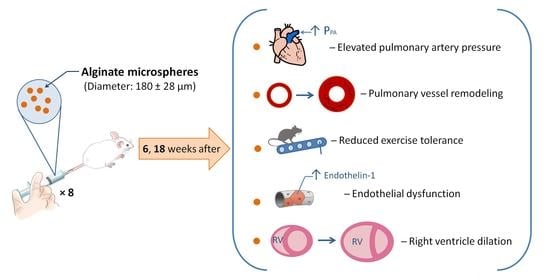
Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Caused by Repeated Intravenous Administration of Partially Biodegradable Sodium Alginate Microspheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Animal Survival
2.2. Treadmill Test
2.3. Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
2.4. Cardiac Catheterization with Manometry
2.5. Histological Examination of the Lung Vessels
2.6. Histological Heart Examination
2.7. Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Embolic Particles
4.3. Experimental Protocol
4.4. Treadmill Test
4.5. Transthoracic Echocardiography
4.6. Cardiac Catheterization with Manometry
4.7. Filling the Vascular Bed of the Lungs, Followed by Histological Examination
4.8. Hematological and Biochemical Parameters
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CO | Cardiac output |
| CTEPH | Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| PECAM-1 | Endothelial–platelet adhesion molecule 1 |
| ELISA | Enzyme immunoassay analysis |
| FGF-1 | Fibroblast growth factor-1 |
| FS | Shortening fraction |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LAP | Left atrial pressure |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| M/G | Mannuronic acid/guluronic acid |
| MIP-1α | Macrophage inflammatory protein 1α |
| MPA | Main pulmonary artery |
| MBG | Marinobufagenin |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| MS | Microspheres |
| MCP-1 | Monocytic chemotactic factor-1 |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| PC | Pulmonary circulation |
| RV | Right ventricle |
| RVMP | Right ventricular mean pressure |
| RVSP | Right ventricular systolic pressure |
| TTE | Transthoracic echocardiography |
| TNF α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosse, S.D.; Nelson, R.E.; Nyarko, K.A.; Richardson, L.C.; Raskob, G.E. The economic burden of incident venous thromboembolism in the United States: A review of estimated attributable healthcare costs. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, I.M.; Pesavento, R.; Bonderman, D.; Yuan, J.X. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A current understanding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riedel, M.; Stanek, V.; Widimsky, J.; Prerovsky, I. Longterm follow-up of patients with pulmonary thromboembolism. Late prognosis and evolution of hemodynamic and respiratory data. Chest 1982, 81, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jimenez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runyon, M.S.; Gellar, M.A.; Sanapareddy, N.; Kline, J.A.; Watts, J.A. Development and comparison of a minimally-invasive model of autologous clot pulmonary embolism in Sprague-Dawley and Copenhagen rats. Thromb. J. 2010, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, C.; Wu, D.; Yang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Lian, N.; Chen, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y. Expression of tissue factor and forkhead box transcription factor O-1 in a rat model for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, M.; Nagaoka, T.; Morio, Y.; Sato, K.; Uchida, K.; Homma, N.; Takahashi, K. Involvement of Rho kinase in the pathogenesis of acute pulmonary embolism-induced polystyrene microspheres in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, J.A.; Marchick, M.R.; Gellar, M.A.; Kline, J.A. Up-regulation of arginase II contributes to pulmonary vascular endothelial cell dysfunction during experimental pulmonary embolism. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 24, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Loza, P.-A.; Jung, P.; Abeßer, M.; Umbenhauer, S.; Williams, T.; Frantz, S.; Schuh, K.; Pelzer, H.-T. Development and Characterization of an Inducible Rat Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertersion. Hypertension 2016, 67, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpov, A.; Anikin, N.; Cherepanov, D.; Mihailova, A.; Krasnova, M.; Smirnov, S.; Mihailov, E.; Chefu, S.; Ivkin, D.; Moiseeva, O.; et al. A new rat model of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension induced by repeated intravenous administration of biodegradable alginate microspheres. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, P.; Kandasubramanian, B. Review of alginate-based hydrogel bioprinting for application in tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Oda, T. Biological activities of alginate. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 72, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate gel particles-A review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axpe, E.; Oyen, M.L. Applications of Alginate-Based Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariyadi, D.M.; Islam, N. Current Status of Alginate in Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 2020, 8886095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekalska, M.; Puciłowska, A.; Szymańska, E.; Ciosek, P.; Winnicka, K. Alginate: Current Use and Future Perspectives in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 7697031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sachan, K.N.; Pushkar, S.; Jha, A.; Bhattcharya, A. Sodium alginate: The wonder polymer for controlled drug delivery. J. Pharm. Res. 2009, 2, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Hu, T. Expression and Correlation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) with Pulmonary Artery Remodeling and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy in Experimental Pulmonary Embolism. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulchrone, A.; Kellihan, H.B.; Forouzan, O.; Hacker, T.A.; Bates, M.L.; Francois, C.J.; Chesler, N.C. A Large Animal Model of Right Ventricular Failure due to Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Focus on Function. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesLauriers, J.; Ugalde, P.; Miro, S.; Ferland, S.; Bergeron, S.; Lacasse, Y.; Provencher, S. Adjustments in cardiorespiratory function after pneumonectomy: Results of the pneumonectomy project. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabinovitch, M.; Guignabert, C.; Humbert, M.; Nicolls, M.R. Inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarck, R.; Wynants, M.; Verbeken, E.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. Contribution of inflammation and impaired angiogenesis to the pathobiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Okada, O.; Tanabe, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Terai, M.; Takiguchi, Y.; Masuda, M.; Nakajima, N.; Hiroshima, K.; Inadera, H.; et al. Plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and pulmonary vascular resistance in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, K.M.; Olle, S.; Fuge, J.; Welte, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Lerch, C.; Maegel, L.; Haller, H.; Jonigk, D.; Schiffer, L. CXCL13 in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smukowska-Gorynia, A.; Marcinkowska, J.; Chmara, E.; Malaczynska-Rajpold, K.; Slawek-Szmyt, S.; Cieslewicz, A.; Janus, M.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Jankiewicz, S.; Komosa, A.; et al. Neopterin as a Biomarker in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Respiration 2018, 96, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölmel, S.; Hobohm, L.; Käberich, A.; Krieg, V.J.; Bochenek, M.L.; Wenzel, P.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; Liebetrau, C.; Hasenfuß, G.; Mayer, E.; et al. Potential Involvement of Osteopontin in Inflammatory and Fibrotic Processes in Pulmonary Embolism and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermair, J.; Redwan, B.; Alias, S.; Jabkowski, J.; Panzenboeck, A.; Kellermair, L.; Winter, M.; Weltermann, A.; Lang, I.M.; Kellermair, J. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 deficiency misguides venous thrombus resolution. Blood 2013, 122, 3376–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabini, D.; Heinemann, A.; Foris, V.; Nagaraj, C.; Nierlich, P.; Bálint, Z.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Lang, I.M.; Klepetko, W.; Olschewski, H.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory markers in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langer, F.; Schramm, R.; Bauer, M.; Tscholl, D.; Kunihara, T.; Schafers, H.J. Cytokine response to pulmonary thromboendarterectomy. Chest 2004, 126, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleby, J.; Bouzina, H.; Lundgren, J.; Radegran, G. Angiogenic and inflammatory biomarkers in the differentiation of pulmonary hypertension. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2017, 51, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpov, A.A.; Puzanov, M.V.; Ivkin, D.Y.; Krasnova, M.V.; Anikin, N.A.; Docshin, P.M.; Moiseeva, O.M.; Galagudza, M.M. Non-inferiority of microencapsulated mesenchymal stem cells to free cells in cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: A rationale for using paracrine factor(s) instead of cells. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 100, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, H.S.; O’Sullivan, J.; Porteous, N.; Ruiz-Hernandez, E.; Kelly, H.M.; O’Brien, F.J.; Duffy, G.P. A collagen cardiac patch incorporating alginate microparticles permits the controlled release of hepatocyte growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 to enhance cardiac stem cell migration and proliferation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e384–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, P.; De Haan, B.; Van Schilfgaarde, R. Effect of the alginate composition on the biocompatibility of alginate-polylysine microcapsules. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.; Gombotz, W.R. Protein release from alginate matrices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 31, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tønnesen, H.H.; Karlsen, J. Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belattmania, Z.; Kaidi, S.; El Atouani, S.; Katif, C.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B.; Vasconcelos, V. Isolation and FTIR-ATR and 1H NMR Characterization of Alginates from the Main Alginophyte Species of the Atlantic Coast of Morocco. Molecules 2020, 25, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Chemical modification of alginates in organic solvent systems. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veiseh, O.; Doloff, J.C.; Ma, M.; Vegas, A.J.; Tam, H.H.; Bader, A.R.; Li, J.; Langan, E.; Wyckoff, J.; Loo, W.S.; et al. Size- and shape-dependent foreign body immune response to materials implanted in rodents and non-human primates. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vegas, A.J.; Veiseh, O.; Doloff, J.C.; Thema, V.; Tam, H.H.; Bratlie, K.M.; Minglin, M.; Bader, A.R.; Langan, E.; Olejnik, K.; et al. Combinatorial hydrogel library enables identification of materials that mitigate the foreign body response in primates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, A.R.; Alnuaimat, H.; Mubarak, K. Pulmonary vasodilator testing and use of calcium channel blockers in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domingo, E.; Grignola, J.C.; Aguilar, R.; Montero, M.A.; Arredondo, C.; Vázquez, M.; Meseguer, M.L.; Bravo, C.; Bouteldja, N.; Hidalgo, C.; et al. In vivo assessment of pulmonary arterial wall fibrosis by intravascular optical coherence tomography in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A new prognostic marker of adverse clinical follow-up. Open Respir. Med. J. 2013, 7, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elkareh, J.; Kennedy, D.J.; Yashaswi, B.; Vetteth, S.; Shidyak, A.; Kim, E.G.R.; Smaili, S.; Periyasamy, S.M.; Hariri, I.M.; Fedorova, L.; et al. Marinobufagenin stimulates fibroblast collagen production and causes fibrosis in experimental uremic cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 2007, 49, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikitina, E.R.; Mikhailov, A.V.; Nikandrova, E.S.; Frolova, E.V.; Fadeev, A.V.; Shman, V.V.; Shilova, V.Y.; Tapilskaya, N.I.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V.; et al. In preeclampsia endogenous cardiotonic steroids induce vascular fibrosis and impair relaxation of umbilical arteries. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagrov, A.; Fedorova, O.V.; Maslova, M.N.; Roukoyatkina, N.I.; Ukhanova, M.V.; Zhabko, E.P. Endogenous plasma Na,K-ATPase inhibitory activity and digoxin like immunoreactivity after acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 1991, 25, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.J.; Shrestha, K.; Sheehey, B.; Li, X.S.; Guggilam, A.; Wu, Y.; Finucan, M.; Gabi, A.; Medert, C.M.; Westfall, K.M.; et al. Elevated Plasma Marinobufagenin, An Endogenous Cardiotonic Steroid, Is Associated With Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Nitrative Stress in Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Parameter | 0 weeks | 1 week | 2 weeks | 3 weeks | 4 weeks | 5 weeks | 6 weeks | 18 weeks | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVSP (mm Hg) | 51.0 ± 14.0 * | 40.5 ± 6.3 | 37.4 ± 13.1 | 41.6 ± 5.7 | 36.2 ± 7.9 | 36.9 ± 5.5 | 37.1 ± 12.8 | 46.0 ± 9.2 * | 25.1 ± 3.7 |
| RVMP (mm Hg) | 18.1 ± 4.4 * | 14.4 ± 1.4 | 13.5 ± 3.4 | 15.6 ± 2.5 * | 12.7 ± 2.1 | 15.3 ± 1.8 * | 13.7 ± 3.9 | 16.1 ± 4.1 * | 8.3 ± 1.8 |
| CO (mL/min) | 25.8 ± 5.5 | 29.5 ± 12.9 | 26.4 ± 9.7 | 29.9 ± 11.0 | 29.7 ± 4.2 | 27.7 ± 8.9 | 24.1 ± 10.7 | 24.8 ± 14.6 | 22.6 ± 7.2 |
| LAP (mm Hg) | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 1.9 | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.4 |
| RVSP/CO (mmHg/mL/min) | 2.05 ± 0.62 * | 1.53 ± 0.45 | 1.83 ± 0.67 | 1.55 ± 0.55 | 1.25 ± 0.36 | 1.69 ± 0.53 | 1.88 ± 1.18 | 2.29 ± 1.25 * | 1.18 ± 0.37 |
| Mean BP (mm Hg) | 60.8 ± 12.2 | 55.5 ± 8.9 | 77.6 ± 13.9 | 60.9 ± 10.6 | 78.8 ± 19.1 | 65.7 ± 18.8 | 65.5 ± 26.5 | 58.8 ± 15.0 | 63.3 ± 9.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karpov, A.A.; Anikin, N.A.; Mihailova, A.M.; Smirnov, S.S.; Vaulina, D.D.; Shilenko, L.A.; Ivkin, D.Y.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Moiseeva, O.M.; Galagudza, M.M. Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Caused by Repeated Intravenous Administration of Partially Biodegradable Sodium Alginate Microspheres. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031149
Karpov AA, Anikin NA, Mihailova AM, Smirnov SS, Vaulina DD, Shilenko LA, Ivkin DY, Bagrov AY, Moiseeva OM, Galagudza MM. Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Caused by Repeated Intravenous Administration of Partially Biodegradable Sodium Alginate Microspheres. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031149
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarpov, Andrei A., Nikita A. Anikin, Aleksandra M. Mihailova, Sergey S. Smirnov, Dariya D. Vaulina, Leonid A. Shilenko, Dmitry Yu. Ivkin, Alexei Y. Bagrov, Olga M. Moiseeva, and Michael M. Galagudza. 2021. "Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Caused by Repeated Intravenous Administration of Partially Biodegradable Sodium Alginate Microspheres" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031149
APA StyleKarpov, A. A., Anikin, N. A., Mihailova, A. M., Smirnov, S. S., Vaulina, D. D., Shilenko, L. A., Ivkin, D. Y., Bagrov, A. Y., Moiseeva, O. M., & Galagudza, M. M. (2021). Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Caused by Repeated Intravenous Administration of Partially Biodegradable Sodium Alginate Microspheres. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031149