Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of Plasmid Carrying shRNA Sequence
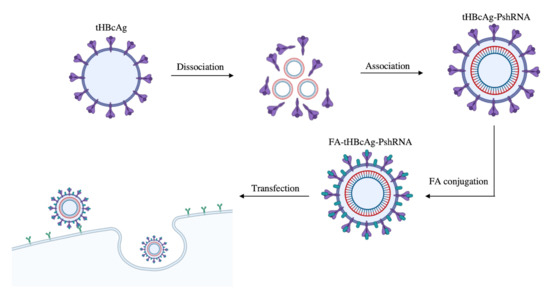
2.2. Encapsidation of PshRNA with tHBcAg VLP and Conjugation of VLP with FA
2.3. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) Analysis
2.4. Silencing of Bcl-2 Gene by FA-tHBcAg-PshRNA VLP
2.5. Viability of HeLa Cells Treated with FA-tHBcAg-PshRNA VLP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of Plasmid Containing shRNA Sequence
4.2. Production and Purification of Truncated Hepatitis B Core Antigen (tHBcAg)
4.3. Encapsidation of Plasmid PshRNA with tHBcAg VLP
4.4. Conjugation of Folic Acid (FA) to tHBcAg VLP
4.5. Density Analysis of tHBcAg VLP Encapsidating PshRNA and Conjugated with FA
4.6. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
4.7. Delivery of Plasmid PshRNA into HeLa Cells Using tHBcAg VLP Conjugated with FA
4.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amer, M.H. Gene therapy for cancer: Present status and future perspective. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2014, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginn, S.L.; Amaya, A.K.; Alexander, I.E.; Edelstein, M.; Abedi, M.R. Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2017: An update. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldini, L. Gene therapy returns to centre stage. Nature 2015, 526, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, G.R.; Pederson, T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upetream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 7371–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, K.; Schnierle, B.S. Selective gene silencing by viral delivery of short hairpin RNA. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liang, W. Development of RNAi technology for targeted therapy—A track of siRNA based agents to RNAi therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.B.; Shearer, M.H.; Kennedy, R.C. DNA vaccines: Successes and limitations in cancer and infectious disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J.; Tiemann, K. Current progress of siRNA/shRNA therapeutics in clinical trials. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 1130–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Dosari, M.S.; Gao, X. Nonviral gene delivery: Principle, limitations, and recent Progress. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohovie, M.J.; Nagasawa, M.; Swartz, J.R. Virus-like particles: Next-generation nanoparticles for targeted therapeutic delivery. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2017, 2, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malam, Y.; Loizidou, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Liposomes and nanoparticles: Nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Chen, R.; Frezzo, J.A.; Katyal, P.; Hill, L.K.; Yin, L.; Srivastava, N.; More, H.T.; Renfrew, P.D.; Bonneau, R.; et al. Efficient dual siRNA and drug delivery using engineered lipoproteoplexes. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2688–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattni, B.S.; Chupin, V.V.; Torchilin, V.P. New developments in liposomal drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10938–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabahy, M.; Wooley, K.L. Design of polymeric nanoparticles for biomedical delivery applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2545–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldão, A.; Mellado, M.C.M.; Castilho, L.R.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Alves, P.M. Virus-like particles in vaccine development. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1149–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.S.; Dyson, M.R.; Murray, K. Hepatitis B virus core antigen: Enhancement of its production in Escherichia coli, and interaction of the core particles with the viral surface antigen. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.F.; Abdullah, M.P.; Yusoff, K.; Tan, W.S. Interactions of hepatitis B core antigen and peptide inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5620–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwowska, K.; Schmid, R.M.; Cohrs, S.; Schibli, R.; Müller, C. Folate receptor-positive gynecological cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo characterization. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariyapong, P.; Chotwiwatthanakun, C.; Somrit, M.; Jitrapakdee, S.; Xing, L.; Cheng, H.R.; Weerachatyanukul, W. Encapsulation and delivery of plasmid DNA by virus-like nanoparticles engineered from Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus. Virus Res. 2014, 179, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, S.; Niikura, M.; Li, T.C.; Takeda, N.; Kusagawa, S.; Takebe, Y.; Miyamura, T.; Yasutomi, Y. DNA vaccine-encapsulated virus-like particles derived from an orally transmissible virus stimulate mucosal and systemic immune responses by oral administration. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shan, W.; Ye, S.; Zhou, X.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, L. Nanoparticle-based co-delivery of siRNA and paclitaxel for dual-targeting of glioblastoma. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Choi, S.H.; Jeon, H.; Kim, I.S.; Ahn, H.J. Chimeric capsid protein as a nanocarrier for siRNA delivery: Stability and cellular uptake of encapsulated siRNA. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8690–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M. The arginine-rich domain of the hepatitis B virus core protein is required for pregenome encapsidation and productive viral positive-strand DNA synthesis but not for virus assembly. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4107–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.H.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B core protein as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Liu, X.; Jia, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, N.; Chen, J.; Fang, F. Pokemon siRNA delivery mediated by RGD-modified HBV core protein suppressed the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2015, 26, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.; Suk, F.-M.; Cajimat, M.; Chua, P.K.; Shih, C. Stability and morphology comparisons of self-assembled virus-like particles from wild-type and mutant human hepatitis B virus capsid proteins. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12950–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, M.Y.T.; Tan, W.S.; Abdullah, N.; Ling, T.C.; Tey, B.T. Heat treatment of unclarified Escherichia coli homogenate improved the recovery efficiency of recombinant hepatitis B core antigen. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 137, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Tal, G.; Lider, O.; Shaul, Y. Cytokine induction by the hepatitis B virus capsid in macrophages is facilitated by membrane heparan sulfate and involves TLR2. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.; Shaul, Y. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis and lysosomal cleavage of hepatitis B virus capsid-like core particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16563–16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.W.; Tan, W.S. Recombinant hepatitis B virus core particles: Association, dissociation and encapsidation of green fluorescent protein. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 151, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Tey, B.T.; Ho, K.L.; Tejo, B.A.; Tan, W.S. Nanoglue: An alternative way to display cell-internalizing peptide at the spikes of hepatitis B virus core nanoparticles for cell-targeting delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Tey, B.T.; Ho, K.L.; Tan, W.S. Delivery of chimeric hepatitis B core particles into liver cells. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biabanikhankahdani, R.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Ho, K.L.; Tan, W.S. pH-responsive virus-like nanoparticles with enhanced tumour-targeting ligands for cancer drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biabanikhankahdani, R.; Bayat, S.; Ho, K.L.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Tan, W.S. A simple add-and-display method for immobilisation of cancer drug on His-tagged virus-like nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biabanikhankahdani, R.; Ho, K.L.; Alitheen, N.B.; Tan, W.S. A dual bioconjugated virus-like nanoparticle as a drug delivery system and comparison with a pH-responsive delivery system. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, B.K.; Yong, C.Y.; Ho, K.L.; Omar, A.R.; Alitheen, N.B.; Tan, W.S. Targeted delivery of cell penetrating peptide virus-like nanoparticles to skin cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Kaul, S.C.; Wadhwa, R.; Miyako, E. Folic acid receptor-mediated targeting enhances the cytotoxicity, efficacy, and selectivity of Withania somnifera leaf extract: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.L.; Wu, L.J.; Tashiro, S.I.; Onodera, S.; Ikejima, T. Oridonin induces apoptosis of HeLa cells via altering expression of Bcl-2/Bax and activating caspase-3/ICAD pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.W.; Wei, N. Inhibition of AKT/FoxO3a signaling induced PUMA expression in response to p53-independent cytotoxic effects of H1: A derivative of tetrandrine. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, B.C.; Scherr, A.L.; Lorenz, S.; Urbanik, T.; Kautz, N.; Elssner, C.; Welte, S.; Bermejo, J.L.; Jäger, D.; Schulze-Bergkamen, H. Beyond cell death—antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins regulate migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooley, A.J.; Gilden, J.; Jacobelli, J.; Beemiller, P.; Trimble, W.S.; Kinoshita, M.; Krummel, M.F. Amoeboid T lymphocytes require the septin cytoskeleton for cortical integrity and persistent motility. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 11, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanger, F.; Coulson, A.R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 94, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Preparation of plasmid DNA by alkaline lysis with SDS: Midipreparation. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2006, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akwiditya, M.A.; Yong, C.Y.; Yusof, M.T.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Ho, K.L.; Tan, W.S. Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052320
Akwiditya MA, Yong CY, Yusof MT, Mariatulqabtiah AR, Ho KL, Tan WS. Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052320
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkwiditya, Made Angga, Chean Yeah Yong, Mohd Termizi Yusof, Abdul Razak Mariatulqabtiah, Kok Lian Ho, and Wen Siang Tan. 2021. "Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052320
APA StyleAkwiditya, M. A., Yong, C. Y., Yusof, M. T., Mariatulqabtiah, A. R., Ho, K. L., & Tan, W. S. (2021). Hepatitis B Virus-Like Particle: Targeted Delivery of Plasmid Expressing Short Hairpin RNA for Silencing the Bcl-2 Gene in Cervical Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052320