ADAR1 Isoforms Regulate Let-7d Processing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
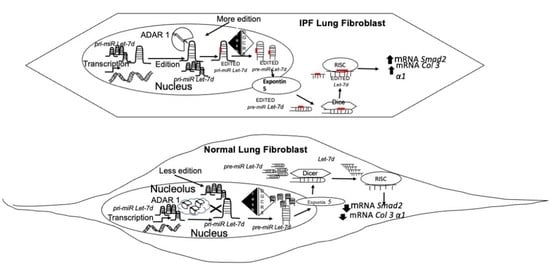
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of ADAR1 Isoforms in Controls and IPF Fibroblasts
2.2. ADAR1 Is Hyperactive in IPF Fibroblasts
2.3. Basal Expression of Let7d and pri-miR-Let7d in Normal and IPF Fibroblasts and Correlation with ADAR1p110 and p150
2.4. The Effect of ADAR1 Isoforms on Let-7d
2.5. Expression of COL3A1 and SMAD2 Targets of Let-7d in IPF
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, Quantitative PCR
4.3. Western Blot
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Generation of ADAR1-p110 Deletion Mutant
4.6. ADAR Catalytic Activity Assay
4.7. Selection of Target mRNA
4.8. Pentostatin Treatment in IPF Fibroblasts
4.9. Statistical Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O. New cellular and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2012, 380, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A.; Kaminski, N. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Aberrant Recapitulation of Developmental Programs? PLoS Med. 2008, 5, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Collard, H.R.; Raghu, G.; Sweet, M.P.; Hays, S.R.; Campos, G.M.; Golden, J.A.; King, T.E., Jr. Does Chronic Microaspiration Cause Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Phan, S.H.; Thannickal, V.J.; Galli, A.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Gabbiani, G. The myofibroblast: One function, multiple origins. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An epithelial/fibroblastic cross-talk disorder. Respir Res. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis, K.; Liu, X.; Hagood, J.S. Myofibroblast differentiation and survival in fibrotic disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, K.; Milosevic, J.; Kaminski, N. MiRNAs in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Trans. Res. 2011, 157, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, K.; Castillo-Negrete, R.; Barreto, G. Non-coding RNAs and nuclear architecture during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Signal 2020, 70, 109593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Banerjee, S.; de Freitas, A.; Sanders, Y.Y.; Ding, Q.; Matalon, S.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. Participation of miR-200 in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Phatol. 2012, 180, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huleihel, L.; Ben-Yehudah, A.; Milosevic, J.; Yu, G.; Pandit, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Yousef, H.; LeJeune, M.; Coon, T.A.; Redinger, C.J.; et al. Let-7d microRNA affects mesenchymal phenotypic properties of lung fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L534–L542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, K.; Singh, I.; Dobersch, S.; Sarvari, P.; Günther, S.; Cordero, J.; Mehta, A.; Wujak, L.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.; Chao, C.-M.; et al. Inactivation of nuclear histone deacetylases by EP300 disrupts the MiCEE complex in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Piña, G.; Ordoñez-Razo, R.M.; Montes, E.; Páramo, I.; Becerril, C.; Salgado, A.; Santibañez-Salgado, J.A.; Maldonado, M.; Ruiz, V. The Role of ADAR1 and ADAR2 in the Regulation of miRNA-21 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 2018, 196, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narry Kim, V. MicroRNA Biogenesis: Coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faller, M.; Guo, F. MicroRNA biogenesis: There’s more than one way to skin a cat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heale, B.S.; Keegan, L.P.; McGurk, L.; Michlewski, G.; Brindle, J.; Stanton, C.M.; Caceres, J.F.; O’Connell, M.A. Editing independent effects of ADARs on the miRNA/siRNAs pathways. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3145–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, D.J.; Mirsky, H.; Vendetti, N.J.; Maas, S. RNA editing of a miRNA precursor. RNA 2004, 10, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.B.; Samuel, C.E. Expression and regulation by interferon of a double stranded-RNA-specific adenosine deaminase from human cells: Evidence for two forms of the deaminase. Mol. Cell Biol. 1995, 15, 5376–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraud, P.; Allain, F.H. ADAR proteins: Double-stranded RNA and Z-DNA binding domains. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 353, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, C.; Barbon, A.; Barlati, S. Activity Regulation of Adenosine Deaminases Acting on RNA (ADARs). Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Bass, B. Inosine exists in mRNA at tissue-specific levels and is most abundant in brain mRNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipeto, M.A.; Court, A.C.; Sadarangani, A.; Santos, N.P.D.; Balaian, L.; Chun, H.J.; Pineda, G.; Morris, S.R.; Mason, C.N.; Geron, I.; et al. ADAR1 Activation Drives Leukaemia Stem Cell Self-Renewal by Impairing Let-7 Biogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, L.A.; Jiang, Q.; Zipeto, M.A.; Lazzari, E.; Ali, S.; Barrett, C.L.; Barrett, C.L.; Frazer, K.A.; Jamieson, C.H.M. An RNA editing fingerprint of cancer stem cell reprogramming. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Hu, P.; Lin, X.; Han, W.; Zhu, L.; Tan, X.; Ye, F.; Wang, G.; Wu, F.; Yin, B.; et al. PTBP1 induces ADAR1 p110 isoform expression through IRES-like dependent translation control and influences cell proliferation in gliomas. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4383–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desterro, J.M.; Keegan, L.P.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M.T.; O’Connell, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Dynamic association of RNA-editing enzymes with the nucleolus. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brümmer, A.; Yang, Y.; Chan, T.W.; Xiao, X. Structure-mediated modulation of mRNA abundance by A-to-I editing. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D. Regulation of microRNA processing in development, differentiation and cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Wang, Q.; Higuchi, M.; Seeburg, P.H.; Shiekhattar, R.; Nishikura, K. Modulation of microRNA processing and expression through RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansam, C.L.; Wells, K.S.; Emeson, R.B. Modulation of RNA editing by functional nucleolar sequestration of ADAR2. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14018–14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikura, K. Functions and Regulation of RNA Editing by ADAR Deaminases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, M.A.; Keegan, L.P. Drosha versus ADAR: Wrangling over pri-miRNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Piña, G.; Rubio, K.; Ordoñez-Razo, R.M.; Barreto, G.; Montes, E.; Becerril, C.; Salgado, A.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.; Aquino-Galvez, A.; Carlos-Reyes, A.; et al. ADAR1 Isoforms Regulate Let-7d Processing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169028
Díaz-Piña G, Rubio K, Ordoñez-Razo RM, Barreto G, Montes E, Becerril C, Salgado A, Cabrera-Fuentes H, Aquino-Galvez A, Carlos-Reyes A, et al. ADAR1 Isoforms Regulate Let-7d Processing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169028
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Piña, Gabriela, Karla Rubio, Rosa M. Ordoñez-Razo, Guillermo Barreto, Eduardo Montes, Carina Becerril, Alfonso Salgado, Héctor Cabrera-Fuentes, Arnoldo Aquino-Galvez, Angeles Carlos-Reyes, and et al. 2022. "ADAR1 Isoforms Regulate Let-7d Processing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169028
APA StyleDíaz-Piña, G., Rubio, K., Ordoñez-Razo, R. M., Barreto, G., Montes, E., Becerril, C., Salgado, A., Cabrera-Fuentes, H., Aquino-Galvez, A., Carlos-Reyes, A., & Ruiz, V. (2022). ADAR1 Isoforms Regulate Let-7d Processing in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169028