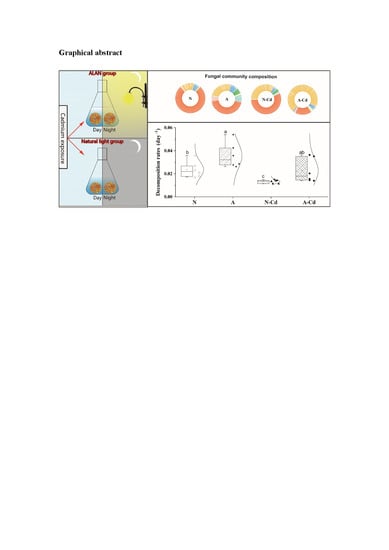
Light Pollution Changes the Toxicological Effects of Cadmium on Microbial Community Structure and Function Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Stream Water Chemistry
2.2. Fungal Communities
2.3. Changes in Extracellular Enzyme Activities
2.4. Microbial Biomass
2.5. Leaf Chemical Characteristics and Mass Loss
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Leaf Conditioning
4.2. Microcosm Experiment
4.3. Leaf Mass Remaining, Lignin, Carbon, and Nitrogen Content
4.4. Fungal Diversity
4.5. Microbial Biomass
4.6. Extracellular Enzyme Activities
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Samples | Sequence | OTUs | Sobs | Shannon | Simpson | ACE | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | 46,086 a | 365 a | 284 a | 3.10 a | 0.15b c | 314 a | 314 a |
| N | 41,864 b | 321 b | 215 ab | 2.04 b | 0.37 a | 243 ab | 249 ab |
| A | 51,507 b | 285 c | 198 b | 2.62 ab | 0.21 bc | 222 b | 220 b |
| N_Cd | 41,698 ab | 307 c | 218 b | 2.30 b | 0.28 b | 248 b | 242 b |
| A_Cd | 40,860 b | 274 c | 171 b | 2.49 ab | 0.18 d | 194 b | 195 b |
| Par. | PH | DO (mg L–1) | Cond. (μs cm–1) | Sal | NTU | OPR (mv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water | 6.78 | 4.81 | 0.036 | 0.017 | 0.44 | 160 |
| Par. | TSS (mg·L–1) | DOC (mg·L–1) | TP | NH4+ (ppm) | T (°C) | TN |
| water | 3.01 | 1.08 | 0.042 | 0.79 | 20.41 | 1.73 |
| Par. | Chla (μg·L–1) | TDS (mg·L–1) | Ca2+ (mg·L–1) | Mg2+ (mg·L–1) | Cd2+ (μg·L–1) | |
| water | 0.77 | 24 | 68 | 4.56 | <0.001 |

References
- Gessner, M.O.; Gulis, V.; Kuehn, K.A.; Chauvet, E.; Suberkropp, K. Fungal decomposers of plant litter in aquatic ecosystems. In TheMycota, Environmental and Microbial Relationships IV; Kubicek, C.P., Druzhin-ina, I.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 4, pp. 301–324. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, G.; Gessner, M.O.; Giller, P.S.; Gulis, V.; Hladyz, S.; Chauvet, E. Continental-scale effects of nutrient pollution on stream ecosystem functioning. Science 2012, 336, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tlili, A.; Jabiol, J.; Behra, R.; Gil-Allué, C.; Gessner, M.O. Chronic exposure effects of silver nanoparticles on stream microbial decomposer communities and ecosystem functions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.; Gaston, K.J. How ecological communities respond to artificial light at night. J. Exp. Zool. Part A. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hölker, F.; Wurzbacher, C.; Weißenborn, C.; Monaghan, M.T.; Holzhauer, S.I.J.; Premke, K. Microbial diversity andcommunity respiration in freshwater sediments influenced by artificial light at night. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2015, 370, 20140130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Somers-Yeates, R.; Bennie, J.; Economou, T.; Hodg-son, D.; Spalding, A.; McGregor, P.K. Light pollution is associated with earlier tree budburst across the united kingdom. Proc. R. Soc. B 2016, 283, 20160813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Holmes, N.D.; Ryan, P.G.; Wilson, K.J.; Faulquier, L.; Murillo, Y.; Corre, M.L. Seabird mortality induced by land-based artificial lights. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Qv, M.; Lv, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H. Can visible light impact litter decomposition under pollution of ZnO nanoparticles? Chemosphere 2017, 187, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.J.; Qv, M.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yin, X.Y.; Wan, N.; Zhang, B.Z.; Zhang, H.Z. The potential phototoxicity of nano-scale ZnO induced by visible light on freshwater ecosystems. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, G.Z.; Zeng, D.J.; Mo, L.; Liao, J.X.; Chen, X.X. Artificial light at night alleviates the negative effect of Pb on freshwater ecosystems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmstrup, M.; Sorensen, J.G.; Overgaard, J.; Bayley, M.; Bindesbøl, A.M.; Slotsbo, S.; Fisker, K.V.; Maraldo, K.; Waagner, D.; Labouriau, R.; et al. Body metal concentrations and glycogen reserves in earthworms (Dendrobaenaoctraedra) from contaminated and uncontaminated forest soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 159, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, D.; Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Temperature modulates AgNP impacts on microbial decomposer activity. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, G.Z.; Mo, L.; Zeng, D.J.; He, H.; Zhou, L.W.; Huang, K.C.; Liao, J.X.; Qiu, S.; Chai, S.F. Does artificial light at night change the impact of silver nanoparticles on microbial decomposers and leaf litter decomposition in streams? Environ. Sci.-Nano. 2019, 6, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.J. Accumulation of cadmium in crop plants and its consequences to human health. Adv. Agron. 1993, 51, 173–212. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen, E.; Kappel, S.; Hans-Joachim, S.; Riegger, U.; Borovec, J.; Mattusch, J.; Heinz, A.; Schmelzer, C.E.H.; Matoušková, Š.; Dickinson, B.; et al. Cadmium toxicity investigated at the physiological and biophysical levels under environmentally relevant conditions using the aquatic model plant Ceratophyllum demersum. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 1244–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, W.X. Differential influences of cu and zn chronic exposure on cd and hg bioaccumulation in an estuarine oyster. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 148, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M.; Hossain, K.; Ismail, N.; Tajarudin, H.A.; Khalil, H.P.S.A. A review on mechanism and future perspectives of cadmium-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevors, J.T.; Stratton, G.W.; Gadd, G.M. Cadmium transport, resistance, and toxicity in bacteria, algae, and fungi. Can. J. Microb. 1986, 32, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, D.; Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Impacts of warming on aquatic decomposers along a gradient of cadmium stress. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 169, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, T.; Bärlocher, F. Effects of cadmium on aquatic hyphomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 48, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, I.R. Effects of Fungal Diversity and Cadmium on Leaf Litter Decomposition in Streams: Studies in Microcosms. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Minho, Braga, Portugal, July 2008; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, M.M.; Carvalho, A.; Pascoal, C.; Rodrigues, F.; Cassio, F. Responses of antioxidant defenses to Cu and Zn stress in two aquatic fungi. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 377, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miersch, J.; Bärlocher, F.; Bruns, I. Effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on growth and thiol content of aquatic hyphomycetes. Hydrobiology 1997, 346, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, M.A.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Dahora, J.S.; Medeiros, A.O. Influence of leaf quality in microbialdecomposition in a headwater stream in the Brazilian Cerrado: A 1-year study. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozema, J.; Björn, L.O.; Bornman, J.F.; Gaberscik, A.; Häder, D.P.; Trost, T.; Germ, M.; Klisch, M.; Gröniger, A.; Sinha, R.P.; et al. The role of UV-B radiation in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems-an experimental and functional analysis of the evolution of UV-absorbing compounds. J. Photoch. Photobio. B 2002, 66, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiard-Triquet, C. Tolerance to Environmental Contaminants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, V.; Koricheva, J.; Duarte, S.; Niyogi, D.K.; Guérold, F. Effects of anthropogenic heavy metal contamination on litter decomposition in streams—A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funck, J.A.; Clivot, H.; Felten, V.; Rousselle, P.; Guerold, F.; Danger, M. Phosphorus availability modulates the toxic effect of silver on aquatic fungi and leaf litter decomposition. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 144–145, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, S.A.; Sarkheil, M.; Behzadi, M.; Veisi, S. Influence of salinity on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) in halophilic microalgae, Dunaliellasalina. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, G.Z.; Du, J.J.; Ma, X.; Lv, Y.N.; Jia, Y.Y.; Jia, X.Q.; Tian, X.J. Contribution of ambient atmospheric exposure to Typhaangustifolia litter decomposition in aquatic environment. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.T.; Ballaré, C.L. Dual role of lignin in plant litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4618–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Huan, Q.H.; Jian, H.L.; Son, N. Effects of visible light radiation on macrophyte litter degradation and nutrient release in water samples from a eutrophic shallow lake. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 32, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkrim, S.; Jebara, S.H.; Saadani, O.; Chiboub, M.; Jebara, M. Effect of Pb-resistant plant growth, romotingrhizobacteria inoculation on growth and lead uptake by Lathyrussativus. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.K.; Schindler, M.; Chauvet, E.; Gessner, M.O. Temperature oscillation coupled with fungal community shifts can modulate warming effects on litter decomposition. Ecology 2009, 90, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duarte, S.; Pascoal, C.; Alves, A.; Correia, A.; Cássio, F. Copper and zinc mixtures induce shifts in microbial communities and reduce leaf litter decomposition in streams. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiblinger, K.M.; Schneider, T.; Roschitzk, B.; Schmid, E.; Eberl, L.; Hämmerle, I. Effects of stoichiometry and temperature perturbations on beech leaf litter decomposition, enzyme activities and protein expression. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4537–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rejmankova, E.; Sirova, D. Wetland macrophyte decomposition under different nutrient conditions: Relationships between decomposition rate, enzyme activities and microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 1963, 44, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, M.O. Proximate lignin and cellulose. In Methods to Study Litter Decomposition: A Practical Guide; Graça, M.A.S., Bärlocher, F., Gessner, M.O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Allison Lab. Colorimetric Enzyme Assays. 1994. Available online: http://allison.bio.uci.edu/protocols/ (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Treat. | pH | DO (mg L–1) | NH4+ (ppm) | NTU | TDS (mg L–1) | TSS (mg L–1) | Cond. (μs cm–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | 6.80 c | 5.35 a | 42 c | 421 b | 24.333 a | 2.000 b | 0.036 c |
| N | 7.38 b | 4.61 d | 56 b | 595 a | 0.011 b | 2.389 a | 0.017 d |
| A | 7.53 a | 4.75 db | 77 a | 671 a | 0.011 b | 0.003 e | 0.016 d |
| N_Cd | 7.39 b | 4.70 bc | 60 b | 136 d | 0.082 b | 0.542 d | 0.122 b |
| A_Cd | 7.33 b | 4.65 cd | 62 b | 290 c | 0.083 b | 1.171 c | 0.125 a |
| Treatment | Carbon mg g–1 | Nitrogen mg g–1 | Phosphorus (mg g–1) | Lignin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 286.73 b | 25.29 b | 1.32b c | 5.10 a |
| A/ALAN | 348.04 b | 26.48 ab | 1.28 c | 2.21 b |
| N_Cd | 327.29 b | 30.81 a | 1.48 ab | 6.45 a |
| A_Cd | 455.59 a | 26.71 ab | 1.60 a | 2.82 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Ding, R.; Chen, X.; Pu, G. Light Pollution Changes the Toxicological Effects of Cadmium on Microbial Community Structure and Function Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020422
Liu Z, Lv Y, Ding R, Chen X, Pu G. Light Pollution Changes the Toxicological Effects of Cadmium on Microbial Community Structure and Function Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(2):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020422
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhuangzhuang, Yanna Lv, Rongcai Ding, Xiaxia Chen, and Gaozhong Pu. 2020. "Light Pollution Changes the Toxicological Effects of Cadmium on Microbial Community Structure and Function Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 2: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020422
APA StyleLiu, Z., Lv, Y., Ding, R., Chen, X., & Pu, G. (2020). Light Pollution Changes the Toxicological Effects of Cadmium on Microbial Community Structure and Function Associated with Leaf Litter Decomposition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(2), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020422