Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Membrane Components
2.2. Lipid Peroxidation
2.3. Physicochemical Properties
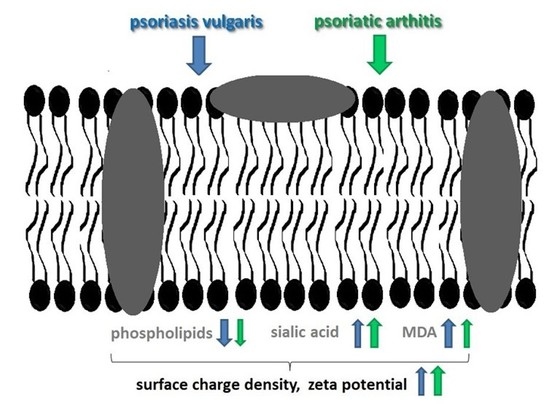
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples for Analysis
4.2. Isolation and Analysis of Phospholipids
4.3. Determination of the Sialic acid Level
4.4. Estimation of Lipid Peroxidation
4.5. Electrochemical Methods
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxy-2-onenal |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CB | Cannabinoid receptor |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| CTA | Total concentrations of negatively |
| CTB | Total concentrations of positively |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GD | Disialoganglioside |
| GT | Trisialoganglioside |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK-STAT | Janus Kinase and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| KAH | Association constants with hydrogen ions |
| KBOH | Association constants with hydroxide ions |
| LPA | Lysophosphatidic acid |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| MAPK/AP | MAP kinase activated protein kinase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like-2 factor |
| NFkB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| PA | Phosphatidic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PI | Phosphatidylinositol |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| TH | T helper lymphocytes |
References
- Fleming, P.; Kraft, J.; Gulliver, W.P.; Lynde, C. The relationship of obesity with the severity of psoriasis: A systematic review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2015, 19, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P.J.; Armstrong, A.W. Managing patients with psoriatic disease: The diagnosis and pharmacologic treatment of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis. Drugs 2014, 74, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. The interplay between keratinocytes and immune cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dogra, S.; Mahajan, R. Psoriasis: Epidemiology, clinical features, co-morbidities, and clinical scoring. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merve, H.M.; Sevilay, K.; Sibel, O.; Başak, B.; Ceren, C.G.; Demirci, T.; Cüneyt, A. Psoriasis and genetics. Interdiscip. Approach Psoriasis 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambrożewicz, E.; Wójcik, P.; Wroński, A.; Łuczaj, W.; Jastrząb, A.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Pathophysiological alterations of redox signaling and endocannabinoid system in granulocytes and plasma of psoriatic patients. Cells 2018, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wójcik, P.; Biernacki, M.; Wroński, A.; Łuczaj, W.; Waeg, G.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Altered lipid metabolism in blood mononuclear cells of psoriatic patients indicates differential changes in psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patente, T.A.; Pinho, M.P.; Oliveira, A.A.; Evangelista, G.C.M.; Bergami-Santos, P.C.; Barbuto, J.A.M. Human dendritic cells: Their heterogeneity and clinical application potential in cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Gilliet, M. Psoriasis: From pathogenesis to targeted therapies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrera, N.; Bitto, A.; Vaccaro, M.; Mannino, F.; Squadrito, V.; Pallio, G.; Arcoraci, V.; Minutoli, L.; Ieni, A.; Lentini, M.; et al. PDRN, a bioactive natural compound, ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis through NF-κB pathway inhibition and Wnt/β-Catenin signaling modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansen, C.; Rittig, A.H.; Mose, M.; Bertelsen, T.; Weimar, I.; Nielsen, J.; Andersen, T.; Rasmussen, T.K.; Deleuran, B.; Iversen, L. STAT2 is involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis by promoting CXCL11 and CCL5 production by keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, T.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Huo, R.; Shen, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; et al. CCN1 promotes IL-1β production in keratinocytes by activating p38 MAPK signaling in psoriasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, J.; Yang, C.; Wen, L.; Liu, L.; Zuo, X.; Zheng, X.; Shi, F.; Zhu, C.; et al. NFKB1 mediates Th1/Th17 activation in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 331, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Biernacki, M.; Wroński, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Cannabidiol effects on phospholipid metabolism in keratinocytes from patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karabowicz, P.; Wroński, A.; Ostrowska, H.; Waeg, G.; Zarkovic, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Reduced proteasome activity and enhanced autophagy in blood cells of psoriatic patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, G.; Bacchetti, T.; Campanati, A.; Simonetti, O.; Liberati, G.; Offidani, A. Correlation between lipoprotein(a) and lipid peroxidation in psoriasis: Role of the enzyme paraoxonase-1. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, H.; Khodarahmi, R.; Sadeghi, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Vaisi-Raygani, A. Antioxidant status in patients with psoriasis. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2014, 32, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktürk, A.S.; Özdoğan, H.K.; Bayramgürler, D.; Çekmen, M.B.; Bilen, N.; Kıran, R. Nitric oxide and malondialdehyde levels in plasma and tissue of psoriasis patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik, P.; Gęgotek, A.; Wroński, A.; Jastrząb, A.; Żebrowska, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Effect of redox imbalance on protein modifications in lymphocytes of psoriatic patients. J. Biochem. 2020, 167, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleńkowska, J.; Gabig-Cimińska, M.; Mozolewski, P. Oxidative stress as an important contributor to the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, T. Oxidative stress in psoriasis and potential therapeutic use of antioxidants. Free. Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalleau, S.; Baradat, M.; Guéraud, F.; Huc, L. Cell death and diseases related to oxidative stress: 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) in the balance. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belikov, A.V.; Schraven, B.; Simeoni, L. T cells and reactive oxygen species. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillis, J.W.; O’Regan, M.H. The role of phospholipases, cyclooxygenases, and lipoxygenases in cerebral ischemic/traumatic injuries. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2003, 15, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, C.; Blanchet, M.R.; Laviolette, M.; Flamand, N. The CB2 receptor and its role as a regulator of inflammation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4449–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soliman, E.; Van Dross, R. Anandamide-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis are mediated by oxidative stress in non-melanoma skin cancer: Receptor-independent endocannabinoid signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.W.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhao, C.F.; Li, X.F.; Yang, X.Y. Differential expression of COX-2 in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Genet Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 12872–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huang, T.; Zheng, J.; Wu, K.; Li, D. Effect of marine-derived n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on C-reactive protein, interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzyńska, I.; Szachowicz-Petelska, B.; Pędzińska-Betiuk, A.; Figaszewski, Z.A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Effects of hypertension and FAAH inhibitor treatment of rats with primary and secondary hypertension considering the physicochemical properties of erythrocytes. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyńska, I.; Szachowicz-Petelska, B.; Weresa, J.; Figaszewski, Z.A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Changes in physicochemical properties of kidney cells membrane as a consequence of hypertension and treatment of hypertensive rats with FAAH inhibitor. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 2019, 299, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyńska, I.; Szachowicz-Petelska, B.; Darewicz, B.; Figaszewski, Z.A. Characterization of human bladder cell membrane during cancer transformation. J. Membrane Biol. 2015, 248, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casares, D.; Escribá, P.V.; Rosselló, C.A. Membrane lipid composition: Effect on membrane and organelle structure, function and compartmentalization and therapeutic avenues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collawn, J.F.; Bebök, Z. Structure and functions of biomembranes. Curr. Top. Membr. 2008, 61, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Moskot, M.; Bocheńska, K.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Banecki, B.; Gabig-Cimińska, M. Abnormal sphingolipid world in inflammation specific for lysosomal storage diseases and skin disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łuczaj, W.; Wroński, A.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R.; Skrzydlewska, E. Lipidomic analysis reveals specific differences between fibroblast and keratinocyte ceramide profile of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Molecules 2020, 25, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietrzak, A.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Chodorowska, G.; Szepietowski, J.C. Lipid disturbances in psoriasis: An update. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 535612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gist, D.L.; Bhushan, R.; Hamarstrom, E.; Sluka, P.; Presta, C.M.; Thompson, J.S.; Kirsner, R.S. Impact of a Performance Improvement CME activity on the care and treatment of patients with psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrząb, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Cannabidiol regulates the expression of keratinocyte proteins involved in the inflammation process through transcriptional regulation. Cells 2019, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, C.C.; Cheng, W.J.; Korinek, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L. Neutrophils in psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavropoulos, A.; Rigopoulou, E.I.; Liaskos, C.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Sakkas, L.I. The role of p38 MAPK in the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, D.P.; Suryakar, A.N.; Ankush, R.D.; Kadam, C.Y.; Deshpande, K.H. Role of oxidative stress in various stages of psoriasis. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 25, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catalá, A.; Diaz, M. Editorial: Impact of lipid peroxidation on the physiology and pathophysiology of cell membrane. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka-Tojo, M.; Tojo, T.; Kosugi, R.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Machida, Y.; Aoyama, N.; Masuda, T.; Izumi, T. Effects of ezetimibe add-on therapy for high-risk patients with dyslipidemia. Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, Y.R.; Cho, D.H.; Park, H.J. Molecular mechanisms and management of a cutaneous inflammatory disorder: Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jonas, A. Lectin cholesterol acyltransferase. BBA–Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1529, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.J.; He, C.; Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.; An, I.-S.; Kim, Y.J. Intercellular and intracellular functions of ceramides and their metabolites in skin (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sano, S. Psoriasis as a barrier disease. Dermatol. Sin. 2015, 33, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, C.; Wen, B.; Hou, G.; Lei, L.; Mei, Z.; Jia, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Lipidomics profiling reveals the role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in psoriasis. Giga Sci. 2017, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rikitake, Y.; Hirata, K.; Kawashima, S.; Takeuchi, S.; Shimokawa, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Inoue, N.; Yokoyama, M. Signaling mechanism underlying COX-2 induction by lysophosphatidylcholine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Gaur, S.N.; Arora, N. Lysophosphatidylcholine plays critical role in allergic airway disease manifestation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, M.C.; Lee, C.S.; Elder, J.T.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Increased phosphatidylinositol kinase activity in psoriatic epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1986, 92, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Lin, X.; Meng, X.; Lin, M. Phosphoinositide-3 kinase/protein kinase-B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in psoriasis pathogenesis. A potential therapeutic target? Acta Derm. Venereol. 2014, 94, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Birukov, K.G.; Levonen, A.L.; Binder, C.J.; Stocki, J. Generation and biological activities of oxidized phospholipids. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1009–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobrzyńska, I.; Gęgotek, A.; Gajko, E.; Skrzydlewska, E.; Figaszewski, Z.A. Effects of rutin on the physicochemical properties of skin fibroblasts membrane disruption following UV radiation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 282, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, M.; Carpentier, S.; Levade, T.; Arrigo, A.P. Potential roles of membrane fluidity and ceramide in hyperthermia and alcohol stimulation of TRAIL apoptosis. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1703–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.G.; Grinstein, S. Sensing phosphatidylserine in cellular membranes. Sensors 2011, 11, 1744–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, J.; Niedoszytko, B. Structural analysis of the cell membranes of red blood cells, lymphocytes and granulocytes in psoriatic patients: A spin label study. Ann. Acad. Med. Gedan. 2005, 35, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Górnicki, A.; Gutsze, A. Erythrocyte membrane fluidity changes in psoriasis: An EPR study. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2001, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. (Ed.) Sialic acid and biology of life: An introduction. In Sialic Acid and Sialoglycoconjugates in the Biology of Life, Health and Disaease; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelsteen, E.; Broby-Johansen, U.; Jeppe-Jensen, D.; Mandel, U. Cell surface glycosylation patterns in psoriasis. APMIS 1990, 98, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, L.; Chan, L.S.; Fox, D.A.; Larsen, J.K.; Voorhees, J.J.; Cooper, K.D.; Baadsgaard, O. Lesional psoriatic T cells contain the capacity to induce a T cell activation molecule CDw6O on normal keratinocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 675–683. [Google Scholar]
- Fougeray, S.; Fleurence, J.; Faraj, S.; Bahri, M.; Cochonneau, D.; Terme, M.; Leclair, M.D.; Thébaud, E.; Paris, F.; Birklé, S. O-acetylated gangliosides: Structure, biosynthesis, immunogenicity, functions and their potential for cancer immunotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, C.; Shantaram, M.; Sharanya, K.; Shenoy, M.M. Lipid-bound sialic acid in psoriasis and its correlation with disease severity. Saudi J. Health Sci. 2015, 4, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macauley, M.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C. Siglec-mediated regulation of immune cell function in disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lubbers, J.; Rodriguez, E.; van Kooyk, Y. Modulation of immune tolerance via Siglec-sialic acid interactions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D. Sialic acid metabolism as a potential therapeutic target of atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, V.S.; Pillai, S. Sialic acid and autoimmune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jellusova, J.; Nitschke, L. Regulation of B cell functions by the sialic acid-binding receptors Siglec-G and CD22. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- French, B.M.; Sendil, S.; Pierson, R.N., 3rd; Azimzadeh, A.M. The role of sialic acids in the immune recognition of xenografts. Xenotransplantation 2017, 24, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-Ling, L.; Peng-Hui, W. Aberrant sialylation of immune cells in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 341–342. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, A.; Minc, N. Gradients of phosphatidylserine contribute to plasma membrane charge localization and cell polarity in fission yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Lopes, M.J.; Alves, J.D. Psoriasis-associated vascular disease: The role of HDL. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gęgotek, A.; Domingues, P.; Wroński, A.; Wójcik, P.; Skrzydlewska, E. Proteomic plasma profile of psoriatic patients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 155, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gęgotek, A.; Domingues, P.; Wroński, A.; Ambrożewicz, E.; Skrzydlewska, E. The proteomic profile of keratinocytes and lymphocytes in psoriatic patients. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, 1800119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jourdian, G.W.; Dean, L.; Roseman, S. The sialic acids. XI. A periodate-resorcinol method for the quantitative estimation of free sialic acids and their glycosides. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.P.; Yazdanpanah, M.; Bhooi, N.; Lehotay, D.C. Determination of aldehydes and other lipid peroxidation products in biological samples by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 228, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gęgotek, A.; Bielawska, K.; Biernacki, M.; Zaręba, I.; Surażyński, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Comparison of protective effect of ascorbic acid on redox and endocannabinoid systems interactions in in vitro cultured human skin fibroblasts exposed to UV radiation and hydrogen peroxide. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrzyńska, I.; Skrzydlewska, E.; Figaszewski, Z.A. Parameters characterizing acid-base equilibria between cell membrane and solution and their application to monitoring the effect of various factors on the membrane. Bioelectrochemistry 2006, 69, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Analysed Parameters | Healthy Subjects (Control) | Psoriasis Vulgaris | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keratinocytes (µg/mg protein) | |||
| PI | 1.11 ± 0.12 | 0.66 ± 0.14 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| PS | 1.64 ± 0.21 | 0.95 ± 0.18 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| PE | 3.35 ± 0.35 | 2.38 ± 0.33 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| PC | 3.99 ± 0.41 | 3.05 ± 0.38 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| Fibroblasts (µg/mg protein) | |||
| PI | 1.73 ± 0.12 | 1.45 ± 0.15 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| PS | 2.76 ± 0.25 | 2.04 ± 0.28 a | a; p < 0.0001 |
| PE | 5.83 ± 0.52 | 4.81 ± 0.49 a | a; p = 0.0009 |
| PC | 7.03 ± 0.68 | 5.72 ± 0.60 a | a; p = 0.0012 |
| Analysed Parameters | Healthy Subjects (Control) | Psoriasis Vulgaris | Psoriatic Arthritis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrocytes (µg/mg Hb) | |||||
| PI | 1.70 ± 0.16 | 1.45 ± 0.17 a | a; p = 0.0318 | 1.57 ± 0.19 | |
| PS | 2.38 ± 0.17 | 2.13 ± 0.23 a | a; p = 0.0145 | 2.24 ± 0.21 | |
| PE | 2.95 ± 0.24 | 2.46 ± 0.25 a | a; p = 0.0005 | 2.68 ± 0.27 | |
| PC | 7.37 ± 0.45 | 6.49 ± 0.42 a | a; p = 0.0017 | 6.82 ± 0.45 | |
| Lymphocytes (µg/mg protein) | |||||
| PI | 1.47 ± 0.11 | 1.20 ± 0.12 a | a; p = 0.0006 | 1.24 ± 0.12 | |
| PS | 2.27 ± 0.25 | 1.71 ± 0.16 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 1.94 ± 0.15 | |
| PE | 7.50 ± 0.71 | 4.90 ± 0.51 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 5.10 ± 0.44 a | a; p = 0.012 |
| PC | 9.26 ± 0.96 | 6.90 ± 0.73 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 7.27 ± 0.81 a | a; p = 0.0182 |
| Granulocytes (µg/mg protein) | |||||
| PI | 2.13 ± 0.28 | 1.05 ± 0.24 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 1.11 ± 0.16 a | a; p = 0.0085 |
| PS | 3.11 ± 0.35 | 1.34 ± 0.14 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 1.68 ± 0.18 x | x; p = 0.0431 |
| PE | 11.84 ± 1.18 | 7.03 ± 0.71 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 8.54 ± 0.80x | x; p = 0.0433 |
| PC | 14.14 ± 1.44 | 6.80 ± 1.04 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 7.39 ± 1.08 a | a; p = 0.0167 |
| Groups | Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTA (10−6 mol/m2) | CTB (10−6 mol/m2) | KAH (102 m3/mol) | KBOH (107 m3/mol) | |||||
| Erythrocytes | ||||||||
| Control | 5.87 ± 0.22 | 1.45 ± 0.11 | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 7.86 ± 0.24 | ||||
| Psoriasis vulgaris | 6.09 ± 0.41 | 1.92 ± 0.16 a | a; p = 0.0036 | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 8.11 ± 0.32 | |||
| Psoriatic arthritis | 6.47 ± 0.42 a | a; p = 0.0173 | 2.09 ± 0.17 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.59 ± 0.06 a, x | a; p = 0.0016 x; p = 0.0486 | 8.41 ± 0.31 a | a; p = 0.004 |
| Lymphocytes | ||||||||
| Control | 1.56 ± 0.11 | 0.99 ± 0.08 | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 2.35 ± 0.10 | ||||
| Psoriasis vulgaris | 3.65 ± 0.37 a | a; p = 0.0085 | 1.92 ± 0.19 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.62 ± 0.06 a | a; p = 0.0004 | 2.71 ± 0.18 a | a; p = 0.0001 |
| Psoriatic arthritis | 4.77 ± 0.46 a, x | a; p < 0.0001 x; p = 0.0126 | 1.78 ± 0.18 a | a; p = 0.0229 | 0.64 ± 0.07 a | a; p = 0.0007 | 2.66 ± 0.15 a | a; p = 0.0043 |
| Granulocytes | ||||||||
| Control | 1.06 ± 0.10 | 1.45 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.05 | 6.16 ± 0.55 | ||||
| Psoriasis vulgaris | 4.04 ± 0.41 a | a; p = 0.0007 | 2.62 ± 0.25 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.64 ± 0.08 a | a; p = 0.0051 | 8.67± 0.89 a | a; p = 0.0007 |
| Psoriatic arthritis | 4.40 ± 0.45 a | a; p = 0.0003 | 1.89 ± 0.18 x | x; p = 0.0117 | 0.79 ± 0.08 a, x | a; p < 0.0001 x; p = 0.0489 | 8.93 ± 0.92 a | a; p = 0.0004 |
| Keratinocytes | ||||||||
| Control | 2.96 ± 0.24 | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 0.53 ± 0.06 | 6.16 ± 0.38 | ||||
| Psoriasis vulgaris | 4.93 ± 0.48 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 1.86 ± 0.19 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.68 ± 0.07 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 7.14 ± 0.59 a | a; p = 0.0001 |
| Fibroblasts | ||||||||
| Control | 3.33 ± 0.30 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | 0.48 ± 0.04 | 7.05 ± 0.41 | ||||
| Psoriasis vulgaris | 5.04 ± 0.52 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.64 ± 0.07 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 0.18 ± 0.04 a | a; p < 0.0001 | 8.09 ± 0.62 a | a; p = 0.0033 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobrzyńska, I.; Szachowicz-Petelska, B.; Wroński, A.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239129
Dobrzyńska I, Szachowicz-Petelska B, Wroński A, Jarocka-Karpowicz I, Skrzydlewska E. Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(23):9129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239129
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobrzyńska, Izabela, Barbara Szachowicz-Petelska, Adam Wroński, Iwona Jarocka-Karpowicz, and Elżbieta Skrzydlewska. 2020. "Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 23: 9129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239129
APA StyleDobrzyńska, I., Szachowicz-Petelska, B., Wroński, A., Jarocka-Karpowicz, I., & Skrzydlewska, E. (2020). Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(23), 9129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239129