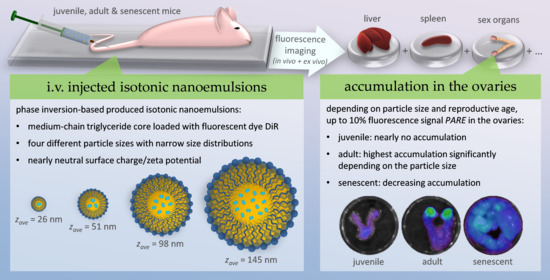
Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Nanoemulsions
2.2. Cytotoxic Properties of the Nanoemulsions
2.3. Nanoemulsion Interaction with the Blood Cells
2.4. In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging
2.5. Ex Vivo Fluorescence Imaging and Biodistribution of the Nanoemulsions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Isotonic Nanoemulsions
3.2. Particle Size Analysis, Zeta Potential, Osmolality, and pH Measurements
3.3. Determination of the IC50 on 3T3 and NHDF Fibroblasts
3.4. Investigation of the Nanoemulsion Interaction with Blood Cells
3.5. Animal Handling
3.6. Fluorescence Imaging
3.7. Image and Data Processing of the Fluorescence Images
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, B.; Maji, R.; Roychowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S. Toxicological Concerns of Engineered Nanosize Drug Delivery Systems. Am. J. Ther. 2016, 23, e139–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ema, M.; Okuda, H.; Gamo, M.; Honda, K. A Review of Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Laboratory Animals. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 67, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navya, P.N.; Daima, H.K. Rational Engineering of Physicochemical Properties of Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications with Nanotoxicological Perspectives. Nano Converg. 2016, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schädlich, A.; Hoffmann, S.; Mueller, T.; Caysa, H.; Rose, C.; Göpferich, A.; Li, J.; Kuntsche, J.; Mäder, K. Accumulation of Nanocarriers in the Ovary: A Neglected Toxicity Risk? J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Du, L.; Tian, X.; Fan, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Keelan, J.A.; Nie, G. Effects of Nanoparticle Size and Gestational Age on Maternal Biodistribution and Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles in Pregnant Mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 230, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yih, T.C.; Wei, C. Nanomedicine in Cancer Treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2005, 1, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsjärvi, S.; Sancey, L.; Dufort, S.; Belloche, C.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Garcion, E.; Coll, J.L.; Hindré, F.; Benoît, J.P. Effect of Particle Size on the Biodistribution of Lipid Nanocapsules: Comparison between Nuclear and Fluorescence Imaging and Counting. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Nouri, M.A.; Osama; Azmy, M.; Awatif; Elshal, O.I.; Ragab, A.; Ragab, M.H.; Elsherbini, A.A.M. Study of the Effect of Silver Nanoparticles Exposure on the Ovary of Rats. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.W.; Jeong, J.K.; Gurunathan, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Das, J.; Kwon, D.N.; Cho, S.G.; Park, C.; Seo, H.G.; Park, J.K.; et al. Male- and Female-Derived Somatic and Germ Cell-Specific Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Mouse. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merian, J.; Boisgard, R.; Decleves, X.; Theze, B.; Texier, I.; Tavitian, B. Synthetic Lipid Nanoparticles Targeting Steroid Organs. J. Nuclear Med. 2013, 54, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lainé, A.L.; Gravier, J.; Henry, M.; Sancey, L.; Béjaud, J.; Pancani, E.; Wiber, M.; Texier, I.; Coll, J.L.; Benoît, J.P.; et al. Conventional versus Stealth Lipid Nanoparticles: Formulation and in Vivo Fate Prediction through FRET Monitoring. J. Control. Release 2014, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steuber, N.; Vo, K.; Wadhwa, R.; Birch, J.; Iacoban, P.; Chavez, P.; Elbayoumi, T.A. Tocotrienol Nanoemulsion Platform of Curcumin Elicit Elevated Apoptosis and Augmentation of Anticancer Efficacy against Breast and Ovarian Carcinomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, S.D.; Sarrel, P.M.; Nelson, L.M. Hormone Replacement Therapy in Young Women with Primary Ovarian Insufficiency and Early Menopause. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wildemeersch, D.; Janssens, D.; Weyers, S. Continuous Combined Parenteral Estrogen Substitution and Intrauterine Progestogen Delivery: The Ideal HST Combination? Maturitas 2005, 51, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snima, K.S.; Jayakumar, R.; Lakshmanan, V.K. In Vitro and in Vivo Biological Evaluation of O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Encapsulated Metformin Nanoparticles for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, M. Role of Metformin in Management of PCOS. JK Sci. 2005, 7, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, M.; Sahin, S. Microparticulate and Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems for Metformin Hydrochloride. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazile, D.V.; Ropert, C.; Huve, P.; Verrecchia, T.; Mariard, M.; Frydman, A.; Veillard, M.; Spenlehauer, G. Body Distribution of Fully Biodegradable [14C]-Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanoparticles Coated with Albumin after Parenteral Administration to Rats. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Choi, H.; Zhou, R.; Chen, I.W. Quantitative Evaluation of the Reticuloendothelial System Function with Dynamic MRI. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawara, K.; Furumoto, K.; Takakura, Y.; Hashida, M.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Surface Hydrophobicity of Particles Is Not Necessarily the Most Important Determinant in Their in Vivo Disposition after Intravenous Administration in Rats. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, K.M. Estrogens and Age-Related Memory Decline in Rodents: What We Have Learned and Where Do We Go from Here? Horm. Behav. 2009, 55, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, E.H.Y.; Chan, C.C.W.; Yeung, W.S.B.; Ho, P.C. Effect of Age on Ovarian Stromal Flow Measured by Three-Dimensional Ultrasound with Power Doppler in Chinese Women with Proven Fertility. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, L.R.; Mackenzie, A.C.L.; Kraemer, D.C.; Morley, J.E.; Farr, S.; Chaffin, C.L.; Merchenthaler, I. Shortened Estrous Cycle Length, Increased FSH Levels, FSH Variance, Oocyte Spindle Aberrations, and Early Declining Fertility in Aging Senescence- Accelerated Mouse Prone-8 (SAMP8) Mice: Concomitant Characteristics of Human Midlife Female Reproductive Agi. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garris, D.R.; Williams, S.K.; West, L. Morphometric Evaluation of Diabetes-associated Ovarian Atrophy in the C57BL/KsJ Mouse: Relationship to Age and Ovarian Function. Anat. Rec. 1985, 211, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendrick, J.L.; Raafat, A.M.; Haslam, S.Z. Mammary Gland Growth and Development from the Postnatal Period to Postmenopause: Ovarian Steroid Receptor Ontogeny and Regulation in the Mouse. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1998, 3, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Or, S. Morphological and Functional Development of the Ovary of the Mouse. I. Morphology and Histochemistry of the Developing Ovary in Normal Conditions and after FSH Treatment. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1963, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, S.L.; Wiles, M.V.; Dunn, S.L.; Taft, R.A. Mouse Estrous Cycle Identification Tool and Images. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, F.; Finch, E. Differential Contributions of Ovarian and Extraovarian Factors to Age-Related Reductions in Plasma Estradiol and Progesterone during the Estrous Cycle of C57BL/6J Mice. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 806–810. [Google Scholar]
- Kopp, C.; Ressel, V.; Wigger, E.; Tobler, I. Influence of Estrus Cycle and Ageing on Activity Patterns in Two Inbred Mouse Strains. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 167, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C.E.; Holmes, D.J. Ovarian Aging in Developmental and Evolutionary Contexts. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1204, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, L.M.; Payne, J. The Influence of Age on Reproductive Capacity in C57BL Mice. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1970, 21, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Adachi, J.; Togashi, M.; Moriguchi, Y. Relationship Fertilization between Rate in IVCS Mice Decline in Fertility and In Vitro It Has Been Reported That Both the Uterus and the Oocyte Are Involved in Age-Related Decline in Fertility [1–3]. When Fertilized Ova from Young Females Are Transferr. J. Reprod. Dev. 1994, 40, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Zhou, W.X.; Cheng, J.P.; Zhang, Y.X. Age-Related Changes in the Oestrous Cycle and Reproductive Hormones in Sensescene-Accelerated Mouse. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2005, 17, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busmann, E.F.; García Martínez, D.; Lucas, H.; Mäder, K. Phase Inversion-Based Nanoemulsions of Medium Chain Triglyceride as Potential Drug Delivery System for Parenteral Applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblond, F.; Davis, S.C.; Valdés, P.A.; Pogue, B.W. Pre-Clinical Whole-Body Fluorescence Imaging: Review of Instruments, Methods and Applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 98, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaffer, B.S.; Grayson, M.H.; Wortham, J.M.; Kubicek, C.B.; McCleish, A.T.; Prajapati, S.I.; Nelon, L.D.; Brady, M.M.; Jung, I.; Hosoyama, T.; et al. Immune Competency of a Hairless Mouse Strain for Improved Preclinical Studies in Genetically Engineered Mice. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2354–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavides, F.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; VanBuskirk, A.M.; Reeve, V.E.; Kusewitt, D.F. The Hairless Mouse in Skin Research. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 53, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schädlich, A.; Kempe, S.; Mäder, K. Non-Invasive in Vivo Characterization of Microclimate PH inside in Situ Forming PLGA Implants Using Multispectral Fluorescence Imaging. J. Control. Release 2014, 179, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, M.; Harms, M.; Lucas, H.; Ebensen, T.; Guzmán, C.A.; Mäder, K. Dual Dye In-Vivo Imaging of Differentially Charged PLGA Carriers Reveals Antigen-Depot Effect, Leading to Improved Immune Responses in Preclinical Models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Ye, Z.; Li, F.; Mahato, R.I. HPMA Polymer-Based Site-Specific Delivery of Oligonucleotides to Hepatic Stellate Cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2009, 19, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenblätter, M.; Ehrchen, J.; Varga, G.; Sunderkötter, C.; Heindel, W.; Roth, J.; Bremer, C.; Wall, A. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Cellular Inflammatory Response in Granuloma Formation Using Fluorescence-Labeled Macrophages. J. Nuclear Med. 2009, 50, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granot, D.; Addadi, Y.; Kalchenlo, V.; Harmelin, A.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Neeman, M. In Vivo Imaging of the Systemic Recruitment of Fibroblasts to the Angiogenic Rim of Ovarian Carcinoma Tumors. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9180–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mérian, J.; Gravier, J.; Navarro, F.; Texier, I. Fluorescent Nanoprobes Dedicated to in Vivo Imaging: From Preclinical Validations to Clinical Translation. Molecules 2012, 17, 5564–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petersen, S.; Fahr, A.; Bunjes, H. Flow Cytometry as a New Approach to Investigate Drug Transfer between Lipid Particles. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehl, M.; Harms, M.; Göttel, B.; Kubas, H.; Schiroky, D.; Mäder, K. Acid-Induced Degradation of Widely Used NIR Dye DiR Causes Hypsochromic Shift in Fluorescence Properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 132, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.C. The Determination of Log Normal Particle Size Distributions by Dynamic Light Scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 117, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roethlisberger, D.; Mahler, H.C.; Altenburger, U.; Pappenberger, A. If Euhydric and Isotonic Do Not Work, What Are Acceptable PH and Osmolality for Parenteral Drug Dosage Forms? J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 106, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranz, M.; Kastango, E.S. A Review of PH and Osmolarity. Int. J. Pharm. Compd. 2002, 6, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Simamora, P.; Pinsuwan, S.; Alvarez, J.M.; Myrdal, P.B.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Effect of PH on Injection Phlebitis. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maupas, C.; Moulari, B.; Béduneau, A.; Lamprecht, A.; Pellequer, Y. Surfactant Dependent Toxicity of Lipid Nanocapsules in HaCaT Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 411, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Hung, Y.C.; Liau, I.; Huang, G.S. Assessment of the in Vivo Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamazaki, K.; Sato, S.; Yunoki, M.; Noda, T.; Moreira, L.F.; Mimura, H.; Orita, K. Kupffer Cell Function in Chronic Liver Injury and after Partial Hepatectomy. Res. Exp. Med. 1994, 194, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, J.; Senninger, N.; Elser, H. The reticuloendothelial system. An overview of function, pathology and recent methods of measurement. Z. Gastroenterol. 1994, 32, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, A.; Knook, D.L. The Reticuloendothelial System and Aging: A Review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1983, 21, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroslow, B.N.; Larrick, J.W. Clearance of Foreign Red Cells from the Blood of Aging Mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1973, 2, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebino, K.Y. Studies on Coprophagy in Experimental Animals. Jikken Dobutsu. 1993, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| Compounds in wt.% | NE25 | NE50 | NE100 | NE150 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DiR loaded MCT 1 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Kolliphor® HS 15 | 20.0 | 8.8 | 5.3 | 4.0 |
| NaCl solution | 25.3 2 | 23.2 3 | 13.3 4 | 8.0 5 |
| ice-cold water | 46.7 | 60.0 | 73.3 | 80.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Busmann, E.F.; Kollan, J.; Mäder, K.; Lucas, H. Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158283
Busmann EF, Kollan J, Mäder K, Lucas H. Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):8283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158283
Chicago/Turabian StyleBusmann, Eike Folker, Julia Kollan, Karsten Mäder, and Henrike Lucas. 2021. "Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 8283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158283
APA StyleBusmann, E. F., Kollan, J., Mäder, K., & Lucas, H. (2021). Ovarian Accumulation of Nanoemulsions: Impact of Mice Age and Particle Size. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 8283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158283