Comparison of Circulating Markers and Mucosal Immune Parameters from Skin and Distal Intestine of Atlantic Salmon in Two Models of Acute Stress
Abstract
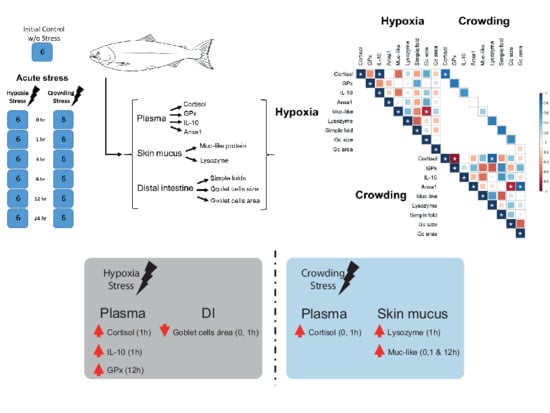
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Plasma Cortisol
2.2. Glutathione Peroxidase Activity
2.3. Immunological Markers
2.4. Histology and Morphometry
2.5. Correlation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design and Sampling
4.2. Cortisol
4.3. Immunological Markers Detection by Indirect ELISA
4.4. Histology and Morphometry
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Portz, D.; Woodley, C.; Cech, J. Stress-associated impacts of short-term holding on fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.; Galhardo, L.; Noble, C.; Damsgård, B.; Spedicato, M.T.; Zupa, W.; Beauchaud, M.; Kulczykowska, E.; Massabuau, J.-C.; Carter, T.J. Biochemistry, Behavioural indicators of welfare in farmed fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinas, I. The mucosal immune system of teleost fish. Biology 2015, 4, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazado, C.C.; Voldvik, V. Temporal control of responses to chemically induced oxidative stress in the gill mucosa of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 205, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, G.K. Stress in Fish; Csermely, P., Ed.; New York Acad Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Tort, L.; Balasch, J.C. Netting the stress responses in fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Rodriguez-Barreto, D.; Martin, S.A.; Van Oosterhout, C.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Cable, J.; Hamilton, A.; Garcia De Leaniz, C.; Consuegra, S.J. Contrasting effects of acute and chronic stress on the transcriptome, epigenome, and immune response of Atlantic salmon. Epigenetics 2018, 13, 1191–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortés, R.; Teles, M.; Tridico, R.; Acerete, L.; Tort, L. Effects of cortisol administered through slow-release implants on innate immune responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Int. J. Genom. 2013. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, R.E.; Sundell, K.; Mayhew, T.M.; Myklebust, R.; Ringo, E. Acute stress alters intestinal function of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Aquaculture 2005, 250, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.J.; Djurhuus, C.B.; Gravholt, C.H.; Iversen, P.; Christiansen, J.S.; Schmitz, O.; Weeke, J.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Møller, N. Metabolism, Effects of cortisol on carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism: Studies of acute cortisol withdrawal in adrenocortical failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3553–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raposo de Magalhães, C.; Schrama, D.; Farinha, A.P.; Revets, D.; Kuehn, A.; Planchon, S.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Cerqueira, M. Protein changes as robust signatures of fish chronic stress: A proteomics approach to fish welfare research. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, S.; Nilsen, T.O.; Kolarevic, J.; Ebbesson, L.O.; Pedrosa, C.; Fivelstad, S.; Hosfeld, C.; Stefansson, S.O.; Terjesen, B.F.; Takle, H. Stocking density limits for post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) with emphasis on production performance and welfare. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosfeld, C.D.; Hammer, J.; Handeland, S.O.; Fivelstad, S.; Stefansson, S.O. Effects of fish density on growth and smoltification in intensive production of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2009, 294, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.V.; Lennox, R.J.; Hinch, S.G.; Cooke, S. Fish out of water: How much air is too much? Fisheries 2015, 40, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Wolf, J. Morphologic effects of the stress response in fish. ILAR J. 2009, 50, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.E.; Sundell, K.; Hansen, T.; Hemre, G.-I.; Myklebust, R.; Mayhew, T.M.; Ringø, E. Acute stress alters the intestinal lining of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. : An electron microscopical study. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 26, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundh, H.; Finne-Fridell, F.; Ellis, T.; Taranger, G.; Niklasson, L.; Pettersen, E.; Wergeland, H.; Sundell, K. Reduced water quality associated with higher stocking density disturbs the intestinal barrier functions of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1346–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djordjevic, B.; Kristensen, T.; Øverli, Ø.; Rosseland, B.; Kiessling, A. Effect of nutritional status and sampling intensity on recovery after dorsal aorta cannulation in free-swimming Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laberge, F.; Yin-Liao, I.; Bernier, N.J. Temporal profiles of cortisol accumulation and clearance support scale cortisol content as an indicator of chronic stress in fish. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coz052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupatsch, I.; Santos, G.; Schrama, J.; Verreth, J. Effect of stocking density and feeding level on energy expenditure and stress responsiveness in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2010, 298, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, S.L.; McGuire, A.; Bernier, N.J.; Vijayan, M.M. Central and peripheral glucocorticoid receptors are involved in the plasma cortisol response to an acute stressor in rainbow trout. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2012, 176, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, T.P.; Lapp, A.F.; Kayes, T.B.; Malison, J.A. Validation of a microtitre plate ELISA for measuring cortisol in fish and comparison of stress responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Aquaculture 1993, 117, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, M.M.; Moon, T.W. Acute handling stress alters hepatic glycogen-metabolism in foof-deprived rainbow-trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 2260–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.B.; Aedo, J.E.; Zuloaga, R.; Valenzuela, C.; Molina, A.; Valdés, J.A. Cortisol induces reactive oxygen species through a membrane glucocorticoid receptor in rainbow trout myotubes. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, T.D.; Thi Mai, N.; Duy Khoa, T.N.; Abol-Munafi, A.B.; Liew, H.J.; Kim, C.-B.; Wong, L.L. Molecular Characterization and Gene Expression of Glutathione Peroxidase 1 in Tor tambroides Exposed to Temperature Stress. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2019, 15, 1176934319853580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tort, L. Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciliberti, M.G.; Albenzio, M.; Inghese, C.; Santillo, A.; Marino, R.; Sevi, A.; Caroprese, M. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation and cytokine production in sheep as affected by cortisol level and duration of stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Montero, A.; Torrecillas, S.; Tort, L.; Ginés, R.; Acosta, F.; Izquierdo, M.; Montero, D. Stress response and skin mucus production of greater amberjack (Seriola dumerili) under different rearing conditions. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 735005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Das, S.; Samal, J.; Thatoi, H. Epidermal mucus, a major determinant in fish health: A review. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, L.R.; Timmerhaus, G.; Torgersen, J.S.; Ytteborg, E.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Handeland, S.; Stefansson, S.O.; Nilsen, T.O.; Calabrese, S.; Ebbesson, L. Impact of fish density and specific water flow on skin properties in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post-smolts. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteban, M.Á.; Cerezuela, R. Fish mucosal immunity: Skin. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Demers, N.E.; Bayne, C.J. The immediate effects of stress on hormones and plasma lysozyme in rainbow trout. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1997, 21, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easy, R.; Ross, N. Changes in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar mucus components following short-and long-term handling stress. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1616–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niklasson, L.; Sundh, H.; Olsen, R.-E.; Jutfelt, F.; Skjødt, K.; Nilsen, T.O.; Sundell, K.S. Effects of cortisol on the intestinal mucosal immune response during cohabitant challenge with IPNV in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hur, S.W.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, B.I.; Park, S.J.; Hwang, H.G.; Jun, J.C.; Myeong, J.I.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.D. Digestive physiological characteristics of the Gobiidae-Characteristics of CCK-producing Cells and Mucus-secreting Goblet Cells of Stomach Fish and Stomachless Fish. Dev. Reprod. 2016, 20, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specian, R.D.; Neutra, M.R. Mechanism of rapid mucus secretion in goblet cells stimulated by acetylcholine. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 85, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Nyström, E.E. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.J.; Moon, C.H.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Park, J.W.; Chung, D.K. Identification and functional analysis of salmon annexin 1 induced by a virus infection in a fish cell line. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13816–13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Lange, B.; González-Aravena, M.; Font, A.; Guzmán, F.; Mercado, L. Detection of peroxiredoxin-like protein in Antarctic sea urchin (Sterechinus neumayeri) under heat stress and induced with pathogen-associated molecular pattern from Vibrio anguillarum. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, C.A.; Gomez, F.A.; Mercado, L.; Ramírez, R.; Marshall, S.H. Piscirickettsia salmonis Imbalances the Innate Immune Response to Succeed in a Productive Infection in a Salmonid Cell Line Model. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djordjevic, B.; Morales-Lange, B.; Øverland, M.; Mercado, L.; Lagos, L. Immune and proteomic responses to the soybean meal diet in skin and intestine mucus of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac. Nutr. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Marker | Source | Dilution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-10 | Mouse | 1:400 | [43] |
| Anxa1 | Mouse | 1:400 | Supplementary Figure S1 |
| Muc-like protein | Mouse | 1:400 | [44] |
| Lysozyme | Rabbit | 1:800 | [44] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Djordjevic, B.; Morales-Lange, B.; McLean Press, C.; Olson, J.; Lagos, L.; Mercado, L.; Øverland, M. Comparison of Circulating Markers and Mucosal Immune Parameters from Skin and Distal Intestine of Atlantic Salmon in Two Models of Acute Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031028
Djordjevic B, Morales-Lange B, McLean Press C, Olson J, Lagos L, Mercado L, Øverland M. Comparison of Circulating Markers and Mucosal Immune Parameters from Skin and Distal Intestine of Atlantic Salmon in Two Models of Acute Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031028
Chicago/Turabian StyleDjordjevic, Brankica, Byron Morales-Lange, Charles McLean Press, Jake Olson, Leidy Lagos, Luis Mercado, and Margareth Øverland. 2021. "Comparison of Circulating Markers and Mucosal Immune Parameters from Skin and Distal Intestine of Atlantic Salmon in Two Models of Acute Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031028
APA StyleDjordjevic, B., Morales-Lange, B., McLean Press, C., Olson, J., Lagos, L., Mercado, L., & Øverland, M. (2021). Comparison of Circulating Markers and Mucosal Immune Parameters from Skin and Distal Intestine of Atlantic Salmon in Two Models of Acute Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031028