In Vivo Electrophysiology of Peptidergic Neurons in Deep Layers of the Lumbar Spinal Cord after Optogenetic Stimulation of Hypothalamic Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Newly Developed In Vivo Extracellular Recordings from Lamina X Neurons
2.2. Newly Developed In Vivo Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recordings from Lamina X Neurons
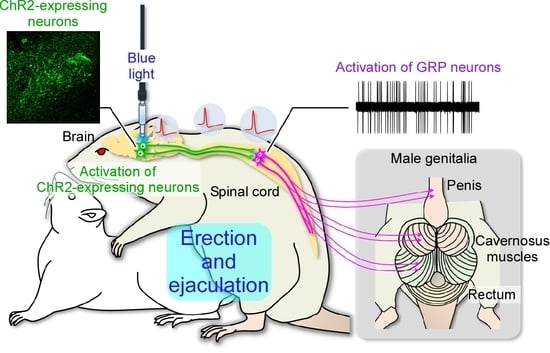
2.3. In Vivo Extracellular Recordings after Optogenetic Stimulation of the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus (PVH)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. In Vivo Preparation
4.3. In Vivo Extracellular Recording from Lamina X Neurons
4.4. In Vivo Patch-Clamp Recording from Lamina X Neurons
4.5. Oxytocin Superfusion
4.6. Optogenetics
4.7. Recording Position
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ChR2 | Channelrhodopsin-2 |
| eYFP | enhanced yellow fluorescent protein |
| Dxtr | human diphtheria toxin receptor |
| Wt | wild-type |
| SEG | spinal ejaculation generator |
| GRP | gastrin-releasing peptide |
| OXTR | oxytocin receptor |
| PVH | paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus |
| sEPSCs | spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents |
References
- Truitt, W.A.; Coolen, L.M. Identification of a potential ejaculation generator in the spinal cord. Science 2002, 297, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truitt, W.A.; Shipley, M.T.; Veening, J.G.; Coolen, L.M. Activation of a subset of lumbar spinothalamic neurons after copulatory behavior in male but not female rats. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ju, G.; Melander, T.; Ceccatelli, S.; Hokfelt, T.; Frey, P. Immunohistochemical evidence for a spinothalamic pathway co-containing cholecystokinin- and galanin-like immunoreactivities in the rat. Neuroscience 1987, 20, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.C.; Newton, B.W. Cholecystokinin-8-like immunoreactivity is sexually dimorphic in a midline population of rat lumbar neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 276, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Zhang, X.; Hokfelt, T. An immunohistochemical investigation of the opioid cell column in lamina X of the male rat lumbosacral spinal cord. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 270, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Zuloaga, D.G.; Hongu, H.; Wada, E.; Wada, K.; Jordan, C.L.; Breedlove, S.M.; Kawata, M. Sexually dimorphic gastrin releasing peptide system in the spinal cord controls male reproductive functions. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H. Sexually dimorphic nuclei in the spinal cord control male sexual functions. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozyrev, N.; Lehman, M.N.; Coolen, L.M. Activation of gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in the lumbosacral spinal cord is required for ejaculation in male rats. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oti, T.; Satoh, K.; Uta, D.; Nagafuchi, J.; Tateishi, S.; Ueda, R.; Takanami, K.; Young, L.J.; Galione, A.; Morris, J.F.; et al. Oxytocin influences male sexual activity via non-synaptic axonal release in the spinal cord. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradaia, A.; Trouslard, J. Nicotinic receptors regulate the release of glycine onto lamina X neurones of the rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, K.D.; Newton, B.W. Intracellular recording of lamina X neurons in a horizontal slice preparation of rat lumbar spinal cord. J. Neurosci. Methods 2000, 100, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotov, V.; Tokhtamysh, A.; Kopach, O.; Dromaretsky, A.; Sheremet, Y.; Belan, P.; Voitenko, N. Functional characterization of lamina X neurons in Ex-Vivo spinal cord preparation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furue, H.; Narikawa, K.; Kumamoto, E.; Yoshimura, M. Responsiveness of rat substantia gelatinosa neurones to mechanical but not thermal stimuli revealed by in vivo patch-clamp recording. J. Physiol. 1999, 521 Pt 2, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, N.; Uta, D.; Ding, H.; Uchida, H.; Saika, F.; Matsuzaki, S.; Fukazawa, Y.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Ko, M.C.; et al. GRP receptor and AMPA receptor cooperatively regulate itch-responsive neurons in the spinal dorsal horn. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 108025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uta, D.; Koga, K.; Furue, H.; Imoto, K.; Yoshimura, M. L-bupivacaine inhibition of nociceptive transmission in rat peripheral and dorsal horn neurons. Anesthesiology 2021, 131, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.J.; Abdelmoumene, M.; Hayashi, H.; Dubner, R. Physiology and morphology of substantia gelatinosa neurons intracellularly stained with horseradish peroxidase. J. Comp. Neurol. 1980, 194, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light, A.R.; Kavookjian, A.M. Morphology and ultrastructure of physiologically identified substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) neurons with axons that terminate in deeper dorsal horn laminae (III-V). J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 267, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J.; Fitzgerald, M. The properties of neurones recorded in the superficial dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 221, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, A.E.; Lange, G.M.; Clemens, L.G. Effects of paraventricular lesions on sex behavior and seminal emission in male rats. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 63, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.K.; Clemens, L.G. Projections of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to the sexually dimorphic lumbosacral region of the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1991, 539, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashida, H. Somato-axodendritic release of oxytocin into the brain due to calcium amplification is essential for social memory. J. Physiol. Sci. 2016, 66, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Stoeckel, M.E.; Klein, M.J. Oxytocin receptors on oxytocin neurones: Histoautoradiographic detection in the lactating rat. J. Physiol. 1994, 480 Pt 1, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, L.W.; Kuypers, H.G. The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus: Cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and organization of projections to the pituitary, dorsal vagal complex, and spinal cord as demonstrated by retrograde fluorescence double-labeling methods. J. Comp. Neurol. 1980, 194, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.K.; Clemens, L.G. Neurophysin-containing pathway from the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to a sexually dimorphic motor nucleus in lumbar spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 336, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuchars, S.A.; Lall, V.K. Sympathetic preganglionic neurons: Properties and inputs. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 829–869. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eijkelkamp, N.; Kavelaars, A.; Elsenbruch, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Holtmann, G.; Heijnen, C.J. Increased visceral sensitivity to capsaicin after DSS-induced colitis in mice: Spinal cord c-Fos expression and behavior. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G749–G757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ness, T.J.; Gebhart, G.F. Characterization of neuronal responses to noxious visceral and somatic stimuli in the medial lumbosacral spinal cord of the rat. J. Neurophysiol. 1987, 57, 1867–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, C.R.; Paxinos, G.; O’Brien, M. Mechanisms of PCA-induced hypothermia, ejaculation, salivation and irritability in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1981, 15, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renyi, L. Ejaculations induced by p-chloroamphetamine in the rat. Neuropharmacology 1985, 24, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, A.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ebiko, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Kimura, Y.; Sakurada, S. Evidence for an involvement of peripheral serotonin in p-chloroamphetamine-induced ejaculation of rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 82, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, B.D.; Akasofu, K.; Citron, J.H.; Daniels, S.B.; Natoli, J.H. Noncontact stimulation from estrous females evokes penile erection in rats. Physiol. Behav. 1994, 55, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uta, D.; Oti, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Sakamoto, H. In Vivo Electrophysiology of Peptidergic Neurons in Deep Layers of the Lumbar Spinal Cord after Optogenetic Stimulation of Hypothalamic Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073400
Uta D, Oti T, Sakamoto T, Sakamoto H. In Vivo Electrophysiology of Peptidergic Neurons in Deep Layers of the Lumbar Spinal Cord after Optogenetic Stimulation of Hypothalamic Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073400
Chicago/Turabian StyleUta, Daisuke, Takumi Oti, Tatsuya Sakamoto, and Hirotaka Sakamoto. 2021. "In Vivo Electrophysiology of Peptidergic Neurons in Deep Layers of the Lumbar Spinal Cord after Optogenetic Stimulation of Hypothalamic Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073400
APA StyleUta, D., Oti, T., Sakamoto, T., & Sakamoto, H. (2021). In Vivo Electrophysiology of Peptidergic Neurons in Deep Layers of the Lumbar Spinal Cord after Optogenetic Stimulation of Hypothalamic Paraventricular Oxytocin Neurons in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073400