.; Dimitrijevic, N.; Manev, H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor 1 mediates behavior-impairing actions of alcohol in Drosophila: Adult RNA interference and pharmacological evidence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5485–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wernicke, C.; Samochowiec, J.; Schmidt, L.G.; Winterer, G.; Smolka, M.; Kucharska-Mazur, J.; Horodnicki, J.; Gallinat, J.; Rommelspacher, H. Polymorphisms in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 1 and 2B subunits are associated with alcoholism-related traits. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpyak, V.M.; Geske, J.R.; Colby, C.L.; Mrazek, D.A.; Biernacka, J.M. Genetic variability in the NMDA-dependent AMPA trafficking cascade is associated with alcohol dependence. Addict. Biol. 2012, 17, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujescu, D.; Soyka, M.; Dahmen, N.; Preuss, U.; Hartmann, A.M.; Giegling, I.; Koller, G.; Bondy, B.; Möller, H.J.; Szegedi, A. GRIN1 locus may modify the susceptibility to seizures during alcohol withdrawal. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Psychiatr. Genet. 2005, 133b, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troutwine, B.; Park, A.; Velez-Hernandez, M.E.; Lew, L.; Mihic, S.J.; Atkinson, N.S. F654A and K558Q Mutations in NMDA Receptor 1 Affect Ethanol-Induced Behaviors in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 2480–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.L.; Salling, M.C.; Almli, L.M.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; Uddin, M.; Galea, S.; Wildman, D.E.; Aiello, A.E.; Bradley, B.; Ressler, K.; et al. Frequency of alcohol consumption in humans; the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors and downstream signaling pathways. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, A.; Muller, K.U.; Banaschewski, T.; Barker, G.J.; Bokde, A.L.W.; Bromberg, U.; Buchel, C.; Conrod, P.; Fauth-Buhler, M.; Papadopoulos, D.; et al. Prediction of alcohol drinking in adolescents: Personality-traits, behavior, brain responses, and genetic variations in the context of reward sensitivity. Biol. Psychol. 2016, 118, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wedow, R.; Li, Y.; Brazel, D.M.; Chen, F.; Datta, G.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; McGuire, D.; Tian, C.; et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urizar, N.L.; Yang, Z.; Edenberg, H.J.; Davis, R.L. Drosophila homer is required in a small set of neurons including the ellipsoid body for normal ethanol sensitivity and tolerance. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4541–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslyn, G.; Ravindranathan, A.; Brush, G.; Schuckit, M.; White, R.L. Human variation in alcohol response is influenced by variation in neuronal signaling genes. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corl, A.B.; Rodan, A.R.; Heberlein, U. Insulin signaling in the nervous system regulates ethanol intoxication in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, S.F.; Peru y Colon de Portugal, R.L.; Gonzalez, D.A.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. S6 Kinase Reflects and Regulates Ethanol-Induced Sedation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15396–15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, P.; Kendler, K.S.; Bettinger, J.C.; Davies, A.G.; Grotewiel, M. An assay for evoked locomotor behavior in Drosophila reveals a role for integrins in ethanol sensitivity and rapid ethanol tolerance. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendler, K.S.; Kalsi, G.; Holmans, P.A.; Sanders, A.R.; Aggen, S.H.; Dick, D.M.; Aliev, F.; Shi, J.; Levinson, D.F.; Gejman, P.V. Genomewide association analysis of symptoms of alcohol dependence in the molecular genetics of schizophrenia (MGS2) control sample. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowmeadow, R.B.; Krishnan, H.R.; Atkinson, N.S. The slowpoke gene is necessary for rapid ethanol tolerance in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowmeadow, R.B.; Krishnan, H.R.; Ghezzi, A.; Al’Hasan, Y.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Atkinson, N.S. Ethanol tolerance caused by slowpoke induction in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A.; Krishnan, H.R.; Atkinson, N.S. Susceptibility to ethanol withdrawal seizures is produced by BK channel gene expression. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghezzi, A.; Pohl, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Atkinson, N.S. BK channels play a counter-adaptive role in drug tolerance and dependence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16360–16365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaliere, S.; Gillespie, J.M.; Hodge, J.J. KCNQ channels show conserved ethanol block and function in ethanol behaviour. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasek, A.W.; Giorgetti, F.; Berger, K.H.; Tayor, S.; Heberlein, U. Lmo genes regulate behavioral responses to ethanol in Drosophila melanogaster and the mouse. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, R.E.; Shell, B.C.; Lee, K.M.; Shelton, K.L.; Mathies, L.D.; Edwards, A.C.; Grotewiel, M. Convergent Evidence From Humans and Drosophila melanogaster Implicates the Transcription Factor MEF2B/Mef2 in Alcohol Sensitivity. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1872–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, E.; Gao, H.; Chu, C.; Ntritsos, G.; Blakeley, P.; Butts, A.R.; Pazoki, R.; Suzuki, H.; Koskeridis, F.; Yiorkas, A.M.; et al. New alcohol-related genes suggest shared genetic mechanisms with neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2019, 3, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muench, C.; Schwandt, M.; Jung, J.; Cortes, C.R.; Momenan, R.; Lohoff, F.W. The major depressive disorder GWAS-supported variant rs10514299 in TMEM161B-MEF2C predicts putamen activation during reward processing in alcohol dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, P.; Orozco, D.; Randhawa, H.; Wolf, F.W. Mef2 induction of the immediate early gene Hr38/Nr4a is terminated by Sirt1 to promote ethanol tolerance. Genes Brain Behav. 2019, 18, e12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozova, T.V.; Ayroles, J.F.; Jordan, K.W.; Duncan, L.H.; Carbone, M.A.; Lyman, R.F.; Stone, E.A.; Govindaraju, D.R.; Ellison, R.C.; Mackay, T.F.; et al. Alcohol sensitivity in Drosophila: Translational potential of systems genetics. Genetics 2009, 183, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozova, T.V.; Anholt, R.R.; Mackay, T.F. Phenotypic and transcriptional response to selection for alcohol sensitivity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozova, T.V.; Anholt, R.R.; Mackay, T.F. Transcriptional response to alcohol exposure in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fochler, S.; Morozova, T.V.; Davis, M.R.; Gearhart, A.W.; Huang, W.; Mackay, T.F.C.; Anholt, R.R.H. Genetics of alcohol consumption in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunez, Y.O.; Mayfield, R.D. Understanding Alcoholism Through microRNA Signatures in Brains of Human Alcoholics. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghezzi, A.; Zomeno, M.; Pietrzykowski, A.Z.; Atkinson, N.S. Immediate-early alcohol-responsive miRNA expression in Drosophila. J. Neurogenet. 2016, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Z.; Kranzler, H.R.; Zhao, H.; Gruen, J.R.; Luo, X.; Gelernter, J. Association of haplotypic variants in DRD2, ANKK1, TTC12 and NCAM1 to alcohol dependence in independent case control and family samples. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.Z.; Kranzler, H.R.; Zhao, H.; Gruen, J.R.; Luo, X.; Gelernter, J. Haplotypic variants in DRD2, ANKK1, TTC12, and NCAM1 are associated with comorbid alcohol and drug dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Endo, K.; Wu, K.; Rodan, A.R.; Heberlein, U.; Davis, R.L. Drosophila fasciclinII is required for the formation of odor memories and for normal sensitivity to alcohol. Cell 2001, 105, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaskar, L.V.; Thangaraj, K.; Kumar, K.P.; Pardhasaradhi, G.; Singh, L.; Rao, V.R. Association between neuropeptide Y gene polymorphisms and alcohol dependence: A case-control study in two independent populations. Eur. Addict. Res. 2013, 19, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilveskoski, E.; Kajander, O.A.; Lehtimäki, T.; Kunnas, T.; Karhunen, P.J.; Heinälä, P.; Virkkunen, M.; Alho, H. Association of neuropeptide y polymorphism with the occurrence of type 1 and type 2 alcoholism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1420–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, J.; Kranzler, H.R.; Malison, R.; Price, L.H.; Van Dyck, C.; Rosenheck, R.A.; Cramer, J.; Southwick, S.; Charney, D.; Krystal, J.; et al. A functional neuropeptide Y Leu7Pro polymorphism associated with alcohol dependence in a large population sample from the United States. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottagui-Tabar, S.; Prince, J.A.; Wahlestedt, C.; Zhu, G.; Goldman, D.; Heilig, M. A novel single nucleotide polymorphism of the neuropeptide Y (NPY) gene associated with alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T.; Harada, S. Polymorphism of the neuropeptide Y gene: An association study with alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 59s–62s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Parrish, C.A.; Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Shen, P. Drosophila neuropeptide F and its receptor, NPFR1, define a signaling pathway that acutely modulates alcohol sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetherill, L.; Schuckit, M.A.; Hesselbrock, V.; Xuei, X.; Liang, T.; Dick, D.M.; Kramer, J.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Tischfield, J.A.; Porjesz, B.; et al. Neuropeptide Y receptor genes are associated with alcohol dependence, alcohol withdrawal phenotypes, and cocaine dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shohat-Ophir, G.; Kaun, K.R.; Azanchi, R.; Mohammed, H.; Heberlein, U. Sexual deprivation increases ethanol intake in Drosophila. Science (N.Y.) 2012, 335, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Comasco, E.; Nordquist, N.; Göktürk, C.; Aslund, C.; Hallman, J.; Oreland, L.; Nilsson, K.W. The clock gene PER2 and sleep problems: Association with alcohol consumption among Swedish adolescents. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 115, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banach, E.; Pawlak, J.; Kapelski, P.; Szczepankiewicz, A.; Rajewska-Rager, A.; Skibinska, M.; Czerski, P.; Twarowska-Hauser, J.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M. Clock genes polymorphisms in male bipolar patients with comorbid alcohol abuse. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linde, K.; Lyons, L.C. Circadian modulation of acute alcohol sensitivity but not acute tolerance in Drosophila. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.A.; Jia, T.; Pinzon, J.H.; Acevedo, S.F.; Ojelade, S.A.; Xu, B.; Tay, N.; Desrivieres, S.; Hernandez, J.L.; Banaschewski, T.; et al. The Arf6 activator Efa6/PSD3 confers regional specificity and modulates ethanol consumption in Drosophila and humans. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peru, Y.C.d.P.R.L.; Acevedo, S.F.; Rodan, A.R.; Chang, L.Y.; Eaton, B.A.; Rothenfluh, A. Adult neuronal Arf6 controls ethanol-induced behavior with Arfaptin downstream of Rac1 and RhoGAP18B. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 17706–17713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojelade, S.A.; Jia, T.; Rodan, A.R.; Chenyang, T.; Kadrmas, J.L.; Cattrell, A.; Ruggeri, B.; Charoen, P.; Lemaitre, H.; Banaschewski, T.; et al. Rsu1 regulates ethanol consumption in Drosophila and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4085–E4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adkins, A.E.; Hack, L.M.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Williamson, V.S.; McMichael, G.O.; Mamdani, M.; Edwards, A.C.; Aliev, F.; Chan, R.F.; Bhandari, P.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Alcohol Dependence Identifies Risk Loci Altering Ethanol-Response Behaviors in Model Organisms. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 911–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaht, M.; Kiive, E.; Veidebaum, T.; Harro, J. A Functional Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 1 (VMAT1) Gene Variant Is Associated with Affect and the Prevalence of Anxiety, Affective, and Alcohol Use Disorders in a Longitudinal Population-Representative Birth Cohort Study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, N.; Helton, S.G.; Schwandt, M.; Zhu, X.; Momenan, R.; Lohoff, F.W. Genetic Variation in the Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 1 (VMAT1/SLC18A1) Gene and Alcohol Withdrawal Severity. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, C.; Sommerlad, D.; Sander, T.; Anghelescu, I.; Dahmen, N.; Szegedi, A.; Mueller, C.; Zill, P.; Soyka, M.; Preuss, U.W. Association of VMAT2 gene polymorphisms with alcohol dependence. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna Austria 1996) 2013, 120, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, S.G.; Franke, P.E.; Hoefgen, B.; Guttenthaler, V.; Lichtermann, D.; Trixler, M.; Knapp, M.; Maier, W.; Wildenauer, D.B. Association of DNA polymorphisms in the synaptic vesicular amine transporter gene (SLC18A2) with alcohol and nicotine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, T.K.; Dempster, E.; Docherty, S.J.; Desrivieres, S.; Lourdsamy, A.; Wodarz, N.; Ridinger, M.; Maier, W.; Rietschel, M.; Schumann, G. Multiple polymorphisms in genes of the adrenergic stress system confer vulnerability to alcohol abuse. Addict. Biol. 2012, 17, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.C.; Woo, K.; Li, H.; Lebestky, T.; Mayer, N.; Sniffen, M.R.; Heberlein, U.; Bainton, R.J.; Hirsh, J.; Wolf, F.W. A pair of dopamine neurons target the D1-like dopamine receptor DopR in the central complex to promote ethanol-stimulated locomotion in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, B.P.; Kalsi, G.; Kuo, P.H.; Vladimirov, V.; Thiselton, D.L.; Vittum, J.; Wormley, B.; Grotewiel, M.S.; Patterson, D.G.; Sullivan, P.F.; et al. Alcohol dependence is associated with the ZNF699 gene, a human locus related to Drosophila hangover, in the Irish Affected Sib Pair Study of Alcohol Dependence (IASPSAD) sample. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholz, H.; Franz, M.; Heberlein, U. The hangover gene defines a stress pathway required for ethanol tolerance development. Nature 2005, 436, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. The genetics of behavioral alcohol responses in Drosophila. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand, A.H.; Perrimon, N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 1993, 118, 401–415. [Google Scholar]
- Jenett, A.; Rubin, G.M.; Ngo, T.T.; Shepherd, D.; Murphy, C.; Dionne, H.; Pfeiffer, B.D.; Cavallaro, A.; Hall, D.; Jeter, J.; et al. A GAL4-driver line resource for Drosophila neurobiology. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodan, A.R.; Kiger, J.A., Jr.; Heberlein, U. Functional dissection of neuroanatomical loci regulating ethanol sensitivity in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9490–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butts, A.R.; Ojelade, S.A.; Pronovost, E.D.; Seguin, A.; Merrill, C.B.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. Altered Actin Filament Dynamics in the Drosophila Mushroom Bodies Lead to Fast Acquisition of Alcohol Consumption Preference. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, A.; Al-Hasan, Y.M.; Krishnan, H.R.; Wang, Y.; Atkinson, N.S. Functional mapping of the neuronal substrates for drug tolerance in Drosophila. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghezzi, A.; Krishnan, H.R.; Lew, L.; Prado, F.J., 3rd; Ong, D.S.; Atkinson, N.S. Alcohol-induced histone acetylation reveals a gene network involved in alcohol tolerance. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.M.; Mathies, L.D.; Grotewiel, M. Alcohol sedation in adult Drosophila is regulated by Cysteine proteinase-1 in cortex glia. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parkhurst, S.J.; Adhikari, P.; Navarrete, J.S.; Legendre, A.; Manansala, M.; Wolf, F.W. Perineurial Barrier Glia Physically Respond to Alcohol in an Akap200-Dependent Manner to Promote Tolerance. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petruccelli, E.; Feyder, M.; Ledru, N.; Jaques, Y.; Anderson, E.; Kaun, K.R. Alcohol Activates Scabrous-Notch to Influence Associated Memories. Neuron 2018, 100, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinzon, J.H.; Reed, A.R.; Shalaby, N.A.; Buszczak, M.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. Alcohol-Induced Behaviors Require a Subset of Drosophila JmjC-Domain Histone Demethylases in the Nervous System. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Peabody, N.C.; Vinson, C.R.; White, B.H. Refined spatial manipulation of neuronal function by combinatorial restriction of transgene expression. Neuron 2006, 52, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, G.L.; Davis, F.P.; Picard, S.; Eddy, S.R. Cell type-specific genomics of Drosophila neurons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9691–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Weake, V.M. Affinity-based isolation of tagged nuclei from Drosophila tissues for gene expression analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Lee, P.J.; Dalton, J.E.; Nomie, K.J.; Stoica, L.; Costa-Mattioli, M.; Chang, P.; Nuzhdin, S.; Arbeitman, M.N.; Dierick, H.A. A versatile method for cell-specific profiling of translated mRNAs in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schauer, T.; Schwalie, P.C.; Handley, A.; Margulies, C.E.; Flicek, P.; Ladurner, A.G. CAST-ChIP maps cell-type-specific chromatin states in the Drosophila central nervous system. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanca, O.; Bellen, H.J.; Schnorrer, F. Gene Tagging Strategies To Assess Protein Expression, Localization, and Function in Drosophila. Genetics 2017, 207, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusanovich, D.A.; Reddington, J.P.; Garfield, D.A.; Daza, R.M.; Aghamirzaie, D.; Marco-Ferreres, R.; Pliner, H.A.; Christiansen, L.; Qiu, X.; Steemers, F.J.; et al. The cis-regulatory dynamics of embryonic development at single-cell resolution. Nature 2018, 555, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, T.F.; Richards, S.; Stone, E.A.; Barbadilla, A.; Ayroles, J.F.; Zhu, D.; Casillas, S.; Han, Y.; Magwire, M.M.; Cridland, J.M.; et al. The Drosophila melanogaster Genetic Reference Panel. Nature 2012, 482, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Massouras, A.; Inoue, Y.; Peiffer, J.; Ramia, M.; Tarone, A.M.; Turlapati, L.; Zichner, T.; Zhu, D.; Lyman, R.F.; et al. Natural variation in genome architecture among 205 Drosophila melanogaster Genetic Reference Panel lines. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, E.G.; Merkes, C.M.; McNeil, C.L.; Hoofer, S.R.; Sen, S.; Broman, K.W.; Long, A.D.; Macdonald, S.J. Genetic dissection of a model complex trait using the Drosophila Synthetic Population Resource. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayfield, R.D.; Harris, R.A.; Schuckit, M.A. Genetic factors influencing alcohol dependence. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morean, M.E.; Corbin, W.R. Subjective response to alcohol: A critical review of the literature. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.A.; Mackillop, J.; Monti, P.M. Subjective responses to alcohol consumption as endophenotypes: Advancing behavioral genetics in etiological and treatment models of alcoholism. Subst. Use Misuse 2010, 45, 1742–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuckit, M.A. Low level of response to alcohol as a predictor of future alcoholism. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuckit, M.A. An overview of genetic influences in alcoholism. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2009, 36, S5–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, A.S.; Rothenfluh, A. I Believe I Can Fly!: Use of Drosophila as a Model Organism in Neuropsychopharmacology Research. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Ghezzi, A.; Wijesekera, T.P.; Atkinson, N.S. Genetics and genomics of alcohol responses in Drosophila. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.G.; Atkinson, N.S. Is alcoholism learned? Insights from the fruit fly. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parr, J.; Large, A.; Wang, X.; Fowler, S.C.; Ratzlaff, K.L.; Ruden, D.M. The inebri-actometer: A device for measuring the locomotor activity of Drosophila exposed to ethanol vapor. J. Neurosci. Methods 2001, 107, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.M.; Heberlein, U. Genetic control of acute ethanol-induced behaviors in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 24, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.W.; Rodan, A.R.; Tsai, L.T.; Heberlein, U. High-resolution analysis of ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 11035–11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohan, F.M.; Graf, J.D. Latitudinal cline in drosophila melanogaster for knockdown resistance to ethanol fumes and for rates of response to selection for further resistance. Evolution 1985, 39, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.H.; Heberlein, U.; Moore, M.S. Rapid and chronic: Two distinct forms of ethanol tolerance in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2004, 28, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, H.R.; Li, X.; Ghezzi, A.; Atkinson, N.S. A DNA element in the slo gene modulates ethanol tolerance. Alcohol (Fayettev. N. Y.) 2016, 51, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayard, M.; McIntyre, J.; Hill, K.R.; Woodside, J., Jr. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 69, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.G.; Khurana, S.; Kuperman, A.; Atkinson, N.S. Neural adaptation leads to cognitive ethanol dependence. Curr. Biol. CB 2012, 22, 2338–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaun, K.R.; Azanchi, R.; Maung, Z.; Hirsh, J.; Heberlein, U. A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devineni, A.V.; Heberlein, U. Preferential ethanol consumption in Drosophila models features of addiction. Curr. Biol. CB 2009, 19, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peru, Y.C.d.P.R.L.; Ojelade, S.A.; Penninti, P.S.; Dove, R.J.; Nye, M.J.; Acevedo, S.F.; Lopez, A.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. Long-lasting, experience-dependent alcohol preference in Drosophila. Addict. Biol. 2014, 19, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskalev, A.; Zhikrivetskaya, S.; Krasnov, G.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Proshkina, E.; Borisoglebsky, D.; Danilov, A.; Peregudova, D.; Sharapova, I.; Dobrovolskaya, E.; et al. A comparison of the transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster in response to entomopathogenic fungus, ionizing radiation, starvation and cold shock. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edenberg, H.J. The genetics of alcohol metabolism: Role of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase variants. Alcohol Res. Health J. Natl. Inst. Alcohol Abus. Alcohol. 2007, 30, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg, H.J.; McClintick, J.N. Alcohol Dehydrogenases, Aldehyde Dehydrogenases, and Alcohol Use Disorders: A Critical Review. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Lee, P.; Stafford, J.M.; von Schimmelmann, M.; Schaefer, A.; Reinberg, D. An AUTS2-Polycomb complex activates gene expression in the CNS. Nature 2014, 516, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narita, S.; Nagahori, K.; Nishizawa, D.; Yoshihara, E.; Kawai, A.; Ikeda, K.; Iwahashi, K. Association between AUTS2 haplotypes and alcohol dependence in a Japanese population. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2016, 28, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, C.; de Celis, J.F. Tay bridge is a negative regulator of EGFR signalling and interacts with Erk and Mkp3 in the Drosophila melanogaster wing. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schweitzer, R.; Shilo, B.Z. A thousand and one roles for the Drosophila EGF receptor. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corl, A.B.; Berger, K.H.; Ophir-Shohat, G.; Gesch, J.; Simms, J.A.; Bartlett, S.E.; Heberlein, U. Happyhour, a Ste20 family kinase, implicates EGFR signaling in ethanol-induced behaviors. Cell 2009, 137, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, I.F.; Eddison, M.; Kaun, K.R.; Heberlein, U. EGFR and FGFR pathways have distinct roles in Drosophila mushroom body development and ethanol-induced behavior. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, E.C.; Allouche, L.; Chapot, P.A.; Vranizan, K.; Moore, M.S.; Heberlein, U.; Wolf, F.W. Ethanol-regulated genes that contribute to ethanol sensitivity and rapid tolerance in Drosophila. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flavell, S.W.; Cowan, C.W.; Kim, T.K.; Greer, P.L.; Lin, Y.; Paradis, S.; Griffith, E.C.; Hu, L.S.; Chen, C.; Greenberg, M.E. Activity-dependent regulation of MEF2 transcription factors suppresses excitatory synapse number. Science (N.Y.) 2006, 311, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalizi, A.; Gaudillière, B.; Yuan, Z.; Stegmüller, J.; Shirogane, T.; Ge, Q.; Tan, Y.; Schulman, B.; Harper, J.W.; Bonni, A. A calcium-regulated MEF2 sumoylation switch controls postsynaptic differentiation. Science (N.Y.) 2006, 311, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawk, J.D.; Abel, T. The role of NR4A transcription factors in memory formation. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ron, D.; Barak, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying alcohol-drinking behaviours. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivachenko, A.; Li, Y.; Abruzzi, K.C.; Rosbash, M. The transcription factor Mef2 links the Drosophila core clock to Fas2, neuronal morphology, and circadian behavior. Neuron 2013, 79, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulipparacharuvil, S.; Renthal, W.; Hale, C.F.; Taniguchi, M.; Xiao, G.; Kumar, A.; Russo, S.J.; Sikder, D.; Dewey, C.M.; Davis, M.M.; et al. Cocaine regulates MEF2 to control synaptic and behavioral plasticity. Neuron 2008, 59, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contet, C. Gene Expression Under the Influence: Transcriptional Profiling of Ethanol in the Brain. Curr. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 1, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osterndorff-Kahanek, E.A.; Becker, H.C.; Lopez, M.F.; Farris, S.P.; Tiwari, G.R.; Nunez, Y.O.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Chronic ethanol exposure produces time- and brain region-dependent changes in gene coexpression networks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Mash, D.C.; Goldman, D. Substance-specific and shared transcription and epigenetic changes in the human hippocampus chronically exposed to cocaine and alcohol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6626–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, L.G.; Foroud, T.; Bice, P.; Gobbett, T.; Ivashina, J.; Edenberg, H.; Lumeng, L.; Li, T.K. A quantitative trait locus for alcohol consumption in selectively bred rat lines. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabbe, J.C. Review. Neurogenetic studies of alcohol addiction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 3201–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.P.; Liang, T.; Liu, L.; Johnson, P.L.; Foroud, T.; Carr, L.G.; Shekhar, A. From QTL to candidate gene: A genetic approach to alcoholism research. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2009, 2, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.K.; Ponomarev, I.; Hitzemann, R.J.; Belknap, J.K.; Tabakoff, B.; Harris, R.A.; Crabbe, J.C.; Blednov, Y.A.; Grahame, N.J.; Phillips, T.J.; et al. Toward understanding the genetics of alcohol drinking through transcriptome meta-analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6368–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.L.; Thiele, T.E. The Role of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in Alcohol and Drug Abuse Disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 136, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, C.L.; Li, T.K.; Lumeng, L.; Hwang, B.H.; Somes, C.; Jimenez, P.; Mathe, A.A. Neuropeptide Y levels in ethanol-naive alcohol-preferring and nonpreferring rats and in Wistar rats after ethanol exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, T.E.; Marsh, D.J.; Ste Marie, L.; Bernstein, I.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Ethanol consumption and resistance are inversely related to neuropeptide Y levels. Nature 1998, 396, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Saver, M.; Chung, P.; Ren, Q.; Lee, T.; Kent, C.F.; Heberlein, U. Dissection of the Drosophila neuropeptide F circuit using a high-throughput two-choice assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8091–E8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grotewiel, M.; Bettinger, J.C. Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans as Discovery Platforms for Genes Involved in Human Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roeder, T.; Seifert, M.; Kahler, C.; Gewecke, M. Tyramine and octopamine: Antagonistic modulators of behavior and metabolism. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Roman, M.E.; Billini, C.E.; Ghezzi, A. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Alcohol Neuroadaptation: Insights from Drosophila. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1179069518779809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, P.J. K(Ca)2 channels: Novel therapeutic targets for treating alcohol withdrawal and escalation of alcohol consumption. Alcohol (Fayettev. N.Y.) 2012, 46, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumann, G.; Liu, C.; O’Reilly, P.; Gao, H.; Song, P.; Xu, B.; Ruggeri, B.; Amin, N.; Jia, T.; Preis, S.; et al. KLB is associated with alcohol drinking, and its gene product beta-Klotho is necessary for FGF21 regulation of alcohol preference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14372–14377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cope, L.M.; Munier, E.C.; Trucco, E.M.; Hardee, J.E.; Burmeister, M.; Zucker, R.A.; Heitzeg, M.M. Effects of the serotonin transporter gene, sensitivity of response to alcohol, and parental monitoring on risk for problem alcohol use. Alcohol (Fayettev. N.Y.) 2017, 59, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemenitas, A.; Kastelic, M.; o Porcelli, S.; Serretti, A.; Dolžan, V.; Kores Plesnicar, B. Alcohol Dependence and Genetic Variability in the Serotonin Pathway among Currently and Formerly Alcohol-Dependent Males. Neuropsychobiology 2015, 72, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, C.; Franklin, J.; Beckett, K.; Ma, J.Z.; Ait-Daoud, N.; Payne, T.J.; Johnson, B.A.; Li, M.D. Association, interaction, and replication analysis of genes encoding serotonin transporter and 5-HT3 receptor subunits A and B in alcohol dependence. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meltzer, H.; Marom, E.; Alyagor, I.; Mayseless, O.; Berkun, V.; Segal-Gilboa, N.; Unger, T.; Luginbuhl, D.; Schuldiner, O. Tissue-specific (ts)CRISPR as an efficient strategy for in vivo screening in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Port, F.; Strein, C.; Stricker, M.; Rauscher, B.; Heigwer, F.; Zhou, J.; Beyersdörffer, C.; Frei, J.; Hess, A.; Kern, K.; et al. A large-scale resource for tissue-specific CRISPR mutagenesis in Drosophila. eLife 2020, 9, e53865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenfluh, A.; Threlkeld, R.J.; Bainton, R.J.; Tsai, L.T.; Lasek, A.W.; Heberlein, U. Distinct behavioral responses to ethanol are regulated by alternate RhoGAP18B isoforms. Cell 2006, 127, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojelade, S.A.; Acevedo, S.F.; Kalahasti, G.; Rodan, A.R.; Rothenfluh, A. RhoGAP18B Isoforms Act on Distinct Rho-Family GTPases and Regulate Behavioral Responses to Alcohol via Cofilin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neasta, J.; Ben Hamida, S.; Yowell, Q.; Carnicella, S.; Ron, D. Role for mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling in neuroadaptations underlying alcohol-related disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckley, J.T.; Laguesse, S.; Phamluong, K.; Morisot, N.; Wegner, S.A.; Ron, D. The First Alcohol Drink Triggers mTORC1-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine D1 Receptor Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cozzoli, D.K.; Kaufman, M.N.; Nipper, M.A.; Hashimoto, J.G.; Wiren, K.M.; Finn, D.A. Functional regulation of PI3K-associated signaling in the accumbens by binge alcohol drinking in male but not female mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruppert, M.; Franz, M.; Saratsis, A.; Velo Escarcena, L.; Hendrich, O.; Gooi, L.M.; Schwenkert, I.; Klebes, A.; Scholz, H. Hangover Links Nuclear RNA Signaling to cAMP Regulation via the Phosphodiesterase 4d Ortholog dunce. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, L.T.; Bainton, R.J.; Blau, J.; Heberlein, U. Lmo mutants reveal a novel role for circadian pacemaker neurons in cocaine-induced behaviors. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, A.W.; Kapfhamer, D.; Kharazia, V.; Gesch, J.; Giorgetti, F.; Heberlein, U. Lmo4 in the nucleus accumbens regulates cocaine sensitivity. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gouzi, J.Y.; Moressis, A.; Walker, J.A.; Apostolopoulou, A.A.; Palmer, R.H.; Bernards, A.; Skoulakis, E.M. The receptor tyrosine kinase Alk controls neurofibromin functions in Drosophila growth and learning. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.S.; DeZazzo, J.; Luk, A.Y.; Tully, T.; Singh, C.M.; Heberlein, U. Ethanol intoxication in Drosophila: Genetic and pharmacological evidence for regulation by the cAMP signaling pathway. Cell 1998, 93, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Chan, T.; Shah, V.; Zhang, S.; Pletcher, S.D.; Roman, G. The propensity for consuming ethanol in Drosophila requires rutabaga adenylyl cyclase expression within mushroom body neurons. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, T.K.; Adams, M.J.; Davies, G.; Howard, D.M.; Hall, L.S.; Padmanabhan, S.; Murray, A.D.; Smith, B.H.; Campbell, A.; Hayward, C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and genetic overlap with other health-related traits in UK Biobank (N = 112 117). Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Q.; Bizon, C.; Gizer, I.R.; Wilhelmsen, K.C.; Ehlers, C.L. Genetic loci for alcohol-related life events and substance-induced affective symptoms: Indexing the “dark side” of addiction. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.K.; Sedore, S.A.; Cronmiller, C.; Hirsh, J. Type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase-deficient Drosophila are viable but show developmental, circadian, and drug response phenotypes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20588–20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, P. A protein kinase C activity localized to neuropeptide Y-like neurons mediates ethanol intoxication in Drosophila melanogaster. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, P. Protein kinase C deficiency-induced alcohol insensitivity and underlying cellular targets in Drosophila. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyyada, R.; Latchooman, N.; Jonaitis, J.; Ayoub, S.S.; Corcoran, O.; Casalotti, S.O. Naltrexone Reverses Ethanol Preference and Protein Kinase C Activation in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ghezzi, A.; Yin, J.C.; Atkinson, N.S. CREB regulation of BK channel gene expression underlies rapid drug tolerance. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Krishnan, H.R.; Ghezzi, A.; Yin, J.C.; Atkinson, N.S. Drug-induced epigenetic changes produce drug tolerance. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hutchison, K.E.; Calhoun, V.D.; Claus, E.D.; Turner, J.A.; Sui, J.; Liu, J. CREB-BDNF pathway influences alcohol cue-elicited activation in drinkers. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghezzi, A.; Li, X.; Lew, L.K.; Wijesekera, T.P.; Atkinson, N.S. Alcohol-Induced Neuroadaptation Is Orchestrated by the Histone Acetyltransferase CBP. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgante, F.; Sørensen, P.; Sorensen, D.A.; Maltecca, C.; Mackay, T.F. Genetic Architecture of Micro-Environmental Plasticity in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.J.; Kumar, S.; Serrano Negron, Y.L.; Harbison, S.T. Genotype Influences Day-to-Day Variability in Sleep in Drosophila melanogaster. Sleep 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ober, U.; Ayroles, J.F.; Stone, E.A.; Richards, S.; Zhu, D.; Gibbs, R.A.; Stricker, C.; Gianola, D.; Schlather, M.; Mackay, T.F.; et al. Using whole-genome sequence data to predict quantitative trait phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preuss, U.W.; Ridinger, M.; Rujescu, D.; Fehr, C.; Koller, G.; Wodarz, N.; Bondy, B.; Soyka, M.; Wong, W.M.; Zill, P. No association of alcohol dependence with HOMER 1 and 2 genetic variants. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Psychiatr. Genet. 2010, 153B, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S. Alcoholic fatty liver: Its pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and fibrosis. Alcohol (Fayettev. N.Y.) 2004, 34, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xie, M.; Huang, L.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Guo, F.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Cocaine activates Rac1 to control structural and behavioral plasticity in caudate putamen. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 75, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, D.M.; Sun, H.; Lobo, M.K.; Cahill, M.E.; Chadwick, B.; Gao, V.; Koo, J.W.; Mazei-Robison, M.S.; Dias, C.; Maze, I.; et al. Rac1 is essential in cocaine-induced structural plasticity of nucleus accumbens neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scaplen, K.M.; Talay, M.; Nunez, K.M.; Salamon, S.; Waterman, A.G.; Gang, S.; Song, S.L.; Barnea, G.; Kaun, K.R. Circuits that encode and guide alcohol-associated preference. eLife 2020, 9, e48730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.S.; Januszewski, M.; Lu, Z.; Takemura, S.-y.; Hayworth, K.J.; Huang, G.; Shinomiya, K.; Maitin-Shepard, J.; Ackerman, D.; Berg, S.; et al. A Connectome of the Adult Drosophila Central Brain. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Carbone, M.A.; Magwire, M.M.; Peiffer, J.A.; Lyman, R.F.; Stone, E.A.; Anholt, R.R.; Mackay, T.F. Genetic basis of transcriptome diversity in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6010–E6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, B.; Boyle, M.; Liu, J.; Liao, L.; Xu, T.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. Brain Proteome Changes Induced by Olfactory Learning in Drosophila. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3763–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enculescu, C.; Kerr, E.D.; Yeo, K.Y.B.; Schenk, G.; Fortes, M.R.S.; Schulz, B.L. Proteomics Reveals Profound Metabolic Changes in the Alcohol Use Disorder Brain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Ma, W.W.; Peng, I.F. Screening of sleep assisting drug candidates with a Drosophila model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.M.; Holloway, S.L.; Jongens, T.A. Using Drosophila as a tool to identify Pharmacological Therapies for Fragile X Syndrome. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 10, e129–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aranda, G.P.; Hinojos, S.J.; Sabandal, P.R.; Evans, P.D.; Han, K.A. Behavioral Sensitization to the Disinhibition Effect of Ethanol Requires the Dopamine/Ecdysone Receptor in Drosophila. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccelli, E.; Li, Q.; Rao, Y.; Kitamoto, T. The Unique Dopamine/Ecdysteroid Receptor Modulates Ethanol-Induced Sedation in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 4647–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, G.L.; Marella, S.; Kaun, K.R.; Wu, J.; Adhikari, P.; Kong, E.C.; Wolf, F.W. Sir2/Sirt1 Links Acute Inebriation to Presynaptic Changes and the Development of Alcohol Tolerance, Preference, and Reward. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5241–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Function | Gene (Gray = Human, White = Fly) | Alcohol Phenotype | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor tyrosine kinase | ALK | LR; AD | [32,33] |
| dAlk | SS | [32] | |
| Cytoskeleton-associated transmembrane protein | ARL6IP5 | AD | [34] |
| Jwa (addicsin) | Rapid Tol (MET and Sed Rec) | [35] | |
| Helix-loop-helix transcription factor | ARNTL | AC | [36] |
| ARNTL2 | AA | [36] | |
| cyc | Rapid Tol (SS) | [37] | |
| Polycomb Repressor Complex 1 Modifier | AUTS23 | AC; Max drinks; AC, post-mortem expression | [38,39,40] |
| tay | SS | [40] | |
| Chloride intracellular channel | CLIC4 | Post-mortem expression | [41] |
| Clic | eRING; SS | [42,43] | |
| Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (norepinephrine synthesis) | DBH | AD; AD in women | [44,45] |
| Tbh | Rapid Tol (MET) | [46] | |
| SS | [47] | ||
| Olfactory preference | [48] | ||
| DOPA decarboxylase (dopamine and serotonin synthesis) | DDC | AC; Drug dependence | [49,50] |
| Ddc | MET | [51] | |
| Correlation b/n expression and EtOH preference or intake | [52] | ||
| Metabotropic GABA receptor subunit | GABBR1 | AD; AD | [53,54] |
| GABA-B-R1 | Sed Rec, Rapid Tol (Sed Rec) | [55] | |
| Glutamate NMDA receptor subunit | GRIN1 | AD; AD; AW seizure susceptibility | [56,57,58] |
| Nmdar1 | Sed Rec | [59] | |
| Post-synaptic adaptor/regulator of glutamatergic synapses | HOMER1 | AC; AC | [60,61] |
| HOMER2 | AC, alcohol-related problems; reward-related learning and memory | [60,62] | |
| homer | Exposure-induced expression, SS, Rapid Tol (SS) | [63] | |
| Insulin-like growth factor receptor | IGF1R | LR | [64] |
| InR | MET | [65] | |
| SS | [66] | ||
| Integrin beta subunit | ITGB2 | LR | [64] |
| mys | SS, Rapid Tol (SS) | [67] | |
| Ca2+ and voltage-sensitive K+ channel | KCNMA1 | AD; AD, early-onset AD | [34,68] |
| slo | Rapid Tol (Sed Rec) | [69] | |
| Rapid Tol (SS), exposure-induced expression | [70] | ||
| AW seizure susceptibility; AW seizure susceptibility | [71,72] | ||
| Voltage-gated K+ channel | KCNQ5 | AD | [68] |
| KCNQ | SS, Rapid Tol (SS) | [73] | |
| MET | [51] | ||
| LIM-type transcriptional regulator | LMO1 | Max drinks | [39] |
| dLmo (Bx) | SS | [74] | |
| MADS-box transcription factor | MEF2B | SRE | [75] |
| MEF2C | AC; AD | [76,77] | |
| Mef2 | SS | [75] | |
| SS, Rapid Tol (SS) | [78] | ||
| Malic enzyme | ME1 | Cocktail drinking | [79] |
| Men (and paralogs) | Various | [11,79,80,81] | |
| Correlation b/n expression and EtOH preference or intake | [52] | ||
| AC | [82] | ||
| Micro-RNA | miR-92 | Post-mortem expression | [83] |
| miR-310 | Exposure-induced expression; Sed Rec | [84] | |
| Cell adhesion molecule | NCAM1 | AD; AD | [85,86] |
| Fas2 | MET | [87] | |
| Neuropeptide Y | NPY | AD; AD; AD; AD; AD; AW | [36,88,89,90,91,92] |
| NPF | SS | [93] | |
| Correlation b/n expression and EtOH preference or intake | [52] | ||
| Neuropeptide Y receptor | NPY2R | AD, AW, comorbid alcohol and cocaine dependence | [94] |
| NPFR | SS | [93] | |
| Alcohol preference | [95] | ||
| Correlation b/n expression and EtOH preference or intake | [52] | ||
| Transcriptional repressor involved in circadian rhythm | PER2 | AC with sleep problems | [96] |
| PER3 | AA/AD | [97] | |
| per | Rapid Tol (Time to Sed) | [37] | |
| Circadian modulation of SS | [98] | ||
| Guanine exchange factor (GEF) | PSD3 | AD, AC, adolescent binge drinking | [99] |
| Efa6 | Alcohol preference, SS, Rapid Tol (SS) | [99] | |
| SS | [100] | ||
| Ras suppressor | RSU1 | AC | [101] |
| ics | Alcohol preference | [101] | |
| Ryanodine receptor | RYR3 | AD, reward anticipation | [102] |
| RyR | Rapid Tol (SS) | [102] | |
| Vesicular monoamine transporter | SLC18A1 | AUD, age at first alcohol use; AW | [103,104] |
| SLC18A2 | AD; AD | [105,106] | |
| Vmat | Correlation b/n expression and EtOH preference or intake | [52] | |
| Norepinephrine transporter | SLC6A2 | AD | [107] |
| DAT | Act | [108] | |
| Nuclear zinc-finger protein | ZNF699 | AD, post-mortem expression | [109] |
| hang | Rapid Tol (MET) | [110] | |
| Rapid Tol (eRING) | [42] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lathen, D.R.; Merrill, C.B.; Rothenfluh, A. Flying Together: Drosophila as a Tool to Understand the Genetics of Human Alcoholism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186649
Lathen DR, Merrill CB, Rothenfluh A. Flying Together: Drosophila as a Tool to Understand the Genetics of Human Alcoholism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLathen, Daniel R., Collin B. Merrill, and Adrian Rothenfluh. 2020. "Flying Together: Drosophila as a Tool to Understand the Genetics of Human Alcoholism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186649
APA StyleLathen, D. R., Merrill, C. B., & Rothenfluh, A. (2020). Flying Together: Drosophila as a Tool to Understand the Genetics of Human Alcoholism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186649