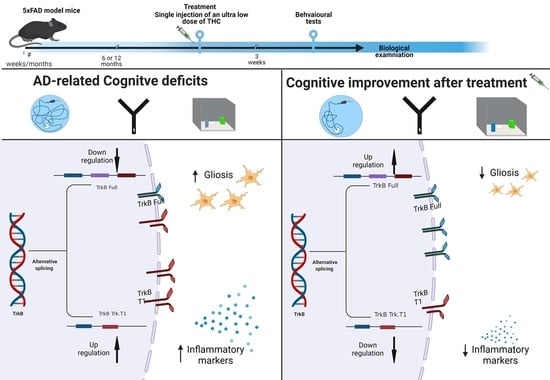
An Ultra-Low Dose of ∆9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Impairments and Modulates TrkB Receptor Expression in a 5XFAD Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ULD-THC Ameliorates AD-Related Cognitive Decline
2.2. The Effect of ULD-THC on AD-Related Imbalance of the Neurotropic Factor Receptors
2.3. The Effect of ULD-THC on AD-Related Inflammatory Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Treatments
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.4. RT-PCR
4.5. Study Design
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. A Century of Alzheimer’s Disease. Science 2006, 314, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Alzheimer’s Disease, a Multifactorial Disorder Seeking Multitherapies. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2010, 6, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, D. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Need for Personalized Therapeutic Approaches. Drug Dev. Res. 2020, 81, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talarico, G.; Trebbastoni, A.; Bruno, G.; de Lena, C. Modulation of the Cannabinoid System: A New Perspective for the Treatment of the Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.U.; Yook, T.H. A Review on Studies of Marijuana for Alzheimer’s Disease—Focusing on CBD, THC. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Bai, G.; Mayl, J.; Lin, X.; Sutherland, K.; Nabar, N.; Cai, J. The Potential Therapeutic Effects of THC on Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 42, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Fan, N.; Teng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Tang, Y.; Sun, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, C. Δ9-THC-Caused Synaptic and Memory Impairments Are Mediated through COX-2 Signaling. Cell 2013, 155, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franke, T.; Irwin, C.; Beindorff, N.; Bouter, Y.; Bouter, C. Effects of Tetrahydrocannabinol Treatment on Brain Metabolism and Neuron Loss in a Mouse Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Nuklearmedizin 2019, 58, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolón, R.M.; Núñez, E.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Castillo, A.I.; Martínez-Orgado, J.A.; Romero, J. The Activation of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors Stimulates in Situ and in Vitro Beta-Amyloid Removal by Human Macrophages. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarejos, M.J.; Perucho, J.; Gomez, A.; Muñoz, M.P.; Fernandez-Estevez, M.; Sagredo, O.; Fernandez Ruiz, J.; Guzman, M.; de Yebenes, J.G.; Mena, M.A. Natural Cannabinoids Improve Dopamine Neurotransmission and Tau and Amyloid Pathology in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 35, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haghani, M.; Shabani, M.; Javan, M.; Motamedi, F.; Janahmadi, M. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Activation Rescues Amyloid SS-Induced Alterations in Behaviour and Intrinsic Electrophysiological Properties of Rat Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Neurones. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Bie, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Activation of the CB2 Receptor System Reverses Amyloid-Induced Memory Deficiency. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fihurka, O.; Hong, Y.; Yan, J.; Brown, B.; Lin, X.; Shen, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gordon, M.N.; Morgan, D.; et al. The Memory Benefit to Aged APP/PS1 Mice from Long-Term Intranasal Treatment of Low-Dose THC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Yan, J.; Brown, B.; Lin, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, N.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Gordon, M.; et al. Low-Dose Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol as Beneficial Treatment for Aged APP/PS1 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, K.; Weinstein, A. The Effects of Cannabinoids on Executive Functions: Evidence from Cannabis and Synthetic Cannabinoids—A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballinger, M.D.; Saito, A.; Abazyan, B.; Taniguchi, Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Ito, K.; Zhu, X.; Segal, H.; Jaaro-Peled, H.; Sawa, A.; et al. Adolescent Cannabis Exposure Interacts with Mutant DISC1 to Produce Impaired Adult Emotional Memory. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 82, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, R.L.A.; Thakur, G.A.; Stewart, W.N.; Bow, J.P.; Bajaj, S.; Makriyannis, A.; McLaughlin, P.J. Effects of a Novel CB1 Agonist on Visual Attention in Male Rats: Role of Strategy and Expectancy in Task Accuracy. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 21, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Cannabinoids Reveal the Necessity of Hippocampal Neural Encoding for Short-Term Memory in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8932–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verrico, C.D.; Gu, H.; Peterson, M.L.; Sampson, A.R.; Lewis, D.A. Repeated Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol Exposure in Adolescent Monkeys: Persistent Effects Selective for Spatial Working Memory. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assaf, F.; Fishbein, M.; Gafni, M.; Keren, O.; Sarne, Y. Pre- and Post-Conditioning Treatment with an Ultra-Low Dose of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Protects against Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Cognitive Damage. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 220, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, M.; Gov, S.; Assaf, F.; Gafni, M.; Keren, O.; Sarne, Y. Long-Term Behavioral and Biochemical Effects of an Ultra-Low Dose of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): Neuroprotection and ERK Signaling. Exp. Brain Res. 2012, 221, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein-Kaminietsky, M.; Gafni, M.; Sarne, Y. Ultralow Doses of Cannabinoid Drugs Protect the Mouse Brain from Inflammation-Induced Cognitive Damage: Ultralow THC Doses Protect Against Inflammation-Induced Cognitive Damage. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarne, Y.; Toledano, R.; Rachmany, L.; Sasson, E.; Doron, R. Reversal of Age-Related Cognitive Impairments in Mice by an Extremely Low Dose of Tetrahydrocannabinol. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 61, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, A.; Vozella, V.; Huff, H.; McNeil, B.; Ahmed, F.; Ghidini, A.; Mahler, S.V.; Huestis, M.A.; Das, A.; Piomelli, D. Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Adolescent and Adult Male Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 374, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agurell, S.; Halldin, M.; Lindgren, J.E.; Ohlsson, A.; Widman, M.; Gillespie, H.; Hollister, L. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Delta 1-Tetrahydrocannabinol and Other Cannabinoids with Emphasis on Man. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolomics of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: Implications in Toxicity. Drug Metab. Rev. 2016, 48, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilkei-Gorzo, A.; Albayram, O.; Draffehn, A.; Michel, K.; Piyanova, A.; Oppenheimer, H.; Dvir-Ginzberg, M.; Rácz, I.; Ulas, T.; Imbeault, S.; et al. A Chronic Low Dose of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Restores Cognitive Function in Old Mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchalant, Y.; Brothers, H.M.; Wenk, G.L. Cannabinoid Agonist WIN-55,212-2 Partially Restores Neurogenesis in the Aged Rat Brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Zingler, D.; Schuhbaeck, K.; Schloetcke, K.; Zingler, C.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Virchow, J.C. The Impact of Age, Weight and Gender on BDNF Levels in Human Platelets and Plasma. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen, P.; Pedersen, M.; Hänninen, T.; Bruunsgaard, H.; Lakka, T.A.; Kivipelto, M.; Hassinen, M.; Rauramaa, T.H.; Pedersen, B.K.; Rauramaa, R. BDNF Is a Novel Marker of Cognitive Function in Ageing Women: The DR’s EXTRA Study. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 90, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, F.; Chen, J.; Dong, W. Chronic Antidepressant Administration Alleviates Frontal and Hippocampal BDNF Deficits in CUMS Rat. Brain Res. 2010, 1366, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xie, C.-W. Neurotrophins Enhance CaMKII Activity and Rescue Amyloid-β-Induced Deficits in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 21, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arancibia, S.; Silhol, M.; Moulière, F.; Meffre, J.; Höllinger, I.; Maurice, T.; Tapia-Arancibia, L. Protective Effect of BDNF against Beta-Amyloid Induced Neurotoxicity in Vitro and in Vivo in Rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, F.F.; Vining, E.R.; Eide, B.L.; Zang, K.; Wang, X.-Y.; Reichardt, L.F. Naturally Occurring Truncated TrkB Receptors Have Dominant Inhibitory Effects on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 3123–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsinger, R.M.D.; Schnarr, J.; Henry, P.; Castelo, V.T.; Fahnestock, M. Quantitation of BDNF MRNA in Human Parietal Cortex by Competitive Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction: Decreased Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 76, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, S.D.; Che, S.; Wuu, J.; Counts, S.E.; Mufson, E.J. Down Regulation of Trk but Not P75 NTR Gene Expression in Single Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons Mark the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease: Down Regulation of Trk. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wuu, J.; Mufson, E.J.; Fahnestock, M. Precursor Form of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Mature Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Are Decreased in the Pre-Clinical Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease: Decreased ProBDNF and BDNF in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Marín, C.; Rey, M.J.; Ribalta, T.; Goutan, E.; Blanco, R.; Tolosa, E.; Martí, E. BDNF and Full-Length and Truncated TrkB Expression in Alzheimer Disease. Implications in Therapeutic Strategies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.; Young, D.; Lawlor, P.; Gai, W.; Waldvogel, H.; Faull, R.L.M.; Dragunow, M. Trk Receptor Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Brain Res. 1996, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomi, S.; Toledano, R.; Nitzan, K.; Dror Shahaf, S.; Break, E.P.; Frenkel, D.; Doron, R. Imbalance in Sirt1 Alternative Splicing in Response to Chronic Stress during the Adolescence Period in Female Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarne, Y. Beneficial and Deleterious Effects of Cannabinoids in the Brain: The Case of Ultra-Low Dose THC. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2019, 45, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesseveur, G.; David, D.J.; Gaillard, M.C.; Pla, P.; Wu, M.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nicolas, V.; Auregan, G.; David, I.; Dranovsky, A.; et al. BDNF Overexpression in Mouse Hippocampal Astrocytes Promotes Local Neurogenesis and Elicits Anxiolytic-like Activities. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Siao, C.-J.; Nagappan, G.; Marinic, T.; Jing, D.; McGrath, K.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Mark, W.; Tessarollo, L.; Lee, F.S.; et al. Neuronal Release of ProBDNF. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramham, C.R.; Messaoudi, E. BDNF Function in Adult Synaptic Plasticity: The Synaptic Consolidation Hypothesis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Angelucci, A.; Costantin, L.; Braschi, C.; Mazzantini, M.; Babbini, F.; Fabbri, M.E.; Tessarollo, L.; Maffei, L.; Berardi, N.; et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Is Required for the Enhancement of Hippocampal Neurogenesis Following Environmental Enrichment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophins: Roles in Neuronal Development and Function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, T.; Matyas, J.J.; Renn, C.L.; Faden, A.I.; Dorsey, S.G.; Wu, J. Function and Mechanisms of Truncated BDNF Receptor TrkB.T1 in Neuropathic Pain. Cells 2020, 9, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, M.E.; Achim, C.L.; Fenner, B.M. Expression of Full-Length and Truncated TrkB in Human Striatum and Substantia Nigra Neurons: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. J. Mol. Histol. 2014, 45, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Cengotitabengoa, M.; MacDowell, K.S.; Alberich, S.; Diaz, F.J.; Garcia-Bueno, B.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R.; Bioque, M.; Berrocoso, E.; Parellada, M.; Lobo, A.; et al. BDNF and NGF Signalling in Early Phases of Psychosis: Relationship With Inflammation and Response to Antipsychotics After 1 Year. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salter, M.W.; Stevens, B. Microglia Emerge as Central Players in Brain Disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhurst, C.N.; Yang, G.; Ninan, I.; Savas, J.N.; Yates, J.R.; Lafaille, J.J.; Hempstead, B.L.; Littman, D.R.; Gan, W.-B. Microglia Promote Learning-Dependent Synapse Formation through Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Cell 2013, 155, 1596–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, N. Cannabinoid and Cannabinoid-like Receptors in Microglia, Astrocytes, and Astrocytomas. Glia 2010, 58, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tselnicker, I.; Keren, O.; Hefetz, A.; Pick, C.G.; Sarne, Y. A Single Low Dose of Tetrahydrocannabinol Induces Long-Term Cognitive Deficits. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 411, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaita, A.; Aso, E. The Cannabis Paradox: When Age Matters. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 661–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Rubio-Casillas, A. Biphasic Effects of THC in Memory and Cognition. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal Beta-Amyloid Aggregates, Neurodegeneration, and Neuron Loss in Transgenic Mice with Five Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutations: Potential Factors in Amyloid Plaque Formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyuk, D.P.; Bol’shakova, A.V.; Vlasova, O.L.; Bezprozvanny, I.B. Possibilities and Prospects of TheBehavioral Test “Morris Water Maze”. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 57, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nitzan, K.; Ellenbogen, L.; Bentulila, Z.; David, D.; Franko, M.; Break, E.P.; Zoharetz, M.; Shamir, A.; Sarne, Y.; Doron, R. An Ultra-Low Dose of ∆9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Impairments and Modulates TrkB Receptor Expression in a 5XFAD Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169449
Nitzan K, Ellenbogen L, Bentulila Z, David D, Franko M, Break EP, Zoharetz M, Shamir A, Sarne Y, Doron R. An Ultra-Low Dose of ∆9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Impairments and Modulates TrkB Receptor Expression in a 5XFAD Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169449
Chicago/Turabian StyleNitzan, Keren, Leah Ellenbogen, Ziv Bentulila, Dekel David, Motty Franko, Emanuela P. Break, Michal Zoharetz, Alon Shamir, Yosef Sarne, and Ravid Doron. 2022. "An Ultra-Low Dose of ∆9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Impairments and Modulates TrkB Receptor Expression in a 5XFAD Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169449
APA StyleNitzan, K., Ellenbogen, L., Bentulila, Z., David, D., Franko, M., Break, E. P., Zoharetz, M., Shamir, A., Sarne, Y., & Doron, R. (2022). An Ultra-Low Dose of ∆9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Impairments and Modulates TrkB Receptor Expression in a 5XFAD Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169449