Novel Insights on Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Based on Coumalic Acid: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Investigation, and Biological Studies
Abstract
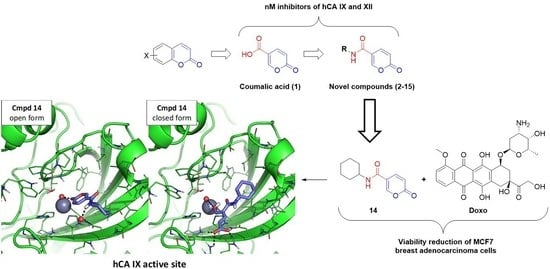
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Synthesis of Compounds 2–15
2.1.2. NMR Studies
2.2. Biological Results
2.2.1. CA Inhibitory Activity of the Target Compounds
2.2.2. Biological Evaluation of Breast Adenocarcinoma Cells (MCF7)
2.3. Molecular Modeling
2.3.1. Molecular Docking
2.3.2. MD Simulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Remarks
General Synthetic Procedure and NMR Data for the Compounds 2–15
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition Screening Assay
3.2.2. Antiviability Effect against Breast Adenocarcinoma Cell Line (MCF7)
3.2.3. Hypoxia Induction and MCF7 Treatment
3.2.4. HGF Culture and Treatment
3.2.5. MTT Assay
3.2.6. Cytotoxicity Assay (LDH Test)
3.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Molecular Modeling Protocols
3.3.1. Molecular Docking
3.3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Supuran, C.T. A Simple Yet Multifaceted Enzyme. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. An overview of the bacterial carbonic anhydrases. Metabolites 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Are Carbonic Anhydrases Suitable Targets to Fight Protozoan Parasitic Diseases? Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5266–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. A highlight on the inhibition of fungal carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for the antifungal armamentarium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. An overview on the recently discovered iota-carbonic anhydrases. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannuzzi, S.; Hewitt, C.S.; Nocentini, A.; Capasso, C.; Costantino, G.; Flaherty, D.P.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition studies of bacterial α-carbonic anhydrases with phenols. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannuzzi, S.; De Luca, V.; Nocentini, A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Coumarins inhibit η-class carbonic anhydrase from Plasmodium falciparum. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emameh, R.Z.; Barker, H.R.; Syrjänen, L.; Urbański, L.; Supuran, C.T.; Parkkila, S. Identification and inhibition of carbonic anhydrases from nematodes. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guglielmi, P.; Rotondi, G.; Secci, D.; Angeli, A.; Chimenti, P.; Nocentini, A.; Bonardi, A.; Gratteri, P.; Carradori, S.; Supuran, C.T. Novel insights on saccharin- and acesulfame-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, modelling investigations and biological activity evaluation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1891–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysteinsson, T.; Gudmundsdottir, H.; Hardarson, A.O.; Berrino, E.; Selleri, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Carta, F. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors of different structures dilate pre-contracted porcine retinal arteries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Novel carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotondi, G.; Guglielmi, P.; Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; De Monte, C.; De Filippis, B.; Maccallini, C.; Amoroso, R.; Cirilli, R.; Akdemir, A.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological activity of selective hCAs inhibitors based on 2-(benzylsulfinyl)benzoic acid scaffold. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berrino, E.; Carta, F. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for the treatment of epilepsy and obesity. In Carbonic Anhydrases; Supuran, C.T., Nocentini, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Michelet, B.; Martin-Mingot, A.; Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T.; Thibaudeau, S. Modulating the Efficacy of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors through Fluorine Substitution. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23068–23082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Emerging role of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 1233–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.C.; Chia, S.; Bedard, P.L.; Chu, Q.; Lyle, M.; Tang, L.; Singh, M.; Zhang, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Renouf, D.J.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of SLC-0111, a Novel Inhibitor of Carbonic Anhydrase IX, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Clin. Trials 2020, 43, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnella, A.; Ferrara, Y.; Auletta, L.; Albanese, S.; Cerchia, L.; Alterio, V.; De Simone, G.; Supuran, C.T.; Zannetti, A. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrases IX/XII by SLC-0111 boosts cisplatin effects in hampering head and neck squamous carcinoma cell growth and invasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppicelli, S.; Andreucci, E.; Ruzzolini, J.; Bianchini, F.; Nediani, C.; Supuran, C.T.; Calorini, L. The Carbonic Anhydrase IX inhibitor SLC-0111 as emerging agent against the mesenchymal stem cell-derived pro-survival effects on melanoma cells. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Supuran, C.T. Novel approaches for designing drugs that interfere with pH regulation. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Angeli, A.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Kiryukhina, A.P.; Milaneschi, A.; De Luca, A.; Bozdag, M.; Carradori, S.; Selleri, S.; Bartolucci, G.; et al. Azidothymidine “clicked” into 1,2,3-Triazoles: First Report on Carbonic Anhydrase-Telomerase Dual-Hybrid Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7392–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhameed, R.A.; Berrino, E.; Almarhoon, Z.; El-Faham, A.; Supuran, C.T. A class of carbonic anhydrase IX/XII–selective carboxylate inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Ascenzio, M.; Secci, D.; Carradori, S.; Zara, S.; Guglielmi, P.; Cirilli, R.; Pierini, M.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Angeli, A.; et al. 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition, HPLC Enantioseparation, and Docking Studies of Saccharin/Isoxazole and Saccharin/Isoxazoline Derivatives as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX and XII Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 2470–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Multitargeting approaches involving carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Hybrid drugs against a variety of disorders. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1702–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, E.; Milazzo, L.; Micheli, L.; Vullo, D.; Angeli, A.; Bozdag, M.; Nocentini, A.; Menicatti, M.; Bartolucci, G.; di Cesare Mannelli, L.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors with carbon monoxide releasing properties for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7233–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspatwar, E.; Berrino, S.; Bua, F.; Carta, C.; Capasso, S.; Parkkila, C.T. Supuran, Toxicity evaluation of sulfamides and coumarins that efficiently inhibit human carbonic anhydrases. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T. Coumarin carbonic anhydrase inhibitors from natural sources. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.; Pham, N.B.; Quinn, R.J. Direct screening of natural product extracts using mass spectrometry. J. Biomol. Screen. 2008, 13, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, A.; Temperini, C.; Vu, H.; Pham, N.B.; Poulsen, S.A.; Scozzafava, A.; Quinn, R.J.; Supuran, C.T. Non-zinc mediated inhibition of carbonic anhydrases: Coumarins are a new class of suicide inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touisni, N.; Maresca, A.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T. Glycosyl coumarin carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors strongly attenuate the growth of primary breast tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8271–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melis, C.; Distinto, S.; Bianco, G.; Meleddu, R.; Cottiglia, F.; Fois, B.; Taverna, D.; Angius, R.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; et al. Targeting Tumor Associated Carbonic Anhydrases IX and XII: Highly Isozyme Selective Coumarin and Psoralen Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, A.; Supuran, C.T. Coumarins incorporating hydroxy- and chloro-moieties selectively inhibit the transmembrane, tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isoforms IX and XII over the cytosolic ones i and II. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4511–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tars, K.; Vullo, D.; Kazaks, A.; Leitans, J.; Lends, A.; Grandane, A.; Zalubovskis, R.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfocoumarins (1,2-benzoxathiine-2,2-dioxides): A class of potent and isoform-selective inhibitors of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraroni, M.; Carta, F.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Thioxocoumarins Show an Alternative Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition Mechanism Compared to Coumarins. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelio, B.; Laronze-Cochard, M.; Miambo, R.; De Grandis, M.; Riccioni, R.; Borisova, B.; Dontchev, D.; Machado, C.; Ceruso, M.; Fontana, A.; et al. 5-Arylisothiazol-3(2H)-one-1,(1)-(di)oxides: A new class of selective tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases (hCA IX and XII) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 175, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, J.; Carta, F.; Vullo, D.; Leitans, J.; Kazaks, A.; Tars, K.; Žalubovskis, R.; Supuran, C.T. N-Substituted and ring opened saccharin derivatives selectively inhibit transmembrane, tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3583–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ascenzio, M.; Carradori, S.; De Monte, C.; Secci, D.; Ceruso, M.; Supuran, C.T. Design, synthesis and evaluation of N-substituted saccharin derivatives as selective inhibitors of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase XII. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ascenzio, M.; Guglielmi, P.; Carradori, S.; Secci, D.; Florio, R.; Mollica, A.; Ceruso, M.; Akdemir, A.; Sobolev, A.P.; Supuran, C.T. Open saccharin-based secondary sulfonamides as potent and selective inhibitors of cancer-related carbonic anhydrase IX and XII isoforms. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeker, J.; Peat, T.S.; Bornaghi, L.F.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Poulsen, S.A. Cyclic secondary sulfonamides: Unusually good inhibitors of cancer-related carbonic anhydrase enzymes. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3522–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cau, Y.; Vullo, D.; Mori, M.; Dreassi, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Botta, M. Potent and selective carboxylic acid inhibitors of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. Molecules 2018, 23, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maresca, A.; Temperini, C.; Pochet, L.; Masereel, B.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Deciphering the mechanism of carbonic anhydrase inhibition with coumarins and thiocoumarins. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petreni, A.; Osman, S.M.; Alasmary, F.A.; Almutairi, T.M.; Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T. Binding site comparison for coumarin inhibitors and amine/amino acid activators of human carbonic anhydrases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocentini, A.; Angeli, A.; Carta, F.; Winum, J.Y.; Zalubovskis, R.; Carradori, S.; Capasso, C.; Donald, W.A.; Supuran, C.T. Reconsidering anion inhibitors in the general context of drug design studies of modulators of activity of the classical enzyme carbonic anhydrase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Exploring the multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases for novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrino, E.; Bua, S.; Mori, M.; Botta, M.; Murthy, V.S.; Vijayakumar, V.; Tamboli, Y.; Bartolucci, G.; Mugelli, A.; Cerbai, E.; et al. Novel sulfamide-containing compounds as selective carbonic anhydrase i inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cau, Y.; Mori, M.; Supuran, C.T.; Botta, M. Mycobacterial carbonic anhydrase inhibition with phenolic acids and esters: Kinetic and computational investigations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 8322–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Cau, Y.; Vignaroli, G.; Laurenzana, I.; Caivano, A.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Botta, M. Hit Recycling: Discovery of a Potent Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor by in Silico Target Fishing. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1964–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, V.; Hilvo, M.; di Fiore, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Pan, P.; Parkkila, S.; Scaloni, A.; Pastorek, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Pedone, C.; et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16233–16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalifah, R.G. The Carbon Dioxide Hydration Activity of Carbonic Anhydrase. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanini, D.; Capperucci, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Angeli, A. Sulfur, selenium and tellurium containing amines act as effective carbonic anhydrase activators. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, B.Z.; Dag, A.; Doğan, B.; Durdagi, S.; Angeli, A.; Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Sonmez, F. Synthesis, biological activity and multiscale molecular modeling studies of bis-coumarins as selective carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors with effective cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, A.; Vaiano, F.; Mari, F.; Bertol, E.; Supuran, C.T. Psychoactive substances belonging to the amphetamine class potently activate brain carbonic anhydrase isoforms VA, VB, VII, and XII. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Colli, M.; Tortorella, P.; Agamennone, M.; Campestre, C.; Loiodice, F.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. Bisphosfonate matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for the treatment of periodontitis: An in vitro study. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bateman, A. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozielski, F. Kinesins and cancer. Kinesins Cancer 2015, 12, 1–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the protein databank and cambridge structural database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunwa, T.H.; Taii, K.; Sadakane, K.; Kawata, Y.; Maruta, S.; Miyanishi, T. Morelloflavone as a novel inhibitor of mitotic kinesin Eg5. J. Biochem. 2019, 166, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.C.; Kolb, E.A.; Sampson, V.B. Recent advances of cell-cycle inhibitor therapies for pediatric cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6489–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Ran, J.; Zhou, J. Non-canonical functions of the mitotic kinesin Eg5. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved Protein-Ligand Docking Using GOLD. Proteins 2003, 54, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and Validation of a Genetic Algorithm for Flexible Docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomon-Ferrer, R.; Case, D.A.; Walker, R.C. An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2013, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Dietrich, U.; Manetti, F.; Botta, M. Molecular dynamics and DFT study on HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein-7 in complex with viral genome. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Nucci, A.; Lang, M.C.D.; Humbert, N.; Boudier, C.; Debaene, F.; Sanglier-Cianferani, S.; Catala, M.; Schult-Dietrich, P.; Dietrich, U.; et al. Functional and structural characterization of 2-amino-4-phenylthiazole inhibitors of the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein with antiviral activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1950–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Lang, M.C.D.; Saladini, F.; Palombi, N.; Kovalenko, L.; de Forni, D.; Poddesu, B.; Friggeri, L.; Giannini, A.; Malancona, S.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Bifunctional Aminothiazoles as Antiretrovirals Targeting the HIV-1 Nucleocapsid Protein. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballone, A.; Picarazzi, F.; Prosser, C.; Davis, J.; Ottmann, C.; Mori, M. Experimental and Computational Druggability Exploration of the 14-3-3ζ/SOS1pS1161PPI Interface. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 6555–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholokh, M.; Improta, R.; Mori, M.; Sharma, R.; Kenfack, C.; Shin, D.; Voltz, K.; Stote, R.H.; Zaporozhets, O.A.; Botta, M.; et al. Tautomers of a Fluorescent G Surrogate and Their Distinct Photophysics Provide Additional Information Channels. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 8106–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mély, Y.; Kuchlyan, J.; Martinez-Fernandez, L.; Mori, M.; Gavvala, K.; Ciaco, S.; Boudier, C.; Richert, L.; Didier, P.; Tor, Y.; et al. What makes thienoguanosine an outstanding fluorescent DNA probe? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16999–17014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.C.; Chafe, S.C.; Supuran, C.T.; Dedhar, S. Cancer Therapeutic Targeting of Hypoxia Induced Carbonic Anhydrase IX: From Bench to Bedside. Cancers 2022, 14, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Entry | Structure | KI (µM) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII | ||
| 1 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.073 | 0.083 |
| 2 |  | >100 | >100 | 3.000 | 0.700 |
| 3 |  | >100 | >100 | 2.900 | 0.800 |
| 4 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.174 | 0.090 |
| 5 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.273 | 0.068 |
| 6 |  | >100 | >100 | 3.100 | 0.700 |
| 7 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.315 | 0.265 |
| 8 |  | >100 | >100 | 3.200 | 0.700 |
| 9 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.082 | 0.089 |
| 10 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.281 | 0.081 |
| 11 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.083 | 0.076 |
| 12 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.146 | 0.080 |
| 13 |  | >100 | >100 | 3.689 | 0.094 |
| 14 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.098 | 0.086 |
| 15 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.326 | 0.087 |
| AAZ | 0.20 | 0.012 | 0.025 | 0.006 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontecorvi, V.; Mori, M.; Picarazzi, F.; Zara, S.; Carradori, S.; Cataldi, A.; Angeli, A.; Berrino, E.; Chimenti, P.; Ciogli, A.; et al. Novel Insights on Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Based on Coumalic Acid: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Investigation, and Biological Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147950
Pontecorvi V, Mori M, Picarazzi F, Zara S, Carradori S, Cataldi A, Angeli A, Berrino E, Chimenti P, Ciogli A, et al. Novel Insights on Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Based on Coumalic Acid: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Investigation, and Biological Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147950
Chicago/Turabian StylePontecorvi, Virginia, Mattia Mori, Francesca Picarazzi, Susi Zara, Simone Carradori, Amelia Cataldi, Andrea Angeli, Emanuela Berrino, Paola Chimenti, Alessia Ciogli, and et al. 2022. "Novel Insights on Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Based on Coumalic Acid: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Investigation, and Biological Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147950
APA StylePontecorvi, V., Mori, M., Picarazzi, F., Zara, S., Carradori, S., Cataldi, A., Angeli, A., Berrino, E., Chimenti, P., Ciogli, A., Secci, D., Guglielmi, P., & Supuran, C. T. (2022). Novel Insights on Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Based on Coumalic Acid: Design, Synthesis, Molecular Modeling Investigation, and Biological Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147950