The Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Survival Role of the Mix of Embryonic Proteoglycans: Electrophysiological Fingerprint, Structural Changes and Regulatory Effects on Neurotrophins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochemical Results
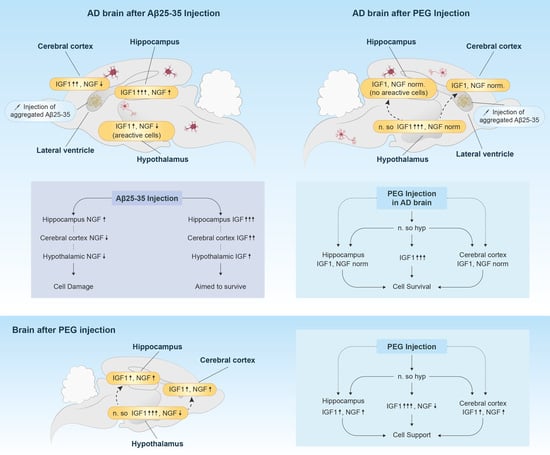
2.1.1. Changes of IGF-1 in Cerebral Cortex, Hippocampus and Hypothalamus
2.1.2. Changes of NGF in Cerebral Cortex, Hippocampus and Hypothalamus
2.2. Morphological Findings
2.3. Electrophysiology
2.3.1. Dynamic Variety/Changes of Spike Activity of Single Neurons of Hippocampus, Nucleus Supraopticus and Sensomotor Cortex Following Acute Injection of PEG
2.3.2. Excitatory and Inhibitory Responses of Hippocampal Neurons to HFS of Entorhinal Cortex
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.3. Composition of PEG
4.4. Preparation of Aβ (25–35) Peptide
4.5. Surgical Procedure for Aβ (25–35) Injection
4.6. Electrophysiology Studies
4.6.1. Electrophysiological Recordings after Acute Injection of PEG
4.6.2. Excitatory and Inhibitory Responses of Hippocampal Neurons to High Frequency Stimulation of Entorhinal Cortex
4.7. Biochemical Studies
4.7.1. Sample Preparation
4.7.2. Assessment of IGF-1 and NGF Using the Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.8. Morphological Study
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steen, E.; Terry, B.M.; Rivera, E.J.; Cannon, J.L.; Neely, T.R.; Tavares, R.; Xu, X.J.; Wands, J.R.; De La Monte, S.M. Impaired Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Expression and Signaling Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s Disease—Is this Type 3 Diabetes? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.J.; Wang, J.L.; Jin, W.L. The Emerging Therapeutic Role of NGF in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, F.F.; Xu, H. APP Regulates NGF Receptor Trafficking and NGF-Mediated Neuronal Differentiation and Survival. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Counts, S.E.; Mufson, E.J. The Role of Nerve Growth Factor Receptors in Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Degeneration in Prodromal Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Kusky, J.; Ye, P. Neurodevelopmental Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 33, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dore, S.; Kar, S.; Quirion, R. Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Protects and Rescues Hippocampal Neurons Against Amyloid- and Human Amylin-Induced Toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4772–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Bakshi, K.P.; Stucky, A.; Fuino, R.L.; Kawaguchi, K.R.; Samoyedny, A.J.; Wilson, R.S.; et al. Demonstrated Brain Insulin Resistance in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Is Associated with IGF-1 Resistance, IRS-1 Dysregulation, and Cognitive Decline. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1316–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carro, E.; Trejo, J.L.; Gomez-Isla, T.; LeRoith, D.; Torres-Aleman, I. Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Regulates Brain Amyloid-β Levels. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenkoyan, K.; Safaryan, K.; Navasardyan, G.; Mkrtchyan, L.; Aghajanov, M. Effects of Beta-Amyloid on Behavioral and Amino Acids Spectrum in Rats’ Brain and Their Modulation by Embryonic Proteins. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavushyan, V.; Matinyan, S.; Danielyan, M.; Aghajanov, M.; Yenkoyan, K. Embryonic Proteoglycans Regulate Monoamines in the Rat Frontal Cortex and Hippocampus in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 140, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanov, M.; Chavushyan, V.; Matinyan, S.; Danielyan, M.; Yenkoyan, K. Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology-Triggered Oxidative Stress, Alterations in Monoamines Levels, and Structural Damage of Locus Coeruleus Neurons Are Partially Recovered by a Mix of Proteoglycans of Embryonic Genesis. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanov, M.I.; Yenkoyan, K.B.; Chavushyan, V.A.; Sarkissian, J.S. The Proline-Rich Hypothalamic Peptide Is a Modulator of Functions of Neurotrophins and Neuronal Activity in Amyloid-Induced Neurodegeneration. Neurochem. J. 2014, 8, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro, E.; Trejo, J.L.; Gerber, A.; Loetscher, H.; Torrado, J.; Metzger, F.; Torres-Aleman, I. Therapeutic Actions of Insulin-Like Growth Factor I on APP/PS2 Mice with Severe Brain Amyloidosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, B.; Beilharz, E.J.; Williams, C.; Synek, B.; Gluckman, P.D.; Faull, R.L.M.; Dragunow, M. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) Immunoreactivity in the Alzheimer’s Disease Temporal Cortex and Hippocampus. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 49, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, E.; Dolev, I.; Fogel, H.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Ruff, E.; Slutsky, I. Amyloid-Β as a Positive Endogenous Regulator of Release Probability at Hippocampal Synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Marchetti, C.; Bianchi, D.; Leinekugel, X.; Poirazi, P.; Migliore, M.; Marie, H. Computational Modeling of the Effects of Amyloid-Beta on Release Probability at Hippocampal Synapses. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavushyan, V.; Soghomonyan, A.; Karapetyan, G.; Simonyan, K.; Yenkoyan, K. Disruption of Cholinergic Circuits as an Area for Targeted Drug Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: In Vivo Assessment of Short-Term Plasticity in Rat Brain. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissman, R.A.; De Blas, A.L.; Armstrong, D.M. GABAA Receptors in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, G.M.; Bloodgood, B.L.; Townsend, M.; Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J.; Sabatini, B.L. Natural Oligomers of the Alzheimer Amyloid-Β Protein Induce Reversible Synapse Loss by Modulating an NMDA-Type Glutamate Receptor-Dependent Signaling Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H. Synaptic Versus Extrasynaptic NMDA Receptor Signalling: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurice, T.; Lockhart, B.P.; Su, T.-P.; Privat, A. Reversion of β25–35-Amyloid Peptide-Induced Amnesia by NMDA Receptor-Associated Glycine Site Agonists. Brain Res. 1996, 731, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780123741219. [Google Scholar]
- Yenkoyan, K.; Safaryan, K.; Chavushyan, V.; Meliksetyan, I.; Navasardyan, G.; Sarkissian, J.; Galoyan, A.; Aghajanov, M. Neuroprotective Action of Proline-Rich Polypeptide-1 in β-amyloid Induced Neurodegeneration in Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aghajanov, M.; Matinyan, S.; Chavushyan, V.; Danielyan, M.; Karapetyan, G.; Mirumyan, M.; Fereshetyan, K.; Harutyunyan, H.; Yenkoyan, K. The Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Survival Role of the Mix of Embryonic Proteoglycans: Electrophysiological Fingerprint, Structural Changes and Regulatory Effects on Neurotrophins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137084
Aghajanov M, Matinyan S, Chavushyan V, Danielyan M, Karapetyan G, Mirumyan M, Fereshetyan K, Harutyunyan H, Yenkoyan K. The Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Survival Role of the Mix of Embryonic Proteoglycans: Electrophysiological Fingerprint, Structural Changes and Regulatory Effects on Neurotrophins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):7084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137084
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghajanov, Michail, Senik Matinyan, Vergine Chavushyan, Margarita Danielyan, Gohar Karapetyan, Margarita Mirumyan, Katarine Fereshetyan, Hayk Harutyunyan, and Konstantin Yenkoyan. 2021. "The Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Survival Role of the Mix of Embryonic Proteoglycans: Electrophysiological Fingerprint, Structural Changes and Regulatory Effects on Neurotrophins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 7084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137084
APA StyleAghajanov, M., Matinyan, S., Chavushyan, V., Danielyan, M., Karapetyan, G., Mirumyan, M., Fereshetyan, K., Harutyunyan, H., & Yenkoyan, K. (2021). The Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Nerve Growth Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Pathology and Survival Role of the Mix of Embryonic Proteoglycans: Electrophysiological Fingerprint, Structural Changes and Regulatory Effects on Neurotrophins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 7084. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137084