Asiatic Acid Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Salmonella via Upregulating LncRNA TVX1 in Microglia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview of LncRNA Sequencing
2.2. Differential Analysis of LncRNA Expression
2.3. Functional Annotation: Gene Ontology (GO)
2.4. Functional Annotation: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)
2.5. AA Decreased the Inflammation Induced by S.T by Upregulating TVX1
2.6. AA Inactivates the S.T-Induced NF-κB Pathway by Upregulating TVX1
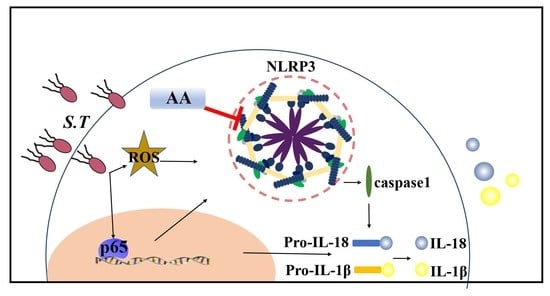
2.7. AA Inactivates the S.T-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome by Upregulating TVX1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Infection and AA Treatment of Microglia
4.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Library Preparation and Sequencing
4.4. Transcriptome Assembly and lncRNA Identification
4.5. Analysis of Differential Expression
4.6. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
4.7. RT-qPCR
4.8. Western Blotting Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- House, D.; Bishop, A.; Parry, C.; Dougan, G.; Wain, J. Typhoid fever: Pathogenesis and disease. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 14, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, J.R.; Worrall, L.J.; Sgourakis, N.G.; DiMaio, F.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Felise, H.B.; Vuckovic, M.; Yu, A.C.; Miller, S.I.; Baker, D.; et al. A refined model of the prototypical Salmonella SPI-1 T3SS basal body reveals the molecular basis for its assembly. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matulova, M.; Havlickova, H.; Sisak, F.; Rychlik, I. Vaccination of chickens with Salmonella Pathogenicity Island (SPI) 1 and SPI2 defective mutants of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Liu, M.; Holden, D.W. Salmonella Effectors SseF and SseG Interact with Mammalian Protein ACBD3 (GCP60) To Anchor Salmonella-Containing Vacuoles at the Golgi Network. Mbio 2016, 7, e00474-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K. Bacterial protein toxins that modify host regulatory GTPases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, W.D.; Chen, L.M.; Schuebel, K.E.; Bustelo, X.R.; Galan, J.E. S-typhimurium encodes an activator of Rho GTPases that induces membrane ruffling and nuclear responses in host cells. Cell 1998, 93, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.L.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Yan, Y.; Gong, T.; Han, J.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, R. RNA viruses promote activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome through a RIP1-RIP3-DRP1 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Solfrizzi, V.; Watling, M.; Imbimbo, B.P. Time to test antibacterial therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2019, 142, 2905–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.E.; Damle, S.S.; Wancewicz, E.V.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hart, C.E.; Mazur, C.; Swayze, E.E.; Kamme, F. A modular analysis of microglia gene expression, insights into the aged phenotype. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.B.; Coelho, P.L.C.; Amparo, J.A.O.; Carneiro, M.M.A.D.; Borges, J.M.P.; Souza, C.D.; Costa, M.D.D.; Mecha, M.; Rodriguez, C.G.; da Silva, V.D.A.; et al. The flavonoid rutin modulates microglial/macrophage activation to a CD150/CD206 M2 phenotype. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 274, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; Rao, Z.; Gerstmeier, J.; Raasch, M.; Weinigel, C.; Rummler, S.; Menche, D.; Muller, R.; Pergola, C.; Mosig, A.; et al. Selective upregulation of TNFalpha expression in classically-activated human monocyte-derived macrophages (M1) through pharmacological interference with V-ATPase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 130, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, D.; Nigro, A.; Romano, A.; De Domenico, S.; Damato, M.; Franck, J.; Coricciati, C.; Wistorski, M.; Cardon, T.; Fournier, I.; et al. Distinct Protein Expression Networks are Activated in Microglia Cells after Stimulation with IFN-gamma and IL-4. Cells 2019, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.P.; Lehrman, E.K.; Stevens, B. The “quad-partite synapse”: Microglia-synapse interactions in the developing and mature CNS. GLIA 2013, 61, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Wang, L.C.; Tsai, H.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, H.L.; Tzeng, S.F.; Hsu, S.M.; Chen, S.H. Microglia Reduce Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Lethality of Mice with Decreased T Cell and Interferon Responses in Brains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, J.P.; Rivest, S. Anti-inflammatory signaling in microglia exacerbates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology. Neuron 2015, 85, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y. LncRNA HOTAIR Participates in Microglia Activation and Inflammatory Factor Release by Regulating the Ubiquitination of MYD88 in Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.S.; Fang, B.; Cao, X.Z.; Chang, Y.; Qiang, Z.Y. Downregulation of LncRNA TUG1 Inhibited TLR4 Signaling Pathway-Mediated Inflammatory Damage After Spinal Cord Ischemia Reperfusion in Rats via Suppressing TRIL Expression. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neur. 2019, 78, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.L.; Ji, B.Y.; Cao, X.; Yu, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, X.Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, J.L. LncRNA-1810034E14Rik reduces microglia activation in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.N.; Wu, J.Y.; Dou, Y.; Xia, B.B.; Rong, W.B.; Rimbach, G.; Lou, Y.J. Asiatic acid protects primary neurons against C-2-ceramide-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 679, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, R.G.; Senut, M.C.; Zemke, D.; Min, J.; Frenkel, M.B.; Greenberg, E.J.; Yu, S.W.; Ahn, N.; Goudreau, J.; Kassab, M.; et al. Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene from Centella asiatica, is neuroprotective in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Bae, O.N.; Serfozo, K.; Hejabian, S.; Moussa, A.; Reeves, M.; Rumbeiha, W.; Fitzgerald, S.D.; Stein, G.; Baek, S.H.; et al. Asiatic acid attenuates infarct volume, mitochondrial dysfunction, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2012, 43, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. The IL-1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, P.; Carmi, Y.; Guttman, O.; Braiman, A.; Cohen, I.; Voronov, E.; White, M.R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. IL-1alpha and IL-1beta recruit different myeloid cells and promote different stages of sterile inflammation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4835–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.W.; Kim, S.J.; Pham, T.H.; Bak, Y.; Oh, J.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Hong, J.T.; Yoon, D.Y. Epimagnolin A inhibits IL-6 production by inhibiting p38/NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soudja, S.M.; Ruiz, A.L.; Marie, J.C.; Lauvau, G. Inflammatory monocytes activate memory CD8(+) T and innate NK lymphocytes independent of cognate antigen during microbial pathogen invasion. Immunity 2012, 37, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Misaghi, S.; Newton, K.; Maltzman, A.; Izrael-Tomasevic, A.; Arnott, D.; Dixit, V.M. NLRP3 recruitment by NLRC4 during Salmonella infection. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Swartzwelter, B.; Gamboni, F.; Neff, C.P.; Richter, K.; Azam, T.; Carta, S.; Tengesdal, I.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; et al. OLT1177, a beta-sulfonyl nitrile compound, safe in humans, inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and reverses the metabolic cost of inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1530–E1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhong, X.; Du, K.; Qian, P.; Yao, W.F.; Gao, H.; Wei, M.J. Baicalin mitigates cognitive impairment and protects neurons from microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasomes and TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Cai, W.; Wu, J. Curcumin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and protects against LPS-induced septic shock. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2132–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Kwatra, M.; Ranjan Panda, S.; Murty, U.S.N.; Naidu, V.G.M. Andrographolide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia through induction of parkin-mediated mitophagy in in-vitro and in-vivo models of Parkinson disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Zhou, X.; Ji, T.; Chen, G. NF-kappaB p65-dependent transcriptional regulation of histone deacetylase 2 contributes to the chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain via the microRNA-183/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Sui, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F. MiR-124 Prevents the Microglial Proinflammatory Response by Inhibiting the Activities of TLR4 and Downstream NLRP3 in Palmitic Acid-Treated BV2 Cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Peng, Z.; Xin, R.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Asiatic Acid Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Salmonella via Upregulating LncRNA TVX1 in Microglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810978
Zou W, Zhang J, Zhang K, Peng Z, Xin R, Wang L, Li J. Asiatic Acid Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Salmonella via Upregulating LncRNA TVX1 in Microglia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810978
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Wenshu, Jingyan Zhang, Kai Zhang, Zhiping Peng, Ruihua Xin, Lei Wang, and Jianxi Li. 2022. "Asiatic Acid Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Salmonella via Upregulating LncRNA TVX1 in Microglia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810978
APA StyleZou, W., Zhang, J., Zhang, K., Peng, Z., Xin, R., Wang, L., & Li, J. (2022). Asiatic Acid Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Salmonella via Upregulating LncRNA TVX1 in Microglia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810978