Association of a Disrupted Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure with Progression of Renal Injury during the Development of Salt-Dependent Hypertension in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes in Body Weight, BP, and Heart Rate
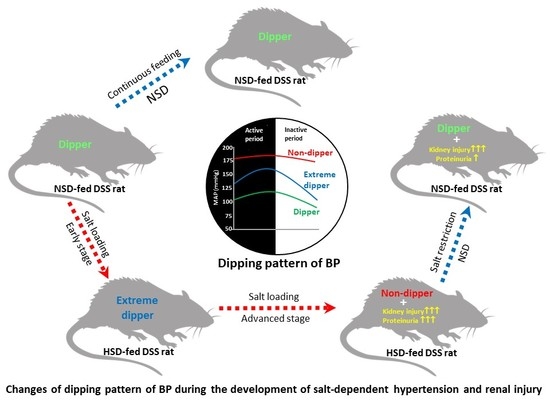
2.2. Changes in the Dipping Pattern of BP
2.2.1. Dipping Pattern of BP During Feeding NSD
2.2.2. Dipping Pattern of BP During Feeding HSD
2.2.3. Dipping Pattern of BP After Transition of HSD to LSD
2.3. Changes in Proteinuria and its Association with the Dipping Pattern of BP
2.4. Renal Tissue Injury and Dipping Pattern of BP in Salt Loaded-DSS Rats
2.5. Urinary Excretion of Sodium, Plasma Cr, and BUN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bankir, L.; Bochud, M.; Maillard, M.; Bovet, P.; Gabriel, A.; Burnier, M. Nighttime blood pressure and nocturnal dipping are associated with daytime urinary sodium excretion in African subjects. Hypertension 2008, 51, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, G.; Dohi, Y.; Fukuda, M. Salt sensitivity and circadian rhythm of blood pressure: the keys to connect CKD with cardiovasucular events. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boggia, J.; Li, Y.; Thijs, L.; Hansen, T.W.; Kikuya, M.; Björklund-Bodegård, K.; Richart, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Kuznetsova, T.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; et al. Prognostic accuracy of day versus night ambulatory blood pressure: a cohort study. Lancet 2007, 370, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Redon, J.; Kesani, A.; Pascual, J.M.; Tacons, J.; Alvarez, V.; Batlle, D. Increase in Nocturnal Blood Pressure and Progression to Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdecchia, P.; Schillaci, G.; Guerrieri, M.; Gatteschi, C.; Benemio, G.; Boldrini, F.; Porcellati, C. Circadian blood pressure changes and left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. Circulation 1990, 81, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, S.; Ogihara, M.; Tamura, C.; Kitazawa, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Kigoshi, T.; Uchida, K. Reversed circadian blood pressure rhythm independently predicts endstage renal failure in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus subjects. J. Diabetes Complicat. 1999, 13, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, G. Kidney and Circadian Blood Pressure Rhythm. Hypertension 2008, 51, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haruhara, K.; Tsuboi, N.; Koike, K.; Fukui, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Ogura, M.; Yokoo, T. Renal histopathological findings in relation to ambulatory blood pressure in chronic kidney disease patients. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, C.; Goldsmith, D.J.; Cox, J.; Dallyn, P.; Kingswood, J.C.; Sharpstone, P. An investigation of the effect of advancing uraemia, renal replacement therapy and renal transplantation on blood pressure diurnal variability. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1997, 12, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzu, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Fujii, T.; Nakamura, S.; Inenaga, T.; Kimura, G. Sodium Restriction Shifts Circadian Rhythm of Blood Pressure from Nondipper to Dipper in Essential Hypertension. Circulation 1997, 96, 1859–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzu, T.; Kimura, G. Diuretics shift circadian rhythm of blood pressure from nondipper to dipper in essential hypertension. Circulation 1999, 100, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kastrup, J.; Wroblewski, H.; Sindrup, J.; Rolighed Christensen, H.; Wiinberg, N. Diurnal blood pressure profile in patients with severe congestive heart failure: dippers and non-dippers. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 1993, 53, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.; Kimura, G. Salt sensitivity and nondippers in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sufiun, A.; Rafiq, K.; Fujisawa, Y.; Rahman, A.; Mori, H.; Nakano, D.; Kobori, H.; Ohmori, K.; Masaki, T.; Kohno, M.; et al. Effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition on circadian blood pressure during the development of salt-dependent hypertension in rats. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, M.; Goto, N.; Kimura, G. Hypothesis on renal mechanism of non-dipper pattern of circadian blood pressure rhythm. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Ingole, S.; Jain, R. Salt sensitivity and its implication in clinical practice. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staessen, J.; Broughton, P.M.G.; Fletcher, A.E.; Markowe, H.L.J.; Marmot, M.G.; Rose, G.; Semmence, A.; Shipley, M.J.; Bulpitt, C.J. The assessment of the relationship between blood pressure and sodium intake using whole-day, daytime and overnight urine collections. J. Hypertens. 1991, 9, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campese, V.M.; Mitra, N.; Sandee, D. Hypertension in renal parenchymal disease: Why is it so resistant to treatment? Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intersalt: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 Hour Urinary sodium and potassium excretion. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bomback, A.S.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Amamoo, M.A.; Klemmer, P.J. Change in Proteinuria After Adding Aldosterone Blockers to ACE Inhibitors or Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in CKD: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udani, S.M.; Koyner, J.L. Effect of blood pressure lowering on markers of kidney disease progression. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2009, 11, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, S.; Bigazzi, R.; Baldari, G.; Sgherri, G.; Campese, V.M. Diurnal Variations of Blood Pressure and Microalbuminuria in Essential Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1994, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Konishi, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Kitabayashi, C.; Kohno, M.; Masaki, T.; Mori, H.; Kobori, H.; Imanishi, M. Regression of glomerular and tubulointerstitial injuries by dietary salt reduction with combination therapy of angiotensin II receptor blocker and calcium channel blocker in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamaguchi, A.; Kim, S.; Izumi, Y.; Iwao, H. Chronic activation of glomerular mitogen-activated protein kinases in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bigazzi, R.; Bianchi, S.; Baldari, D.; Sgherri, G.; Baldari, G.; Campese, V.M. Microalbuminuria in salt-sensitive patients. A marker for renal and cardiovascular risk factors. Hypertension 1994, 23, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, G.; Brenner, B.M. Implications of the linear pressure-natriuresis relationship and importance of sodium sensitivity in hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.; Munemura, M.; Usami, T.; Nakao, N.; Takeuchi, O.; Kamiya, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kimura, G. Nocturnal blood pressure is elevated with natriuresis and proteinuria as renal function deteriorates in nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goto, N.; Uchida, K.; Morozumi, K.; Ueki, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Katayama, A.; Haba, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Nakao, A.; et al. Circadian blood pressure rhythm is disturbed by nephrectomy. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Kobori, H.; Morishita, A.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Nakano, D.; Nishiyama, A. Effects of the novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor blocker, esaxerenone (CS-3150), on blood pressure and urinary angiotensinogen in low-renin Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, A.; Kobori, H. Independent regulation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the kidney. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobori, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Abe, Y.; Navar, L.G. Enhancement of intrarenal angiotensinogen in Dahl salt-sensitive rats on high salt diet. Hypertension 2003, 41, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.; Fujisawa, Y.; Nakano, D.; Hitomi, H.; Nishiyama, A. Effect of a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, luseogliflozin, on circadian rhythm of sympathetic nervous function and locomotor activities in metabolic syndrome rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Yamazaki, D.; Sufiun, A.; Kitada, K.; Hitomi, H.; Nakano, D.; Nishiyama, A. A novel approach to adenine-induced chronic kidney disease associated anemia in rodents. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Age (Weeks) | Urinary Sodium (UnaV), mmol/day | Plasma Cr (mg/dL) | BUN (mg/dL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSD | HSD | NSD | HSD | NSD | HSD | |
| 7 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | Before HSD | 0.24 ± 0.02 | Before HSD | 51 ± 2 | Before HSD |
| 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 54 ± 2 | ||||
| 9 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | 2 weeks after | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 2 weeks after | 52 ± 3 | 2 weeks after |
| 25.64 ± 0.85 *† | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 57 ± 3 | ||||
| 12 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 5 weeks after | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 5 weeks after | 53 ± 1 | 5 weeks after |
| 23.90 ± 0.40 *† | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 59 ± 2 | ||||
| 15 | 0.52 ± 0.06 * | 8 weeks after | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 8 weeks after | 51 ±1 | 8 weeks after |
| 25.60 ± 1.15 *† | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 63 ± 1 | ||||
| 17 | 0.44 ± 0.05 * | 10 weeks after | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 10 weeks after | 53 ± 1 | 10 weeks after |
| 20.76 ± 0.80 *† | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 61 ± 2 | ||||
| 21 | 0.44 ± 0.05 * | 4 weeks after switching to NSD | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 4 weeks after switching to NSD | 53 ± 1 | 4 weeks after switching to NSD |
| 0.76 ± 0.19 * | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 44 ± 5 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sufiun, A.; Rahman, A.; Rafiq, K.; Fujisawa, Y.; Nakano, D.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T.; Nishiyama, A. Association of a Disrupted Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure with Progression of Renal Injury during the Development of Salt-Dependent Hypertension in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062248
Sufiun A, Rahman A, Rafiq K, Fujisawa Y, Nakano D, Kobara H, Masaki T, Nishiyama A. Association of a Disrupted Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure with Progression of Renal Injury during the Development of Salt-Dependent Hypertension in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062248
Chicago/Turabian StyleSufiun, Abu, Asadur Rahman, Kazi Rafiq, Yoshihide Fujisawa, Daisuke Nakano, Hideki Kobara, Tsutomu Masaki, and Akira Nishiyama. 2020. "Association of a Disrupted Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure with Progression of Renal Injury during the Development of Salt-Dependent Hypertension in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062248
APA StyleSufiun, A., Rahman, A., Rafiq, K., Fujisawa, Y., Nakano, D., Kobara, H., Masaki, T., & Nishiyama, A. (2020). Association of a Disrupted Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure with Progression of Renal Injury during the Development of Salt-Dependent Hypertension in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062248