Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice
Abstract
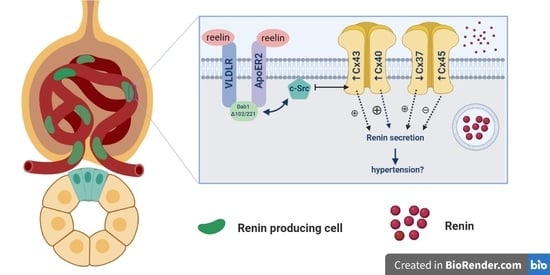
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cx37 Expression
2.2. Cx40 Expression
2.3. Cx43 Expression
2.4. Cx45 Expression
2.5. Panx1 Expression
2.6. Renin Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Dab1 Conventional Mutants and Sample Collection
4.2. Immunofluorescence
4.3. Tissue Preparation for Light Microscopy (LM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
4.5. Semi-Quantifcation of Cx Expression
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanner, F.; Sorensen, C.M.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Connexins and the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1143–R1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Kitazono, T. Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization (EDH) in Diabetes: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pogoda, K.; Kameritsch, P.; Mannell, H.; Pohl, U. Connexins in the control of vasomotor function. Acta Physiol. 2019, 225, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasen, T.; Johnstone, S.; Vidal-Brime, L.; Lynn, K.S.; Koval, M. Connexins: Synthesis, Post-Translational Modifications, and Trafficking in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Gal, L.; Pellegrin, M.; Santoro, T.; Mazzolai, L.; Kurtz, A.; Meda, P.; Wagner, C.; Haefliger, J.A. Connexin37-Dependent Mechanisms Selectively Contribute to Modulate Angiotensin II -Mediated Hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, W.Y.; Ma, K.T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.S.; et al. The enhancement of Cx45 expression and function in renal interlobar artery of spontaneously hypertensive rats at different age. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2015, 40, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naus, C.C.; Giaume, C. Bridging the gap to therapeutic strategies based on connexin/pannexin biology. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinken, M.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. The role of intercellular communication via “gap junctions” in disease. Ned. Tijdschr. Voor Geneeskd. 2003, 147, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Van Campenhout, R.; Cooreman, A.; Leroy, K.; Rusiecka, O.M.; Van Brantegem, P.; Annaert, P.; Muyldermans, S.; Devoogdt, N.; Cogliati, B.; Kwak, B.R.; et al. Non-canonical roles of connexins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2020, 153, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, M.; Decrock, E.; Leybaert, L.; Bultynck, G.; Himpens, B.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Non-channel functions of connexins in cell growth and cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedner, P.; Steinhauser, C.; Theis, M. Functional redundancy and compensation among members of gap junction protein families? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solan, J.L.; Lampe, P.D. Kinase programs spatiotemporally regulate gap junction assembly and disassembly: Effects on wound repair. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 50, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michalski, K.; Syrjanen, J.L.; Henze, E.; Kumpf, J.; Furukawa, H.; Kawate, T. The Cryo-EM structure of pannexin 1 reveals unique motifs for ion selection and inhibition. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Decrock, E.; Vinken, M.; De Vuyst, E.; Krysko, D.V.; D’Herde, K.; Vanhaecke, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Rogiers, V.; Leybaert, L. Connexin-related signaling in cell death: To live or let die? Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luetic, M.; Vitlov Uljevic, M.; Masek, T.; Benzon, B.; Vukojevic, K.; Filipovic, N. PUFAs supplementation affects the renal expression of pannexin 1 and connexins in diabetic kidney of rats. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, A.B.; Kavvadas, P.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Functional roles of connexins and pannexins in the kidney. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2015, 72, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosovic, I.; Filipovic, N.; Benzon, B.; Vukojevic, K.; Saraga, M.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Bocina, I.; Saraga-Babic, M. Spatio-temporal patterning of different connexins in developing and postnatal human kidneys and in nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type (CNF). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krattinger, N.; Alonso, F.; Capponi, A.; Mazzolai, L.; Nicod, P.; Meda, P.; Haefliger, J.A. Increased expression of renal cyclooxygenase-2 and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in hypertensive Cx40-deficient mice. J. Vasc. Res. 2009, 46, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweda, F.; Kurtz, L.; de Wit, C.; Janssen-Bienhold, U.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Substitution of connexin40 with connexin45 prevents hyperreninemia and attenuates hypertension. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, G.I.; Fernandez, P.; Velarde, V.; Saez, J.C. Angiotensin II-Induced Mesangial Cell Damaged Is Preceded by Cell Membrane Permeabilization Due to Upregulation of Non-Selective Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, X.; Huang, J.; Gong, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, H. Connexin43 regulates high glucose-induced expression of fibronectin, ICAM-1 and TGF-beta1 via Nrf2/ARE pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidaway, P. Chronic kidney disease: Targeting connexin-43 reduces progression of CKD in mice. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, G.W.; Chadjichristos, C.E.; Kavvadas, P.; Tang, S.C.W.; Yiu, W.H.; Green, C.R.; Potter, J.A.; Siamantouras, E.; Squires, P.E.; Hills, C.E. Blocking Connexin-43 mediated hemichannel activity protects against early tubular injury in experimental chronic kidney disease. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Hou, S.; Feng, L.; Shen, P.; Nan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, D.; Feng, J. Vinpocetine Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Targeting Astrocytic Connexin43 via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoneshima, H.; Nagata, E.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamada, M.; Nakajima, K.; Miyata, T.; Ogawa, M.; Mikoshiba, K. A novel neurological mutant mouse, yotari, which exhibits reeler-like phenotype but expresses CR-50 antigen/reelin. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 29, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Setsu, T.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kikkawa, S.; Terashima, T.; Maeda, K. Cortical layer V neurons in the auditory and visual cortices of normal, reeler, and yotari mice. Kobe J. Med Sci. 2010, 56, E50–E59. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, M. Scrambler and yotari disrupt the disabled gene and produce a reeler-like phenotype in mice. Nature 1997, 389, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racetin, A.; Juric, M.; Filipovic, N.; Solic, I.; Kosovic, I.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Kunac, N.; Zekic Tomas, S.; Saraga, M.; Soljic, V.; et al. Expression and localization of DAB1 and Reelin during normal human kidney development. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racetin, A. The expression patterns of REELIN, NOTCH2, LC3B, and CASPASE-3 in the postnatal kidney of Dab1-/- (yotari) mice. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, A. Renal connexins and blood pressure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toubas, J.; Beck, S.; Pageaud, A.L.; Huby, A.C.; Mael-Ainin, M.; Dussaule, J.C.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Alteration of connexin expression is an early signal for chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F24–F32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sala, G.; Badalamenti, S.; Ponticelli, C. The Renal Connexome and Possible Roles of Connexins in Kidney Diseases. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2016, 67, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, P.A.; Chen, S.; Armando, I. Connections in chronic kidney disease: Connexin 43 and connexin 37 interaction. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F21–F23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sequeira Lopez, M.L.; Pentz, E.S.; Nomasa, T.; Smithies, O.; Gomez, R.A. Renin cells are precursors for multiple cell types that switch to the renin phenotype when homeostasis is threatened. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Capisano, M.C.; Ortiz, P.A.; Harding, P.; Garvin, J.L.; Beierwaltes, W.H. Adenylyl cyclase isoform v mediates renin release from juxtaglomerular cells. Hypertension 2007, 49, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atchison, D.K.; Ortiz-Capisano, M.C.; Beierwaltes, W.H. Acute activation of the calcium-sensing receptor inhibits plasma renin activity in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R1020–R1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Capisano, M.C.; Ortiz, P.A.; Harding, P.; Garvin, J.L.; Beierwaltes, W.H. Decreased intracellular calcium stimulates renin release via calcium-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase. Hypertension 2007, 49, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beierwaltes, W.H. The role of calcium in the regulation of renin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F1–F11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.; Yao, J. Connexin Hemichannels Contribute to the Activation of cAMP Signaling Pathway and Renin Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanner, F.; von Maltzahn, J.; Maxeiner, S.; Toma, I.; Sipos, A.; Kruger, O.; Willecke, K.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Connexin45 is expressed in the juxtaglomerular apparatus and is involved in the regulation of renin secretion and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R371–R380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steppan, D.; Geis, L.; Pan, L.; Gross, K.; Wagner, C.; Kurtz, A. Lack of connexin 40 decreases the calcium sensitivity of renin-secreting juxtaglomerular cells. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2018, 470, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerl, M.; Vockl, J.; Kurt, B.; van Veen, T.A.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Inducible deletion of connexin 40 in adult mice causes hypertension and disrupts pressure control of renin secretion. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machura, K.; Neubauer, B.; Muller, H.; Tauber, P.; Kurtz, A.; Kurtz, L. Connexin 40 is dispensable for vascular renin cell recruitment but is indispensable for vascular baroreceptor control of renin secretion. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2015, 467, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, L.; Gerl, M.; Kriz, W.; Wagner, C.; Kurtz, A. Replacement of connexin 40 by connexin 45 causes ectopic localization of renin-producing cells in the kidney but maintains in vivo control of renin gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F403–F409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudara, V.; Bechberger, J.; Freitas-Andrade, M.; De Bock, M.; Wang, N.; Bultynck, G.; Naus, C.C.; Leybaert, L.; Giaume, C. The connexin43 mimetic peptide Gap19 inhibits hemichannels without altering gap junctional communication in astrocytes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whyte-Fagundes, P.; Zoidl, G. Mechanisms of pannexin1 channel gating and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensbak, B.; Mikkelsen, H.B.; Gustafsson, F.; Christensen, T.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H. Expression of connexin 37, 40, and 43 mRNA and protein in renal preglomerular arterioles. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 115, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, F.; Mikkelsen, H.B.; Arensbak, B.; Thuneberg, L.; Neve, S.; Jensen, L.J.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H. Expression of connexin 37, 40 and 43 in rat mesenteric arterioles and resistance arteries. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 119, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, A. Connexins, renin cell displacement and hypertension. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, T.H.; Sorensen, C.M.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H. Connexin abundance in resistance vessels from the renal microcirculation in normo- and hypertensive rats. APMIS 2009, 117, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Postnatal Day | Part of Kidney | Cx37 | Cx40 | Cx43 | Cx45 | Panx1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | Y | WT | Y | WT | Y | WT | Y | WT | Y | ||
| 4 | G | + | + | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | + | + | + | + |
| PCT | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | + | |
| DCT | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | |
| M | + | +++ | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | +++ | - | - | |
| 14 | G | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | ++ | ++/+++ |
| PCT | +++ | + | + | + | + | + | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | |
| DCT | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | |
| M | + | + | + | ++ | + | +/++ | ++ | +++ | + | + | |
| Antibodies | Host | Dilution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Anti-Cx37/GJA4 ab181701 | Rabbit | 1:500 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| Anti-Cx40/GJA5 ab213688 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Cx43&GJA1 ab87645 | Goat | 1:200 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Cx45/GJA7 ab135474 Anti-pannexin 1/PANX1 | Rabbit Rabbit | 1:100 1:300 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) | |
| Smooth Muscle Actin (M0851) Renin ab134783 [7D3-E3] | Mouse Mouse | 1:200 1:100 | Dako (Glostrup, Denmark) Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Secondary | Anti-Goat IgG, Alexa Fluor® 488, ab150129 | Donkey | 1:400 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| Anti-Rabbit IgG, Alexa Fluor® 488, 711-545-152 | Donkey | 1:400 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., (Baltimore, PA, USA) | |
| Anti-Mouse IgG, Rhodamine Red™-X, 715-295-151 | Donkey | 1:400 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., (Baltimore, PA, USA) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lozić, M.; Filipović, N.; Jurić, M.; Kosović, I.; Benzon, B.; Šolić, I.; Kelam, N.; Racetin, A.; Watanabe, K.; Katsuyama, Y.; et al. Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031284
Lozić M, Filipović N, Jurić M, Kosović I, Benzon B, Šolić I, Kelam N, Racetin A, Watanabe K, Katsuyama Y, et al. Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLozić, Mirela, Natalija Filipović, Marija Jurić, Ivona Kosović, Benjamin Benzon, Ivana Šolić, Nela Kelam, Anita Racetin, Koichiro Watanabe, Yu Katsuyama, and et al. 2021. "Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031284
APA StyleLozić, M., Filipović, N., Jurić, M., Kosović, I., Benzon, B., Šolić, I., Kelam, N., Racetin, A., Watanabe, K., Katsuyama, Y., Ogata, M., Saraga-Babić, M., & Vukojević, K. (2021). Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031284