Intranuclear Delivery of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B p65 in a Rat Model of Tooth Replantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation and Transduction Efficiency of nt-p65-TMD
2.2. Viability and NO Release of nt-p65-TMD-Treated RAW264.7 Cells
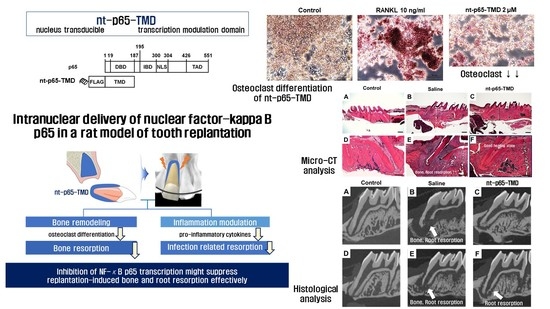
2.3. Osteoclast Differentiation of nt-p65-TMD-Treated RAW264.7 Cells
2.4. Replantation of Rat Maxillary First Molar
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Production of Nucleus-Transducible Form of p65-TMD
4.2. In Vitro Study
4.2.1. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
4.2.2. Western Blot
4.2.3. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
4.2.4. Osteoclast Differentiation
4.3. In Vivo Study
4.3.1. Replantation of Rat Maxillary First Molar
4.3.2. Micro-Microcomputed Tomography (CT) Image Analysis
4.3.3. Histological Examination
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| nt-p65-TMD | Nucleus-transducible form of p65-transcription modulation domain |
| TRAP | Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase |
References
- Panzarini, S.R.; Gulinelli, J.L.; Poi, W.R.; Sonoda, C.K.; Pedrini, D.; Brandini, D.A. Treatment of root surface in delayed tooth replantation: A review of literature. Dent. Traumatol. 2008, 24, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trope, M.; Moshonov, J.; Nissan, R.; Buxt, P.; Yesilsoy, C. Short vs. Long-term calcium hydroxide treatment of established inflammatory root resorption in replanted dog teeth. Dent. Traumatol. 1995, 11, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvig, K.A.; Bjorvatn, K.; Bogle, G.C.; Wikesjö, U.M.E. Effect of stannous fluoride and tetracycline on periodontal repair after delayed tooth replantation in dogs. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1992, 100, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, J.O.; Borum, M.K.; Jacobsen, H.L.; Andreasen, F.M. Replantation of 400 avulsed permanent incisors. 4. Factors related to periodontal ligament healing. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1995, 11, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.M.; Liewehr, F.R.; West, L.A.; Patton, W.R.; McPherson, J.C.; Runner, R.R. Human periodontal ligament cell viability in milk and milk substitutes. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, B.D.M.; Dutra, K.L.; Kuntze, M.M.; Bortoluzzi, E.A.; Flores-Mir, C.; Reyes-Carmona, J.; Felippe, W.T.; Porporatti, A.L.; De Luca Canto, G. Incidence of root resorption after the replantation of avulsed teeth: A meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poi, W.R.; Sonoda, C.K.; Martins, C.M.; Melo, M.E.; Pellizzer, E.P.; de Mendonça, M.R.; Panzarini, S.R. Storage media for avulsed teeth: A literature review. Braz. Dent. J. 2013, 24, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunraj, M.N. Dental root resorption. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 1999, 88, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of nf-kappab in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, N.; Soysa, N.S.; Hayashi, J.; Khan, M.; Shimoda, A.; Shimokawa, H.; Ritzeler, O.; Akiyoshi, K.; Aoki, K.; Ohya, K. Suppression of nf-kappab increases bone formation and ameliorates osteopenia in ovariectomized mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4626–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.D.; Cheon, S.Y.; Park, T.Y.; Shin, B.Y.; Oh, H.; Ghosh, S.; Koo, B.N.; Lee, S.K. Intranuclear interactomic inhibition of nf-kappab suppresses LPS-induced severe sepsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kam, E.H.; Ho, C.C.; Kim, E.J.; Chung, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.D.; Lee, S.W.; Koo, B.N. Cell-penetrating interactomic inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa b in a mouse model of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kam, E.H.; Ho, C.C.; Lee, S.K.; Koo, B.N. Intranuclear delivery of synthetic nuclear factor-kappa b p65 reduces inflammasomes after surgery. Biochem. Pharm. 2018, 158, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Dai, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, L. Cimifugin inhibits inflammatory responses of raw264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Juan, S.H.; Shen, S.C.; Hsu, F.L.; Chen, Y.C. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by flavonoids in raw264.7 macrophages involves heme oxygenase-1. Biochem. Pharm. 2003, 66, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Hayashi, M.; Fukunaga, T.; Kurata, K.; Oh-Hora, M.; Feng, J.Q.; Bonewald, L.F.; Kodama, T.; Wutz, A.; Wagner, E.F.; et al. Evidence for osteocyte regulation of bone homeostasis through rankl expression. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, S.L.; Ross, F.P. Genetic regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Onal, M.; Jilka, R.L.; Weinstein, R.S.; Manolagas, S.C.; O’Brien, C.A. Matrix-embedded cells control osteoclast formation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Kinosaki, M.; Murali, R.; Greene, M.I. The TNF receptor superfamily: Role in immune inflammation and bone formation. Immunol. Res. 2003, 27, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnay, B.G.; Haridas, V.; Ni, J.; Moore, P.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Characterization of the intracellular domain of receptor activator of nf-kappab (rank). Interaction with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors and activation of nf-kappab and c-jun n-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20551–20555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, N.; Kadono, Y.; Naito, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Tanaka, S.; Inoue, J. Segregation of traf6-mediated signaling pathways clarifies its role in osteoclastogenesis. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, B.R.; Josien, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Vologodskaia, M.; Steinman, R.M.; Choi, Y. The traf family of signal transducers mediates nf-kappab activation by the trance receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28355–28359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizukami, J.; Takaesu, G.; Akatsuka, H.; Sakurai, H.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Sakurai, N. Receptor activator of nf-kappab ligand (rankl) activates tak1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase through a signaling complex containing rank, tab2, and traf6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lomaga, M.A.; Yeh, W.C.; Sarosi, I.; Duncan, G.S.; Furlonger, C.; Ho, A.; Morony, S.; Capparelli, C.; Van, G.; Kaufman, S.; et al. Traf6 deficiency results in osteopetrosis and defective interleukin-1, cd40, and LPS signaling. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naito, A.; Azuma, S.; Tanaka, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Takaki, S.; Takatsu, K.; Nakao, K.; Nakamura, K.; Katsuki, M.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Severe osteopetrosis, defective interleukin-1 signalling and lymph node organogenesis in traf6-deficient mice. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 1999, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, H.; Kim, S.; Koga, T.; Nishina, H.; Isshiki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Saiura, A.; Isobe, M.; Yokochi, T.; Inoue, J.; et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor nfatc1 (nfat2) integrate rankl signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliprantis, A.O.; Ueki, Y.; Sulyanto, R.; Park, A.; Sigrist, K.S.; Sharma, S.M.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Olsen, B.R.; Glimcher, L.H. Nfatc1 in mice represses osteoprotegerin during osteoclastogenesis and dissociates systemic osteopenia from inflammation in cherubism. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreasen, J.O.; Hjorting-Hansen, E. Replantation of teeth. I. Radiographic and clinical study of 110 human teeth replanted after accidental loss. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1966, 24, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, F.; Mirhadi, H.; Geramizadeh, B.; Sahebi, S. Comparison of soymilk, powdered milk, hank’s balanced salt solution and tap water on periodontal ligament cell survival. Dent. Traumatol. 2012, 28, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Okamoto, R. Effect of splinting upon healing after immediate replantation of rat upper incisors. Histomorphological study. Rev. Odontol. UNESP 1995, 24, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sae-Lim, V.; Metzger, Z.; Trope, M. Local dexamethasone improves periodontal healing of replanted dogs’ teeth. Endod. Dent. Traumatol. 1998, 14, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, D.Y.; Lim, Y.A.; Cheng, Y.L.; Lok, K.Z.; Chunduri, P.; Baik, S.H.; Drummond, G.R.; Dheen, S.T.; Sobey, C.G.; Jo, D.G.; et al. Evidence that nf-κb and mapk signaling promotes NLRP inflammasome activation in neurons following ischemic stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Imamura, R.; Kushiyama, H.; Suda, T. Nlrp3 mediates nf-κb activation and cytokine induction in microbially induced and sterile inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempster, D.W.; Moonga, B.S.; Stein, L.S.; Horbert, W.R.; Antakly, T. Glucocorticoids inhibit bone resorption by isolated rat osteoclasts by enhancing apoptosis. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 154, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Shimada, A.; Shibata, T.; Shimoda, S.; Oida, S.; Kawasaki, K.; Nifuji, A. Long-term effects of local pretreatment with alendronate on healing of replanted rat teeth. J. Periodontal Res. 2008, 43, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Komatsu, K.; Shimada, A.; Shimoda, S.; Oida, S.; Kawasaki, K.; Chiba, M. Effects of alendronate on restoration of biomechanical properties of periodontium in replanted rat molars. J. Periodontal Res. 2004, 39, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.M.; Ahn, M.H.; Chae, W.J.; Jung, Y.G.; Park, J.C.; Song, H.M.; Kim, Y.E.; Shin, J.A.; Park, C.S.; Park, J.W.; et al. Intranasal delivery of the cytoplasmic domain of ctla-4 using a novel protein transduction domain prevents allergic inflammation. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, D.; Glucksam, Y.; Zor, T. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pi3k) inhibitor ly294002 modulates cytokine expression in macrophages via p50 nuclear factor kappa b inhibition, in a pi3k-independent mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choi, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, T.K. Ly294002 inhibits LPS-induced no production through a inhibition of nf-κb activation: Independent mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 99, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poi, W.R.; Sonoda, C.K.; Amaral, M.F.; Queiroz, A.F.; França, A.B.; Brandini, D.A. Histological evaluation of the repair process of replanted rat teeth after storage in resveratrol dissolved in dimethyl sulphoxide. Dent. Traumatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CTSK | GGGATGTTGGCGATGCA | CCAGCTACTTGAGGTCCATCTTC |
| NFATc1 | CACTGGCGCTGCAACAAGA | CATTCCGGAGCTCAGCAGAATAA |
| TRAF6 | ACCTGAACGCGCCTTCTG | CATCCAGCTGACTCGTTTCATAA |
| TRAP | CAAAGGTGCAGCCTTTGTGTC | TCACAGTCCGGATTGAGCTCA |
| GAPDH | CTGGCACAGGGTATACAGGGTTAG | ACTGGTGCCGTTTATGCCTTG |
| Event | Score | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Bone resorption | 0 | No resorption present |
| 1 | Resorption occurred in <1/3 of the bone surface | |
| 2 | Resorption occurred in >1/3 and <2/3 of the bone surface | |
| 3 | Resorption occurred in >2/3 of the bone surface | |
| Root resorption | 0 | No resorption present |
| 1 | Resorption occurred in <1/3 of the root surface | |
| 2 | Resorption occurred in >1/3 and <2/3 of the root surface | |
| 3 | Resorption occurred in >2/3 of the root surface | |
| Ankylosis | 0 | No ankylosis present |
| 1 | Ankylosis present | |
| Pulp mineralization | 0 | No pulp mineralization present |
| 1 | Pulp mineralization present |
| Event | Score | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Bone resorption | 0 | No resorption present |
| 1 | Resorption occurred in <1/3 of the bone surface | |
| 2 | Resorption occurred in >1/3 and <2/3 of the bone surface | |
| 3 | Resorption occurred in >2/3 of the bone surface | |
| Root resorption | 0 | No resorption present |
| 1 | Resorption occurred in <1/3 of the root surface | |
| 2 | Resorption occurred in >1/3 and <2/3 of the root surface | |
| 3 | Resorption occurred in >2/3 of the root surface | |
| Inflammation at the epithelial insertion | 0 | Absence or occasional presence of inflammatory cells |
| 1 | Inflammatory process restricted to lamina propria of the internal part of epithelium | |
| 2 | Inflammatory process extending apically to the small portion of the connective tissue underlying the lamina propria of the internal portion of the gingival epithelium | |
| 3 | Inflammatory process reaching the proximity of the alveolar bone crest | |
| Inflammation in the PDL | 0 | Absence or occasional presence of inflammatory cells |
| 1 | Inflammatory process present only in the apical, coronal or small lateral area of PDL | |
| 2 | Inflammatory process reaching more than half of the lateral PDL of the root | |
| 3 | Inflammatory process in the whole PDL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, C.-M.; Mo, S.; Jeon, M.; Jung, U.-W.; Shin, Y.; Shin, J.-S.; Shin, B.-Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, H.-J.; Song, J.S. Intranuclear Delivery of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B p65 in a Rat Model of Tooth Replantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041987
Kang C-M, Mo S, Jeon M, Jung U-W, Shin Y, Shin J-S, Shin B-Y, Lee S-K, Choi H-J, Song JS. Intranuclear Delivery of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B p65 in a Rat Model of Tooth Replantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041987
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Chung-Min, Seunghan Mo, Mijeong Jeon, Ui-Won Jung, Yooseok Shin, Jin-Su Shin, Bo-Young Shin, Sang-Kyou Lee, Hyung-Jun Choi, and Je Seon Song. 2021. "Intranuclear Delivery of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B p65 in a Rat Model of Tooth Replantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041987
APA StyleKang, C. -M., Mo, S., Jeon, M., Jung, U. -W., Shin, Y., Shin, J. -S., Shin, B. -Y., Lee, S. -K., Choi, H. -J., & Song, J. S. (2021). Intranuclear Delivery of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B p65 in a Rat Model of Tooth Replantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041987