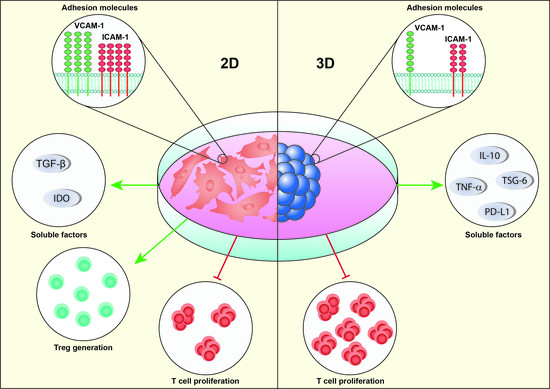
Regulatory T-Cell Enhancement, Expression of Adhesion Molecules, and Production of Anti-Inflammatory Factors Are Differentially Modulated by Spheroid-Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spheroid Formation and Morphological Analysis
2.2. MSCs Characterization
2.3. Assembly of MSCs into 3D-MSCs Increases Apoptosis and LDH Release
2.4. 2D-MSCs Exhibit a Higher Immunosuppressive Potential Than 3D-MSCs
2.5. 3D-MSCs Promote a Superior Suppression of T-Cell Activation Markers Compared with 2D-MSCs
2.6. 2D-MSCs Induce the Enhancement of Classical Treg Cells, while 3D-MSCs Reduce the Levels of Non-Classical CD8+CD28− Tregs
2.7. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 Expression Is Higher in 2D-MSCs Exposed to an Inflammatory Medium
2.8. MSC Culture Condition Impacts the mRNA Expressions of Different Immune-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Adipose-Derived MSCs Culture
4.2. Spheroid Generation and Dissociation
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Immunophenotypic Characterization
4.5. Viability Assay
4.6. Determination of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release
4.7. Immunosuppression Assay
4.8. T-Cell Activation Assay
4.9. Treg Quantification Assay
4.10. Inflammatory Medium Obtention
4.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.12. VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 Expression
4.13. Real-Time PCR
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Covas, D.T.; Panepucci, R.A.; Fontes, A.M.; Silva, W.A., Jr.; Orellana, M.D.; Freitas, M.C.C.; Neder, L.; Santos, A.R.D.; Peres, L.C.; Jamur, M.C.; et al. Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Obtained from Diverse Human Tissues Share Functional Properties and Gene-Expression Profile with CD146+ Perivascular Cells and Fibroblasts. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Meirelles, L.; Fontes, A.M.; Covas, D.T.; Caplan, A.I. Mechanisms Involved in the Therapeutic Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Carvalho, A.É.; Cardoso, M.H.; Alencar-Silva, T.; Bogéa, G.M.R.; Carvalho, J.L.; Franco, O.L.; Saldanha-Araujo, F. Dissecting the Relationship between Antimicrobial Peptides and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najar, M.; Raicevic, G.; Crompot, E.; Fayyad-Kazan, H.; Bron, D.; Toungouz, M.; Lagneaux, L. The Immunomodulatory Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A Story of a Regulatory Network. J. Immunother. 2016, 39, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, R.; Saldanha-Araujo, F. Mechanisms of T-Cell Immunosuppression by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: What Do We Know so Far? Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 216806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Jiang, S.; Shi, S.; Sun, L. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Active and Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Multicenter Clinical Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naserian, S.; Leclerc, M.; Shamdani, S.; Uzan, G. Current Preventions and Treatments of aGVHD: From Pharmacological Prophylaxis to Innovative Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 607030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, G.; Linetsky, E.; Correa, D.; Messinger Cayetano, S.; Alvarez, R.A.; Kouroupis, D.; Alvarez Gil, A.; Poggioli, R.; Ruiz, P.; Marttos, A.C.; et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Double-Blind, Phase 1/2a, Randomized Controlled Trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha-Araujo, F.; Melgaço Garcez, E.; Silva-Carvalho, A.E.; Carvalho, J.L. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A New Piece in the Puzzle of COVID-19 Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yuan, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Song, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z.; Fu, J.-L.; et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treatment for Severe COVID-19: 1-Year Follow-up Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Sensébé, L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture: The Missing Link in Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, A.I.; Leach, J.K. Concise Review: Optimizing Expansion of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/stromal Cells for Clinical Applications. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Cássia Noronha, N.; Mizukami, A.; Caliári-Oliveira, C.; Cominal, J.G.; Rocha, J.L.M.; Covas, D.T.; Swiech, K.; Malmegrim, K.C.R. Priming Approaches to Improve the Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungwirth, N.; Salinas Tejedor, L.; Jin, W.; Gudi, V.; Skripuletz, T.; Stein, V.M.; Tipold, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Stangel, M.; Baumgärtner, W.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Form 3D Clusters Following Intraventricular Transplantation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 65, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, L.; Sarukhan, A.; Dander, E.; Castor, M.; Cibella, J.; Soldani, C.; Trovato, A.E.; Ploia, C.; Luca, G.; Calvitti, M.; et al. Encapsulated Mesenchymal Stem Cells for in Vivo Immunomodulation. Leukemia 2013, 27, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartosh, T.J.; Ylöstalo, J.H.; Bazhanov, N.; Kuhlman, J.; Prockop, D.J. Dynamic Compaction of Human Mesenchymal Stem/precursor Cells into Spheres Self-Activates Caspase-Dependent IL1 Signaling to Enhance Secretion of Modulators of Inflammation and Immunity (PGE2, TSG6, and STC1). Stem Cells 2013, 31, 2443–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, Y.-J.; Kwon, Y.-R.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-J. Enhanced Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells by Three-Dimensional Culture and Azacitidine. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhang, S.H.; Lee, S.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, T.-J.; Kim, B.-S. Transplantation of Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Spheroids Enhances Vascularization. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Young, T.-H. Short-Term Spheroid Formation Enhances the Regenerative Capacity of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Promoting Stemness, Angiogenesis, and Chemotaxis. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, J.A.; McDevitt, T.C. Pre-Conditioning Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Spheroids for Immunomodulatory Paracrine Factor Secretion. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosh, T.J.; Ylöstalo, J.H.; Mohammadipoor, A.; Bazhanov, N.; Coble, K.; Claypool, K.; Lee, R.H.; Choi, H.; Prockop, D.J. Aggregation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) into 3D Spheroids Enhances Their Antiinflammatory Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13724–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burand, A.J., Jr.; Di, L.; Boland, L.K.; Boyt, D.T.; Schrodt, M.V.; Santillan, D.A.; Ankrum, J.A. Aggregation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Eliminates Their Ability to Suppress Human T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ianni, M.; Del Papa, B.; De Ioanni, M.; Moretti, L.; Bonifacio, E.; Cecchini, D.; Sportoletti, P.; Falzetti, F.; Tabilio, A. Mesenchymal Cells Recruit and Regulate T Regulatory Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Seidel, C.; Ebner, R.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Spheroid-Based Drug Screen: Considerations and Practical Approach. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagamba, B.C.; Grudzinski, P.B.; Ely, P.B.; de Jesus Hartmann Nader, P.; Nardi, N.B.; da Silva Meirelles, L. Induction of Expression of CD271 and CD34 in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Cultured as Spheroids. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 7357213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arufe, M.C.; De la Fuente, A.; Fuentes-Boquete, I.; De Toro, F.J.; Blanco, F.J. Differentiation of Synovial CD-105(+) Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Chondrocyte-like Cells through Spheroid Formation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frith, J.E.; Thomson, B.; Genever, P.G. Dynamic Three-Dimensional Culture Methods Enhance Mesenchymal Stem Cell Properties and Increase Therapeutic Potential. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2010, 16, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, E.; Salerno, S.; Barbieri, G.; De Bartolo, L.; Drioli, E.; Bader, A. Mass Transfer and Metabolic Reactions in Hepatocyte Spheroids Cultured in Rotating Wall Gas-Permeable Membrane System. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, L.M.; Dodd, N.J.F.; Owen, S.F.; Purcell, W.M.; Jackson, S.K.; Jha, A.N. Direct Measurements of Oxygen Gradients in Spheroid Culture System Using Electron Parametric Resonance Oximetry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149492. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.C.; Hung, B.P.; Browne-Bourne, S.; Zhou, D.; Yeung, J.; Genetos, D.C.; Leach, J.K. Measurement of Oxygen Tension within Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20160851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ylostalo, J.H.; Bartosh, T.J.; Tiblow, A.; Prockop, D.J. Unique Characteristics of Human Mesenchymal Stromal/progenitor Cells Pre-Activated in 3-Dimensional Cultures under Different Conditions. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezquer, F.; Morales, P.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Santapau, D.; Lespay-Rebolledo, C.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. Intravenous Administration of Anti-Inflammatory Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Reduces Chronic Alcohol Intake and Abolishes Binge-Drinking. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ylöstalo, J.H.; Bartosh, T.J.; Coble, K.; Prockop, D.J. Human Mesenchymal Stem/stromal Cells Cultured as Spheroids Are Self-Activated to Produce Prostaglandin E2 That Directs Stimulated Macrophages into an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B.; Yin, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; et al. Substrate-Independent Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Three-Dimensional Culture. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follin, B.; Juhl, M.; Cohen, S.; Pedersen, A.E.; Kastrup, J.; Ekblond, A. Increased Paracrine Immunomodulatory Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Three-Dimensional Culture. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2016, 22, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, R.; Zibert, A.; Laryea, M.; Göbel, U.; Däubener, W.; Dilloo, D. Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Inhibit Allogeneic T-Cell Responses by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-Mediated Tryptophan Degradation. Blood 2004, 103, 4619–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- François, M.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; Li, M.; Galipeau, J. Human MSC Suppression Correlates with Cytokine Induction of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Bystander M2 Macrophage Differentiation. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, K.; Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Roberts, A.I.; Li, F.; Han, Y.; Rabson, A.B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Kynurenic Acid, an IDO Metabolite, Controls TSG-6-Mediated Immunosuppression of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounayar, M.; Kefaloyianni, E.; Smith, B.; Solhjou, Z.; Maarouf, O.H.; Azzi, J.; Chabtini, L.; Fiorina, P.; Kraus, M.; Briddell, R.; et al. PI3kα and STAT1 Interplay Regulates Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immune Polarization. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of Type-I- and Type-II-Interferon-Mediated Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Schwartz, D.M.; Villarino, A.V.; Gadina, M.; McInnes, I.B.; Laurence, A. The JAK-STAT Pathway: Impact on Human Disease and Therapeutic Intervention. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryan, M.M.; Patel, M.; Hogan, K.; Lipat, A.J.; Scandolara, R.; Das, R.; Bruker, C.; Galipeau, J.; Chinnadurai, R. Ruxolitinib Inhibits IFNγ Licensing of Human Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2021, 27, 389.e1–e389.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, M.E.; Maitra, B.; Szekely, E.; Koç, O.N. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Require Monocyte-Mediated Activation to Suppress Alloreactive T Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Rasmusson, I.; Götherström, C.; Seidel, C.; Sundberg, B.; Sundin, M.; Rosendahl, K.; Tammik, C.; Ringdén, O. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Expression of CD25 (interleukin-2 Receptor) and CD38 on Phytohaemagglutinin-Activated Lymphocytes. Scand. J. Immunol. 2004, 60, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, R.; Tong, C.K.; Seow, H.F.; Vidyadaran, S.; Dazzi, F. The Immunosuppressive Effects of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Target T Cell Proliferation but Not Its Effector Function. Cell. Immunol. 2008, 251, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerquis, J.; Romieu-Mourez, R.; François, M.; Routy, J.-P.; Young, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Eliopoulos, N. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Transiently Increase Cytokine Production by Activated T Cells before Suppressing T-Cell Proliferation: Effect of Interferon-γ and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Stimulation. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saldanha-Araujo, F.; Haddad, R.; de Farias, K.C.R.M.; de Paula Alves Souza, A.; Palma, P.V.; Araujo, A.G.; Orellana, M.D.; Voltarelli, J.C.; Covas, D.T.; Zago, M.A.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote the Sustained Expression of CD69 on Activated T Lymphocytes: Roles of Canonical and Non-Canonical NF-κB Signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Sun, Q.; Guo, S. Immunosuppressive Property of MSCs Mediated by Cell Surface Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.-N.; Jeon, M.-S.; Yi, T.; Song, S.U. ICOSL Expression in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Induction of Regulatory T Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Chu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, W.; Xu, F.; Zhou, F.; et al. The Therapeutic Effect of ICAM-1-Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, K.; Ryan, J.M.; Tobin, L.; Murphy, M.J.; Barry, F.P.; Mahon, B.P. Cell Contact, Prostaglandin E(2) and Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Play Non-Redundant Roles in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Induction of CD4+CD25(High) Forkhead Box P3+ Regulatory T Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezrich, J.D.; Fechner, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, B.P.; Burlingham, W.J.; Bradfield, C.A. An Interaction between Kynurenine and the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Can Generate Regulatory T Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3190–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deynoux, M.; Sunter, N.; Ducrocq, E.; Dakik, H.; Guibon, R.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; Brisson, L.; Rouleux-Bonnin, F.; le Nail, L.-R.; Hérault, O.; et al. A Comparative Study of the Capacity of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Lines to Form Spheroids. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Xiang, A.P. CD8+CD28- T Cells: Not Only Age-Related Cells but a Subset of Regulatory T Cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Carvalho, A.É.; Rodrigues, L.P.; Schiavinato, J.L.; Alborghetti, M.R.; Bettarello, G.; Simões, B.P.; de Assis Rocha Neves, F.; Panepucci, R.A.; de Carvalho, J.L.; Saldanha-Araujo, F. GVHD-Derived Plasma as a Priming Strategy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva-Carvalho, A.É.; da Silva, I.G.M.; Corrêa, J.R.; Saldanha-Araujo, F. Regulatory T-Cell Enhancement, Expression of Adhesion Molecules, and Production of Anti-Inflammatory Factors Are Differentially Modulated by Spheroid-Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214349
Silva-Carvalho AÉ, da Silva IGM, Corrêa JR, Saldanha-Araujo F. Regulatory T-Cell Enhancement, Expression of Adhesion Molecules, and Production of Anti-Inflammatory Factors Are Differentially Modulated by Spheroid-Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(22):14349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214349
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva-Carvalho, Amandda Évelin, Ingrid Gracielle Martins da Silva, José Raimundo Corrêa, and Felipe Saldanha-Araujo. 2022. "Regulatory T-Cell Enhancement, Expression of Adhesion Molecules, and Production of Anti-Inflammatory Factors Are Differentially Modulated by Spheroid-Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 22: 14349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214349
APA StyleSilva-Carvalho, A. É., da Silva, I. G. M., Corrêa, J. R., & Saldanha-Araujo, F. (2022). Regulatory T-Cell Enhancement, Expression of Adhesion Molecules, and Production of Anti-Inflammatory Factors Are Differentially Modulated by Spheroid-Cultured Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(22), 14349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214349