Platelet Activation in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia is Followed by Platelet Death via Complex Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Pathways
Abstract
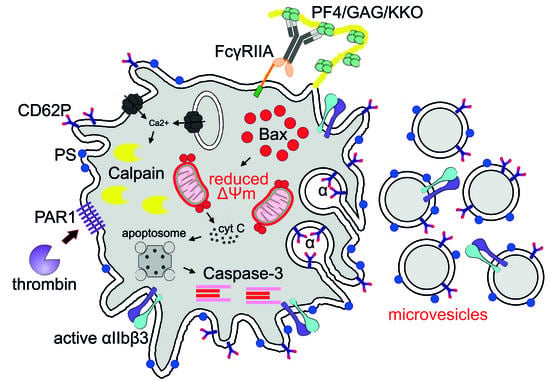
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Subpopulations of Live Activated and Dying Platelets
2.2. Apoptotic Markers in Platelets induced by KKO/PF4
2.3. KKO/PF4-induced Calpain Activation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Platelet Isolation and Incubation with Immune Complexes Containing PF4
3.2. Flow Cytometry
3.3. Western Blot Analysis
3.4. Assay of Calpain Activity
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIT PF4 | Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia Platelet factor 4 |
| PS ADP KKO RTO ΔΨm CD62P mAb IV.3 PAC1 | Phosphatidylserine Adenosine diphosphate Pathogenic monoclonal anti-PF4/heparin antibody Non-pathogenic monoclonal anti-PF4/heparin antibody Mitochondrial membrane potential P-selectin FcγRIIA-blocking antibody, clone IV.3 Monoclonal antibody reacting with the active integrin αIIbβ3 |
| PRP FITC FSC/SSC PE SDS-PAGE EDANS PAR1 | Platelet-rich plasma Fluorescein isothiocyanate Forward scatter/Side scatter Phycoerythrin Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis 5-((2-Aminoethyl)amino)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid Protease-activated receptor 1 |
References
- Pishko, A.; Cuker, A. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Transfus. Med. Hemost. 2019, 104, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selling, K.; Warkentin, T.E. Autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maličev, E.; Kozak, M.; Rožman, P. Evaluation of a flow cytometric assay for the confirmation of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Warkentin, T.E.; Denomme, G.A.; Hayward, C.P.; Kelton, J.G. A diagnostic test for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: Detection of platelet microparticles using flow cytometry. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 95, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutwiler, V.; Madeeva, D.; Ahn, H.S.; Andrianova, I.; Hayes, V.; Hayes, X.L.; Zheng, X.L.; Cines, D.B.; McKenzie, S.E.; Poncz, M.; et al. Platelet transactivation by monocytes promotes thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2016, 127, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, M.; Hayward, C.P.; Warkentin, T.E.; Horsewood, P.; Chorneyko, K.A.; Kelton, J.G. Morphological analysis of microparticle generation in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2000, 96, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.M.; Arepally, G.M. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Hematol. Am. Soc Hematol. Educ. Program. 2013, 2013, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomareva, A.A.; Nevzorova, T.A.; Mordakhanova, E.R.; Andrianova, I.A.; Rauova, L.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Intracellular origin and ultrastructure of platelet-derived microparticles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, O.V.; Nevzorova, T.A.; Mordakhanova, E.R.; Ponomareva, A.A.; Andrianova, I.A.; Le Minh, G.; Daminova, A.G.; Peshkova, A.D.; Tokhtaeva, E.; Alber, M.; et al. Fatal dysfunction and disintegration of thrombin-stimulated platelets. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepally, G.M.; Kamei, S.; Park, K.S.; Kamei, K.; Li, Z.Q.; Liu, W.; Siegel, D.L.; Kisiel, W.; Cines, D.B.; Poncz, M. Characterization of a murine monoclonal antibody that mimics heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies. Blood 2000, 95, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachais, B.S.; Litvinov, R.I.; Yarovoi, S.V.; Rauova, L.; Hinds, J.L.; Rux, A.H.; Arepally, G.M.; Poncz, M.; Cuker, A.; Weisel, J.W.; et al. Dynamic antibody-binding properties in the pathogenesis of HIT. Blood 2012, 120, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuker, A.; Rux, A.H.; Hinds, J.L.; Dela Cruz, M.; Yarovoi, S.V.; Brown, I.A.; Yang, W.; Konkle, B.A.; Arepally, G.M.; Watson, S.P.; et al. Novel diagnostic assays for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2013, 121, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauova, L.; Zhai, L.; Kowalska, M.A.; Arepally, G.M.; Cines, D.B.; Poncz, M. Role of platelet surface PF4 antigenic complexes in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia pathogenesis: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Blood 2006, 107, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Rand, M.; Schmugge, M.; Speer, O. Omi/HtrA2 and XIAP are components of platelet apoptosis signalling. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 109, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Bevers, E.M.; Lindhout, T. Platelet activation and blood Coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 88, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Yuan, Y.; Josefsson, E.C.; White, M.J.; Yao, Y.; Mason, K.D.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Henley, K.J.; Ono, A.; Hsiao, S.; et al. Two distinct pathways regulate platelet phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant function. Blood 2009, 114, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Segawa, K.; Fujii, T. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morel, O.; Jesel, L.; Freyssinet, J.-M.; Toti, F. Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Formation of Circulating Microparticles. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 31, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, J.; Lin, L. Platelet apoptosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2015, 39, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Chaurasia, S.N.; Nayak, M.K.; Mallick, R.L.; Dash, D. Sirtuin inhibition induces apoptosis-like changes in platelets and thrombocytopenia. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12290–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Chang, D.C. Dynamics and structure of the Bax-Bak complex responsible for releasing mitochondrial proteins during apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Josefsson, E.C.; Dowling, M.R.; Lebois, M.; Kile, B.T. The regulation of platelet life span. In Platelets, 3rd ed.; Michelson, A.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bevers, E.M.; Williamson, P.L. Phospholipid scramblase: An update. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2724–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Kruchten, R.; Mattheij, N.J.A.; Saunders, C.; Feijge, M.A.H.; Swieringa, F.; Wolf, J.L.N.; Collins, P.W.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Bevers, E.M. Both TMEM16F-dependent and TMEM16F-independent pathways contribute to phosphatidylserine exposure in platelet apoptosis and platelet activation. Blood 2013, 121, 1850–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danial, N.N.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Cell death: Critical control points. Cell 2004, 116, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Sun, R.; Zhao, L.; Du, J.; Ruan, C.; Dai, K. Calpain activator dibucaine induces platelet apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nevzorova, T.A.; Mordakhanova, E.R.; Daminova, A.G.; Ponomareva, A.A.; Andrianova, I.A.; Le Minh, G.; Rauova, L.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Platelet factor 4-containing immune complexes induce platelet activation followed by calpain-dependent platelet death. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauova, L.; Hirsch, J.D.; Greene, T.K.; Zhai, L.; Hayes, V.M.; Kowalska, M.A.; Cines, D.B.; Poncz, M. Monocyte-bound PF4 in the pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2010, 116, 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, H.S.; Foster, C.; Boykow, G.; Stamford, A.; Manna, M.; Graziano, M. Inhibition of cellular action of thrombin by N3-cyclopropyl-7-[[4-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]methyl]-7H-pyrrolo[3,2-f]quinazoline-1,3-diamine (SCH 79797), a nonpeptide thrombin receptor antagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mordakhanova, E.R.; Nevzorova, T.A.; Synbulatova, G.E.; Rauova, L.; Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Platelet Activation in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia is Followed by Platelet Death via Complex Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072556
Mordakhanova ER, Nevzorova TA, Synbulatova GE, Rauova L, Weisel JW, Litvinov RI. Platelet Activation in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia is Followed by Platelet Death via Complex Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(7):2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072556
Chicago/Turabian StyleMordakhanova, Elmira R., Tatiana A. Nevzorova, Gulnaz E. Synbulatova, Lubica Rauova, John W. Weisel, and Rustem I. Litvinov. 2020. "Platelet Activation in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia is Followed by Platelet Death via Complex Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 7: 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072556
APA StyleMordakhanova, E. R., Nevzorova, T. A., Synbulatova, G. E., Rauova, L., Weisel, J. W., & Litvinov, R. I. (2020). Platelet Activation in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia is Followed by Platelet Death via Complex Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21072556