Dual Fluorescence Splicing Reporter Minigene Identifies an Antisense Oligonucleotide to Skip Exon v8 of the CD44 Gene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of a Dual Fluorescence-Based Splicing Reporter Minigene
2.2. Construction of the Second Version of Minigene, FMv2
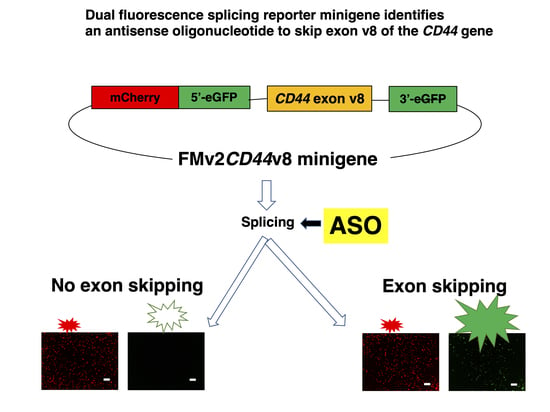
2.3. Construction of FMv2CD44v8 Carrying Exon V8 of the CD44 Gene
2.4. Identification of Exon Skippable ASO Using FMv2CD44v8
2.5. Application of FMv2CD44v8 for a High Throughput Screening
3. Discussion
Limitation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Construction of Minigenes
4.3. Minigene Transfection and Expression
4.4. Fluorescence Analysis
4.5. mRNA Analysis
4.6. Antisense Oligonucleotides
4.7. Determination of EC50
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| RT | Reverse transcription |
| DMD | Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| GFP | Green fluorescence protein |
| ENA | 2′-O,4′-C-Ethylene-bridged nucleic acid |
| EC50 | Half maximal effective concentration |
| FS | Fluorescence strength |
References
- Krawczak, M.; Thomas, N.S.T.; Hundrieser, B.; Mort, M.; Wittig, M.; Hampe, J.; Cooper, D.N. Single base-pair substitutions in exon-intron junctions of human genes: Nature, distribution, and consequences for mRNA splicing. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Yang, M.; Yiya, K.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X. ExonSkipDB: Functional annotation of exon skipping event in human. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D896–D907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, Y.; Nishio, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Nakamura, H.; Matsuo, M. Modulation of in vitro splicing of the upstream intron by modifying an intra-exon sequence which is deleted from the dystrophin gene in dystrophin Kobe. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, M.; Takeshima, Y.; Nishio, H. Contributions of Japanese patients to development of antisense therapy for DMD. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramono, Z.A.; Takeshima, Y.; Alimsardjono, H.; Ishii, A.; Takeda, S.; Matsuo, M. Induction of exon skipping of the dystrophin transcript in lymphoblastoid cells by transfecting an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide complementary to an exon recognition sequence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 226, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.; Pyle, A. Exon Skipping Therapy. Cell 2016, 167, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma Rus, A.; Corey, D. The 10th Oligonucleotide Therapy Approved: Golodirsen for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Mastaglia, F.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S. Precision medicine through antisense oligonucleotide-mediated exon skipping. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, N.; Gazzoli, I.; Krause, S.; Mamchaoui, K.; Mouly, V.; Aartsma Rus, A. Antisense-mediated Skipping of dysferlin exons in control and dysferlinopathy patient-derived cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, E.; Ramsbottom, S.; Srivastava, S.; Booth, P.; Alkanderi, S.; McLafferty, S.; Devlin, L.; White, K.; Gunay Aygun, M.; Miles, C.; et al. Targeted exon skipping rescues ciliary protein composition defects in Joubert syndrome patient fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, T.; Horinouchi, T.; Adachi, T.; Terakawa, M.; Takaoka, Y.; Omachi, K.; Takasato, M.; Takaishi, K.; Shoji, T.; Onishi, Y.; et al. Development of an exon skipping therapy for X-linked Alport syndrome with truncating variants in COL4A5. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.; Vilela, R.; Rocha, M.; Santos, J.; Coutinho, M.; Gaspar, P.; Prata, M.; Alves, S. Development of an antisense oligonucleotide-mediated exon skipping therapeutic strategy for Mucolipidosis II: Validation at RNA level. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.K.; Malerba, A.; Popplewell, L.; Foster, K.; Dickson, G. Antisense-induced myostatin exon skipping leads to muscle hypertrophy in mice following octa-guanidine morpholino oligomer treatment. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung Htut, M.; Comerford, I.; Johnsen, R.; Foyle, K.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S. Reduction of integrin alpha 4 activity through splice modulating antisense oligonucleotides. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, O.; Okazaki, S.; Saya, H. Redox regulation in stem-like cancer cells by CD44 variant isoforms. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5191–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wei, D. Concise review: Emerging role of CD44 in cancer stem cells: A promising biomarker and therapeutic target. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Iwama, E.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Shibahara, D.; Harada, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nagano, O.; Saya, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Okamoto, I. CD44 variant-dependent regulation of redox balance in EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A target for treatment. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Awano, H.; Yagi, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Watanabe, N.; Goda, R.; Koizumi, M.; Takeshima, Y.; Matsuo, M. 2’-O-Methyl RNA/Ethylene-Bridged Nucleic Acid Chimera Antisense Oligonucleotides to Induce Dystrophin Exon 45 Skipping. Genes 2017, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishida, A.; Kataoka, N.; Takeshima, Y.; Yagi, M.; Awano, H.; Ota, M.; Itoh, K.; Hagiwara, M.; Matsuo, M. Chemical treatment enhances skipping of a mutated exon in the dystrophin gene. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wai, H.; Douglas, A.G.L.; Baralle, D. RNA splicing analysis in genomic medicine. Int. J. Biochem. 2019, 108, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Cooper, T. Minigene reporter for identification and analysis of cis elements and trans factors affecting pre-mRNA splicing. BioTechniques 2006, 41, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, B.; Zillmer, A.; Lu, P.; Benrashid, E.; Wang, M.; Doran, T.; Shaban, M.; Wu, X.; Lu, Q. Guanine analogues enhance antisense oligonucleotide-induced exon skipping in dystrophin gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiulpakov, A.; Zubkova, N.; Makretskaya, N.; Krasnova, T.; Melnikova, A.; Fedyaeva, A.; Vasilyev, E.; Petrov, V.; Rubtsov, P. Minigene splicing assessment of 20 novel synonymous and intronic glucokinase gene variants identified in patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Matsuo, M. Nucleic Acid Drug for Inducing Skipping of Variant Exon of CD44 Gene and Increasing Expression of Normal Type CD44 mRNA. U.S. Patent 10174319 B2, 8 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gaildrat, P.; Killian, A.; Martins, A.; Tournier, I.; Frebourg, T.; Tosi, M. Use of splicing reporter minigene assay to evaluate the effect on splicing of unclassified genetic variants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 653, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, D.A.; Sharif, O.; Anderson, P.; Tu, B.; Welch, G.; Zhou, Y.; Caldwell, J.S.; Engels, I.H.; Brinker, A. Identification of small molecule and genetic modulators of AON-induced dystrophin exon skipping by high-throughput screening. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sazani, P.; Kang, S.H.; Maier, M.A.; Wei, C.; Dillman, J.; Summerton, J.; Manoharan, M.; Kole, R. Nuclear antisense effects of neutral, anionic and cationic oligonucleotide analogs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 3965–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kendall, G.C.; Mokhonova, E.I.; Moran, M.; Sejbuk, N.E.; Wang, D.W.; Silva, O.; Wang, R.T.; Martinez, L.; Lu, Q.L.; Damoiseaux, R.; et al. Dantrolene enhances antisense-mediated exon skipping in human and mouse models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 164ra160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Khaniani, M. Restoration of correct splicing in IVSI-110 mutation of β-globin gene with antisense oligonucleotides: Implications and applications in functional assay development. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 700–707. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Damoiseaux, R.; Chen, L.; Black, D.L. A broadly applicable high-throughput screening strategy identifies new regulators of Dlg4 (Psd-95) alternative splicing. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Harvey, S.; Cheng, C. A high-throughput screen identifies small molecule modulators of alternative splicing by targeting RNA G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3667–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimo, T.; Tachibana, K.; Obika, S. Construction of a tri-chromatic reporter cell line for the rapid and simple screening of splice-switching oligonucleotides targeting DMD exon 51 using high content screening. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, P.; Gorham, J.; Ito, K.; Seidman, C. In vivo and In vitro methods to identify DNA sequence variants that alter RNA Splicing. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2018, 97, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habara, Y.; Doshita, M.; Hirozawa, S.; Yokono, Y.; Yagi, M.; Takeshima, Y.; Matsuo, M. A strong exonic splicing enhancer in dystrophin exon 19 achieve proper splicing without an upstream polypyrimidine tract. J. Biochem. 2008, 143, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habara, Y.; Takeshima, Y.; Awano, H.; Okizuka, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Saiki, K.; Yagi, M.; Matsuo, M. In vitro splicing analysis showed that availability of a cryptic splice site is not a determinant for alternative splicing patterns caused by +1G-->A mutations in introns of the dystrophin gene. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nozu, K.; Iijima, K.; Kawai, K.; Nozu, Y.; Nishida, A.; Takeshima, Y.; Fu, X.J.; Hashimura, Y.; Kaito, H.; Nakanishi, K.; et al. In vivo and in vitro splicing assay of SLC12A1 in an antenatal salt-losing tubulopathy patient with an intronic mutation. Hum. Genet. 2009, 126, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, T.; Nozu, K.; Ueda, H.; Fujimaru, R.; Hisatomi, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Kato, H.; Nangaku, M.; Miyata, T.; Sawai, T.; et al. Functional splicing analysis in an infantile case of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome caused by digenic mutations in C3 and MCP genes. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Mishima, E.; Jutabha, P.; Ouchi, M.; Kojima, K.; Kawai, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Anzai, N.; Nagasaki, M. Contribution of Rare Variants of the SLC22A12 Gene to the Missing Heritability of Serum Urate Levels. Genetics 2020, 214, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niba, E.T.; Nishida, A.; Tran, V.K.; Vu, D.C.; Matsumoto, M.; Awano, H.; Lee, T.; Takeshima, Y.; Nishio, H.; Matsuo, M. Cryptic splice activation but not exon skipping is observed in minigene assays of dystrophin c.9361+1G>A mutation identified by NGS. J. Hum. Genet. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, T.; Nozu, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Fujimura, J.; Horinouchi, T.; Minamikawa, S.; Mori, N.; Fujimaru, R.; Nakanishi, K.; et al. An in vitro splicing assay reveals the pathogenicity of a novel intronic variant in ATP6V0A4 for autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horinouchi, T.; Nozu, K.; Yamamura, T.; Minamikawa, S.; Nagano, C.; Sakakibara, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Shima, Y.; Morisada, N.; Ishiko, S.; et al. Determination of the pathogenicity of known COL4A5 intronic variants by in vitro splicing assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, T.; Nozu, K.; Yamamura, T.; Minamikawa, S.; Omori, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Fujimura, J.; Ashida, A.; Kitamura, M.; Kawano, M.; et al. Detection of Splicing Abnormalities and Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in X-linked Alport Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okubo, M.; Noguchi, S.; Hayashi, S.; Nakamura, H.; Komaki, H.; Matsuo, M.; Nishino, I. Exon skipping induced by nonsense/frameshift mutations in DMD gene results in Becker muscular dystrophy. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| ASO | Sequence |
|---|---|
| ASO#1 | 5’-aCTaTgaCTggagTCCaTaT-3’ |
| ASO#2 | 5’-TTgCagTaggCTgaagCgTT-3’ |
| ASO#3 | 5’-CaaaCCTgTgTTTggaTTTg-3’ |
| ASO#4 | 5’-aagaggTCCTgTCCTgTCCa-3’ |
| ASO#12 | 5’-CCaCCaaaCCTgTgTTTgga-3’ |
| ASO#13 | 5’-CTgTCCaaaTCTTCCaCCaa-3’ |
| ASO#14 | 5’-gCgTTgTCaTTgaaagaggT-3’ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukushima, S.; Farea, M.; Maeta, K.; Rani, A.Q.M.; Fujioka, K.; Nishio, H.; Matsuo, M. Dual Fluorescence Splicing Reporter Minigene Identifies an Antisense Oligonucleotide to Skip Exon v8 of the CD44 Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239136
Fukushima S, Farea M, Maeta K, Rani AQM, Fujioka K, Nishio H, Matsuo M. Dual Fluorescence Splicing Reporter Minigene Identifies an Antisense Oligonucleotide to Skip Exon v8 of the CD44 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(23):9136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239136
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukushima, Sachiyo, Manal Farea, Kazuhiro Maeta, Abdul Qawee Mahyoob Rani, Kazumichi Fujioka, Hisahide Nishio, and Masafumi Matsuo. 2020. "Dual Fluorescence Splicing Reporter Minigene Identifies an Antisense Oligonucleotide to Skip Exon v8 of the CD44 Gene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 23: 9136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239136
APA StyleFukushima, S., Farea, M., Maeta, K., Rani, A. Q. M., Fujioka, K., Nishio, H., & Matsuo, M. (2020). Dual Fluorescence Splicing Reporter Minigene Identifies an Antisense Oligonucleotide to Skip Exon v8 of the CD44 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(23), 9136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239136