Role of NLRs in the Regulation of Type I Interferon Signaling, Host Defense and Tolerance to Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Type I Interferons
1.1. Immune Response to Infection and Tissue Tolerance are Influenced by the Type I Interferon Response
1.2. Induction of Type I Interferon Response by Nucleic Acid Sensing
1.3. Induction of Type I Interferon Responses by Membrane Bound TLRs
1.4. Induction of Interferon Responses by NLRs
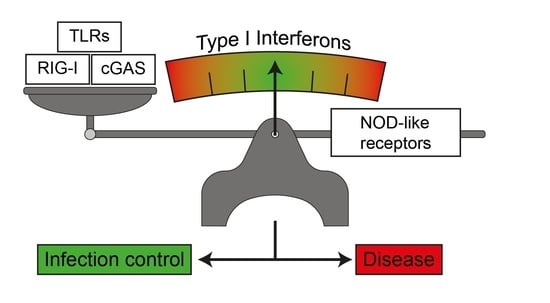
2. Negative Regulatory Feedback on Type I Interferon Responses by NLRs
2.1. NLRX1
2.2. NLRC3
2.3. NLRC5
2.4. NLRP2
2.5. NLRP4
2.6. NLRP11
2.7. NLRP12
2.8. NLRP14
3. Synergistic Effect of NLRs on Type I IFN Responses upon Nucleic Acid and Bacterial Sensing
3.1. NOD1
3.2. NOD2
3.3. NLRC4
3.4. NLRP6
3.5. NLRP9
4. Type I IFN Modulates the Quality of the NLR Response to Infection
NLRP3
5. NLR-Mediated Diseases Join the Expanding Spectrum of Interferonopathies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negishi, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Yanai, H. The Interferon (Ifn) Class of Cytokines and the Ifn Regulatory Factor (Irf) Transcription Factor Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, D.C.; Grant, F.J.; Rixon, M.W.; Kindsvogel, W. Interferon-Epsilon; ZymoGenetics: Seattle, WA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, O.M.; Bohlander, S.; Allen, G. Nomenclature of the Human Interferon Genesa. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleur, L.; David, W.; Nardelli, B.; Tsareva, T.; Mather, D.; Feng, P.; Semenuk, M.; Taylor, K.; Buergin, M.; Chinchilla, D.; et al. Interferon-Κ, a Novel Type I Interferon Expressed in Human Keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39765–39771. [Google Scholar]
- Kotenko, V.S.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. Ifn-Lambdas Mediate Antiviral Protection through a Distinct Class Ii Cytokine Receptor Complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokunina-Olsson, L.; Muchmore, B.; Tang, W.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Park, H.; Dickensheets, H.; Hergott, D.; Porter-Gill, P.; Mumy, A.; Kohaar, I.; et al. A Variant Upstream of Ifnl3 (Il28b) Creating a New Interferon Gene Ifnl4 Is Associated with Impaired Clearance of Hepatitis C Virus. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzé, G.; Lutfalla, G.; Gresser, I. Genetic Transfer of a Functional Human Interferon Alpha Receptor into Mouse Cells: Cloning and Expression of Its Cdna. Cell 1990, 60, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, D.; Cohen, B.; Rubinstein, M. The Human Interferon Alpha/Beta Receptor: Characterization and Molecular Cloning. Cell 1994, 77, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanski, P.; Witte, M.; Kellum, M.; Rubinstein, M.; Hackett, R.; Pitha, P.; Colamonici, O.R. Cloning and Expression of a Long Form of the Beta Subunit of the Interferon Alpha Beta Receptor That Is Required for Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 21606–21611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, B.; Novick, D.; Barak, S.; Rubinstein, M. Ligand-Induced Association of the Type I Interferon Receptor Components. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 4208–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, M.; Briscoe, J.; Laxton, C.; Guschin, D.; Ziemiecki, A.; Silvennoinen, O.; Harpur, A.G.; Barbieri, G.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Schindler, C.; et al. The Protein Tyrosine Kinase Jak1 Complements Defects in Interferon-Alpha/Beta and -Gamma Signal Transduction. Nature 1993, 366, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, L.; Fellous, M.; Stark, G.R.; Pellegrini, S. A Protein Tyrosine Kinase in the Interferon Alpha/Beta Signaling Pathway. Cell 1992, 70, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanski, P.; Fish, E.; Nadeau, O.W.; Witte, M.; Platanias, L.C.; Yan, H.; Krolewski, J.; Pitha, P.; Colamonici, O.R. A Region of the Beta Subunit of the Interferon Alpha Receptor Different from Box 1 Interacts with Jak1 and Is Sufficient to Activate the Jak-Stat Pathway and Induce an Antiviral State. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26388–26393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Krishnan, K.; Greenlund, A.C.; Gupta, S.; Lim, J.T.; Schreiber, R.D.; Schindler, C.W.; Krolewski, J.J. Phosphorylated Interferon-Alpha Receptor 1 Subunit (Ifnar1) Acts as a Docking Site for the Latent Form of the 113 Kda Stat2 Protein. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.; Shuai, K.; Prezioso, V.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Interferon-Dependent Tyrosine Phosphorylation of a Latent Cytoplasmic Transcription Factor. Science 1992, 257, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-Stat Pathways and Transcriptional Activation in Response to Ifns and Other Extracellular Signaling Proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.Y. A Transcription Factor with Sh2 and Sh3 Domains Is Directly Activated by an Interferon Alpha-Induced Cytoplasmic Protein Tyrosine Kinase(S). Cell 1992, 70, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Fu, X.Y.; Improta, T.; Aebersold, R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Proteins of Transcription Factor Isgf-3: One Gene Encodes the 91-and 84-Kda Isgf-3 Proteins That Are Activated by Interferon Alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7836–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehret, B.G.; Reichenbach, P.; Schindler, U.; Horvath, C.M.; Fritz, S.; Nabholz, M.; Bucher, P. DNA Binding Specificity of Different Stat Proteins. Comparison of in Vitro Specificity with Natural Target Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6675–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decker, T.; Lew, D.J.; Mirkovitch, J.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Cytoplasmic Activation of Gaf, an Ifn-Gamma-Regulated DNA-Binding Factor. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.D.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stats: Transcriptional Control and Biological Impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, G.; Velazquez, L.; Scrobogna, M.; Fellous, M.; Pellegrini, S. Activation of the Protein Tyrosine Kinase Tyk2 by Interferon Alpha/Beta. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 223, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamonici, R.O.; Uyttendaele, H.; Domanski, P.; Yan, H.; Krolewski, J.J. P135tyk2, an Interferon-Alpha-Activated Tyrosine Kinase, Is Physically Associated with an Interferon-Alpha Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Krishnan, K.; Lim, J.T.; Contillo, L.G.; Krolewski, J.J. Molecular Characterization of an Alpha Interferon Receptor 1 Subunit (Ifnar1) Domain Required for Tyk2 Binding and Signal Transduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 207–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colamonici, O.; Yan, H.; Domanski, P.; Handa, R.; Smalley, D.; Mullersman, J.; Witte, M.; Krishnan, K.; Krolewski, J. Direct Binding to and Tyrosine Phosphorylation of the Alpha Subunit of the Type I Interferon Receptor by P135tyk2 Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 8133–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caraglia, M.; Abbruzzese, A.; Leardi, A.; Pepe, S.; Budillon, A.; Baldassare, G.; Selleri, C.; de Lorenzo, S.; Fabbrocini, A.; Giuberti, G.; et al. Interferon-A Induces Apoptosis in Human Kb Cells through a Stress-Dependent Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Pathway That Is Antagonized by Epidermal Growth Factor. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Génin, P.; Mamane, Y.; Hiscott, J. Selective DNA Binding and Association with the Creb Binding Protein Coactivator Contribute to Differential Activation of Alpha/Beta Interferon Genes by Interferon Regulatory Factors 3 and 7. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6342–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Fish, E.N.; Sher, D.A.; Gardziola, C.; White, M.F.; Platanias, L.C. Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Serine Kinase by Ifn-Alpha. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus Interference. I. The Interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I Interferons in Infectious Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Medzhitov, R. Type I Interferons in Host Defense. Immunity 2006, 25, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, U.; Steinhoff, U.; Reis, L.F.; Hemmi, S.; Pavlovic, J.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Aguet, M. Functional Role of Type I and Type Ii Interferons in Antiviral Defense. Science 1994, 264, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koerner, I.; Kochs, G.; Kalinke, U.; Weiss, S.; Staeheli, P. Protective Role of Beta Interferon in Host Defense against Influenza a Virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boisson-Dupuis, S.; Kong, X.F.; Okada, S.; Cypowyj, S.; Puel, A.; Abel, L.; Casanova, J.L. Inborn Errors of Human Stat1: Allelic Heterogeneity Governs the Diversity of Immunological and Infectious Phenotypes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, B.; Lambourne, J.; Porter, S.; Hodgson, T. Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis Due to Gain-of-Function Mutation in Stat1. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumlee, R.C.; Lee, C.; Beg, A.A.; Decker, T.; Shuman, H.A.; Schindler, C. Interferons Direct an Effective Innate Response to Legionella Pneumophila Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30058–30066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiavoni, G.; Mauri, C.; Carlei, D.; Belardelli, F.; Pastoris, M.C.; Proietti, E. Type I Ifn Protects Permissive Macrophages from Legionella Pneumophila Infection through an Ifn-Gamma-Independent Pathway. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, A.J.; Hoshino, Y.; Hoshino, S.; Jones, M.B.; Nolan, A.; Weiden, M.D. Exogenous Gamma and Alpha/Beta Interferon Rescues Human Macrophages from Cell Death Induced by Bacillus Anthracis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opitz, B.; Vinzing, M.; van Laak, V.; Schmeck, B.; Heine, G.; Günther, S.; Preissner, R.; Slevogt, H.; N’Guessan, P.D.; Eitel, J.; et al. Legionella Pneumophila Induces Ifnbeta in Lung Epithelial Cells Via Ips-1 and Irf3, Which Also Control Bacterial Replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36173–36179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bukholm, G.; Berdal, B.P.; Haug, C.; Degré, M. Mouse Fibroblast Interferon Modifies Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Infant Mice. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niesel, W.D.; Hess, C.B.; Cho, Y.J.; Klimpel, K.D.; Klimpel, G.R. Natural and Recombinant Interferons Inhibit Epithelial Cell Invasion by Shigella spp. Infect. Immun. 1986, 52, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Biondo, C.; Beninati, C.; Zummo, S.; Galbo, R.; Tomasello, F.; Gambuzza, M.; Macrì, G.; Ruggeri, A.; et al. Type I Ifn Signaling Is Crucial for Host Resistance against Different Species of Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3126–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, E.S.; Sit, B.; Shaker, A.; Currie, E.; Tan, J.M.; van Rijn, J.; Higgins, D.E.; Brumell, J.H. Type I Interferon Promotes Cell-to-Cell Spread of Listeria Monocytogenes. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rayamajhi, M.; Humann, J.; Penheiter, K.; Andreasen, K.; Lenz, L.L. Induction of Ifn-Alphabeta Enables Listeria Monocytogenes to Suppress Macrophage Activation by Ifn-Gamma. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, N.; McComb, S.; Mulligan, R.; Dudani, R.; Krishnan, L.; Sad, S. Type I Interferon Induces Necroptosis in Macrophages During Infection with Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMicking, J.D. Interferon-Inducible Effector Mechanisms in Cell-Autonomous Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondo, C.; Signorino, G.; Costa, A.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Galbo, R.; Bellantoni, A.; Malara, A.; Beninati, C.; Teti, G.; et al. Recognition of Yeast Nucleic Acids Triggers a Host-Protective Type I Interferon Response. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Fresno, C.; Soulat, D.; Roth, S.; Blazek, K.; Udalova, I.; Sancho, D.; Ruland, J.; Ardavin, C. Interferon-Beta Production Via Dectin-1-Syk-Irf5 Signaling in Dendritic Cells Is Crucial for Immunity to C. Albicans. Immunity 2013, 38, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riedelberger, M.; Penninger, P.; Tscherner, M.; Seifert, M.; Jenull, S.; Brunnhofer, C.; Scheidl, B.; Tsymala, I.; Bourgeois, C.; Petryshyn, A.; et al. Type I Interferon Response Dysregulates Host Iron Homeostasis and Enhances Candida Glabrata Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, I.; Scott, J.M.; Kakarla, T.; Duriancik, D.M.; Choi, S.; Cho, C.; Lee, T.; Park, H.; French, A.R.; Beli, E.; et al. Activation Mechanisms of Natural Killer Cells During Influenza Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, J.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Direct Action of Type I Ifn on Nk Cells Is Required for Their Activation in Response to Vaccinia Viral Infection in Vivo. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautier, G.; Humbert, M.; Deauvieau, F.; Scuiller, M.; Hiscott, J.; Bates, E.E.; Trinchieri, G.; Caux, C.; Garrone, P. A Type I Interferon Autocrine-Paracrine Loop Is Involved in Toll-Like Receptor-Induced Interleukin-12p70 Secretion by Dendritic Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.S.; van den Elsen, P.J. Nlrc5: A Key Regulator of Mhc Class I-Dependent Immune Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerincx, A.; Castro, W.; Guarda, G.; Kufer, T.A. Nlrc5, at the Heart of Antigen Presentation. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lugrin, J.; Martinon, F. The Aim2 Inflammasome: Sensor of Pathogens and Cellular Perturbations. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Ascano, M.; Wu, Y.; Barchet, W.; Gaffney, B.L.; Zillinger, T.; Serganov, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Jones, R.A.; Hartmann, G.; et al. Cyclic [G(2’,5’)Pa(3’,5’)P] Is the Metazoan Second Messenger Produced by DNA-Activated Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase. Cell 2013, 153, 1094–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ablasser, A.; Goldeck, M.; Cavlar, T.; Deimling, T.; Witte, G.; Röhl, I.; Hopfner, K.P.; Ludwig, J.; Hornung, V. Cgas Produces a 2’-5’-Linked Cyclic Dinucleotide Second Messenger That Activates Sting. Nature 2013, 498, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic Gmp-Amp Containing Mixed Phosphodiester Linkages Is an Endogenous High-Affinity Ligand for Sting. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burdette, D.L.; Monroe, K.M.; Sotelo-Troha, K.; Iwig, J.S.; Eckert, B.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Vance, R.E. Sting Is a Direct Innate Immune Sensor of Cyclic Di-Gmp. Nature 2011, 478, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Barber, G.N. Sting Is an Endoplasmic Reticulum Adaptor That Facilitates Innate Immune Signalling. Nature 2008, 455, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C.; Chen, Z.J. Structural Basis of Sting Binding with and Phosphorylation by Tbk1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I Interferon [Corrected] Gene Induction by the Interferon Regulatory Factor Family of Transcription Factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase Is a Cytosolic DNA Sensor That Activates the Type I Interferon Pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Shu, C.; Yi, G.; Chaton, C.T.; Shelton, C.L.; Diao, J.; Zuo, X.; Kao, C.C.; Herr, A.B.; Li, P. Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase Is Activated by Double-Stranded DNA-Induced Oligomerization. Immunity 2013, 39, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schoggins, J.W.; MacDuff, D.A.; Imanaka, N.; Gainey, M.D.; Shrestha, B.; Eitson, J.L.; Mar, K.B.; Richardson, R.B.; Ratushny, A.V.; Litvak, V.; et al. Pan-Viral Specificity of Ifn-Induced Genes Reveals New Roles for Cgas in Innate Immunity. Nature 2014, 505, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopfner, K.P.; Hornung, V. Molecular Mechanisms and Cellular Functions of Cgas-Sting Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Wu, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Pivotal Roles of Cgas-Cgamp Signaling in Antiviral Defense and Immune Adjuvant Effects. Science 2013, 341, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paijo, J.; Döring, M.; Spanier, J.; Grabski, E.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Schmidt, T.; Witte, G.; Messerle, M.; Hornung, V.; Kaever, V.; et al. Cgas Senses Human Cytomegalovirus and Induces Type I Interferon Responses in Human Monocyte-Derived Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lio, C.W.; McDonald, B.; Takahashi, M.; Dhanwani, R.; Sharma, N.; Huang, J.; Pham, E.; Benedict, C.A.; Sharma, S. Cgas-Sting Signaling Regulates Initial Innate Control of Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7789–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, D.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.T.; Du, F.; Aroh, C.; Yan, N.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase Is an Innate Immune Sensor of Hiv and Other Retroviruses. Science 2013, 341, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, K.; Prabakaran, T.; Laustsen, A.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Rahbæk, S.H.; Jensen, S.B.; Nielsen, R.; Leber, J.H.; Decker, T.; Horan, K.A.; et al. Listeria Monocytogenes Induces Ifnβ Expression through an Ifi16-, Cgas- and Sting-Dependent Pathway. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchmeier, N.A.; Schreiber, R.D. Requirement of Endogenous Interferon-Gamma Production for Resolution of Listeria Monocytogenes Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7404–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handa, K.; Suzuki, R.; Matsui, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Kumagai, K. Natural Killer (Nk) Cells as a Responder to Interleukin 2 (Il 2). Ii. Il 2-Induced Interferon Gamma Production. J. Immunol. 1983, 130, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yeruva, L.; Marinov, A.; Prantner, D.; Wyrick, P.B.; Lupashin, V.; Nagarajan, U.M. The DNA Sensor, Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase, Is Essential for Induction of Ifn-Β During Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, R.O.; Bell, S.L.; MacDuff, D.A.; Kimmey, J.M.; Diner, E.J.; Olivas, J.; Vance, R.E.; Stallings, C.L.; Virgin, H.W.; Cox, J.S. The Cytosolic Sensor Cgas Detects Mycobacterium Tuberculosis DNA to Induce Type I Interferons and Activate Autophagy. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, A.C.; Cai, H.; Li, T.; Franco, L.H.; Li, X.D.; Nair, V.R.; Scharn, C.R.; Stamm, C.E.; Levine, B.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Cyclic Gmp-Amp Synthase Is an Innate Immune DNA Sensor for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wassermann, R.; Gulen, M.F.; Sala, C.; Perin, S.G.; Lou, Y.; Rybniker, J.; Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Schmidt, T.; Hornung, V.; Cole, S.T.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Differentially Activates Cgas- and Inflammasome-Dependent Intracellular Immune Responses through Esx-1. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.; Orellana, M.A.; Schreiber, R.D.; Remington, J.S. Interferon-Gamma: The Major Mediator of Resistance against Toxoplasma Gondii. Science 1988, 240, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Crawford, R.M.; Hockmeyer, J.T.; Meltzer, M.S.; Nacy, C.A. Leishmania Major Amastigotes Initiate the L-Arginine-Dependent Killing Mechanism in Ifn-Gamma-Stimulated Macrophages by Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 4290–4297. [Google Scholar]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Gack, M.U. Rig-I-Like Receptors: Their Regulation and Roles in Rna Sensing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Eisenächer, K.; Kirchhofer, A.; Brzózka, K.; Lammens, A.; Lammens, K.; Fujita, T.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Krug, A.; Hopfner, K.P. The C-Terminal Regulatory Domain Is the Rna 5’-Triphosphate Sensor of Rig-I. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gack, M.U.; Shin, Y.C.; Joo, C.H.; Urano, T.; Liang, C.; Sun, L.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Chen, Z.; Inoue, S.; et al. Trim25 Ring-Finger E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Is Essential for Rig-I-Mediated Antiviral Activity. Nature 2007, 446, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Seya, T. Riplet/Rnf135, a Ring Finger Protein, Ubiquitinates Rig-I to Promote Interferon-Beta Induction During the Early Phase of Viral Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayman, T.J.; Hsu, A.C.; Kolesnik, T.B.; Dagley, L.F.; Willemsen, J.; Tate, M.D.; Baker, P.J.; Kershaw, N.J.; Kedzierski, L.; Webb, A.I.; et al. Riplet, and Not Trim25, Is Required for Endogenous Rig-I-Dependent Antiviral Responses. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalinski, E.; Lunardi, T.; McCarthy, A.A.; Louber, J.; Brunel, J.; Grigorov, B.; Gerlier, D.; Cusack, S. Structural Basis for the Activation of Innate Immune Pattern-Recognition Receptor Rig-I by Viral Rna. Cell 2011, 147, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, F.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Skaug, B.; Jiang, Q.X.; Chen, Z.J. Mavs Forms Functional Prion-Like Aggregates to Activate and Propagate Antiviral Innate Immune Response. Cell 2011, 146, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lad, S.P.; Yang, G.; Scott, D.A.; Chao, T.H.; Jda, S.C.; de la Torre, J.C.; Li, E. Identification of Mavs Splicing Variants That Interfere with Rigi/Mavs Pathway Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2277–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.G.; Wang, Y.Y.; Han, K.J.; Li, L.Y.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. Visa Is an Adapter Protein Required for Virus-Triggered Ifn-Beta Signaling. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Pietras, E.M.; He, J.Q.; Kang, J.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Oganesyan, G.; Shahangian, A.; Zarnegar, B.; Shiba, T.L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Regulation of Antiviral Responses by a Direct and Specific Interaction between Traf3 and Cardif. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Cheng, G. Modulation of the Interferon Antiviral Response by the Tbk1/Ikki Adaptor Protein Tank. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11817–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, W.C.; Moore, P.A.; LaFleur, D.W.; Tombal, B.; Pitha, P.M. Characterization of the Interferon Regulatory Factor-7 and Its Potential Role in the Transcription Activation of Interferon a Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 29210–29217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Au, W.C.; Moore, P.A.; Lowther, W.; Juang, Y.T.; Pitha, P.M. Identification of a Member of the Interferon Regulatory Factor Family That Binds to the Interferon-Stimulated Response Element and Activates Expression of Interferon-Induced Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11657–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juang, Y.T.; Lowther, W.; Kellum, M.; Au, W.C.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.M. Primary Activation of Interferon a and Interferon B Gene Transcription by Interferon Regulatory Factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9837–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Heylbroeck, C.; Pitha, P.M.; Hiscott, J. Virus-Dependent Phosphorylation of the Irf-3 Transcription Factor Regulates Nuclear Translocation, Transactivation Potential, and Proteasome-Mediated Degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Foy, E.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Akira, S.; et al. Shared and Unique Functions of the Dexd/H-Box Helicases Rig-I, Mda5, and Lgp2 in Antiviral Innate Immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Lucas, R.M.; Liu, L.; Stow, J.L. Signalling, Sorting and Scaffolding Adaptors for Toll-Like Receptors. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs239194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynagh, P.N. Tlr Signalling and Activation of Irfs: Revisiting Old Friends from the Nf-Kappab Pathway. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, S.; Akira, S. Toll-Like Receptors and Type I Interferons. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15319–15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Sato, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Coban, C.; Hemmi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Terai, K.; Matsuda, M.; Inoue, J.; Uematsu, S.; et al. Interferon-Alpha Induction through Toll-Like Receptors Involves a Direct Interaction of Irf7 with Myd88 and Traf6. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Yanai, H.; Mizutani, T.; Negishi, H.; Shimada, N.; Suzuki, N.; Ohba, Y.; Takaoka, A.; Yeh, W.C.; Taniguchi, T. Role of a Transductional-Transcriptional Processor Complex Involving Myd88 and Irf-7 in Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15416–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, N.J.; Symmons, M.F.; Gangloff, M.; Bryant, C.E. Assembly and Localization of Toll-Like Receptor Signalling Complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The Role of Pattern-Recognition Receptors in Innate Immunity: Update on Toll-Like Receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liwinski, T.; Zheng, D.; Elinav, E. The Microbiome and Cytosolic Innate Immune Receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 297, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, J.P.; Davis, B.K. Caterpiller: A Novel Gene Family Important in Immunity, Cell Death, and Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 387–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.B.; Bergstralh, D.T.; Duncan, J.A.; Lei, Y.; Morrison, T.E.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Accavitti-Loper, M.A.; Madden, V.J.; Sun, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Nlrx1 Is a Regulator of Mitochondrial Antiviral Immunity. Nature 2008, 451, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girardin, S.E.; Boneca, I.G.; Carneiro, L.A.; Antignac, A.; Jehanno, M.; Viala, J.; Tedin, K.; Taha, M.K.; Labigne, A.; Zahringer, U.; et al. Nod1 Detects a Unique Muropeptide from Gram-Negative Bacterial Peptidoglycan. Science 2003, 300, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girardin, S.E.; Boneca, I.G.; Viala, J.; Chamaillard, M.; Labigne, A.; Thomas, G.; Philpott, D.J.; Sansonetti, P.J. Nod2 Is a General Sensor of Peptidoglycan through Muramyl Dipeptide (Mdp) Detection. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8869–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inohara, N.; Koseki, T.; del Peso, L.; Hu, Y.; Yee, C.; Chen, S.; Carrio, R.; Merino, J.; Liu, D.; Ni, J.; et al. Nod1, an Apaf-1-Like Activator of Caspase-9 and Nuclear Factor-Kappab. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14560–14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inohara, N.; Ogura, Y.; Chen, F.F.; Muto, A.; Nuñez, G. Human Nod1 Confers Responsiveness to Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2551–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamaillard, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Horie, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Qiu, S.; Saab, L.; Ogura, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Fukase, K.; Kusumoto, S.; et al. An Essential Role for Nod1 in Host Recognition of Bacterial Peptidoglycan Containing Diaminopimelic Acid. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inohara, N.; Ogura, Y.; Fontalba, A.; Gutierrez, O.; Pons, F.; Crespo, J.; Fukase, K.; Inamura, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Host Recognition of Bacterial Muramyl Dipeptide Mediated through Nod2. Implications for Crohn’s Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5509–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes Ruiz, V.M.; Ramirez, J.; Naseer, N.; Palacio, N.M.; Siddarthan, I.J.; Yan, B.M.; Boyer, M.A.; Pensinger, D.A.; Sauer, J.D.; Shin, S. Broad Detection of Bacterial Type Iii Secretion System and Flagellin Proteins by the Human Naip/Nlrc4 Inflammasome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13242–13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinon, F.; Tschopp, J. Inflammatory Caspases: Linking an Intracellular Innate Immune System to Autoinflammatory Diseases. Cell 2004, 117, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuenzel, S.; Till, A.; Winkler, M.; Hasler, R.; Lipinski, S.; Jung, S.; Grotzinger, J.; Fickenscher, H.; Schreiber, S.; Rosenstiel, P. The Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor Nlrc5 Is Involved in Ifn-Dependent Antiviral Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, T.B.; Li, A.; Biswas, A.; Lee, K.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Bayir, E.; Iliopoulos, D.; van den Elsen, P.J.; Kobayashi, K.S. Nlr Family Member Nlrc5 Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Mhc Class I Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13794–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steimle, V.; Siegrist, C.A.; Mottet, A.; Lisowska-Grospierre, B.; Mach, B. Regulation of Mhc Class Ii Expression by Interferon-Gamma Mediated by the Transactivator Gene Ciita. Science 1994, 265, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerincx, A.; Rodriguez, G.M.; Steimle, V.; Kufer, T.A. Nlrc5 Controls Basal Mhc Class I Gene Expression in an Mhc Enhanceosome-Dependent Manner. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchard, M.; Rebé, C.; Derangère, V.; Togbé, D.; Ryffel, B.; Boidot, R.; Humblin, E.; Hamman, A.; Chalmin, F.; Berger, H.; et al. The Receptor Nlrp3 Is a Transcriptional Regulator of Th2 Differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, B.; Schoultz, I.; Neerincx, A.; Napolitano, L.M.; Birkner, K.; Bennek, E.; Sellge, G.; Lerm, M.; Meroni, G.; Söderholm, J.D.; et al. Trim27 Negatively Regulates Nod2 by Ubiquitination and Proteasomal Degradation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Shaw, M.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Nunez, G. Nod-Like Receptors: Role in Innate Immunity and Inflammatory Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 365–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufer, T.A.; Sansonetti, P.J. Nlr Functions Beyond Pathogen Recognition. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werts, C.; Rubino, S.; Ling, A.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. Nod-Like Receptors in Intestinal Homeostasis, Inflammation, and Cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, M.; Knight, J.; Tobita, M.; Soltys, J.; Panitch, H.; Mao-Draayer, Y. The Effect of Interferon-Beta on Mouse Neural Progenitor Cell Survival and Differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.H.; Roy, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Kapoor, A.; Duggal, P.; Wojcik, G.L.; Pass, R.F.; Arav-Boger, R. Role of Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain 1 (Nod1) and Its Variants in Human Cytomegalovirus Control in Vitro and in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7818–E7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berrington, W.R.; Iyer, R.; Wells, R.D.; Smith, K.D.; Skerrett, S.J.; Hawn, T.R. Nod1 and Nod2 Regulation of Pulmonary Innate Immunity to Legionella Pneumophila. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Asano, N.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Gorelick, P.L.; Tsuji, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Chiba, T.; Fuss, I.J.; Kitani, A.; Strober, W. Nod1 Contributes to Mouse Host Defense against Helicobacter Pylori Via Induction of Type I Ifn and Activation of the Isgf3 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1645–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kudo, M.; Arai, H.; Strober, W.; Chiba, T. Sensing of Commensal Organisms by the Intracellular Sensor Nod1 Mediates Experimental Pancreatitis. Immunity 2012, 37, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvarnhammar, A.M.; Petterson, T.; Cardell, L.O. Nod-Like Receptors and Rig-I-Like Receptors in Human Eosinophils: Activation by Nod1 and Nod2 Agonists. Immunology 2011, 134, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.K.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Fortune, S.M.; Coulombe, F.; Behr, M.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Sassetti, C.M.; Kelliher, M.A. Nod2, Rip2 and Irf5 Play a Critical Role in the Type I Interferon Response to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, A.; Chang, T.H.; Harnack, R.; Frohlich, V.; Tominaga, K.; Dube, P.H.; Xiang, Y.; Bose, S. Activation of Innate Immune Antiviral Responses by Nod2. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Forman, M.; Arav-Boger, R. Activation of Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain 2 (Nod2) by Human Cytomegalovirus Initiates Innate Immune Responses and Restricts Virus Replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnicki-Ocwieja, T.; DeFrancesco, A.S.; Chung, E.; Darcy, C.T.; Bronson, R.T.; Kobayashi, K.S.; Hu, L.T. Nod2 Suppresses Borrelia Burgdorferi Mediated Murine Lyme Arthritis and Carditis through the Induction of Tolerance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang Foreman, H.C.; van Scoy, S.; Cheng, T.F.; Reich, N.C. Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 by Site Specific Phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, D.; Planet, P.J.; Soong, G.; Narechania, A.; Prince, A. Induction of Type I Interferon Signaling Determines the Relative Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus Aureus Strains. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, Q.; Yang, F.; Cao, W.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H. Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Antagonizes Nod2-Mediated Antiviral Effects by Inhibiting Nod2 Protein Expression. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00124-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morosky, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Sarkar, S.N.; Coyne, C.B. Retinoic Acid-Induced Gene-I (Rig-I) Associates with Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-2 (Nod2) to Negatively Regulate Inflammatory Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28574–28583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Q.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Xie, X.; Hu, J. Mdp up-Regulates the Gene Expression of Type I Interferons in Human Aortic Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 3599–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, I.C.; Moore, C.B.; Schneider, M.; Lei, Y.; Davis, B.K.; Scull, M.A.; Gris, D.; Roney, K.E.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Bowzard, J.B.; et al. Nlrx1 Protein Attenuates Inflammatory Responses to Infection by Interfering with the Rig-I-Mavs and Traf6-Nf-Κb Signaling Pathways. Immunity 2011, 34, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhu, L.; Matsueda, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Hong, J.; Songyang, Z.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Nlrx1 Negatively Regulates Tlr-Induced Nf-Κb Signaling by Targeting Traf6 and Ikk. Immunity 2011, 34, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Wen, H.; Yu, Y.; Taxman, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Widman, D.G.; Swanson, K.V.; Wen, K.W.; Damania, B.; Moore, C.B.; et al. The Mitochondrial Proteins Nlrx1 and Tufm Form a Complex That Regulates Type I Interferon and Autophagy. Immunity 2012, 36, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Hopcraft, S.E.; Yang, F.; Petrucelli, A.; Guo, H.; Ting, J.P.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B. Nlrx1 Negatively Modulates Type I Ifn to Facilitate Kshv Reactivation from Latency. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Xue, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, R.; Xie, Q.; Guo, M.; Li, G.; Yang, D.; Zhu, H. Nlrx1 Mediates Mavs Degradation to Attenuate the Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Innate Immune Response through Pcbp2. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fekete, T.; Bencze, D.; Szabo, A.; Csoma, E.; Biro, T.; Bacsi, A.; Pazmandi, K. Regulatory Nlrs Control the Rlr-Mediated Type I Interferon and Inflammatory Responses in Human Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, M.E.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kim, T.H.; Uddin, M.B.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, E.; Ma, J.Y.; Jung, J.U.; Kim, C.J.; et al. Fas-Associated Factor-1 Positively Regulates Type I Interferon Response to Rna Virus Infection by Targeting Nlrx1. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Konig, R.; Deng, M.; Riess, M.; Mo, J.; Zhang, L.; Petrucelli, A.; Yoh, S.M.; Barefoot, B.; Samo, M.; et al. Nlrx1 Sequesters Sting to Negatively Regulate the Interferon Response, Thereby Facilitating the Replication of Hiv-1 and DNA Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ling, A.; Soares, F.; Croitoru, D.O.; Tattoli, I.; Carneiro, L.A.; Boniotto, M.; Benko, S.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. Post-Transcriptional Inhibition of Luciferase Reporter Assays by the Nod-Like Receptor Proteins Nlrx1 and Nlrc3. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28705–28716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebsamen, M.; Vazquez, J.; Tardivel, A.; Guarda, G.; Curran, J.; Tschopp, J. Nlrx1/Nod5 Deficiency Does Not Affect Mavs Signalling. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Tattoli, I.; Wortzman, M.E.; Arnoult, D.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. Nlrx1 Does Not Inhibit Mavs-Dependent Antiviral Signalling. Innate Immun. 2013, 19, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mo, J.; Swanson, K.V.; Wen, H.; Petrucelli, A.; Gregory, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Schneider, M.; Jiang, Y.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Nlrc3, a Member of the Nlr Family of Proteins, Is a Negative Regulator of Innate Immune Signaling Induced by the DNA Sensor Sting. Immunity 2014, 40, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortier, A.; Doiron, K.; Saleh, M.; Grinstein, S.; Gros, P. Restriction of Legionella Pneumophila Replication in Macrophages Requires Concerted Action of the Transcriptional Regulators Irf1 and Irf8 and Nod-Like Receptors Naip5 and Nlrc4. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4794–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neerincx, A.; Lautz, K.; Menning, M.; Kremmer, E.; Zigrino, P.; Hösel, M.; Büning, H.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Kufer, T.A. A Role for the Human Nucleotide-Binding Domain, Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing Family Member Nlrc5 in Antiviral Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 26223–26232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjan, P.; Singh, N.; Kumar, A.; Neerincx, A.; Kremmer, E.; Cao, W.; Davis, W.G.; Katz, J.M.; Gangappa, S.; Lin, R.; et al. Nlrc5 Interacts with Rig-I to Induce a Robust Antiviral Response against Influenza Virus Infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, L.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.Y.; Legras, X.; Hong, J.; Ji, J.; Shen, P.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Z.J.; et al. Nlrc5 Negatively Regulates the Nf-Kappab and Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways. Cell 2010, 141, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, H.; Pandey, S.; Zou, J.; Kumagai, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Akira, S.; Kawai, T. Nlrc5 Deficiency Does Not Influence Cytokine Induction by Virus and Bacteria Infections. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, Y.; Cui, J.; Li, Q.; Zou, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Enhanced Tlr-Induced Nf-Κb Signaling and Type I Interferon Responses in Nlrc5 Deficient Mice. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benkő, S.; Kovács, E.G.; Hezel, F.; Kufer, T.A. Nlrc5 Functions Beyond Mhc I Regulation-What Do We Know So Far? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruey, J.M.; Bruey-Sedano, N.; Newman, R.; Chandler, S.; Stehlik, C.; Reed, J.C. Pan1/Nalp2/Pypaf2, an Inducible Inflammatory Mediator That Regulates Nf-Kappab and Caspase-1 Activation in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51897–51907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Kozma, M.; Nagyőszi, P.; Nagy, K.; Fazakas, C.; Haskó, J.; Molnár, K.; Farkas, A.E.; Végh, A.G.; Váró, G.; et al. Expression of Pattern Recognition Receptors and Activation of the Non-Canonical Inflammasome Pathway in Brain Pericytes. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lang, X.; Sun, S.; Gao, C.; Hu, J.; Ding, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, T. Nlrp2 Negatively Regulates Antiviral Immunity by Interacting with Tbk1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pothlichet, J.; Meunier, I.; Davis, B.K.; Ting, J.P.; Skamene, E.; von Messling, V.; Vidal, S.M. Type I Ifn Triggers Rig-I/Tlr3/Nlrp3-Dependent Inflammasome Activation in Influenza a Virus Infected Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathinam, V.A.; Vanaja, S.K.; Waggoner, L.; Sokolovska, A.; Becker, C.; Stuart, L.M.; Leong, J.M.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Trif Licenses Caspase-11-Dependent Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation by Gram-Negative Bacteria. Cell 2012, 150, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Stevenson, H.L.; Scott, M.J.; Ismail, N. Type I Interferon Contributes to Noncanonical Inflammasome Activation, Mediates Immunopathology, and Impairs Protective Immunity During Fatal Infection with Lipopolysaccharide-Negative Ehrlichiae. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lian, Y.G.; Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xu, Q.L.; Xia, X.J. Nlrp4 Is an Essential Negative Regulator of Fructose-Induced Cardiac Injury in Vitro and in Vivo. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 91, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, D.; Songyang, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Nlrp4 Negatively Regulates Type I Interferon Signaling by Targeting the Kinase Tbk1 for Degradation Via the Ubiquitin Ligase Dtx4. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Tan, P.; Xie, W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, R.-F.; Cui, J. Usp38 Inhibits Type I Interferon Signaling by Editing Tbk1 Ubiquitination through Nlrp4 Signalosome. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, T.; Li, S.; Pan, W.; Tien, P.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.B.; Wu, S. Dyrk2 Negatively Regulates Type I Interferon Induction by Promoting Tbk1 Degradation Via Ser527 Phosphorylation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Seregin, S.S.; Yang, D.; Fukase, K.; Chamaillard, M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Inohara, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Nunez, G. The Nlrp6 Inflammasome Recognizes Lipoteichoic Acid and Regulates Gram-Positive Pathogen Infection. Cell 2018, 175, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Cui, S.; Pan, W.; Jackson, R.; Zheng, Y.; Rongvaux, A.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.; et al. Nlrp6 Regulates Intestinal Antiviral Innate Immunity. Science 2015, 350, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Ding, S.; Wang, P.; Wei, Z.; Pan, W.; Palm, N.W.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, H.B.; Wang, G.; et al. Nlrp9b Inflammasome Restricts Rotavirus Infection in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Nature 2017, 546, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, K.; Becker, E.; Kienes, I.; Sowa, A.; Postma, Y.; Gloria, Y.C.; Weber, A.N.R.; Kufer, T.A. The Nlr Family Pyrin Domain-Containing 11 Protein Contributes to the Regulation of Inflammatory Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Su, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jin, S.; Xie, W.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R.; Cui, J. Nlrp11 Disrupts Mavs Signalosome to Inhibit Type I Interferon Signaling and Virus-Induced Apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 2160–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Su, Z.; Lin, M.; Ou, J.; Zhao, W.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.F. Nlrp11 Attenuates Toll-Like Receptor Signalling by Targeting Traf6 for Degradation Via the Ubiquitin Ligase Rnf19a. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.T.; Chen, L.; Lin, D.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Tsao, Y.P.; Guo, H.; Li, F.J.; Tseng, W.T.; Tam, J.W.; Chao, C.W.; et al. Nlrp12 Regulates Anti-Viral Rig-I Activation Via Interaction with Trim25. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Normand, S.; Waldschmitt, N.; Neerincx, A.; Martinez-Torres, R.J.; Chauvin, C.; Couturier-Maillard, A.; Boulard, O.; Cobret, L.; Awad, F.; Huot, L.; et al. Proteasomal Degradation of Nod2 by Nlrp12 in Monocytes Promotes Bacterial Tolerance and Colonization by Enteropathogens. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Lee, A.; Sitharam, R.; Kesner, J.; Rabadan, R.; Shapira, S.D. Germ-Cell-Specific Inflammasome Component Nlrp14 Negatively Regulates Cytosolic Nucleic Acid Sensing to Promote Fertilization. Immunity 2017, 46, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Simmons, A.; Capria, V.; LeRoith, T.; Wilson, J.E.; Heid, B.; Philipson, C.W.; Qin, Q.; Hontecillas-Magarzo, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; et al. Nlrx1 Suppresses Tumorigenesis and Attenuates Histiocytic Sarcoma through the Negative Regulation of Nf-Kappab Signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33096–33110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Sater, A.A.; Saïd-Sadier, N.; Lam, V.M.; Singh, B.; Pettengill, M.A.; Soares, F.; Tattoli, I.; Lipinski, S.; Girardin, S.E.; Rosenstiel, P.; et al. Enhancement of Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Chlamydial Infection by the Mitochondrial Nod-Like Family Member Nlrx1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41637–41645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tattoli, I.; Carneiro, L.A.; Jehanno, M.; Magalhaes, J.G.; Shu, Y.; Philpott, D.J.; Arnoult, D.; Girardin, S.E. Nlrx1 Is a Mitochondrial Nod-Like Receptor That Amplifies Nf-Kappab and Jnk Pathways by Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species Production. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, B.L.; Ganesan, S.; Comstock, A.T.; Faris, A.N.; Hershenson, M.B.; Sajjan, U.S. Nod-Like Receptor X-1 Is Required for Rhinovirus-Induced Barrier Dysfunction in Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3705–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Sun, G.; Yang, Q.; Chen, C.; Qi, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Nlrx1 Accelerates Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxity in Hei-Oc1 Cells Via Promoting Generation of Ros and Activation of Jnk Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.; Lenarcic, E.M.; Yamane, D.; Wauthier, E.; Mo, J.; Guo, H.; McGivern, D.R.; González-López, O.; Misumi, I.; Reid, L.M.; et al. Nlrx1 Promotes Immediate Irf1-Directed Antiviral Responses by Limiting Dsrna-Activated Translational Inhibition Mediated by Pkr. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Killackey, S.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Soares, F.; Zhang, A.B.; Abdel-Nour, M.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. The Mitochondrial Nod-Like Receptor Nlrx1 Modifies Apoptosis through Sarm1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 453, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, S.C.; Huang, P.R.; Almeida-da-Silva, C.L.C.; Atanasova, K.R.; Yilmaz, O.; Ojcius, D.M. Nlrx1 Modulates Differentially Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation and Nf-Κb Signaling During Fusobacterium Nucleatum Infection. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Qin, L. Nlrx1 Attenuates Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses in Myocardial Ischemia by Inhibiting Mavs-Dependent Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 76, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoult, D.; Soares, F.; Tattoli, I.; Castanier, C.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. An N-Terminal Addressing Sequence Targets Nlrx1 to the Mitochondrial Matrix. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, M.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Roberts, R.A.; Zhang, L.; Swanson, K.V.; Wen, H.; Davis, B.K.; Allen, I.C.; Holl, E.K.; Ye, Z.; et al. The Innate Immune Sensor Nlrc3 Attenuates Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Via Modification of the Signaling Adaptor Traf6 and Transcription Factor Nf-Κb. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimura, T.; Oyama, Y.; Deng, M.; Guo, H.; Wilson, J.E.; Rampanelli, E.; Cook, K.D.; Misumi, I.; Tan, X.; Chen, L.; et al. The Innate Immune Sensor Nlrc3 Acts as a Rheostat That Fine-Tunes T Cell Responses in Infection and Autoimmunity. Immunity 2018, 49, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Man, S.M.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kesavardhana, S.; Zhu, Q.; Burton, A.R.; Sharma, B.R.; Qi, X.; Pelletier, S.; Vogel, P.; et al. Nlrc3 Is an Inhibitory Sensor of Pi3k-Mtor Pathways in Cancer. Nature 2016, 540, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eren, E.; Berber, M.; Ozoren, N. Nlrc3 Protein Inhibits Inflammation by Disrupting Nalp3 Inflammasome Assembly Via Competition with the Adaptor Protein Asc for Pro-Caspase-1 Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12691–12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Du, X.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, X.; He, W.; Wen, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, C.; et al. Nlrc3 Negatively Regulates Cd4+ T Cells and Impacts Protective Immunity During Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tocker, A.M.; Durocher, E.; Jacob, K.D.; Trieschman, K.E.; Talento, S.M.; Rechnitzer, A.A.; Roberts, D.M.; Davis, B.K. The Scaffolding Protein Iqgap1 Interacts with Nlrc3 and Inhibits Type I Ifn Production. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, W.H.; Shu, D.H.; Zhen, Y.; Hilliard, B.; Priest, S.O.; Cesaroni, M.; Ting, J.P.; Cohen, P.L. Prion-Like Aggregation of Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein in Lupus Patients Is Associated with Increased Levels of Type I Interferon. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Deng, M.; Petrucelli, A.S.; Zhu, C.; Mo, J.; Zhang, L.; Tam, J.W.; Ariel, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; et al. Viral DNA Binding to Nlrc3, an Inhibitory Nucleic Acid Sensor, Unleashes Sting, a Cyclic Dinucleotide Receptor That Activates Type I Interferon. Immunity 2019, 50, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benko, S.; Magalhaes, J.G.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. Nlrc5 Limits the Activation of Inflammatory Pathways. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meissner, T.B.; Li, A.; Liu, Y.J.; Gagnon, E.; Kobayashi, K.S. The Nucleotide-Binding Domain of Nlrc5 Is Critical for Nuclear Import and Transactivation Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waldburger, J.M.; Masternak, K.; Muhlethaler-Mottet, A.; Villard, J.; Peretti, M.; Landmann, S.; Reith, W. Lessons from the Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome: Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Mhc Class Ii Expression. Immunol. Rev. 2000, 178, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehli, F.; Ludigs, K.; Heinz, L.X.; Seguin-Estevez, Q.; Ferrero, I.; Braun, M.; Schroder, K.; Rebsamen, M.; Tardivel, A.; Mattmann, C.; et al. Nlrc5 Deficiency Selectively Impairs Mhc Class I- Dependent Lymphocyte Killing by Cytotoxic T Cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lech, M.; Avila-Ferrufino, A.; Skuginna, V.; Susanti, H.E.; Anders, H.J. Quantitative Expression of Rig-Like Helicase, Nod-Like Receptor and Inflammasome-Related Mrnas in Humans and Mice. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Wang, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Imamura, R.; Suda, T. Pypaf3, a Pyrin-Containing Apaf-1-Like Protein, Is a Feedback Regulator of Caspase-1-Dependent Interleukin-1beta Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21720–21725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eibl, C.; Grigoriu, S.; Hessenberger, M.; Wenger, J.; Puehringer, S.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Wagner, R.N.; Proell, M.; Reed, J.C.; Page, R.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Nlrp4 Pyrin Domain. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 7330–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jounai, N.; Kobiyama, K.; Shiina, M.; Ogata, K.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeshita, F. Nlrp4 Negatively Regulates Autophagic Processes through an Association with Beclin1. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, T.; Aikawa, C.; Minowa-Nozawa, A.; Nakagawa, I. The Intracellular Microbial Sensor Nlrp4 Directs Rho-Actin Signaling to Facilitate Group a Streptococcus-Containing Autophagosome-Like Vacuole Formation. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1841–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorentino, L.; Stehlik, C.; Oliveira, V.; Ariza, M.E.; Godzik, A.; Reed, J.C. A Novel Paad-Containing Protein That Modulates Nf-Kappa B Induction by Cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35333–35340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, B.H.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Quan, F.S.; Guo, Z.K.; Zhang, Y. Developmental Expression and Possible Functional Roles of Mouse Nlrp4e in Preimplantation Embryos. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2013, 49, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Dixon, M.; Zucchelli, M.; Hambiliki, F.; Levkov, L.; Hovatta, O.; Kere, J. Expression Analysis of the Nlrp Gene Family Suggests a Role in Human Preimplantation Development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Lin, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, W. Expression and Localization of Nlrp4g in Mouse Preimplantation Embryo. Zygote 2015, 23, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y. Nlrp4g Is an Oocyte-Specific Gene but Is Not Required for Oocyte Maturation in the Mouse. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2014, 26, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, W. Expression Analysis of Nlrp4a-Nlrp4f During Mouse Development. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2013, 12, 754–759. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Pascal, G.; Monget, P. Evolution and Functional Divergence of Nlrp Genes in Mammalian Reproductive Systems. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Manji, G.A.; Grenier, J.M.; Al-Garawi, A.; Merriam, S.; Lora, J.M.; Geddes, B.J.; Briskin, M.; DiStefano, P.S.; Bertin, J. Pypaf7, a Novel Pyrin-Containing Apaf1-Like Protein That Regulates Activation of Nf-Kappa B and Caspase-1-Dependent Cytokine Processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29874–29880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vladimer, G.I.; Weng, D.; Paquette, S.W.; Vanaja, S.K.; Rathinam, V.A.; Aune, M.H.; Conlon, J.E.; Burbage, J.J.; Proulx, M.K.; Liu, Q.; et al. The Nlrp12 Inflammasome Recognizes Yersinia Pestis. Immunity 2012, 37, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ataide, M.A.; Andrade, W.A.; Zamboni, D.S.; Wang, D.; Mdo, C.S.; Franklin, B.S.; Elian, S.; Martins, F.S.; Pereira, D.; Reed, G.; et al. Malaria-Induced Nlrp12/Nlrp3-Dependent Caspase-1 Activation Mediates Inflammation and Hypersensitivity to Bacterial Superinfection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truax, A.D.; Chen, L.; Tam, J.W.; Cheng, N.; Guo, H.; Koblansky, A.A.; Chou, W.C.; Wilson, J.E.; Brickey, W.J.; Petrucelli, A.; et al. The Inhibitory Innate Immune Sensor Nlrp12 Maintains a Threshold against Obesity by Regulating Gut Microbiota Homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silveira, T.N.; Gomes, M.T.; Oliveira, L.S.; Campos, P.C.; Machado, G.G.; Oliveira, S.C. Nlrp12 Negatively Regulates Proinflammatory Cytokine Production and Host Defense against Brucella Abortus. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, I.C.; Wilson, J.E.; Schneider, M.; Lich, J.D.; Roberts, R.A.; Arthur, J.C.; Woodford, R.M.; Davis, B.K.; Uronis, J.M.; Herfarth, H.H.; et al. Nlrp12 Suppresses Colon Inflammation and Tumorigenesis through the Negative Regulation of Noncanonical Nf-Κb Signaling. Immunity 2012, 36, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, M.H.; Man, S.M.; Vogel, P.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. Salmonella Exploits Nlrp12-Dependent Innate Immune Signaling to Suppress Host Defenses During Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lich, J.D.; Williams, K.L.; Moore, C.B.; Arthur, J.C.; Davis, B.K.; Taxman, D.J.; Ting, J.P. Monarch-1 Suppresses Non-Canonical Nf-Kappab Activation and P52-Dependent Chemokine Expression in Monocytes. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jéru, I.; Duquesnoy, P.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Cochet, E.; Yu, J.W.; Lackmy-Port-Lis, M.; Grimprel, E.; Landman-Parker, J.; Hentgen, V.; Marlin, S.; et al. Mutations in Nalp12 Cause Hereditary Periodic Fever Syndromes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerveld, G.H.; Korver, C.M.; van Pelt, A.M.; Leschot, N.J.; van der Veen, F.; Repping, S.; Lombardi, M.P. Mutations in the Testis-Specific Nalp14 Gene in Men Suffering from Spermatogenic Failure. Hum. Reprod. 2006, 21, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Cao, S.; Fu, H.; Fan, X.; Xiong, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, K.; Meng, T.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. A Noncanonical Role of Nod-Like Receptor Nlrp14 in Pgclc Differentiation and Spermatogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22237–22248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, B.; Bromfield, E.G.; Cui, J.; de Iuliis, G.N. Heat Shock Protein A2 (Hspa2): Regulatory Roles in Germ Cell Development and Sperm Function. In The Role of Heat Shock Proteins in Reproductive System Development and Function; MacPhee, D., Ed.; Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 222, pp. 67–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hamatani, T.; Falco, G.; Carter, M.G.; Akutsu, H.; Stagg, C.A.; Sharov, A.A.; Dudekula, D.B.; VanBuren, V.; Ko, M.S. Age-Associated Alteration of Gene Expression Patterns in Mouse Oocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertin, J.; Nir, W.J.; Fischer, C.M.; Tayber, O.V.; Errada, P.R.; Grant, J.R.; Keilty, J.J.; Gosselin, M.L.; Robison, K.E.; Wong, G.H. Human Card4 Protein Is a Novel Ced-4/Apaf-1 Cell Death Family Member That Activates Nf-Kappab. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12955–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kufer, T.A.; Kremmer, E.; Adam, A.C.; Philpott, D.J.; Sansonetti, P.J. The Pattern-Recognition Molecule Nod1 Is Localized at the Plasma Membrane at Sites of Bacterial Interaction. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, A.T.; Mimuro, H.; Kufer, T.A.; Lo, C.; Wheeler, R.; Turner, L.J.; Thomas, B.J.; Malosse, C.; Gantier, M.P.; Casillas, L.N.; et al. The Immune Receptor Nod1 and Kinase Rip2 Interact with Bacterial Peptidoglycan on Early Endosomes to Promote Autophagy and Inflammatory Signaling. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travassos, L.H.; Carneiro, L.A.; Ramjeet, M.; Hussey, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Magalhães, J.G.; Yuan, L.; Soares, F.; Chea, E.; le Bourhis, L.; et al. Nod1 and Nod2 Direct Autophagy by Recruiting Atg16l1 to the Plasma Membrane at the Site of Bacterial Entry. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keestra, A.M.; Winter, M.G.; Auburger, J.J.; Frässle, S.P.; Xavier, M.N.; Winter, S.E.; Kim, A.; Poon, V.; Ravesloot, M.M.; Waldenmaier, J.F.; et al. Manipulation of Small Rho Gtpases Is a Pathogen-Induced Process Detected by Nod1. Nature 2013, 496, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bielig, H.; Lautz, K.; Braun, P.R.; Menning, M.; Machuy, N.; Brügmann, C.; Barisic, S.; Eisler, S.A.; Andree, M.; Zurek, B.; et al. The Cofilin Phosphatase Slingshot Homolog 1 (Ssh1) Links Nod1 Signaling to Actin Remodeling. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukazawa, A.; Alonso, C.; Kurachi, K.; Gupta, S.; Lesser, C.F.; McCormick, B.A.; Reinecker, H.C. Gef-H1 Mediated Control of Nod1 Dependent Nf-Kappab Activation by Shigella Effectors. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inohara, N.; Koseki, T.; Lin, J.; del Peso, L.; Lucas, P.C.; Chen, F.F.; Ogura, Y.; Núñez, G. An Induced Proximity Model for Nf-Kappa B Activation in the Nod1/Rick and Rip Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27823–27831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vegna, S.; Gregoire, D.; Moreau, M.; Lassus, P.; Durantel, D.; Assenat, E.; Hibner, U.; Simonin, Y. Nod1 Participates in the Innate Immune Response Triggered by Hepatitis C Virus Polymerase. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6022–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.G.; Park, J.H.; Reimer, T.; Baker, D.P.; Kawai, T.; Kumar, H.; Akira, S.; Wobus, C.; Núñez, G. Viral Infection Augments Nod1/2 Signaling to Potentiate Lethality Associated with Secondary Bacterial Infections. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.W.; Hu, Y.W.; Cao, L.; Ouyang, S.; Bi, Y.H.; Nie, P.; Chang, M.X. Nod1 Promotes Antiviral Signaling by Binding Viral Rna and Regulating the Interaction of Mda5 and Mavs. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2216–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, N.O.; Stepanaukas, R.; Pedersen, A.G.; Hansen, M.; Nybroe, O. Occurrence and Degradation of Peptidoglycan in Aquatic Environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 46, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Inohara, N.; Benito, A.; Chen, F.F.; Yamaoka, S.; Nunez, G. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 Family Member That Is Restricted to Monocytes and Activates Nf-Kappab. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4812–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogura, Y.; Lala, S.; Xin, W.; Smith, E.; Dowds, T.A.; Chen, F.F.; Zimmermann, E.; Tretiakova, M.; Cho, J.H.; Hart, J.; et al. Expression of Nod2 in Paneth Cells: A Possible Link to Crohn’s Ileitis. Gut 2003, 52, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, G.; Rossi, R.; Commere, P.H.; Jay, P.; Sansonetti, P.J. The Cytosolic Bacterial Peptidoglycan Sensor Nod2 Affords Stem Cell Protection and Links Microbes to Gut Epithelial Regeneration. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnich, N.; Aguirre, J.E.; Reinecker, H.C.; Xavier, R.; Podolsky, D.K. Membrane Recruitment of Nod2 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Is Essential for Nuclear Factor—κB Activation in Muramyl Dipeptide Recognition. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opitz, B.; Püschel, A.; Schmeck, B.; Hocke, A.C.; Rosseau, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Schumann, R.R.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain Proteins Are Innate Immune Receptors for Internalized Streptococcus Pneumoniae. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36426–36432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamaillard, M.; Philpott, D.; Girardin, S.E.; Zouali, H.; Lesage, S.; Chareyre, F.; Bui, T.H.; Giovannini, M.; Zaehringer, U.; Penard-Lacronique, V.; et al. Gene-Environment Interaction Modulated by Allelic Heterogeneity in Inflammatory Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3455–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hugot, J.P.; Chamaillard, M.; Zouali, H.; Lesage, S.; Cézard, J.P.; Belaiche, J.; Almer, S.; Tysk, C.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gassull, M.; et al. Association of Nod2 Leucine-Rich Repeat Variants with Susceptibility to Crohn’s Disease. Nature 2001, 411, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli-Richard, C.; Lesage, S.; Rybojad, M.; Prieur, A.M.; Manouvrier-Hanu, S.; Häfner, R.; Chamaillard, M.; Zouali, H.; Thomas, G.; Hugot, J.P. Card15 Mutations in Blau Syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaluso, F.; Nothnagel, M.; Parwez, Q.; Petrasch-Parwez, E.; Bechara, F.G.; Epplen, J.T.; Hoffjan, S. Polymorphisms in Nacht-Lrr (Nlr) Genes in Atopic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupfer, C.; Thomas, P.G.; Anand, P.K.; Vogel, P.; Milasta, S.; Martinez, J.; Huang, G.; Green, M.; Kundu, M.; Chi, H.; et al. Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 2-Mediated Mitophagy Regulates Inflammasome Activation During Virus Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herskovits, A.A.; Auerbuch, V.; Portnoy, D.A. Bacterial Ligands Generated in a Phagosome Are Targets of the Cytosolic Innate Immune System. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 13, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, D.; Martin, F.J.; Soong, G.; Harfenist, B.S.; Aguilar, J.L.; Ratner, A.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Schindler, C.; Prince, A. Streptococcus Pneumoniae DNA Initiates Type I Interferon Signaling in the Respiratory Tract. MBio 2011, 2, e00016-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stockinger, S.; Reutterer, B.; Schaljo, B.; Schellack, C.; Brunner, S.; Materna, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Murray, P.J.; et al. Ifn Regulatory Factor 3-Dependent Induction of Type I Ifns by Intracellular Bacteria Is Mediated by a Tlr- and Nod2-Independent Mechanism. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 7416–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coulombe, F.; Fiola, S.; Akira, S.; Cormier, Y.; Gosselin, J. Muramyl Dipeptide Induces Nod2-Dependent Ly6c(High) Monocyte Recruitment to the Lungs and Protects against Influenza Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Bel, M.; Gosselin, J. Leukotriene B4 Enhances Nod2-Dependent Innate Response against Influenza Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, L.; Xu, X.X.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z.; Chen, J. Mutual Regulation of Nod2 and Rig-I in Zebrafish Provides Insights into the Coordination between Innate Antibacterial and Antiviral Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Asano, N.; Meng, G.; Yamashita, K.; Arai, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Fuss, I.J.; Kitani, A.; Shimosegawa, T.; et al. Nod2 Downregulates Colonic Inflammation by Irf4-Mediated Inhibition of K63-Linked Polyubiquitination of Rick and Traf6. Mucosal. Immunol. 2014, 7, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Asano, N.; Murray, P.J.; Ozato, K.; Tailor, P.; Fuss, I.J.; Kitani, A.; Strober, W. Muramyl Dipeptide Activation of Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain 2 Protects Mice from Experimental Colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 545–559. [Google Scholar]
- Castellaneta, A.; Sumpter, T.L.; Chen, L.; Tokita, D.; Thomson, A.W. Nod2 Ligation Subverts Ifn-Alpha Production by Liver Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Inhibits Their T Cell Allostimulatory Activity Via B7-H1 up-Regulation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6922–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franchi, L.; Amer, A.; Body-Malapel, M.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; Özören, N.; Jagirdar, R.; Inohara, N.; Vandenabeele, P.; Bertin, J.; Coyle, A.; et al. Cytosolic Flagellin Requires Ipaf for Activation of Caspase-1 and Interleukin 1β in Salmonella-Infected Macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, E.A.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M.; Dors, M.; Clark, A.E.; Bader, M.W.; Miller, S.I.; Aderem, A. Cytoplasmic Flagellin Activates Caspase-1 and Secretion of Interleukin 1β Via Ipaf. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, A.; Franchi, L.; Kanneganti, T.D.; Body-Malapel, M.; Ozören, N.; Brady, G.; Meshinchi, S.; Jagirdar, R.; Gewirtz, A.; Akira, S.; et al. Regulation of Legionella Phagosome Maturation and Infection through Flagellin and Host Ipaf. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35217–35223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Driggers, P.H.; Ennist, D.L.; Gleason, S.L.; Mak, W.H.; Marks, M.S.; Levi, B.Z.; Flanagan, J.R.; Appella, E.; Ozato, K. An Interferon Gamma-Regulated Protein That Binds the Interferon-Inducible Enhancer Element of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3743–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karki, R.; Lee, E.; Place, D.; Samir, P.; Mavuluri, J.; Sharma, B.R.; Balakrishnan, A.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Geiger, R.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Irf8 Regulates Transcription of Naips for Nlrc4 Inflammasome Activation. Cell 2018, 173, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chassaing, B.; Shi, Z.; Uchiyama, R.; Zhang, Z.; Denning, T.L.; Crawford, S.E.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Iskarpatyoti, J.A.; Estes, M.K.; et al. Viral Infection. Prevention and Cure of Rotavirus Infection Via Tlr5/Nlrc4-Mediated Production of Il-22 and Il-18. Science 2014, 346, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghimire, L.; Paudel, S.; Jin, L.; Jeyaseelan, S. The Nlrp6 Inflammasome in Health and Disease. Mucosal. Immunol. 2020, 13, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, P.K.; Kanneganti, T.D. Targeting Nlrp6 to Enhance Immunity against Bacterial Infections. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoma, H.; Hanabuchi, S.; Kim, T.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugimoto, N.; Liu, Y.J. The Dhx33 Rna Helicase Senses Cytosolic Rna and Activates the Nlrp3 Inflammasome. Immunity 2013, 39, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marleaux, M.; Anand, K.; Latz, E.; Geyer, M. Crystal Structure of the Human Nlrp9 Pyrin Domain Suggests a Distinct Mode of Inflammasome Assembly. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.J.; Park, H.H. Crystal Structure of the Human Nlrp9 Pyrin Domain Reveals a Bent N-Terminal Loop That May Regulate Inflammasome Assembly. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2396–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome: Molecular Activation and Regulation to Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochnicki, T.; Mangan, M.S.; Latz, E. Recent Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of the Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation. F1000Reaserch 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magupalli, V.G.; Negro, R.; Tian, Y.; Hauenstein, A.V.; di Caprio, G.; Skillern, W.; Deng, Q.; Orning, P.; Alam, H.B.; Maliga, Z.; et al. Hdac6 Mediates an Aggresome-Like Mechanism for Nlrp3 and Pyrin Inflammasome Activation. Science 2020, 369, eaas8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, F.G.; Horvath, G.; Stutz, A.; Alnemri, E.S.; MacDonald, K.; Speert, D.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Wu, J.; Monks, B.G.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Cutting Edge: Nf-Kappab Activating Pattern Recognition and Cytokine Receptors License Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation by Regulating Nlrp3 Expression. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Kang, S.; Farias, A.; Qin, F.; Alnemri, E.S. Non-Transcriptional Priming and Deubiquitination Regulate Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36617–36622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, N.; Liu, Z.S.; Xue, W.; Bai, Z.F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.J.; Cai, H.; Zhan, X.Y.; et al. Nlrp3 Phosphorylation Is an Essential Priming Event for Inflammasome Activation. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veeranki, S.; Duan, X.; Panchanathan, R.; Liu, H.; Choubey, D. Ifi16 Protein Mediates the Anti-Inflammatory Actions of the Type-I Interferons through Suppression of Activation of Caspase-1 by Inflammasomes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarda, G.; Braun, M.; Staehli, F.; Tardivel, A.; Mattmann, C.; Förster, I.; Farlik, M.; Decker, T.; Pasquier, R.A.D.; Romero, P.; et al. Type I Interferon Inhibits Interleukin-1 Production and Inflammasome Activation. Immunity 2011, 34, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Cuellar, E.; Tsuchiya, K.; Hara, H.; Fang, R.; Sakai, S.; Kawamura, I.; Akira, S.; Mitsuyama, M. Cutting Edge: Nitric Oxide Inhibits the Nlrp3 Inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5113–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, P.G.; Dash, P.; Aldridge, J.R., Jr.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Reynolds, C.; Funk, A.J.; Martin, W.J.; Lamkanfi, M.; Webby, R.J.; Boyd, K.L.; et al. The Intracellular Sensor Nlrp3 Mediates Key Innate and Healing Responses to Influenza a Virus Via the Regulation of Caspase-1. Immunity 2009, 30, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Triantafilou, K.; Kar, S.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Triantafilou, M. Rhinovirus-Induced Calcium Flux Triggers Nlrp3 and Nlrc5 Activation in Bronchial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, I.C.; Scull, M.A.; Moore, C.B.; Holl, E.K.; McElvania-TeKippe, E.; Taxman, D.J.; Guthrie, E.H.; Pickles, R.J.; Ting, J.P. The Nlrp3 Inflammasome Mediates in Vivo Innate Immunity to Influenza a Virus through Recognition of Viral Rna. Immunity 2009, 30, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.; Iwasaki, A. Influenza Virus Activates Inflammasomes Via Its Intracellular M2 Ion Channel. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.Y.; Moriyama, M.; Chang, M.F.; Ichinohe, T. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Viroporin 3a Activates the Nlrp3 Inflammasome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Juliana, C.; Hong, S.; Datta, P.; Hwang, I.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Yu, J.W.; Alnemri, E.S. The Mitochondrial Antiviral Protein Mavs Associates with Nlrp3 and Regulates Its Inflammasome Activity. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, N.; Natarajan, K.; Clatworthy, M.R.; Wang, Z.; Germain, R.N. The Adaptor Mavs Promotes Nlrp3 Mitochondrial Localization and Inflammasome Activation. Cell 2013, 153, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crow, Y.J.; Manel, N. Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome and the Type I Interferonopathies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; Steiner, A.; Harapas, C.R.; Masters, S.L. An Update on Autoinflammatory Diseases: Interferonopathies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döffinger, R.; Helbert, M.R.; Barcenas-Morales, G.; Yang, K.; Dupuis, S.; Ceron-Gutierrez, L.; Espitia-Pinzon, C.; Barnes, N.; Bothamley, G.; Casanova, J.L.; et al. Autoantibodies to Interferon-Gamma in a Patient with Selective Susceptibility to Mycobacterial Infection and Organ-Specific Autoimmunity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, e10–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmann, B.; Hemingway, C.; Stephens, A.; Davidson, R.; Goodsall, A.; Anderson, S.; Nicol, M.; Schölvinck, E.; Relman, D.; Waddell, S.; et al. Acquired Predisposition to Mycobacterial Disease Due to Autoantibodies to Ifn-Gamma. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection with Interferon and Small Molecule Direct Antivirals: Viral Kinetics and Modeling. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 30, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, A.S.J.; Kwok, R.; Ahmed, T. Alpha-Interferon Treatment in Hepatitis B. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghany, M.G.; Morgan, T.R. Hepatitis C Guidance 2019 Update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases-Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Hepatology 2020, 71, 686–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodero, M.P.; Crow, Y.J. Type I Interferon—Mediated Monogenic Autoinflammation: The Type I Interferonopathies, a Conceptual Overview. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayne, C.B.; Albeituni, S.; Nichols, K.E.; Cron, R.Q. The Immunology of Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limmroth, V.; Putzki, N.; Kachuck, N.J. The Interferon Beta Therapies for Treatment of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: Are They Equally Efficacious? A Comparative Review of Open-Label Studies Evaluating the Efficacy, Safety, or Dosing of Different Interferon Beta Formulations Alone or in Combination. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2011, 4, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, S.; Río, J.; Urcelay, E.; Nurtdinov, R.; Bustamante, M.F.; Fernández, O.; Oliver, B.; Zettl, U.; Brassat, D.; Killestein, J.; et al. Nlrp3 Inflammasome Is Associated with the Response to Ifn-Β in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Brain 2015, 138, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Williams, K.L.; Oliver, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Rajan, J.V.; Miao, E.A.; Shinohara, M.L. Interferon-Β Therapy against Eae Is Effective Only When Development of the Disease Depends on the Nlrp3 Inflammasome. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, E.S.; Girard-Guyonvarc’h, C.; Holzinger, D.; de Jesus, A.A.; Tariq, Z.; Picarsic, J.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Foell, D.; Grom, A.A.; Ammann, S.; et al. Interleukin-18 Diagnostically Distinguishes and Pathogenically Promotes Human and Murine Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, M.H.; Vogel, P.; Malireddi, R.K.; Body-Malapel, M.; Anand, P.K.; Bertin, J.; Green, D.R.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The Nod-Like Receptor Nlrp12 Attenuates Colon Inflammation and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satie, A.P.; Mazaud-Guittot, S.; Seif, I.; Mahé, D.; He, Z.; Jouve, G.; Jégou, B.; Dejucq-Rainsford, N. Excess Type I Interferon Signaling in the Mouse Seminiferous Tubules Leads to Germ Cell Loss and Sterility. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23280–23295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulusoy, E.; Cayan, S.; Yilmaz, N.; Aktaş, S.; Acar, D.; Doruk, E. Interferon Alpha-2b May Impair Testicular Histology Including Spermatogenesis in a Rat Model. Arch. Androl. 2004, 50, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, M.; Fujioka, H.; Tatsumi, N.; Inaba, Y.; Okada, H.; Arakawa, S.; Kamidono, S. Levels of Interferon Alpha and Gamma in Seminal Plasma of Normozoospermic, Oligozoospermic, and Azoospermic Men. Arch. Androl. 1998, 40, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novikov, A.; Cardone, M.; Thompson, R.; Shenderov, K.; Kirschman, K.D.; Mayer-Barber, K.D.; Myers, T.G.; Rabin, R.L.; Trinchieri, G.; Sher, A.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Triggers Host Type I Ifn Signaling to Regulate Il-1β Production in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2540–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, T.S.; Prince, A.S. Activation of Inflammasome Signaling Mediates Pathology of Acute P. Aeruginosa Pneumonia. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boxx, G.M.; Cheng, G. The Roles of Type I Interferon in Bacterial Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deretic, V. Autophagy as an Innate Immunity Paradigm: Expanding the Scope and Repertoire of Pattern Recognition Receptors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Name | Activator/Ligand | Induction by Type I IFN | Function in Type I IFN Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOD1 | iE-DAP | ↑ [123] | Positive regulation of type I interferon responses [124,125,126,127,128] |
| NOD2 | MDP; viral ssRNA | Unknown | Positive regulation of type I interferon responses [128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137] |
| NLRX1 | Unidentified | Unknown | Negative regulation of RIG-I/MAVS- and STING-dependent type I interferon response [105,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148] |
| NLRC3 | Unidentified | Unknown | Negative regulation of type I interferon response by disruption of proper STING trafficking [149] |
| NLRC4 | NAIP | Unknown | Enhanced IFN response by Irf8 [150] |
| NLRC5 | Unidentified | Unknown | Induction of MHC class I expression [114,115,151] Regulation of type I interferon responses but controversial data [114,115,143,151,152,153,154,155,156] |
| NLRP2 | Unidentified | ↑ [157,158] | Negative regulation of IFN-β response by inhibiting TBK1 [159] |
| NLRP3 | ROS; membrane rupture; cathepsins; K+ efflux; dsRNA | ↑ [160,161,162] | No known functions in regulation of IFN response |
| NLRP4 | Unidentified | Unknown | Negative regulation of type I interferon response through degradation of TBK1 by recruitment of DTX4 [163,164,165,166] |
| NLRP6 | lipoteichoic acid | ↑ [167] | Positive regulation of type I and III IFN responses by interaction with Dhx15 to form a sensor for dsRNA [168] |
| NLRP9 | Unidentified | Unknown | Nlrp9b: Restriction of rotavirus infection by complex formation with Dhx9 which recognizes short dsRNA [169] |
| NLRP11 | Unidentified | Unknown | Negative regulation of type I interferon response [170,171,172] |
| NLRP12 | Unidentified | Unknown | Inhibition of type I interferon response via the degradation of RIG-I and NOD2 [173,174] |
| NLRP14 | Unidentified | Unknown | Negative regulation of type I interferon response through degradation of TBK1 [175] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kienes, I.; Weidl, T.; Mirza, N.; Chamaillard, M.; Kufer, T.A. Role of NLRs in the Regulation of Type I Interferon Signaling, Host Defense and Tolerance to Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031301
Kienes I, Weidl T, Mirza N, Chamaillard M, Kufer TA. Role of NLRs in the Regulation of Type I Interferon Signaling, Host Defense and Tolerance to Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031301
Chicago/Turabian StyleKienes, Ioannis, Tanja Weidl, Nora Mirza, Mathias Chamaillard, and Thomas A. Kufer. 2021. "Role of NLRs in the Regulation of Type I Interferon Signaling, Host Defense and Tolerance to Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031301
APA StyleKienes, I., Weidl, T., Mirza, N., Chamaillard, M., & Kufer, T. A. (2021). Role of NLRs in the Regulation of Type I Interferon Signaling, Host Defense and Tolerance to Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031301