Associating Air Pollution with Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Parameters in Lymphocytes of the General Population in Zagreb (Croatia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Population Characteristics
2.2. Baseline Frequency of the Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus (CBMN) Assay Parameters
2.3. Air Pollution Exposure
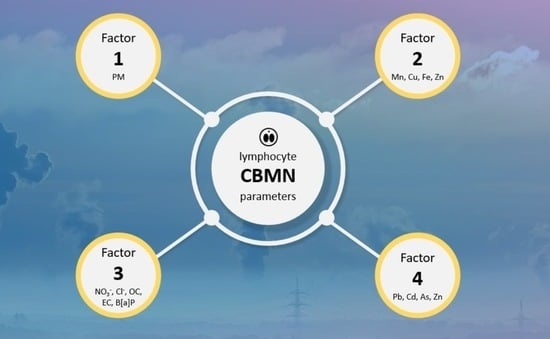
2.4. Influence of Air Pollution on the Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus (CBMN) Assay Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Sample and Participant Selection
4.2. Blood Sampling
4.3. Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus (CBMN) Assay
4.4. Variables Tested
4.4.1. Age, Sex, and Lifestyle Factors
4.4.2. Air Pollution Measurements
Gravimetric Analysis
Metal Analysis
Benzo(a)pyrene (B[a]P) Analysis
Organic (OC) and Elemental (EC) Carbon Analysis
Water-Soluble-Anions Analysis
4.5. Data Processing
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lelieveld, J.; Pöschl, U. Chemists can help to solve the air-pollution health crisis. Nature 2017, 551, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Pozzer, A.; Pöschl, U.; Fnais, M.; Haines, A.; Münzel, T. Loss of life expectancy from air pollution compared to other risk factors: A worldwide perspective. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boogaard, H.; Walker, K.; Cohen, A.J. Air pollution: The emergence of a major global health risk factor. Int. Health 2019, 11, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomenko, S.; Cirach, M.; Pereira-Barboza, E.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Premature mortality due to air pollution in European cities: A health impact assessment. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e121–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe—2021 Report—European Environment Agency (EEA); EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2008, 152, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive 2004/107/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15/12/2004 Relating to Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, Nickel and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, and Sulfur Dioxide; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006; ISBN 9289021926. [Google Scholar]
- Stanek, L.W.; Brown, J.S.; Stanek, J.; Gift, J.; Costa, D.L. Air Pollution Toxicology—A Brief Review of the Role of the Science in Shaping the Current Understanding of Air Pollution Health Risks. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, S8–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe—2017 Report; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; ISBN 9789292139216. [Google Scholar]
- Jaafari, J.; Naddafi, K.; Yunesian, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Ghozikali, M.G.; Shamsollahi, H.R.; Nazmara, S.; Yaghmaeian, K. Characterization, risk assessment and potential source identification of PM10 in Tehran. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo-Castañeda, D.M.; Teixeira, E.C.; Schneider, I.L.; Lara, S.R.; Silva, L.F.O. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric PM1.0 of urban environments: Carcinogenic and mutagenic respiratory health risk by age groups. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardawaj, A.; Habib, G.; Nema, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S. A Review of Ultrafine Particle-Related Pollution during Vehicular Motion, Health Effects and Control. J. Environ. Sci. Public Health 2017, 1, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandotiya, B. Health Effects of Air Pollution in Urban Environment. In Climate Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity in Arid and Semi-Arid Zones; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Proietti, C.; Anav, A.; Ciancarella, L.; D’Elia, I.; Fares, S.; Fornasier, M.F.; Fusaro, L.; Gualtieri, M.; Manes, F.; et al. Impacts of air pollution on human and ecosystem health, and implications for the National Emission Ceilings Directive: Insights from Italy. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habre, R.; Zhou, H.; Eckel, S.P.; Enebish, T.; Fruin, S.; Bastain, T.; Rappaport, E.; Gilliland, F. Short-term effects of airport-associated ultrafine particle exposure on lung function and inflammation in adults with asthma. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idowu, O.; Semple, K.; Ramadass, K.; O’Connor, W.; Hansbro, P.; Thavamani, P. Beyond the obvious: Environmental health implications of polar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamraev, K.; Cheriyan, D.; Choi, J.-H. A review on health risk assessment of PM in the construction industry—Current situation and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Air quality, health impacts and burden of disease due to air pollution (PM10, PM2.5, NO2 and O3): Application of AirQ+ model to the Camp de Tarragona County (Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Rodopoulou, S.; Ostro, B.; Alessandrini, E.; Basagaña, X.; Díaz, J.; Faustini, A.; Gandini, M.; Karanasiou, A.; et al. Which specific causes of death are associated with short term exposure to fine and coarse particles in Southern Europe? Results from the MED-PARTICLES project. Environ. Int. 2014, 67, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segersson, D.; Eneroth, K.; Gidhagen, L.; Johansson, C.; Omstedt, G.; Nylén, A.E.; Forsberg, B. Health Impact of PM10, PM2.5 and Black Carbon Exposure Due to Different Source Sectors in Stockholm, Gothenburg and Umea, Sweden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Liang, B.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Yang, F.; Peng, C.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J. Measurement of size-segregated airborne particulate bound polycyclic aromatic compounds and assessment of their human health impacts—A case study in a megacity of southwest China. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lin, T.; Syed, J.H.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Li, J. Concentration, source identification, and exposure risk assessment of PM2.5-bound parent PAHs and nitro-PAHs in atmosphere from typical Chinese cities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, H.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; et al. Radiative and heterogeneous chemical effects of aerosols on ozone and inorganic aerosols over East Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effect of airborne particulate matter of 2.5 μm or less on preterm birth: A national birth cohort study in China. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.; Dentener, F.; Van Dingenen, R.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, L.E.; Andersen, Z.J.; Sram, R.J.; Kohlová, M.B.; Gurzau, E.S.; Fucic, A.; Gribaldo, L.; Rossner, P.; Rossnerova, A.; Máca, V.; et al. Perinatal health in the Danube region—New birth cohort justified. Rev. Environ. Health 2017, 32, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santovito, A.; Gendusa, C.; Cervella, P.; Traversi, D. In vitro genomic damage induced by urban fine particulate matter on human lymphocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beelen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Wolf, K.; Samoli, E.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality: An analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project. Lancet 2014, 383, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaroni, G.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Badaloni, C.; Beelen, R.; Caracciolo, B.; De Faire, U.; Erbel, R.; Eriksen, K.T.; et al. Long term exposure to ambient air pollution and incidence of acute coronary events: Prospective cohort study and meta-analysis in 11 European cohorts from the ESCAPE Project. BMJ 2014, 348, f7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512, Erratum in Lancet 2018, 391, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.S. Planetary health: Protecting human health on a rapidly changing planet. Lancet 2017, 390, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Langrish, J.P.; Nair, H.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Global association of air pollution and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žero, S.; Žužul, S.; Huremović, J.; Pehnec, G.; Bešlić, I.; Rinkovec, J.; Godec, R.; Kittner, N.; Pavlović, K.; Požar, N.; et al. New Insight into the Measurements of Particle-Bound Metals in the Urban and Remote Atmospheres of the Sarajevo Canton and Modeled Impacts of Particulate Air Pollution in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 7052–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Health Effects of Particulate Matter, Policy Implications for Countries in Eastern Europe, Caucasus and Central Asia; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution—REVIHAAP Project: Final Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, I.; Hemkens, L.; Bucher, H.C.; Hoffmann, B.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N.; Schikowski, T.; Probst-Hensch, N.M. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Diabetes Mellitus in Europe and North America: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewtas, J. Air pollution combustion emissions: Characterization of causative agents and mechanisms associated with cancer, reproductive, and cardiovascular effects. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2007, 636, 95–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, M.S.; Galvão, M.F.D.O.; de Medeiros, S.R.B. Cell death pathways of particulate matter toxicity. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Patel, P.; Puett, R.; Rajagopalan, S. Air Pollution as a Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daellenbach, K.R.; Uzu, G.; Jiang, J.; Cassagnes, L.-E.; Leni, Z.; Vlachou, A.; Stefenelli, G.; Canonaco, F.; Weber, S.; Segers, A.; et al. Sources of particulate-matter air pollution and its oxidative potential in Europe. Nature 2020, 587, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R. Potentially harmful aerosols concentrate in European urban centres. Nature 2020, 587, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Oreščanin, V.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay parameters in peripheral blood lymphocytes of the general population: Contribution of age, sex, seasonal variations and lifestyle factors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.; Buraczewska, I.; Kruszewski, M. Micronucleus Assay: The State of Art, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopjar, N.; Kašuba, V.; Milić, M.; Rozgaj, R.; Želježić, D.; Gajski, G.; Mladinic, M.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V. Normal and Cut-Off Values of the Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay on Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes in the Croatian General Population. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2010, 61, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M. The micronucleus test—Most widely used in vivo genotoxicity test. Genes Environ. 2016, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaj-Vrhovac, V.; Gajski, G.; Ravlić, S. Efficacy of HUMN criteria for scoring the micronucleus assay in human lymphocytes exposed to a low concentration of p,p’-DDT. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Oreščanin, V.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V. Cytogenetic status of healthy children assessed with the alkaline comet assay and the cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2013, 750, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Lovrenčić, M.V.; Božičević, S.; Rubelj, I.; Nanić, L.; Vidaček, N.; Bendix, L.; Peraica, M.; Rašić, D.; et al. Analysis of health-related biomarkers between vegetarians and non-vegetarians: A multi-biomarker approach. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerić, M.; Popić, J.; Gajski, G.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V. Cytogenetic status of interventional radiology unit workers occupationally exposed to low-dose ionising radiation: A pilot study. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 843, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossnerova, A.; Spatova, M.; Rossner, P.; Solansky, I.; Sram, R.J. The impact of air pollution on the levels of micronuclei measured by automated image analysis. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2009, 669, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, C.; Merlo, F.; Rabboni, R.; Valerio, F.; Abbondandolo, A. Cytogenetic biomonitoring in traffic police workers: Micronucleus test in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1997, 30, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M.; Chang, W.P.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Holland, N.; Bonassi, S.; Zeiger, E. HUman MicronNucleus project HUMN Project: Detailed Description of the Scoring Criteria for the Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Using Isolated Human Lymphocyte Cultures. Mutat. Res. 2003, 534, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M. Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Cytome Assay Evolution into a More Comprehensive Method to Measure Chromosomal Instability. Genes 2020, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gekara, N.O. DNA damage-induced immune response: Micronuclei provide key platform. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2999–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.; Umegaki, K.; Fenech, M. Nucleoplasmic bridges are a sensitive measure of chromosome rearrangement in the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. Mutagenesis 2003, 18, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonassi, S.; Znaor, A.; Ceppi, M.; Lando, C.; Chang, W.P.; Holland, N.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Zeiger, E.; Ban, S.; Barale, R.; et al. An increased micronucleus frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes predicts the risk of cancer in humans. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonassi, S.; El-Zein, R.; Bolognesi, C.; Fenech, M. Micronuclei frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and cancer risk: Evidence from human studies. Mutagenesis 2011, 26, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesyan, A.; Mišík, M.; Cherkas, A.; Serhiyenko, V.; Staudinger, M.; Holota, S.; Yatskevych, O.; Melnyk, S.; Holzmann, K.; Knasmüller, S. Use of Micronucleus Experiments for the Detection of Human Cancer Risks: A Brief Overview. Proc. Shevchenko Sci. Soc. Med. Sci. 2021, 65, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, F.; Kassie, F.; Knasmüller, S.; Kevekordes, S.; Mersch-Sundermann, V. Use of primary blood cells for the assessment of exposure to occupational genotoxicants in human biomonitoring studies. Toxicology 2004, 198, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, F.; Kassie, F.; Knasmüller, S.; Boedecker, R.H.; Mann, M.; Mersch-Sundermann, V. The use of the alkaline comet assay with lymphocytes in human biomonitoring studies. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2004, 566, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M. Cytogenetic Methods for Measuring Effects of Occupational Exposure. In An Essential Guide to Occupational Exposure; Marques de Oliveira, M.M., Barreira Morais, S., Martins Rodrigues, F.P.L., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 127–166. ISBN 978-1-68507-819-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric Aerosols: Composition, Transformation, Climate and Health Effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dingenen, R.; Raes, F.; Putaud, J.-P.; Baltensperger, U.; Charron, A.; Facchini, M.-C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.-C.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—1: Physical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2561–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Van Dingenen, R.; Alastuey, A.; Bauer, H.; Birmili, W.; Cyrys, J.; Flentje, H.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hansson, H.C.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—3: Physical and chemical characteristics of particulate matter from 60 rural, urban, and kerbside sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Alastuey, A.; Areskoug, H.; Ceburnis, D.; Čech, J.; Genberg, J.; Harrison, R.M.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Kiss, G.; Laj, P.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology-4: Harmonized concentrations of carbonaceous aerosol at 10 regional background sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, M.; Gysel, M.; Bukowiecki, N.; Müller, T.; Weingartner, E.; Areskoug, H.; Fiebig, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kouvarakis, G.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology-5: Climatology of black carbon optical properties at 9 regional background sites across Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Alastuey, A.; Andrade, M.; Angelov, C.; Artiñano, B.; Backman, J.; Baltensperger, U.; Bonasoni, P.; Bukowiecki, N.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—6: Scattering properties of atmospheric aerosol particles from 28 ACTRIS sites. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7877–7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, M.; Cavalli, F.; Putaud, J.P.; Fröhlich, R.; Petit, J.E.; Aas, W.; Äijälä, M.; Alastuey, A.; Allan, J.D.; Aurela, M.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—7: High-time resolution chemical characteristics of submicron particulate matter across Europe. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 10, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Raes, F.; Van Dingenen, R.; Brüggemann, E.; Facchini, M.-C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hüglin, C.; Laj, P.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—2: Chemical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2579–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, J.; Bird, M.G.; Burke, T.A.; Doerrer, N.G.; Needham, L.; Robison, S.H.; Sheldon, L.; Zenick, H. Strategic Biomonitoring Initiatives: Moving the Science Forward. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, J.; Ewers, U.; Wilhelm, M. Human biomonitoring: State of the art. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2007, 210, 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Human Biomonitoring: Facts and Figures; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ladeira, C.; Viegas, S. Human Biomonitoring—An overview on biomarkers and their application in Occupational and Environmental Health. Biomonitoring 2016, 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution Biomarkers in Environmental and Human Biomonitoring. Open Biomarkers J. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajpayee, M.; Dhawan, A. Biomarkers for Monitoring Adverse Health Effects of Air Pollution in Humans. J. Transl. Toxicol. 2014, 1, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, M.Z.; Hopf, N.B.; Viegas, S.; Price, A.B.; Paini, A.; van Thriel, C.; Benfenati, E.; Ndaw, S.; Bessems, J.; Behnisch, P.A.; et al. Towards a systematic use of effect biomarkers in population and occupational biomonitoring. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Semren, T.; Lovaković, B.T.; Oreščanin, V.; Pizent, A. Application of the comet assay for the evaluation of DNA damage from frozen human whole blood samples: Implications for human biomonitoring. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 319, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JakovljeviĆ, I.; Pehnec, G.; Sisovic, A.; Vađić, V.; Davila, S.; Godec, R. Concentrations of PAHs and other gaseous pollutants in the atmosphere of a rural area. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godec, R.; Jakovljević, I.; Šega, K.; Čačković, M.; Bešlić, I.; Davila, S.; Pehnec, G. Carbon species in PM10 particle fraction at different monitoring sites. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljević, I.; Pehnec, G.; Vađić, V.; Čačković, M.; Tomašić, V.; Jelinić, J.D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 Particle Fractions in an Urban Area. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 843–854. [Google Scholar]
- JakovljeviĆ, I.; Pehnec, G.; Vadjić, V.; Šišović, A.; Davila, S.; Bešlić, I. Carcinogenic activity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bounded on particle fraction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15931–15940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šišović, A.; Pehnec, G.; Jakovljević, I.; Hujić, M.; Vađić, V.; Bešlić, I. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons at Different Crossroads in Zagreb, Croatia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehnec, G.; Jakovljević, I.; Šišović, A.; Bešlić, I.; Vađić, V. Influence of ozone and meteorological parameters on levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the air. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callén, M.S.; Lopez, J.M.; Mastral, A.M. Seasonal variation of benzo(a)pyrene in the Spanish airborne PM10. Multivariate linear regression model applied to estimate BaP concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchia, A.M.; Chiavarini, S.; Pezza, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmospheric particulate matter in the city of Naples (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3731–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehnec, G.; Jakovljević, I.; Godec, R.; Štrukil, Z.S.; Žero, S.; Huremović, J.; Džepina, K. Carcinogenic organic content of particulate matter at urban locations with different pollution sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Baumbach, G.; Kuch, B.; Scheffknecht, G. Particle-phase concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air of rural residential areas in southern Germany. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Official Gazette No. 77 Uredba o Razinama Onečišćujućih Tvari u Zraku/Regulation on Levels of Air Pollutants. Croatia. 2020; Volume 77, pp. 1–11.
- Vađić, V.; Žužul, S.; Rinkovec, J.; Pehnec, G. Metali u Sitnim Česticama u Zraku Zagreba. Sigurnost 2013, 55, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bešlić, I.; Burger, J.; Cadoni, F.; Centioli, D.; Kranjc, I.; Van den Bril, B.; Rinkovec, J.; Šega, K.; Zang, T.; Žužul, S.; et al. Determination of As, Cd, Ni and Pb in PM10—Comparison of Different Sample Work-up and Analysis Methods. Gefahrst. Reinhalt. Der Luft 2020, 81, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadjić, V.; Žužul, S.; Pehnec, G. Zinc Levels in Suspended Particulate Matter in Zagreb Air. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksic, J.; Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M.; Bartonova, A.; Radenkovic, M.; Yttri, K.-E.; Matic-Besarabic, S.; Ignjatovic, L. Physical and chemical characterization of the particulate matter suspended in aerosols from the urban area of Belgrade. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2009, 74, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perišić, M.; Rajšić, S.; Šoštarić, A.; Mijić, Z.; Stojić, A. Levels of PM10-bound species in Belgrade, Serbia: Spatio-temporal distributions and related human health risk estimation. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žero, S.; Huremović, J.; Memić, M.; Muhić-Šarac, T. Determination of total and bioaccessible metals in airborne particulate matter from an urban and a rural area at Sarajevo. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, A. Sources of metal pollution in the urban atmosphere (A case study: Tuzla, Istanbul). J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pellón, A.; Fernández-Olmo, I. Airborne concentration and deposition of trace metals and metalloids in an urban area downwind of a manganese alloy plant. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.; Coutinho, M.; Rodrigues, J.; Ginja, J.; Borrego, C. Long-term monitoring of trace metals in PM10 and total gaseous mercury in the atmosphere of Porto, Portugal. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Donateo, A.; Chirizzi, D.; Belosi, F. Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 and Their Metals Content in Different Typologies of Sites in South-Eastern Italy. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Gazette No. 133/2005 Uredba o Graničnim Vrijednostima Onečišćujućih Tvari u Zraku/Regulation on Levels of Air Pollutants. Croatia. 2005; pp. 1–9.
- Tunno, B.J.; Shmool, J.L.C.; Michanowicz, D.R.; Tripathy, S.; Chubb, L.; Kinnee, E.; Cambal, L.; Roper, C.; Clougherty, J.E. Spatial variation in diesel-related elemental and organic PM2.5 components during workweek hours across a downtown core. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, I.; Viana, M.; Moreno, T.; Bouso, L.; Pandolfi, M.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Forns, J.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; Querol, X. Outdoor infiltration and indoor contribution of UFP and BC, OC, secondary inorganic ions and metals in PM2.5 in schools. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.G.; Vratolis, S.; Georgieva, E.; Török, S.; Šega, K.; Veleva, B.; Osán, J.; Bešlić, I.; Kertész, Z.; Pernigotti, D.; et al. Sources and geographic origin of particulate matter in urban areas of the Danube macro-region: The cases of Zagreb (Croatia), Budapest (Hungary) and Sofia (Bulgaria). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čačković, M.; Šega, K.; Vađić, V.; Bešlić, I. Characterisation of Major Acidic Anions in TSP and PM10 in Zagreb Air. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čačković, M.; Vađić, V.; Šega, K.; Beslic, I. Acidic Anions in PM10 Particle Fraction in Zagreb Air, Croatia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, R.; Jakovljević, I.; Davila, S.; Šega, K.; Bešlić, I.; Rinkovec, J.; Pehnec, G. Air pollution levels near crossroads with different traffic density and the estimation of health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3935–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, R.; Čačković, M.; Šega, K.; Bešlić, I. Winter Mass Concentrations of Carbon Species in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 in Zagreb Air, Croatia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Evtyugina, M.; Vicente, A.M.P.; Vicente, E.D.; Nunes, T.V.; Silva, P.M.A.; Duarte, M.A.C.; Pio, C.A.; Amato, F.; Querol, X. Chemical profiling of PM10 from urban road dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-H.; Wang, J.M.; Hilker, N.; Debosz, J.; Sofowote, U.; Su, Y.; Noble, M.; Healy, R.M.; Munoz, T.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; et al. Temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related PM2.5 sources: Comparison of exhaust and non-exhaust emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, R.; Šega, K.; Bešlić, I.; Davila, S. Carbon Mass Concentrations in Southern Zagreb during a Five-Year Period. In Proceedings of the 5th WeBIOPATR Workshop & Conference, Belgrade, Serbia, 14–16 October; Ovašević-Stojanović, M., Bartoňová, A., Eds.; Vinča Institute of Nuclear Science: Belgrade, Serbia, 2016; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Duan, S.G.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R.Q.; Wang, K. Comparative major components and health risks of toxic elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of PM2.5 in winter and summer in Zhengzhou: Based on three-year data. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yue, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, R. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of sub-micrometer particles (PM1) in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 118, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.; Jørgensen, H.E.; Larsen, J.C.; Poulsen, M. City air pollution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other mutagens: Occurrence, sources and health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 189–190, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Jahan, S.A.; Kabir, E.; Brown, R.J.C. A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura-Enya, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hisamatsu, Y. Mutagenic activities and physicochemical properties of selected nitrobenzanthrones. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, O.; Miaud, C.; Ficetola, G.F.; Bocher, A.; Mouchet, F.; Guittonneau, S.; Devaux, A. Variation in genotoxic stress tolerance among frog populations exposed to UV and pollutant gradients. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 95, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, T.; Ohnuki, G.; Ibuki, Y. Solar-simulated light-exposed benzo[a]pyrene induces phosphorylation of histone H2AX. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2008, 650, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfsten, D.P.; Schaeffer, D.; Mulveny, D.C. The Effects of Near Ultraviolet Radiation on the Toxic Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Animals and Plants: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 33, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Xia, Q.; Yan, J.; Herreno-Saenz, D.; Wu, Y.-S.; Tang, I.-W.; Fu, P.P. Photoirradiation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons with UVA Light—A Pathway Leading to the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species, Lipid Peroxidation, and DNA Damage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2006, 3, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bukowska, B.; Mokra, K.; Michałowicz, J. Benzo[a]pyrene—Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Mechanisms of Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan-Gordo, C.; Fthenou, E.; Pedersen, M.; Espinosa, A.; Chatzi, L.; Beelen, R.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Decordier, I.; Hoek, G.; Merlo, D.F.; et al. Outdoor air pollution exposures and micronuclei frequencies in lymphocytes from pregnant women and newborns in Crete, Greece (Rhea cohort). Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santovito, A.; Gendusa, C. Micronuclei frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes of healthy subjects living in Turin (North-Italy): Contribution of body mass index, age and sex. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2020, 47, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossnerova, A.; Spatova, M.; Pastorkova, A.; Tabashidze, N.; Veleminsky, M.; Balascak, I.; Solansky, I.; Sram, R.J. Micronuclei levels in mothers and their newborns from regions with different types of air pollution. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2011, 715, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, D.M.; van Herwijnen, M.H.M.; Pedersen, M.; Knudsen, L.E.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Sram, R.J.; Staal, Y.C.M.; Bajak, E.; van Delft, J.H.M.; Kleinjans, J.C.S. Genome-wide differential gene expression in children exposed to air pollution in the Czech Republic. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2006, 600, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.; Wichmann, J.; Autrup, H.; Dang, D.A.; Decordier, I.; Hvidberg, M.; Bossi, R.; Jakobsen, J.; Loft, S.; Knudsen, L.E. Increased micronuclei and bulky DNA adducts in cord blood after maternal exposures to traffic-related air pollution. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, F.; Hrelia, P.; Angelini, S.; Carbone, F.; Forti, G.C.; Barbieri, A.; Sanguinetti, G.; Mattioli, S.; Violante, F.S. Effects of environmental benzene: Micronucleus frequencies and haematological values in traffic police working in an urban area. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2005, 583, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, D.S.V.; Matsuda, M.; Toffoletto, O.; Garcia, M.L.B.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Marquezini, M.V. Workers of São Paulo city, Brazil, exposed to air pollution: Assessment of genotoxicity. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018, 834, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Tian, Y.; Piao, F.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Li, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sakai, S.; et al. Genotoxic damage in female residents exposed to environmental air pollution in Shenyang city, China. Cancer Lett. 2006, 240, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordo, M.; Maciel-Ruiz, J.A.; Salazar, A.M.; Robles-Morales, R.; Veloz-Martínez, M.G.; Pacheco-Limón, J.H.; Nepomuceno-Hernández, A.E.; Ayala-Yáñez, R.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Ostrosky-Wegman, P. Particulate matter-associated micronuclei frequencies in maternal and cord blood lymphocytes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2019, 60, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Jing, J.X.; Sun, G.X. Study of environmental pollution and damage of cytogenetic materials in urban residents. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 1997, 18, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lemos, A.T.; de Lemos, C.T.; Coronas, M.V.; da Rocha, J.R.; Vargas, V.M.F. Integrated study of genotoxicity biomarkers in schoolchildren and inhalable particles in areas under petrochemical influence. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, K.; Gunn, L.; Duramad, P.; Jeng, M.; Scalf, R.; Holland, N. Application of a geographic information system to explore associations between air pollution and micronucleus frequencies in African American children and adults. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2006, 47, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Niu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Genotoxicity and chronic health effects of automobile exhaust: A study on the traffic policemen in the city of Lanzhou. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 1998, 415, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopardi, P.; Zijno, A.; Marcon, F.; Conti, L.; Carere, A.; Verdina, A.; Galati, R.; Tomei, F.; Baccolo, T.P.; Crebelli, R. Analysis of micronuclei in peripheral blood lymphocytes of traffic wardens: Effects of exposure, metabolic genotypes, and inhibition of excision repair in vitro by ARA-C. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2003, 41, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, E.M.; Ballantine, J.A.; Ellard, S.; Evans, W.E.; Jones, C.; Kilic, N.; Lewis, R.I. Biomonitoring study of a group of workers potentially exposed to traffic fumes. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1997, 30, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørck, T.A.; Loock, K.V.; Poulsen, M.B.; Siersma, V.D.; Nielsen, J.K.S.; Hertel, O.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Knudsen, L.E. Micronucleus frequency in Danish schoolchildren and their mothers from the DEMOCOPHES population. Mutagenesis 2015, 31, gev054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, S.; Ladeira, C.; Costa-Veiga, A.; Perelman, J.; Gajski, G. Forgotten public health impacts of cancer—An overview. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, C.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Analysis of nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by liquid chromatography with fluorescence and mass spectrometry detection: Air particulate matter, soot, and reaction product studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehnec, G.; Jakovljević, I. Carcinogenic Potency of Airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Relation to the Particle Fraction Size. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birch, M.E.; Cary, R.A. Elemental Carbon-Based Method for Monitoring Occupational Exposures to Particulate Diesel Exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincey, P.; Butterfield, D.; Green, D.; Coyle, M.; Cape, J.N. An evaluation of measurement methods for organic, elemental and black carbon in ambient air monitoring sites. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5085–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godec, R. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Carbon in Airborne Particulates; University of Zagreb, Faculty of Science: Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Conroy, R.M. Stings in the Tails: Detecting and Dealing with Censored Data. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2005, 5, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, A.M.; Wild, P. Bivariate Left-Censored Measurements in Biomonitoring: A Bayesian Model for the Determination of Biological Limit Values Based on Occupational Exposure Limits. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2017, 61, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Women | Men | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 89 | 41 | 130 |
| Age (years) | 38.06 ± 13.94 | 38.12 ± 11.99 | 38.08 ± 13.31 |
| Age range (years) | 19–80 | 24–68 | 19–80 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.99 ± 3.92 | 25.74 ± 3.00 | 23.99 ± 3.84 |
| Current smokers | 27 | 11 | 38 |
| Alcohol consumers | 51 | 32 | 83 |
| Physical activity | 26 | 24 | 50 |
| Family history of cancer | 39 | 11 | 50 |
| Women | Men | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNi | |||
| Mean | 5.28 ± 2.81 | 4.76 ± 2.84 | 5.12 ± 2.82 |
| Range | 1–13 | 1–12 | 1–13 |
| NPBs | |||
| Mean | 1.09 ± 1.35 | 1.51 ± 1.79 | 1.22 ± 1.51 |
| Range | 0–7 | 0–7 | 0–7 |
| NBUDs | |||
| Mean | 3.43 ± 2.05 | 3.51 ± 2.21 | 3.45 ± 2.10 |
| Range | 0–10 | 0–10 | 0–10 |
| NDI | |||
| Mean | 2.01 ± 0.12 | 1.98 ± 0.12 | 2.00 ± 0.12 |
| Range | 1.60–2.38 | 1.61–2.16 | 1.60–2.38 |
| Pollutant | Average 3 Days Before | Average 7 Days Before | Average 30 Days Before |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 (µg/m3) | |||
| Mean ± SD | 29 ± 15 | 30 ± 13 | 32 ± 13 |
| Range | 11–81 | 15–67 | 13–60 |
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | |||
| Mean ± SD | 23 ± 14 | 23 ± 13 | 25 ± 12 |
| Range | 9–68 | 9–59 | 8–50 |
| PM1 (µg/m3) | |||
| Mean ± SD | 16 ± 9 | 17 ± 9 | 18 ± 8 |
| Range | 7–39 | 7–50 | 7–35 |
| OC (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 8.16 ± 4.42 | 8.33 ± 4.37 | 8.74 ± 4.28 |
| Range | 3.02–25.40 | 3.50–19.48 | 3.74–16.59 |
| EC (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 1.07 ± 0.57 | 1.14 ± 0.51 | 1.10 ± 0.39 |
| Range | 0.22–2.94 | 0.27–2.36 | 0.42–1.84 |
| SO42− (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 4.31 ± 5.22 | 4.09 ± 3.60 | 4.40 ± 2.28 |
| Range | 0.51–31.30 | 1.40–19.88 | 1.32–10.64 |
| NO3− (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 3.17 ± 3.31 | 3.41 ± 3.22 | 3.58 ± 2.90 |
| Range | 0.25–13.10 | 0.34–16.10 | 0.34–11.54 |
| Cl− (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.20 ± 0.29 | 0.22 ± 0.31 | 0.21 ± 0.24 |
| Range | 0.01–1.42 | 0.01–1.44 | 0.01–0.97 |
| Pb (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.006 ± 0.005 | 0.006 ± 0.003 | 0.006 ± 0.003 |
| Range | 0.002–0.036 | 0.003–0.021 | 0.003–0.013 |
| Mn (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.006 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.001 |
| Range | 0.002–0.012 | 0.003–0.010 | 0.003–0.011 |
| Cd (ng/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.217 ± 0.161 | 0.222 ± 0.161 | 0.229 ± 0.128 |
| Range | 0.068–0.884 | 0.068–0.837 | 0.072–0.666 |
| As (ng/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.554 ± 0.491 | 0.569 ± 0.461 | 0.562 ± 0.220 |
| Range | 0.156–2.310 | 0.231–2.852 | 0.269–1.191 |
| Ni (ng/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.977 ± 1.052 | 1.057 ± 0.956 | 1.169 ± 1.078 |
| Range | LOD-5.018 | LOD-5.454 | 0.067–6.240 |
| Cu (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.012 ± 0.005 | 0.013 ± 0.005 | 0.013 ± 0.004 |
| Range | 0.004–0.034 | 0.005–0.025 | 0.006–0.033 |
| Fe (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.300 ± 0.153 | 0.325 ± 0.121 | 0.303 ± 0.078 |
| Range | 0.086–0.958 | 0.142–0.712 | 0.179–0.612 |
| Zn (µg/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 0.021 ± 0.010 | 0.021 ± 0.009 | 0.022 ± 0.007 |
| Range | 0.008–0.057 | 0.011–0.055 | 0.011–0.044 |
| B[a]P (ng/m3) * | |||
| Mean ± SD | 1.033 ± 1.242 | 1.024 ± 1.075 | 1.151 ± 1.081 |
| Range | LOD-5.307 | 0.039–3.517 | 0.050–3.508 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Pehnec, G.; Matković, K.; Rinkovec, J.; Jakovljević, I.; Godec, R.; Žužul, S.; Bešlić, I.; Cvitković, A.; et al. Associating Air Pollution with Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Parameters in Lymphocytes of the General Population in Zagreb (Croatia). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710083
Gajski G, Gerić M, Pehnec G, Matković K, Rinkovec J, Jakovljević I, Godec R, Žužul S, Bešlić I, Cvitković A, et al. Associating Air Pollution with Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Parameters in Lymphocytes of the General Population in Zagreb (Croatia). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):10083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710083
Chicago/Turabian StyleGajski, Goran, Marko Gerić, Gordana Pehnec, Katarina Matković, Jasmina Rinkovec, Ivana Jakovljević, Ranka Godec, Silva Žužul, Ivan Bešlić, Ante Cvitković, and et al. 2022. "Associating Air Pollution with Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Parameters in Lymphocytes of the General Population in Zagreb (Croatia)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 10083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710083
APA StyleGajski, G., Gerić, M., Pehnec, G., Matković, K., Rinkovec, J., Jakovljević, I., Godec, R., Žužul, S., Bešlić, I., Cvitković, A., Wild, P., Guseva Canu, I., & Hopf, N. B. (2022). Associating Air Pollution with Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Parameters in Lymphocytes of the General Population in Zagreb (Croatia). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 10083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231710083