Praeruptorin B Mitigates the Metastatic Ability of Human Renal Carcinoma Cells through Targeting CTSC and CTSV Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Pra-B on Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity in Human RCC Cells and Normal HK2 Cells
2.2. Pra-B Inhibited Cell Migration and Invasion in 786-O and ACHN Cells
2.3. Pra-B Inhibits the Expression of CTSC and CTSV in 786-O Cells
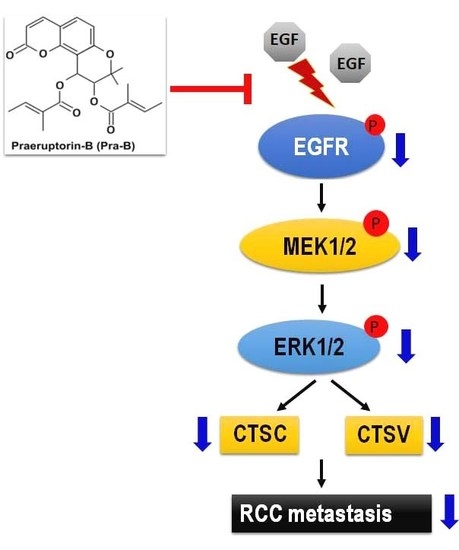
2.4. Pra-B Suppressed Activation of the MEK–ERK Signaling Pathway
2.5. Pra-B Attenuated EGF-Induced Migration and Invasion Ability through the Activation of EGFR–MEK–ERK Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Cell Migration and Invasion
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znaor, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Laversanne, M.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. International variations and trends in renal cell carcinoma incidence and mortality. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Mijn, J.C.; Mier, J.W.; Broxterman, H.J.; Verheul, H.M. Predictive biomarkers in renal cell cancer: Insights in drug resistance mechanisms. Drug Resist. Update 2014, 17, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Bang, O.S. Pyranocoumarins from Root Extracts of Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn with Multidrug Resistance Reversal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules 2015, 20, 20967–20978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, G.F.; Li, J.R.; Zhu, Z.G.; Tian, Y.X.; Wu, S.Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.J.; et al. Pyranocoumarins isolated from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages through inhibition of NF-kappaB and STAT3 activation. Inflammation 2012, 35, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.Y.; Wu, F.H.; Wang, J.S.; Li, J.; Kong, L.Y. Attenuation of airway hyperreactivity and T helper cell type 2 responses by coumarins from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhail, P. Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of the genus Peucedanum: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 235–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, J.T.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, S.W.; Moon, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Ryu, B.J.; Oh, J.; Kim, M.S.; Erkhembaatar, M.; Son, Y.J.; et al. Anti-osteoclastogenic activity of praeruptorin A via inhibition of p38/Akt-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling and PLCgamma-independent Ca2+ oscillation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenjie, W.; Houqing, L.; Liming, S.; Ping, Z.; Gengyun, S. Effects of praeruptorin C on blood pressure and expression of phospholamban in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Chu, S.S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, M.; Wu, X.; Peng, H.S. Tissue-Specific Metabolite Profiling on the Different Parts of Bolting and Unbolting Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn (Qianhu) by Laser Microdissection Combined with UPLC-Q/TOF(-)MS and HPLC(-)DAD. Molecules 2019, 24, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, W.F.; Zhang, J.X.; Wu, J.Y.; Tse, K.W.; Wang, C.; Cheung, H.Y.; Yang, M.S. Pyranocoumarin(+/−)-4′-O-acetyl-3′-O-angeloyl-cis-khellactone induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Fong, W.F.; Zhang, J.X.; Leung, C.H.; Kwong, H.L.; Yang, M.S.; Li, D.; Cheung, H.Y. Reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer cells by pyranocoumarins isolated from Radix Peucedani. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 473, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; Del Rio Hernandez, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabeshima, K.; Inoue, T.; Shimao, Y.; Sameshima, T. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion: Role for cell migration. Pathol. Int. 2002, 52, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonska-Trypuc, A.; Matejczyk, M.; Rosochacki, S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gocheva, V.; Joyce, J.A. Cysteine cathepsins and the cutting edge of cancer invasion. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joyce, J.A.; Hanahan, D. Multiple roles for cysteine cathepsins in cancer. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1516–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toss, M.; Miligy, I.; Gorringe, K.; Mittal, K.; Aneja, R.; Ellis, I.; Green, A.; Rakha, E. Prognostic significance of cathepsin V (CTSV/CTSL2) in breast ductal carcinoma in situ. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, I.; Velasco, G.; Cazorla, M.; Fueyo, A.; Campo, E.; Lopez-Otin, C. Cathepsin L2, a novel human cysteine proteinase produced by breast and colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Yu, L.; Zhou, H. Elevated CTSL2 expression is associated with an adverse prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4035–4043. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.P.; Yue, X.; Li, S.Q. Cathepsin C Interacts with TNF-alpha/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Promote Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, P.M.; Wilder, C.L.; Platt, M.O. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates cathepsin K and V activity via juxtacrine monocyte-endothelial cell signaling and JNK activation. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2012, 367, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudzinska, M.; Parodi, A.; Soond, S.M.; Vinarov, A.Z.; Korolev, D.O.; Morozov, A.O.; Daglioglu, C.; Tutar, Y.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr. The Role of Cysteine Cathepsins in Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Chiou, H.L.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Kao, S.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Timosaponin AIII inhibits metastasis of renal carcinoma cells through suppressing cathepsin C expression by AKT/miR-129-5p axis. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 13332–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramucci, L.; Pranteda, A.; Bossi, G. Insights of Crosstalk between p53 Protein and the MKK3/MKK6/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, J.S.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Figlin, R.A. Adjuvant treatment for renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizman, N.; Adashek, J.J.; Hsu, J.; Bergerot, P.G.; Bergerot, C.D.; Pal, S.K. Adjuvant treatment in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 16, 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chiou, H.L.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, P.N.; Lin, M.T.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chou, M.C. Praeruptorin-B Inhibits 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-Induced Cell Invasion by Targeting AKT/NF-kappaB via Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/-9 Expression in Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, R.A.; Khokha, R.; Hill, R.P. Molecular mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis: An integrated view. Curr. Mol. Med. 2003, 3, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizovisek, M.; Fonovic, M.; Turk, B. Cysteine cathepsins in extracellular matrix remodeling: Extracellular matrix degradation and beyond. Matrix Biol. 2019, 75, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Song, S. Cathepsin D enhances breast cancer invasion and metastasis through promoting hepsin ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Cui, M.; Zhang, L.; Song, L. FOXM1 facilitates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion by inducing Cathepsin D. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68180–68190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Lim, S.K.; Choong, L.Y.; Lee, H.; Chen, Y.; Chong, P.K.; Ashktorab, H.; Wang, T.T.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Yeoh, K.G.; et al. Cathepsin S mediates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via a putative network of metastasis-associated proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4767–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, G.; Wang, R.; Sun, A.; Wei, J.; Peng, K.; Dai, Q.; Yang, W.; Lin, Q. The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 mediates cell migration signaling of EGFR in lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.H.; Bhasin, S.; Khanna, P.; Joshi, M.; Joslin, P.M.; Saxena, R.; Amin, S.; Liu, S.; Sindhu, S.; Walker, S.R.; et al. Study of Cathepsin B inhibition in VEGFR TKI treated human renal cell carcinoma xenografts. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshacharyulu, P.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Haridas, D.; Jain, M.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K. Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maennling, A.E.; Tur, M.K.; Niebert, M.; Klockenbring, T.; Zeppernick, F.; Gattenlohner, S.; Meinhold-Heerlein, I.; Hussain, A.F. Molecular Targeting Therapy against EGFR Family in Breast Cancer: Progress and Future Potentials. Cancers 2019, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Chang, W.S.; Cheung, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Huang, C.C.; Yang, Y.N.; Kuo, C.P.; Kuo, C.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Liu, K.J.; et al. Targeting cathepsin S induces tumor cell autophagy via the EGFR-ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioachim, E.; Kamina, S.; Demou, A.; Kontostolis, M.; Lolis, D.; Agnantis, N.J. Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in human breast cancer in comparison with cathepsin D, stromelysin-1, CD44, extracellular matrix components, P53, Rb, C-erbB-2, EGFR, steroid receptor content and proliferation. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Padmavathi, G.; Rathnakaram, S.R.; Monisha, J.; Bordoloi, D.; Roy, N.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Potential of butein, a tetrahydroxychalcone to obliterate cancer. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Singh, S.; Piazza, G.A.; Contreras, C.M.; Panyam, J.; Singh, A.P. Honokiol: A novel natural agent for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2020 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, M.; Conti, A.; Porta, C.; Procopio, G.; Sternberg, C.N.; Basso, U.; De Giorgi, U.; Bracarda, S.; Rizzo, M.; Ortega, C.; et al. Sunitinib, pazopanib or sorafenib for the treatment of patients with late relapsing metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.H.; Lin, C.L.; Chiou, H.L.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Hsieh, Y.H. Praeruptorin A Inhibits Human Cervical Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion by Suppressing MMP-2 Expression and ERK1/2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Chien, H.W.; Wang, K.; Lin, C.L.; Chiou, H.L.; Lee, C.Y.; Chen, P.N.; Hsieh, Y.H. Melatonin attenuates epidermal growth factor-induced cathepsin S expression in ARPE-19 cells: Implications for proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Teng, Y.H.; Lu, F.J.; Hsu, W.H.; Lin, C.L.; Hung, C.C.; Tung, J.N.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Liu, C.J. Beta-mangostin suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion through inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and activating the ERK and JNK pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2360–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-L.; Hung, T.-W.; Ying, T.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-M. Praeruptorin B Mitigates the Metastatic Ability of Human Renal Carcinoma Cells through Targeting CTSC and CTSV Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082919
Lin C-L, Hung T-W, Ying T-H, Lin C-J, Hsieh Y-H, Chen C-M. Praeruptorin B Mitigates the Metastatic Ability of Human Renal Carcinoma Cells through Targeting CTSC and CTSV Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082919
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chia-Liang, Tung-Wei Hung, Tsung-Ho Ying, Chi-Jui Lin, Yi-Hsien Hsieh, and Chien-Min Chen. 2020. "Praeruptorin B Mitigates the Metastatic Ability of Human Renal Carcinoma Cells through Targeting CTSC and CTSV Expression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082919
APA StyleLin, C. -L., Hung, T. -W., Ying, T. -H., Lin, C. -J., Hsieh, Y. -H., & Chen, C. -M. (2020). Praeruptorin B Mitigates the Metastatic Ability of Human Renal Carcinoma Cells through Targeting CTSC and CTSV Expression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082919