Combinations of Piperine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
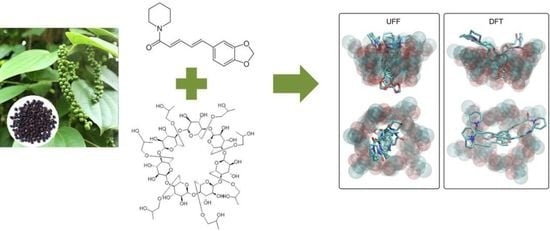
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Theoretical Studies
3.3. Preparation of Piperine–HP-β-CD Mixture
3.4. Characterization of Piperine–HP-β-CD Mixture
3.4.1. XRPD
3.4.2. DSC
3.4.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations
3.4.4. NMR Analysis
3.5. Apparent Solubility and Permeability through Membranes Simulating GIT Walls and BBB of the Piperine–HP-β-CD Mixture
3.6. Biological Activity
3.6.1. Antioxidant Activity
3.6.2. Determination of Hyaluronidase Inhibition
3.6.3. Determination of AChE and BuChE Inhibition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BuChE | Butyrylcholinesterase |
| CD | Cyclodextrin |
| DAD | Diode-array detector |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| FT-IR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HP | Hydroxypropyl |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| PAMPA | Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay |
| Papp | Apparent permeability coefficient |
| UFF | Universal force field |
| XRPD | X-ray powder diffraction |
References
- Song, Y.; Cao, C.; Xu, Q.; Gu, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, X.; Xu, S.; Wu, E.; Huang, J.H. Piperine Attenuates TBI-Induced Seizures via Inhibiting Cytokine-Activated Reactive Astrogliosis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgani, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour, G.D.; Nikzad, M. Piperine—The bioactive compound of black pepper: From isolation to medicinal formulations. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Córdova Martínez, A.; Seco-Calvo, J. Iron and physical activity: Bioavailability enhancers, properties of black pepper (bioperine®) and potential applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasiłowicz, A.; Tykarska, E.; Lewandowska, K.; Kozak, M.; Miklaszewski, A.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Szymanowska, D.; Plech, T.; Jenczyk, J.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin as an effective carrier of curcumin–piperine nutraceutical system with improved enzyme inhibition properties. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaini, E.; Afriyani, A.; Fitriani, L.; Ismed, F.; Horikawa, A.; Uekusa, H. Improved Solubility and Dissolution Rates in Novel Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine with Succinic Acid. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; He, Y. The inhibiting role of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate on piperine crystallization to enhance its dissolution from its amorphous solid dispersion and permeability. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 39523–39531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezawa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Tunvichien, S.; Suzuki, R.; Kanamoto, I. Changes in the physicochemical properties of piperine/β-cyclodextrin due to the formation of inclusion complexes. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, B.N.; Ozdemir, N.; Hill, L.E.; Gomes, C.L. Synthesis and characterization of nano-encapsulated black pepper oleoresin using hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin for antioxidant and antimicrobial applications. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, N1913–N1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilaqueo, M.; Millao, S.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Campos-Vega, R.; Acevedo, F.; Shene, C.; Rubilar, M. Inclusion of piperine in β-cyclodextrin complexes improves their bioaccessibility and in vitro antioxidant capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesi, E.; Vikmon, M.; Szente, L. Cyclodextrins in food technology and human nutrition: Benefits and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1981–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyclodextrins Used as Excipients Report Report Published in Support of the ’Questions and Answers on Cyclodextrins Used as Excipients in Medicinal Products for Human Use’ (EMA/CHMP/495747/2013); European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2017.
- Ottinger, A.E.; Kao, L.M.; Carrillo-Carrasco, N.; Yanjanin, N.; Kanakatti Shankar, R.; Janssen, M.; Brewster, M.; Scott, I.; Xu, X.; Cradock, J. Collaborative development of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for the treatment of Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, V.; Patel, G.; Abu-Thabit, N.Y. Responsive cyclodextrins as polymeric carriers for drug delivery applications. In Stimuli Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 555–580. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, K.L.; Bartlett, G.J.; Diehl, R.C.; Agirre, J.; Gallagher, T.; Kiessling, L.L.; Woolfson, D.N. Carbohydrate–aromatic interactions in proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15152–15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Darra, N.; Rajha, H.N.; Debs, E.; Saleh, F.; El-Ghazzawi, I.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G. Comparative study between ethanolic and β-cyclodextrin assisted extraction of polyphenols from peach pomace. Int. J. Food Sci. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tutunchi, P.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Hamishehkar, H.; Alizadeh, A. Extraction of red beet extract with β-cyclodextrin-enhanced ultrasound assisted extraction: A strategy for enhancing the extraction efficacy of bioactive compounds and their stability in food models. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezawa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Murata, I.; Takao, K.; Sugita, Y.; Kanamoto, I. Characterization of the dissolution behavior of piperine/cyclodextrins inclusion complexes. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2018, 19, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Di, X. Effects of piperine on the intestinal permeability and pharmacokinetics of linarin in rats. Molecules 2014, 19, 5624–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Han, J.; Jiang, A.; Huang, R.; Fu, T.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Li, W.; Li, J. Involvement of metabolism-permeability in enhancing the oral bioavailability of curcumin in excipient-free solid dispersions co-formed with piperine. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Yuan, Z.; Qu, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y. Piperine enhances the bioavailability of silybin via inhibition of efflux transporters BCRP and MRP2. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Chand, S. Improved bioavailability of atenolol with piperine in rats. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, E.A.; Majumdar, S.; Alsheteli, A.; Alshehri, S.; Alsulays, B.; Feng, X.; Gryczke, A.; Kolter, K.; Langley, N.; Repka, M.A. Hot melt extrusion as an approach to improve solubility, permeability and oral absorption of a psychoactive natural product, piperine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, M.; Zuo, Z. Efficient brain uptake of piperine and its pharmacokinetics characterization after oral administration. Xenobiotica 2018, 48, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenmann, D.E.; Dürig, C.; Jähne, E.A.; Smieško, M.; Culot, M.; Gosselet, F.; Cecchelli, R.; Helms, H.C.C.; Brodin, B.; Wimmer, L. In vitro blood–brain barrier permeability predictions for GABAA receptor modulating piperine analogs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Songngam, S.; Sukwattanasinitt, M.; Siralertmukul, K.; Sawasdee, P. A 5, 7-Dimethoxyflavone/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex with anti-butyrylcholinesterase activity. Aaps Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2014, 15, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rappé, A.K.; Casewit, C.J.; Colwell, K.S.; Goddard, W.A., III; Skiff, W.M. UFF, a full periodic table force field for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, J.; Kleist, C.; Jakobtorweihen, S.; Hansen, N. Validation and comparison of force fields for native cyclodextrins in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 1608–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipis, C.A. Adventures of quantum chemistry in the realm of inorganic chemistry. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2004, 25, 19–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Mai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J. Mechanism and Improved Dissolution of Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion by Alkalizers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marciniec, B.; Stawny, M.; Kozak, M.; Naskrent, M. The influence of radiation sterilization on thiamphenicol. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 69, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionato, L.D.; Petrone, L.; Baldut, M.; Bonafede, S.L.; Segall, A.I. Comparison between the dissolution profiles of nine meloxicam tablet brands commercially available in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.; Kansy, M.; Avdeef, A.; Senner, F. Permeation of permanently positive charged molecules through artificial membranes—Influence of physico-chemical properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 31, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High throughput artificial membrane permeability assay for blood–brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Piotrowska, H.; Kucińska, M.; Murias, M.; Bylka, W. Cytotoxic activity of physodic acid and acetone extract from Hypogymnia physodes against breast cancer cell lines. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, K.; Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Załuski, D.; Makowska-Wąs, J.; Sobolewska, D.; Janeczko, Z.; Żmudzki, P. In vitro anti-denaturation and anti-hyaluronidase activities of extracts and galactolipids from leaves of Impatiens parviflora DC. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Szymanowska, D.; Maciejewska, P.; Kmiecik, D.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Kulczyński, B.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. In vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibition and antimicrobial activity of chia seeds (Salvia hispanica). Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stasiłowicz, A.; Rosiak, N.; Tykarska, E.; Kozak, M.; Jenczyk, J.; Szulc, P.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Lewandowska, K.; Płazińska, A.; Płaziński, W.; et al. Combinations of Piperine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084195
Stasiłowicz A, Rosiak N, Tykarska E, Kozak M, Jenczyk J, Szulc P, Kobus-Cisowska J, Lewandowska K, Płazińska A, Płaziński W, et al. Combinations of Piperine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):4195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084195
Chicago/Turabian StyleStasiłowicz, Anna, Natalia Rosiak, Ewa Tykarska, Maciej Kozak, Jacek Jenczyk, Piotr Szulc, Joanna Kobus-Cisowska, Kornelia Lewandowska, Anita Płazińska, Wojciech Płaziński, and et al. 2021. "Combinations of Piperine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 4195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084195
APA StyleStasiłowicz, A., Rosiak, N., Tykarska, E., Kozak, M., Jenczyk, J., Szulc, P., Kobus-Cisowska, J., Lewandowska, K., Płazińska, A., Płaziński, W., & Cielecka-Piontek, J. (2021). Combinations of Piperine with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 4195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084195