Gene Therapy in Hemophilia: Recent Advances
Abstract
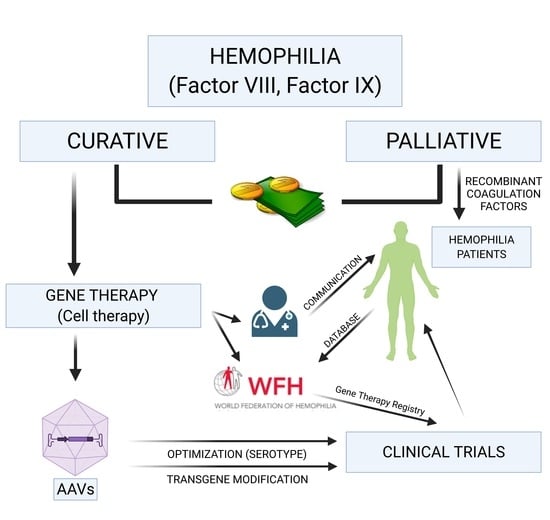
:1. Introduction
2. Advanced Therapies in Hemophilia
3. Adeno-Associated Virus, the Vectors of Choice. Optimization
4. Gene Therapy Educational Programs for Patients
5. The World Federation of Hemophilia Gene Therapy Registry and the Global Multidisciplinary Consensus Framework on Hemophilia Gene Therapy
6. Cost-Effectiveness of Gene Therapy for Hemophilia
7. Current Gene Therapy Clinical Trials in Hemophilia
7.1. Hemophilia A
7.2. Hemophilia B
7.3. Padua Variants of Factor IX. An Exciting Alternative for Gene Therapy in HB
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castaman, G.; Matino, D. Hemophilia A and B: Molecular and Clinical Similarities and Differences. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannucci, P.M.; Franchini, M. Is Haemophilia B Less Severe than Haemophilia A? Haemophilia 2013, 19, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchero, A.; Sholzberg, M.; Matino, D. The Evolution of Hemophilia Care: Clinical and Laboratory Advances, Opportunities, and Challenges. Hämostaseologie 2020, 40, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeo, F.; Mariz, S.; Brunetta, A.L.; Stoyanova-Beninska, V.; Penttila, K.; Magrelli, A. Haemophilia, State of the Art and New Therapeutic Opportunities, a Regulatory Perspective. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, M.; Hanabusa, H.; Taki, M.; Matsushita, T.; Sato, T.; Fukutake, K.; Fukazawa, N.; Yoneyama, K.; Yoshida, H.; Nogami, K. Factor VIII–Mimetic Function of Humanized Bispecific Antibody in Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Vora, S.; Kulkarni, B.; Mota, L.; Vijapurkar, M.; Quadros, L.; Ghosh, K. Contribution of Natural Anticoagulant and Fibrinolytic Factors in Modulating the Clinical Severity of Haemophilia Patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasi, K.J.; Rangarajan, S.; Georgiev, P.; Mant, T.; Creagh, M.D.; Lissitchkov, T.; Bevan, D.; Austin, S.; Hay, C.R.; Hegemann, I.; et al. Targeting of Antithrombin in Hemophilia A or B with RNAi Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machin, N.; Ragni, M.V. An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia A and B. J. Blood Med. 2018, 9, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dockal, M.; Hartmann, R.; Fries, M.; Thomassen, M.C.L.G.D.; Heinzmann, A.; Ehrlich, H.; Rosing, J.; Osterkamp, F.; Polakowski, T.; Reineke, U.; et al. Small Peptides Blocking Inhibition of Factor Xa and Tissue Factor-Factor VIIa by Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weyand, A.C.; Grzegorski, S.J.; Rost, M.S.; Lavik, K.I.; Ferguson, A.C.; Menegatti, M.; Richter, C.E.; Asselta, R.; Duga, S.; Peyvandi, F.; et al. Analysis of Factor V in Zebrafish Demonstrates Minimal Levels Needed for Early Hemostasis. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, V.; Seoane-Vazquez, E.; Fawaz, S.; Brown, L.; Rodriguez-Monguio, R. The Landscape of Cellular and Gene Therapy Products: Authorization, Discontinuations, and Cost. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2019, 30, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.S.; Hardingham, T.E. Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Sources of Cells and Differentiation Potential. J. Stem Cells 2012, 7, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolios, G.; Moodley, Y. Introduction to Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine. Respiration 2013, 85, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacakova, L.; Zarubova, J.; Travnickova, M.; Musilkova, J.; Pajorova, J.; Slepicka, P.; Kasalkova, N.S.; Svorcik, V.; Kolska, Z.; Motarjemi, H.; et al. Stem Cells: Their Source, Potency and Use in Regenerative Therapies with Focus on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells—A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Liao, J.; Cai, X. Different Sources of Stem Cells and Their Application in Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 13, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olgasi, C.; Talmon, M.; Merlin, S.; Cucci, A.; Richaud-Patin, Y.; Ranaldo, G.; Colangelo, D.; Di Scipio, F.; Berta, G.N.; Borsotti, C.; et al. Patient-Specific IPSC-Derived Endothelial Cells Provide Long-Term Phenotypic Correction of Hemophilia A. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Q.; Wang, H.-H.; Cheng, T.; Yuan, W.-P.; Ma, Y.-P.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Ren, Z.-H. Genetic Correction and Hepatic Differentiation of Hemophilia B-Specific Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2017, 32, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Wu, M.-S.; Jeng, H.-Y.; Chang, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ling, T.-Y. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Based Therapy: Mechanism, Systemic Safety and Biodistribution for Precision Clinical Applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapies: Immunomodulatory Properties and Clinical Progress. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.A.; Roncarolo, M.G. Gene Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, M.W.; Brady, J.T.; Whiteley, L.O.; Khan, K.N. Development Challenges Associated with RAAV-Based Gene Therapies. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 46, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguela, X.M.; High, K.A. Entering the Modern Era of Gene Therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, H.J.; Weber, W.; Fussenegger, M. Synthetic Biology: Emerging Concepts to Design and Advance Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toon, K.; Bentley, E.M.; Mattiuzzo, G. More than Just Gene Therapy Vectors: Lentiviral Vector Pseudotypes for Serological Investigation. Viruses 2021, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantore, A.; Naldini, L. WFH State-of-the-art Paper 2020: In Vivo Lentiviral Vector Gene Therapy for Haemophilia. Haemophilia 2021, 27, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, H.K.; Rasal, K.D.; Chakrapani, V.; Ninawe, A.S.; Vengayil, D.T.; Asrafuzzaman, S.; Sundaray, J.K.; Jayasankar, P. Gene Editing Tools: State-of-the-Art and the Road Ahead for the Model and Non-Model Fishes. Transgenic Res. 2017, 26, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, P. Gene Editing for Cell Engineering: Trends and Applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Ascending Dose Study of Genome Editing by Zinc Finger Nuclease Therapeutic SB-FIX in Subjects with Severe Hemophilia B. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02695160. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02695160?term=NCT02695160&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Adachi, H.; Hengesbach, M.; Yu, Y.-T.; Morais, P. From Antisense RNA to RNA Modification: Therapeutic Potential of RNA-Based Technologies. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, V.R.; Weber, J.; Samelson-Jones, B.J. Gene Therapy for Inherited Bleeding Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swystun, L.L.; Lillicrap, D. Gene Therapy for Coagulation Disorders. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapin, J.C.; Monahan, P.E. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia: Progress to Date. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, R.W.; Casto, B.C.; Hammon, W. McD. Adenovirus-Associated Defective Virus Particles. Science 1965, 149, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadarella, G.; Di Minno, A.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Mahlangu, J.; Di Minno, G. The Evolving Landscape of Gene Therapy for Congenital Haemophilia: An Unprecedented, Problematic but Promising Opportunity for Worldwide Clinical Studies. Blood Rev. 2021, 46, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdera, H.C.; Kuranda, K.; Mingozzi, F. AAV Vector Immunogenicity in Humans: A Long Journey to Successful Gene Transfer. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 723–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulk, N.K.; Pekrun, K.; Zhu, E.; Nygaard, S.; Li, B.; Xu, J.; Chu, K.; Leborgne, C.; Dane, A.P.; Haft, A.; et al. Bioengineered AAV Capsids with Combined High Human Liver Transduction In Vivo and Unique Humoral Seroreactivity. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniel, H.D.-J.; Kumar, S.; Kannangai, R.; Lakshmi, K.M.; Agbandje-Mckenna, M.; Coleman, K.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, A.; Abraham, A.M. Prevalence of Adeno-Associated Virus 3 Capsid Binding and Neutralizing Antibodies in Healthy and Hemophilia B Individuals from India. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, H.C.J. T Cell-Mediated Immune Responses to AAV and AAV Vectors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Wong, H.; Ng, C.M. Rational Clinical Dose Selection of Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Gene Therapy Based on Allometric Principles. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesbach, W.; O’Mahony, B.; Key, N.S.; Makris, M. How to Discuss Gene Therapy for Haemophilia? A Patient and Physician Perspective. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeeke, E.; Michelsen, S.; Hauber, B.; Peerlinck, K.; Hermans, C.; Lambert, C.; Goldman, M.; Simoens, S.; Huys, I. Patient Perspectives Regarding Gene Therapy in Haemophilia: Interviews from the PAVING Study. Haemophilia 2021, 27, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, D.P.; Branchford, B.R.; Hendry, S.; Ledniczky, R.; Sidonio, R.F.; Négrier, C.; Kim, M.; Rice, M.; Minshall, M.; Arcé, C.; et al. Optimizing Language for Effective Communication of Gene Therapy Concepts with Hemophilia Patients: A Qualitative Study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidonio, R.F.; Pipe, S.W.; Callaghan, M.U.; Valentino, L.A.; Monahan, P.E.; Croteau, S.E. Discussing Investigational AAV Gene Therapy with Hemophilia Patients: A Guide. Blood Rev. 2021, 47, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkle, B.A.; Coffin, D.; Pierce, G.F.; Clark, C.; George, L.; Iorio, A.; Mahlangu, J.; Naccache, M.; O’Mahony, B.; Peyvandi, F.; et al. World Federation of Hemophilia Gene Therapy Registry. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. The World Federation of Hemophilia Gene Therapy Registry (WFH GTR). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04883710. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT04883710?cond=Hemophilia&sort=nwst&draw=2&rank=2 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Pierce, G.F.; Pasi, K.J.; Coffin, D.; Kaczmarek, R.; Lillicrap, D.; Mahlangu, J.; Rottellini, D.; Sannié, T.; Srivastava, A.; VandenDriessche, T.; et al. Towards a Global Multidisciplinary Consensus Framework on Haemophilia Gene Therapy: Report of the 2nd World Federation of Haemophilia Gene Therapy Round Table. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drayton Jackson, M.; Bartman, T.; McGinniss, J.; Widener, P.; Dunn, A.L. Optimizing Patient Flow in a Multidisciplinary Haemophilia Clinic Using Quality Improvement Methodology. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miesbach, W.; Pasi, K.J.; Pipe, S.W.; Hermans, C.; O’Mahony, B.; Guelcher, C.; Steiner, B.; Skinner, M.W. Evolution of Haemophilia Integrated Care in the Era of Gene Therapy: Treatment Centre’s Readiness in United States and EU. Haemophilia 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Merchan, E.C. The Cost of Hemophilia Treatment: The Importance of Minimizing It without Detriment to Its Quality. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannucci, P.M.; Cortesi, P.A.; Di Minno, M.N.D.; Sanò, M.; Mantovani, L.G.; Di Minno, G. Comparative Analysis of the Pivotal Studies of Extended Half-life Recombinant FVIII Products for Treatment of Haemophilia A. Haemophilia 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Equity vs. Equality: What’s the Difference? World Health Organization. Milken Institute School of Public Health. 2020. Available online: https://onlinepublichealth.gwu.edu/resources/equity-vs-equality/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Machin, N.; Ragni, M.V.; Smith, K.J. Gene Therapy in Hemophilia A: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolous, N.S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Davidoff, A.M.; Devidas, M.; Jacobs, T.W.; Meagher, M.M.; Nathwani, A.C.; Neufeld, E.J.; Piras, B.A.; et al. The Cost-Effectiveness of Gene Therapy for Severe Hemophilia B: Microsimulation Study from the United States Perspective. Blood 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, L.P.; Jiao, B.; Dabbous, O. Gene Therapy May Not Be as Expensive as People Think: Challenges in Assessing the Value of Single and Short-Term Therapies. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- EU Clinical Trials Register. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. An Exploration of the Impact of Gene Therapy on the Lives of People with Haemophilia and Their Families. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04723680. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04723680?term=NCT04723680&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Gene Therapy Study in Severe Haemophilia a Patients (270-201). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02576795. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02576795?term=NCT02576795&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Single-Arm Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec in Hemophilia a Patients at a Dose of 4E13 vg/kg (BMN270-302). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03392974. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03392974?term=NCT03392974&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Single-Arm Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec in Hemophilia a Patients (BMN 270-301). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03370913. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03370913?term=NCT03370913&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Pasi, K.J.; Rangarajan, S.; Mitchell, N.; Lester, W.; Symington, E.; Madan, B.; Laffan, M.; Russell, C.B.; Li, M.; Pierce, G.F.; et al. Multiyear Follow-up of AAV5-HFVIII-SQ Gene Therapy for Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Gene Therapy Study in Severe Hemophilia a Patients with Antibodies against AAV5 (270-203). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03520712. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03520712?term=NCT03520712&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Nathwani, A.C.; Reiss, U.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Rosales, C.; Chowdary, P.; McIntosh, J.; Della Peruta, M.; Lheriteau, E.; Patel, N.; Raj, D.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Factor IX Gene Therapy in Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Dose-Escalation Study of a Self Complementary Adeno-Associated Viral Vector for Gene Transfer in Hemophilia B. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00979238. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00979238?term=NCT00979238&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. A Factor IX Gene Therapy Study (FIX-GT) (FIX-GT). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03369444. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03369444?term=NCT03369444&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Trial of AAV5-hFIX in Severe or Moderately Severe Hemophilia B. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02396342. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02396342?term=NCT02396342&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Dose Confirmation Trial of AAV5-hFIXco-Padua. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03489291. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03489291?term=NCT03489291&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Miesbach, W.; Meijer, K.; Coppens, M.; Kampmann, P.; Klamroth, R.; Schutgens, R.; Tangelder, M.; Castaman, G.; Schwäble, J.; Bonig, H.; et al. Gene Therapy with Adeno-Associated Virus Vector 5–Human Factor IX in Adults with Hemophilia B. Blood 2018, 131, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Drygalski, A.; Giermasz, A.; Castaman, G.; Key, N.S.; Lattimore, S.; Leebeek, F.W.G.; Miesbach, W.; Recht, M.; Long, A.; Gut, R.; et al. Etranacogene Dezaparvovec (AMT-061 Phase 2b): Normal/near Normal FIX Activity and Bleed Cessation in Hemophilia B. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3241–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. HOPE-B: Trial of AMT-061 in Severe or Moderately Severe Hemophilia B Patients. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03569891. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03569891?term=NCT03569891&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Konkle, B.A.; Walsh, C.E.; Escobar, M.A.; Josephson, N.C.; Young, G.; von Drygalski, A.; McPhee, S.W.J.; Samulski, R.J.; Bilic, I.; de la Rosa, M.; et al. BAX 335 Hemophilia B Gene Therapy Clinical Trial Results: Potential Impact of CpG Sequences on Gene Expression. Blood 2021, 137, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. HOPE-B: Open-Label Single Ascending Dose of Adeno-associated Virus Serotype 8 Factor IX Gene Therapy in Adults with Hemophilia B. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01687608. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01687608?term=NCT01687608&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Lombardi, S.; Aaen, K.H.; Nilsen, J.; Ferrarese, M.; Gjølberg, T.T.; Bernardi, F.; Pinotti, M.; Andersen, J.T.; Branchini, A. Fusion of Engineered Albumin with Factor IX Padua Extends Half-life and Improves Coagulant Activity. Br. J. Haematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simioni, P.; Tormene, D.; Tognin, G.; Gavasso, S.; Bulato, C.; Iacobelli, N.P.; Finn, J.D.; Spiezia, L.; Radu, C.; Arruda, V.R. X-Linked Thrombophilia with a Mutant Factor IX (Factor IX Padua). N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, L.A.; Sullivan, S.K.; Giermasz, A.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Ducore, J.; Cuker, A.; Sullivan, L.M.; Majumdar, S.; Teitel, J.; et al. Hemophilia B Gene Therapy with a High-Specific-Activity Factor IX Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudele, J.M.; Finn, J.D.; Siner, J.I.; Martin, N.B.; Niemeyer, G.P.; Zhou, S.; Mingozzi, F.; Lothrop, C.D.; Arruda, V.R. AAV Liver Expression of FIX-Padua Prevents and Eradicates FIX Inhibitor without Increasing Thrombogenicity in Hemophilia B Dogs and Mice. Blood 2015, 125, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Finn, J.D.; George, L.A.; Camire, R.M.; Arruda, V.R. Hyperactivity of Factor IX Padua (R338L) Depends on Factor VIIIa Cofactor Activity. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Finn, J.D.; Raffini, L.J.; Merricks, E.P.; Camire, R.M.; Nichols, T.C.; Arruda, V.R. Evolutionary Insights into Coagulation Factor IX Padua and Other High-Specific-Activity Variants. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.M.; George, L.A.; Carr, M.E.; Samelson-Jones, B.J.; Arruda, V.R.; Murphy, J.E.; Rybin, D.; Rupon, J.; High, K.A.; Tiefenbacher, S. Factor IX Assay Discrepancies in the Setting of Liver Gene Therapy Using a Hyperfunctional Variant Factor IX-Padua. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Factor IX Gene Therapy with PF-06838435 in Adult Males with Moderately Severe to Severe Hemophilia B (BENEGENE-2). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03861273. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03861273?term=NCT03861273&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Almeida-Porada, G. A New “FIX” for Hemophilia B Gene Therapy. Blood 2021, 137, 2860–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; De Wolf, D.; Nguyen, P.A.; Pham, Q.H.; Samara-Kuko, E.; Landau, J.; Blouse, G.E.; Chuah, M.K.; VandenDriessche, T. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B Using CB 2679d-GT: A Novel Factor IX Variant with Higher Potency than Factor IX Padua. Blood 2021, 137, 2902–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapugi, M.; Cunningham, K. Corticosteroids. Orthop. Nurs. 2019, 38, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Blomberg, P. Gene therapy—From idea to reality. Lakartidningen 2017, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Lippi, G.; Favaloro, E.J. Gene therapy for hemophilias: The end of phenotypic testing or the start of a new era? Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2020, 31, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, P.; Lillicrap, D. Hemophilia Gene Therapy: Approaching the First Licensed Product. Hemasphere 2021, 5, e540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriart, J.A.B. Precision medicine/personalized medicine: A critical analysis of movements in the transformation of biomedicine in the early 21st century. Cad. Saude Publica 2019, 35, e00153118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baynam, G.; Molster, C.; Bauskis, A.; Kowal, E.; Savarirayan, R.; Kelaher, M.; Easteal, S.; Massey, L.; Garvey, G.; Goldblatt, J.; et al. Indigenous Genetics and Rare Diseases: Harmony, Diversity and Equity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1031, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.W.; Nugent, D.; Wilton, P.; O’Mahony, B.; Dolan, G.; O’Hara, J.; Berntorp, E. Achieving the unimaginable: Health equity in haemophilia. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Recombinant Vector | Type of Hemophilia |
|---|---|
| Adeno-associated virus serotype 5 vector containing a variant of B-domain deleted human FVIII a known as BMN 270) | HA |
| Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 6 vector encoding B-domain deleted human FVIII (known as SB-525) | HA |
| Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vector containing a functional copy of the codon-optimized FVIII’s cDNA encoding B-domain deleted FVIII | HA |
| Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing a bioengineered capsid and a codon-optimized expression cassette to drive the expression of the SQ form of a B-domain deleted human FVIII (known as SPK-8011) | HA |
| Non-replicating adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vector expressing the Padua variant (R338L) of human FIX b, under the control of the liver-specific apolipoproteín E/alpha1-antitrypsin (hAAT) enhancer | HB |
| Adeno-associated virus serotype rh10 vector containing the human FIX gene | HB |
| Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 3 vector containing a codon-optimized expression cassette encoding a variant of human FIX known as FLT180a | HB |
| Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing codon-optimized FIX-Padua (known as AMT-061) | HB |
| Lentiviral vector encoding human FVIII or FIX | HA and HB |
| Title | NCT Number | Intervention | Sponsor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene therapy study in patients with severe HA with antibodies against AAV5 a | NCT03520712 | Adeno-associated virus serotype 5 vector containing a B-deleted variant of FVIII b (valoctocogene roxaparvovec) | BioMarin Pharmaceutical |
| Gene therapy study in patients with severe HA | NCT02576795 | Valoctocogene roxaparvovec-BMN 270 | BioMarin Pharmaceutical |
| Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of valoctocogene roxaparvovec in patients with HA | NCT03370913 | Valoctocogene roxaparvovec | BioMarin Pharmaceutical |
| Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of volactocogene roxaparvovec combined with prophylactic administration of corticosteroids in HA | NCT04323098 | Valoctocogene roxaparvovec | BioMarin Pharmaceutical |
| Single-arm study evaluating the efficacy and safety of a dose of 4 × 1013 vg/kg of valoctocogene roxaparvovec in patients with HA | NCT03391974 | Valoctocogene roxaparvovec | BioMarin Pharmaceutical |
| Gene therapy for HA | NCT03001830 | New adeno-associated virus serotype 8 capsid vector pseudotype encoding FVIII-V3 (AAV2/8-HLP-FVIII-V3) | University College, London/Medical Research Council |
| Safety and dose-escalation study of an adeno-associated virus vector used as gene therapy in HA | NCT03370172 | Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 (AAV8) expressing FVIII Factor VIII (BDD-FVIII) (BAX 888) | Baxalta, now part of Shire |
| Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of PF-07055480 in adults with moderate or severe HA | NCT04370054 | Recombinant AAV2/6 encoding B-domain deleted FVIII cDNA | UniQure Biopharma BV |
| Gene therapy study of recombinant AAV2/6 with the FVIII gene (SB-525) in patients with severe HA | NCT03061201 | Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 6 (AAV6) encoding B-domain deleted human FVIII cDNA | Pfizer |
| Study of AAV5-hFIX c in patients with moderate or severe HB | NCT02396342 | AAV5 containing the human FIX gene (AAV5-hFIX) | UniQure Biopharma BV |
| Dose confirmation trial of AAV5-hFIXco-Padua | NCT03489291 | Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 5 (AAV5) vector containing the Padua variant of a codon-optimized complementary human FIX under the control of a liver-specific promoter (AAV5-hFIXco-Padua, AMT-061) | UniQure Biopharma BV |
| HOPE-B: Study of AMT-061 in patients with moderate or severe HB | NCT03569891 | AAV5-hFIXco-Padua, AMT-061 | UniQure Biopharma BV |
| Single ascending dose of adeno-associated virus serotype 8 of FIX in adults with HB | NCT01687608 | Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 for FIX gene therapy (AskBio009) | Baxalta now part of Shire |
| Phase 1–2 study of SHP648, an adeno-associated virus vector for gene therapy in patients with HB | NCT04394286 | Adeno-associated virus serotype 8 (AAV8) vector expressing FIX Padua (SHP648) | Baxalta now part of Shire |
| Dose-escalation study of a complementary adeno-associated virus gene therapy vector in patients with HB | NCT00979238 | Self-complementary adeno-associated virus serotype 8 (AAV8) vector expressing a transgene of codon-optimized FIX (scAAV2/8-LP1-hFIXco) | St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)/Hemophilia of Georgia, Inc./Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia/University College, London |
| Long-term safety and efficacy study of SPK-9001 in patients with HB | NCT03307980 | Non-replicating adeno-associated virus serotype 2 (AAV2) vector expressing the Padua variant (R338L) of human FIX under the control of the liver-specific apolipoproteín E (Apo E) enhancer (PF-06838435/fidanacogene elaparvovec) | Pfizer |
| Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of gene therapy with PF-06838435 in adult males with moderate or severe HB | NCT03861273 | Fidanacogene elaparvovec | Pfizer |
| Lentiviral FVIII Gene Therapy | NCT03217032 | Lentiviral factor VIII gene. Modified autologous stem cells (YUVAGT-F801) | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute |
| Lentiviral FIX Gene Therapy | NCT03961243 | Lentiviral factor IX gene. Modified autologous stem cells (YUVA-GT-F901) | Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Merchán, E.C.; De Pablo-Moreno, J.A.; Liras, A. Gene Therapy in Hemophilia: Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147647
Rodríguez-Merchán EC, De Pablo-Moreno JA, Liras A. Gene Therapy in Hemophilia: Recent Advances. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147647
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Merchán, E. Carlos, Juan Andres De Pablo-Moreno, and Antonio Liras. 2021. "Gene Therapy in Hemophilia: Recent Advances" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147647
APA StyleRodríguez-Merchán, E. C., De Pablo-Moreno, J. A., & Liras, A. (2021). Gene Therapy in Hemophilia: Recent Advances. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147647