Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets
Abstract
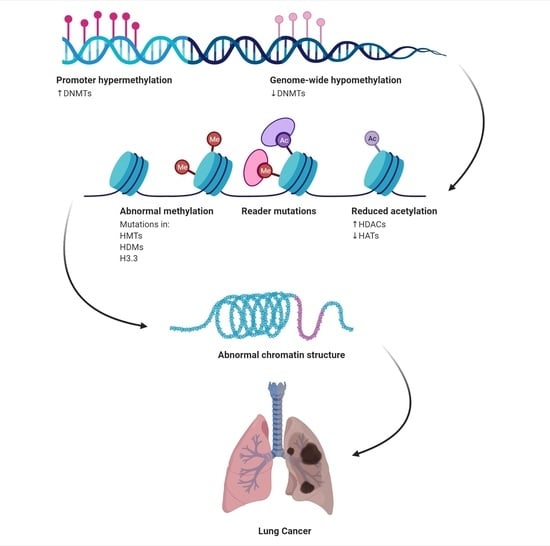
:1. Introduction
Lung Cancer Initiation and Signalling Pathways
2. Epigenetics in Lung Cancer
2.1. Histone Modifications
2.2. Histone Modifications Cross Talk
2.3. Histone Acetylation/Deacetylation
2.4. Histone Methylation
2.5. The Histone Code of Lung Cancer
2.6. Histone Deacetylase Expression in Lung Cancer
3. Lung Cancer Therapeutics
3.1. Histone Modifications in Lung Therapeutics
3.1.1. Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors in Preclinical Studies
3.1.2. Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors (HDIs) in Clinical Use
3.1.3. Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA, Vorinostat)
3.2. Modifiers of Histone Methylation
3.3. Combination Therapy in Lung Cancer Using Histone Modifying Agents
3.3.1. Preclinical Combination Therapy
3.3.2. Clinical Studies of Combined Therapies with Histone Modifiers
3.4. Combinatory Epigenetic Therapy
3.5. Combination Therapy of Histone Modifiers and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
4. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Adenocarcinoma |
| ATRA | All-Trans Retinoic Acid |
| AMI-1 | Arginine Methyltransferase Inhibitor 1 |
| ATO | Arsenic Trioxide |
| AZA | Azathioprine |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CR | Complete Response |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DAPK | Death-Associated Protein Kinase |
| DNA DSB | DNA Double Strands Break |
| DNMT | DNA Methyltransferase |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| HDI(s) | HDAC Inhibitors |
| HATs | Histone Acetyltransferases |
| HDACs | Histone Deacetylases |
| HDI | Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors |
| HDMs | Histone Demethylases |
| KDMs | Histone Lysine Demethylases |
| KMTs | Histone Lysine Methyltransferases |
| HMTs | Histone Methyltransferases |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| ICI | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor |
| IL | Interleukins |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ICAM-1 | Intracellular Adhesion Molecule-1 |
| LCC | Large Cell Cancer |
| lncRNAs | Long Non-Coding RNAs |
| LSD1 | Lysine Specific Demethylase |
| MAGEA3 | Melanoma-Associated Antigen A3 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 |
| MDS | Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| MICA | MHC Class I Chain-Related Molecules |
| mRNA | Micro RNA |
| MUC1 | Mucinous Glycoprotein-1 |
| NNK | Nicotine-Derived Nitrosamine Ketone |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| ncRNAs | Non-Coding RNAs |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma |
| PR | Partial Response |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| P2RD | Phase 2 Suitable Dose |
| PTMs | Post-Translational Modifications |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| PRMT5 | Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RFS | Relapse-Free Survival |
| RECIST | Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours |
| SCLC | Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| SAHA/Vorinostat | Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid |
| SO2 | Sulphur Dioxide |
| TSA | Trichostatin A |
| TSG | Tumour Suppression Genes |
| TKI | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| abb | ddd |
| AC | Adenocarcinoma |
References
- Jemal, A.; Center, M.M.; DeSantis, C.; Ward, E.M. Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalemkerian, G.P.; Loo, B.W.; Akerley, W.; Attia, A.; Bassetti, M.; Boumber, Y.; Decker, R.; Dobelbower, M.C.; Dowlati, A.; Downey, R.J.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmani, L.; Askin, F.; Gabrielson, E.; Li, Q.K. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52 Pt 1, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Noguchi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Geisinger, K.R.; Yatabe, Y.; Beer, D.G.; Powell, C.A.; Riely, G.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhu, H.; Wen, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, T.; Fan, M. Metastasis Patterns and Prognosis of Octogenarians with NSCLC: A Population-based Study. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K. WHO Classification of tumours: Tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. Pathol. Genet. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cantone, L.; Nordio, F.; Hou, L.; Apostoli, P.; Bonzini, M.; Tarantini, L.; Angelici, L.; Bollati, V.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Inhalable metal-rich air particles and histone H3K4 dimethylation and H3K9 acetylation in a cross-sectional study of steel workers. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Arita, A.; Sun, H.; Costa, M. Effects of nickel, chromate, and arsenite on histone 3 lysine methylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 236, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarpia, M.; Aguilar, A.; Chaib, I.; Cardona, A.F.; Fancelli, S.; Laguia, F.; Bracht, J.W.P.; Cao, P.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Karachaliou, N.; et al. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Signaling Pathways, Metabolism, and PD-1/PD-L1 Antibodies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, I.B.; Joe, A. Oncogene Addiction. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3077–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adcock, I.M.; Caramori, G.; Barnes, P.J. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer. New Mol. Insights 2011, 81, 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Shahadin, M.S.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Latif, M.T.; Greene, C.M.; Hassan, T. Challenges and future direction of molecular research in air pollution-related lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinets, T.V.; Foy, B.D. Tumorigenesis: The adaptation of mammalian cells to sustained stress environment by epigenetic alterations and succeeding matched mutations. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansari, J.; Shackelford, R.E.; El-Osta, H. Epigenetics in non-small cell lung cancer: From basics to therapeutics. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peschansky, V.J.; Wahlestedt, C. Non-coding RNAs as direct and indirect modulators of epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.X.S.Y.; Li, X. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling reveals novel epigenetic signatures in squamous cell lung cancer. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 901–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, N.; George, T.L.; Otterson, G.A.; Verschraegen, C.; Wen, H.; Carbone, D.; Herman, J.; Bertino, E.M.; He, K. Advances in epigenetic therapeutics with focus on solid tumors. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, H.; Jalal, S.I. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Hype or Hope? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlacci, W.; Tzankov, A.; Veits, L.; Zelger, B.; Bihl, M.P.; Foerster, A.; Augustin, F.; Fiegl, M.; Savic, S. A Comprehensive Analysis of p16 Expression, Gene Status, and Promoter Hypermethylation In Surgically Resected Non-small Cell Lung Carcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audia, J.E.; Campbell, R.M. Histone Modifications and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a019521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, G.D.; Poirier, M.G. Post-Translational Modifications of Histones That Influence Nucleosome Dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2274–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 2007, 447, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ozark, P.A.; Fantini, D.; Marshall, S.A.; Rendleman, E.J.; Cozzolino, K.A.; Louis, N.; He, X.; Morgan, M.A.; et al. Resetting the epigenetic balance of Polycomb and COMPASS function at enhancers for cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, T.; Read, A. Human Molecular Genetics; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Marks, P.A. Prospects: Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 96, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunstein, M. Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 1197, 389, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, A.; Gemma, A.; Noro, R.; Kataoka, K.; Matsuda, K.; Nara, M.; Okano, T.; Seike, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kawakami, A.; et al. Antitumor activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells: Development of a molecular predictive model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, P. Discovery and development of SAHA as an anticancer agent. Oncogen 2007, 26, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggs, M.G.; Whittaker, R.G.; Neumann, J.R.; Ingram, V.M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature 1977, 268, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.M.; Muir, T.W. Histones: At the Crossroads of Peptide and Protein Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2296–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Jiang, X.J.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, D.S. Histone methyltransferases: Novel targets for tumor and developmental defects. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2159–2175. [Google Scholar]
- D’Oto, A.; Tian, Q.; Davidoff, A.M.; Yang, J. Histone demethylases and their roles in cancer epigenetics. J. Med. Oncol. Ther. 2016, 1, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Rechem, C.; Whetstine, J.R. Examining the impact of gene variants on histone lysine methylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, H.P. A DNA Hypomethylation signature predicts antitumor activity of LSD1 inhibitors in SCLC. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takashina, T.; Kinoshita, I.; Kikuchi, J.; Shimizu, Y.; Sakakibara-Konishi, J.; Oizumi, S.; Nishimura, M.; Dosaka-Akita, H. Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, P.K.; Reynoird, N.; Khatri, P.; Jansen, P.W.T.C.; Wilkinson, A.W.; Liu, S.; Barbash, O.; van Aller, G.S.; Huddleston, M.; Dhanak, D.; et al. SMYD3 links lysine methylation of MAP3K2 to Ras-driven cancer. Nature 2014, 10, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tao, X.; Shen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, B.; Xia, Z. The molecular landscape of histone lysine methyltransferases and demethylases in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Villar-Garea, A.; Boix-Chornet, M.; Espada, J.; Schotta, G.; Bonaldi, T.; Haydon, C.; Ropero, S.; Petrie, K.; et al. Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broeck, A.; Brambilla, E.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Lantuejoul, S.; Brambilla, C.; Eymin, B.; Khochbin, S.; Gazzeri, S. Loss of histone H4K20 trimethylation occurs in preneoplasia and influences prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlesi, F.; Giaccone, G.; Gallegos-Ruiz, M.I.; Loundou, A.; Span, S.W.; Kruyt, P.L.A.; Rodriguez, J. Global histone modifications predict prognosis of resected non small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4358–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligson, D.B.; Horvath, S.; Brian, M.A.M.; Mah, V.; Yu, H.; Tze, S.; Wang, Q.; Chia, D.; Goodglick, L.; Kurdistani, S.K. Global levels of histone modifications predict prognosis in different cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurdistani, S.K. Histone modifications in cancer biology and prognosis. Prog. Drug Res. 2011, 67, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Esteller, M. Epigenetics provides a new generation of oncogenes and tumour-suppressor genes. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteller, M. Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Moriyama, S.; Nakashima, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kiriyama, M.; Fukai, I.; Yamakawa, Y.; Fujii, Y. Histone deacetylase 1 mRNA expression in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2004, 46, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Saito, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Takahashi, T. Reduced expression of class II histone deacetylase genes is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartling, B.; Hofmann, H.; Boettger, T.; Hansen, G.; Burdach, S.; Silber, R.; Simma, A. Comparative application of antibody and gene array for expression profiling in human squamous cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2005, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonke, J.J.; Belderbos, J. Adaptive radiotherapy for lung cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 20, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.S.; Baldwin, D.R. Recent advances in the management of lung cancer. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, s41–s46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Kelly, R.J. New Strategies in Lung Cancer: Epigenetic Therapy for Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2244–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, D.H.; Kwon, S.O.; Kim, W.J.; Hong, Y. Identification of Serial DNA Methylation Changes in the Blood Samples of Patients with Lung Cancer. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2019, 82, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Kijima, M.; Akita, M.; Beppu, T. Potent and specific inhibition of mammalian histone deacetylase both in vivo and in vitro by trichostatin A. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 17174–17179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrener, R.; Beamish, H.; Burgess, A.; Waterhouse, N.J.; Giles, N.; Fairlie, D.P.; Gabrielli, B. Tumor cell-selective cytotoxicity by targeting cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Kummar, S.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Shibata, S.; LoRusso, P.; Yerk, M.; Holleran, J.; Lin, Y.; Beumer, J.; Harvey, R.D.; et al. Phase I study of vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors and hepatic dysfunction: A national cancer institute organ dysfunction working group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4507–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imre, G.; Gekeler, V.; Leja, A.; Beckers, T.; Boehm, M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress the inducibility of nuclear factor kappaB by tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor-1 down regulation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5409–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.; Gordon, G.; Maulik, G.; Doerre, G.; Liu, B.C.; Bueno, R.; Sugarbaker, D.; Jaklitsch, M. Histone deacetylation is directly involved in desilencing the expression of the catalytic subunit of telomerase in normal lung fibroblast. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2005, 9, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, E.; Pacherník, J.; Harničarová, A.; Kovarik, A.; Kovaríková, M.; Hofmanová, J.; Skalníková, M.; Kozubek, M.; Kozubek, S. Nuclear levels and patterns of histone H3 modification and HP1 proteins after inhibition of histone deacetylases. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5035–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Khoury, V.; Gomez, D.; Liautaud-Roger, F.; Trussardi-Régnier, A.; Dufer, J. Effects of the histone deacetylaseinhibitor trichostatin A on nuclear texture and c-jungene expression in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant human H69 lung carcinoma cells. Cytom. A 2004, 62, 109–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, M.; Igishi, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Chikumi, H.; Shigeoka, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Morita, M.; Yasuda, K.; Hitsuda, Y.; Shimizu, E. Suppression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is a determinant of the sensitivity to a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, FK228, in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H. Induction of apoptosis by trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is associated with inhibitionof cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kitazono, M.; Bates, S.; Fok, P.; Fojo, T.; Blagosklonny, M. V The histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228 (desipeptide) restores expression and function of pseudo-null p53. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2002, 1, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.K.; Cho, Y.; Datta, A.; Anumanthan, G.; Ham, A.L.; Carbone, D.P.; Datta, P.K. Elucidating the mechanism of regulation of transforming growth factor ß Type II receptor expression in human lung cancer cell lines. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, S.; Fields, C.R.; Su, N.; Pan, Y.; Robertson, K.D. Pharmacologic inhibition of epigenetic modifications, coupled with gene expression profiling, reveals novel targets of aberrant DNA methylation and histone deacetylation in lung cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2621–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brzeziańska, E.; Dutkowska, A.; Antczak, A. The significance of epigenetic alterations in lung carcinogenesis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 40, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, U.; Möller, M.; Husseini, S.A.; Manderscheid, C.; Häusler, J.; Geisslinger, G.; Niederberger, E. Inhibition of HDAC Enzymes Contributes to Differential Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Proteins in the TLR-4 Signaling Cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, K.C.; Fu, A.; Osusky, K.; Huamani, J.; Hallahan, D.E.; Geng, L. Histone deacetylase inhibitor NVP-LAQ824 sensitizes human nonsmall cell lung cancer to the cytotoxic effects of ionizing radiation. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2007, 18, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Maitland, M.L.; Frankel, P.; Argiris, A.E.; Koczywas, M.; Gitlitz, B.; Thomas, S.; Espinoza-Delgado, I.; Vokes, E.E.; Gandara, D.R.; et al. Carboplatin and paclitaxel in combination with either vorinostat or placebo for first-line therapy of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witta, S.E.; Jotte, R.M.; Konduri, K.; Neubauer, M.A.; Spira, A.I.; Ruxer, R.L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Hirsch, F.R. Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib with and without entinostat in patients with advanced non_small-cell lung cancer who progressed on prior chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.K.; O’Connor, O.A.; Krug, M.L. Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3923–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Dumez, H.; Chen, C.; Ricker, J.L.; Randolph, S.S.; Schöffski, P. Early phase II trial of oral vorinostat in relapsed or refractory breast, colorectal, or non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2008, 26, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynor, A.M.; Dubey, S.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Kolesar, J.M.; Schell, K.; Huie, M.S.; Groteluschen, D.L.; Marcotte, S.M.; Hallahan, C.M.; Weeks, H.R.; et al. Vorinostat (NSC# 701852) in Patients with Relapsed Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Wisconsin Oncology Network Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrump, D.S.; Fischette, M.R.; Nguyen, D.M.; Zhao, M. Clinical and molecular responses in lung cancer patients receiving romidepsin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, T.; Valone, F.; Lipera, W.; Irwin, D.; Paroly, W.; Natale, R.; Sreedharan, S.; Keer, H.; Lum, B.; Scappaticci, F.; et al. Phase II trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor pivaloyloxymethyl butyrate (Pivanex, AN-9) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Foster, B.J.; Meyer, M.; Wozniak, A.; Heilbrun, L.K.; Flaherty, L.; Zalupski, M.; Radulovic, L.; Valdivieso, M.; Lorusso, P.M. Chronic Oral Administration of CI-994: A Phase I Study. Investig. New Drugs 2001, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Parise, R.A.; Ramananthan, R.K.; Lagattuta, T.F.; Musguire, L.A.; Stoller, R.G.; Potter, D.M.; Argiris, A.E.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Egorin, M.J.; et al. Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Study of Vorinostat, A Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel for Advanced Solid Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3605–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.R.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Gillenwater, H.H.; Petroni, G.R.; Burks, S.G.; Philips, J.; Rehm, P.K.; Olazagasti, J.; Kozower, B.D.; Bao, Y. Phase I Trial of Induction Histone Deacetylase and Proteasome Inhibition Followed by Surgery in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasari, A.; Gore, L.; Messersmith, W.A.; Diab, S.; Jimeno, A.; Weekes, C.D.; Lewis, K.D.; Drabkin, H.A.; Flaig, T.W.; Camidge, D.R. A phase I study of sorafenib and vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors with expanded cohorts in renal cell carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 31, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguart, N.; Rosell, R.; Cardenal, F.; Cardona, A.F.; Isla, D.; Palmero, R.; Moran, T.; Rolfo, C.; Pallarès, M.C.; Insa, A.; et al. Phase I/II trial of vorinostat (SAHA) and erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations after erlotinib progression. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Haura, E.; Chiappori, A.; Tanvetyanon, T.; Williams, C.C.; Pinder-Schenck, M.; Kish, J.A.; Kreahling, J.; Lush, R.; Neuger, A.; et al. A phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of panobinostat, an HDAC inhibitor, combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced aerodigestive tract tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, D.A.; Boehm, K.A.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Wagener, D.J.; Krishnamurthi, S.S.; Rosemurgy, A.; Grove, W.; Macdonald, K.; Gulyas, S.; Clark, M.; et al. Gemcitabine plus CI-994 offers no advantage over gemcitabine alone in the treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of a phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauer, L.R.; Olivares, J.; Cunningham, C.; Williams, A.; Grove, W.; Kraker, A.; Olson, S.; Nemunaitis, J. Phase I study of oral CI-994 in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in the treatment of patients with advancedsolid tumors. Cancer Investig. 2004, 22, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juergens, R.A.; Wrangle, J.; Vendetti, F.P.; Murphy, S.C.; Zhao, M.; Coleman, B.; Sebree, R.; Rodgers, K.; Hooker, C.M.; Franco, N.; et al. Combination Epigenetic Therapy Has Efficacy in Patients with Refractory Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, B.F.; Karpenko, M.J.; Liu, Z.; Aimiuwu, J.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Chan, K.K.; Grever, M.R.; Otterson, G.A. Phase I study of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in combination with valproic acid in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 71, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Gilbert, J.; Rudek, M.A.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Gore, S.; Jiemjit, A.; Zhao, M.; Baker, S.; Ambinder, R.F.; Herman, J.G.; et al. A Phase I Dose-Finding Study of 5-Azacytidine in Combination with Sodium Phenylbutyrate in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6241–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candelaria, M.; Gallardo-Rincón, D.; Arce, C.; Cetina, L.; Aguilar-Ponce, J.; Arrieta, O.; González-Fierro, A.; Chávez-Blanco, A.; de la Cruz-Hernández, E.; Camargo, M.; et al. A phase II study of epigenetic therapy with hydralazine and magnesium valproate to overcome chemotherapy resistance in refractory solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.; Rifkind, R.A.; Richon, V.M.; Breslow, R.; Miller, T.; Kelly, W.K. Histone deacetylases and cancer: Causes and therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, O.H.; Göttlicher, M.; Heinzel, T. Histone deacetylase as a therapeutic target. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 12, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiades, N.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Richardson, P.G. Molecular sequelae of histone deacetylase inhibition in human malignant B cells. Blood 2003, 101, 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, E.; Chen, J.; Kim, S.; Han, L.; He, S.; Shi, W.; Simonyan, V.; Sun, Y.; Thiessen, P.; Wang, J.; et al. PubChem3D: A new resource for scientists. J. Chemin. 2011, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deroanne, C.F.; Bonjean, K.; Servotte, S.; Devy, L.; Colige, A.; Clausse, N.; Blacher, S.; Verdin, E.; Foidart, J.; Nusgens, B.V.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents altering vascular endothelial growth factor signalling. Oncogene 2002, 17, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchion, D.C.; Bicaku, E.; Daud, A.I.; Richon, V.; Sullivan, D.M.; Munster, P.N. Sequence-specific potentiation of topoisomerase II inhibitors by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, P.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ramalingam, S.; Belani, C.P. The effect of p53 gene status on the interaction of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid-SAHA) with carboplatin in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Caron, C.; Matthias, G.; Hess, D.; Khochbin, S.; Matthias, P. HDAC-6 interacts with and deacetylates tubulin and microtubules in vivo. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blagosklonny, M.V.; Robey, R.; Sackett, D.L.; Du, L.; Traganos, F.; Darzynkiewicz, Z.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors all induce p21 but differentially cause tubulin acetylation, mitotic arrest, and cytotoxicity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 937–941. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Quan, C.; Zheng, L.; Huang, K. Lung Cancer Therapy Targeting Histone Methylation: Opportunities and Challenges. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, M.; Ishimura, A.; Wanna-Udom, S.; Suzuki, T. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by KDM6A histone demethylase in lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tong, X.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, K.; et al. In vivo CRISPR screening unveils histone demethylase UTX as an important epigenetic regulator in lung tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3978–E3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.; Trojer, P. Targeting histone lysine methylation in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przespolewski, A.; Wang, E.S. Inhibitors of LSD1 as a potential therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuco, V.; De Cesare, M.; Cincinelli, R.; Nannei, R.; Pisano, C.; Zaffaroni, N.; Zunino, F. Synergistic Antitumor Effects of Novel HDAC Inhibitors and Paclitaxel In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- del Bufalo, D.; Desideri, M.; de Luca, T.; di Martile, M.; Gabellini, C.; Monica, V.; Busso, S.; Eramo, A.; de Maria, R.; Milella, M.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition synergistically enhances pemetrexed cytotoxicity through induction of apoptosis and autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Peyton, M.; Xie, Y.; Soh, J.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Frenkel, E.P. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Romidepsin Enhances Anti-Tumor Effect of Erlotinib in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Cell Lines 2009, 4, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witta, S.E.; Gemmill, R.M.; Hirsch, F.R.; Coldren, C.D.; Hedman, K.; Ravdel, L.; Helfrich, B.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Chan, D.C.; Sugita, M.; et al. Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greve, G.; Schiffmann, I.; Pfeifer, D.; Pantic, M.; Schüler, J.; Lübbert, M. The pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat acts as a sensitizer for erlotinib activity in EGFR-mutated and -wildtype non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greve, G.; Schiffmann, I.; Lübbert, M. Epigenetic priming of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines to the antiproliferative and differentiating effects of all-trans retinoic acid. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Fukazawa, T.; Yamatsuji, T.; Matsuoka, J.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, Y.; Durbin, M.; Naomoto, Y. Anti-tumor effect in human lung cancer by a combination treatment of novel histone deacetylase inhibitors: SL142 or SL325 and retinoic acids. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilov, V.; Lavrenkov, K.; Ariad, S. Sodium Valproate, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Enhances the Efficacy of Vinorelbine-Cis-platin- based Chemoradiation in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6565–6572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, T.; Teng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Mei, Q. Sensitization to gamma-irradiation-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vendetti, F.P.; Topper, M.; Huang, P.; Dobromilskaya, I.; Easwaran, H.; Wrangle, J.; Baylin, S.B.; Poirier, J.; Rudin, C.M. Evaluation of azacitidine and entinostat as sensitization agents to cytotoxic chemotherapy in preclinical models of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 6, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiau, R.; Chen, K.; Wen, Y.; Chuang, C.; Yeh, S. Genistein and beta-carotene enhance the growth-inhibitory effect of trichostatin A in A549 cells. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, N.; Kawamata, N.; Takeuchi, S.; Yin, D.; Chien, W.; Miller, C.W.; Koeffler, H.P. SAHA, a HDAC inhibitor, has profound anti-growth activity against non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, M.; Price, T.; Townsend, A.; Sweeney, C.; Spencer, A.; Sukumaran, S.; Longenecker, A.; Lee, L.; Lay, A.; Sharma, G.; et al. Phase 1 clinical trial of the novel proteasome inhibitor marizomib with the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat in patients with melanoma, pancreatic and lung cancer based on in vitro assessments of the combination. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2303–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.; Yao, J.; Chang, S.; Lee, P.; Lee, T. Enhanced suppression of tumor growth by concomitant treatment of human lung cancer cells with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and arsenic trioxide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 257, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.K.; Jin, H.O.; Lee, H.C.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, E.S. Combined effects of sulindac and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on apoptosis induction in human lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajbouj, K.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Omar, H.A.; Sharif-Askari, N.S.; Shafarin, J.; Elmoselhi, A.B.; Ihmaid, A.; Ali, S.A.; Alalool, A.; et al. PRMT5 Selective Inhibitor Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy of Cisplatin in Lung Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, E.E.; Bachman, K.E.; Myöhänen, S.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B. Synergy of demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in the re-expression of genes silenced in cancer. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, A.-J.; Momparler, L.F.; Hurtubise, A.; Momparler, R.L. Antineoplastic action of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine and phenylbutyrate on human lung carcinoma cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2002, 13, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinsky, S.A.; Klinge, D.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Issa, J.P. Inhibition of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation prevents murine lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7089–7093. [Google Scholar]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roulois, D.; Loo Yau, H.; Singhania, R.; Wang, Y.; Danesh, A.; Shen, S.Y.; Han, H.; Liang, G.; Jones, P.A.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. DNA-Demethylating Agents Target Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inducing Viral Mimicry by Endogenous Transcripts. Cell 2015, 162, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, N.; Chen, Z.J. Intrinsic antiviral immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Héninger, E.; Krueger, T.E.G.; Lang, J.M. Augmenting antitumor immune responses with epigenetic modifying agents. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpf, A.R.; Jones, D.A. Reactivating the expression of methylation silenced genes in human cancer. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5496–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehndiratta, S.; Lin, M.-H.; Wu, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Wu, T.-Y.; Chuang, K.-H.; Chao, M.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Pan, S.-L.; Chen, M.-C.; et al. N-alkyl-hydroxybenzoyl anilide hydroxamates as dual inhibitors of HDAC and HSP90, downregulating IFN-γ induced PD-L1 expression. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, D.; Moufarrij, S.; Villagra, A. Immunoepigenetics Combination Therapies: An Overview of the Role of HDACs in Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, M. New modalities of cancer treatment for NSCLC: Focus on immunotherapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Drug | Target/ Mechanism of Action | Phase of Trial | Number of Patients | Outcomes | Clinical Trial Identifier/ Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors | |||||
| Vorinostat | Prevents enzymatic activities of class I and II HDACs, elicits cell arrest, differentiation, and/or apoptosis, antiproliferative, G1/G2 cell cycle arrest, disrupts VEGF signalling | Phase I | 2 NSCLC/73 patients | CR = 1, PR = 3, unconfirmed PR = 2, linear pharmacokinetics with good bioavailability | NCT00045006 [72] |
| Phase II | 16 patients | SD = 8, PR = 1, PD = 3 | NCT00565227 [73] | ||
| Phase II | 8 patients | SD (3.7 months) = 8, OS = 7.1 months | NCT00126451 [74] | ||
| Romidepsin | Triggers p21 expression, H4 acetylation, shift gene signature to normal epithelia | Phase II | 19 Lung Cancer patients | Transient SD = 9 | NCT00020202 [75] |
| Pivanex | Induces tumour cell differentiation and/or apoptosis | Phase II | 47 refractory NSCLC patients | PR = 6.4%, SD (>12 weeks) = 30%, MS = 6.2 months1 year survival rate = 26% | [76] |
| Cl-994 | Inhibits histone deacetylation, G1-S phase cell arrest | Phase I | 53 solid tumours | PR = 1 heavily-pre-treated NSCLC patient SD = 3 (1 NSCLC patient) | [77] |
| Combination therapy | |||||
| Vorinostat + Carboplatin /Paclitaxel | - | Phase I | 28 advanced solid tumour patients | PR = 11 (10 NSCLC), SD = 7 Linear Pharmacokinetics | [78] |
| Vorinostat + Carboplatin/ Paclitaxel | Enhances the anti-cancer effects of platinum compounds and taxanes | Phase II | 94 advanced (stage IIIB or IV NSCLC patients) | Enhanced response rate (34%) OS = 13 months | NCT01413750 [70] |
| Vorinostat + Bortezomib | Combined induction proteasome and histone deacetylase inhibition | Phase I | 21 patients | Tumour necrosis (30%) | [79] |
| Vorinostat + Sorafenib | - | Phase I | 17 patients with advanced solid tumours | Unconfirmed PR = 2 (1 NSCLC patient) | [80] |
| Vorinostat + Erlotinib | - | Phase I/II | 33 advanced NSCLC EGFR mutant patients | PFS = 8 weeks OS = 10.3 months | NCT00503971 [81] |
| Panobinostat + Erlotinib | - | Phase I | 35 NSCLC/42 patients with advanced tumours | Disease control rate = 54%, NSCLC PR =3, SD = 3 PFS = 4.7 months, OS = 41 months, (EGFR mutation) | NCT00738751 [82] |
| Entinostat + Erlotinib | - | Phase II | 132 stage IIIB and IV NSCLC patients | Longer OS (9.4 months) in high E-cadherin patients | NCT00602030 [71] |
| Pivanex + Docetaxel | Synergistic action for growth inhibition of NSCLC cell lines in vitro and for improved survival in animal models | Phase I Phase IIb | 12 patients 225 patients | Results not published | NCT00073385 |
| Cl-994 + Gemcitabine | - | Phase II | 26 NSCLC/174 patients | PR = 8, OR = 12%, MS = 194 days | NCT00005093 [83] |
| Cl-994 + Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | - | Phase I | 30 patients with advanced solid tumours | H3 acetylation levels <1.5-fold times baseline = PD, H3 acetylation levels ≥1.5-fold times baseline = Clinical response/SD, PR = 5 (3 NSCLC) | [84] |
| Azacitidine + Entinostat | Inhibition of promoter methylation | I/II | 45 advanced, refractory NSCLC | MS = 6.4 months, CR =1, PR = 1 | NCT00387465 [85] |
| Decitabine + valproic acid | Inhibitors of DNA methylation and histone deacetylases | I | 8 patients with advanced NSCLC with prior chemotherapy | SD = 1 | NCT00084981 [86] |
| Decitabine + vorinostat | Inhibitors of DNA methylation and histone deacetylases | I | 2 patients with NSCLC/44 with advanced tumours | SD = 29% | NCT00275080 [85] |
| Azacitidine + sodium phenylbutyrate | Inhibitors of DNA methylation and histone deacetylases | I | 1 NSCLC/27 refractory Solid Tumours | SD = 1, PD = 26 | NCT00005639 [87] |
| Hydralazine+ magnesium valproate | Reduction in global DNA methylation, histone deacetylase activity, and promoter demethylation were observed | II | 1 NSCLC/17 refractory solid tumours | PR = 4, SD = 8 | NCT00404508 [88] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajbouj, K.; Al-Ali, A.; Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Hamid, Q. Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111701
Bajbouj K, Al-Ali A, Ramakrishnan RK, Saber-Ayad M, Hamid Q. Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111701
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajbouj, Khuloud, Abeer Al-Ali, Rakhee K. Ramakrishnan, Maha Saber-Ayad, and Qutayba Hamid. 2021. "Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111701
APA StyleBajbouj, K., Al-Ali, A., Ramakrishnan, R. K., Saber-Ayad, M., & Hamid, Q. (2021). Histone Modification in NSCLC: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(21), 11701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111701